BIOL 1400 Exam 3: Plant, Fungi & Animal Diversity
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Plants
Multicellular autotrophs; more complex than bacteria and protists, they have specific structures, they make their own food, and provide for all other organisms.
Autotrophs
organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis
What did plants evolve from?
Charophytes (green algae)
Biological evolution
change in living organisms over time (survive and pass down useful traits)
What three structures are specific to plants?
Cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall provides structural support, protection, and helps maintain cell shape in plant cells.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells, allowing them to convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose and hold pigment.
What is the function of the vacuole?
The vacuole stores sugars and pigment
What traits do modern plants share with their green algae ancestor?
Cell walls of cellulose
Store carbs in starch
Chloroplasts
Flagellated sperm
What does flagellated mean?
Cells or organisms that have a flagellum, a tail-like structure used for movement.
What adaptations do plants have to survive on land?
Structure prevents water loss; support/transport of nutrients through vessels; reproductive and developmental features
Adaptation
a genetic trait gained through evolution
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
CO2 + H₂O + sunlight→ C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose)+ O₂
What is the pigment in plants called?
Chlorophyll
What is the gas exchange in plants?
Take in CO2 and release O2 & H2O
Guard cells
Makes the opening for the stoma; it opens more based on how much water is in them (more water = more open)
Stoma (Stomata)
Opening that takes in CO2 on a plant, controlled by guard cells
Nonvascular
No vessels (charophytes and bryophytes)
Bryophytes
Mosses; earliest plant type, the only land plant with no vessels
Why will bryophytes never get big?
No vessels to carry nutrients
What type of plants are most successful?
Those that utilize pollen and seeds; gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seedless plants
Must be somewhere with access to water at all times; mosses and ferns both require water for reproduction (flagellated sperm)
How do seedless plants reproduce?
Seedless plants require water for the flagellated sperm to swim to the egg for fertilization.
Ferns
No seeds; vessels make them bigger
What is xylem?
The vascular tissue in plants responsible for the transport of water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
What is phloem?
The vascular tissue in plants that transports sugars downward from the leaves.
Gymnosperms
Seed-producing plants (conifers) found in taiga
Angiosperms
Flowering plants
What percent of plants are angiosperms?
80%
Why are seed plants so successful?
Seeds protect and provide food for embryo; they don’t require water to reproduce; seeds and pollen are easily dispersible through animals and wind.
Pollen
A fine powder produced by seed plants that contains sperm. It is carried by wind or animals to fertilize plant eggs.
When do you see male cones?
Spring
How do you know a gymnosperm is ready for reproduction?
Seed splits apart
What structure helps a gymnosperm seed to travel?
a wing-like structure; wind
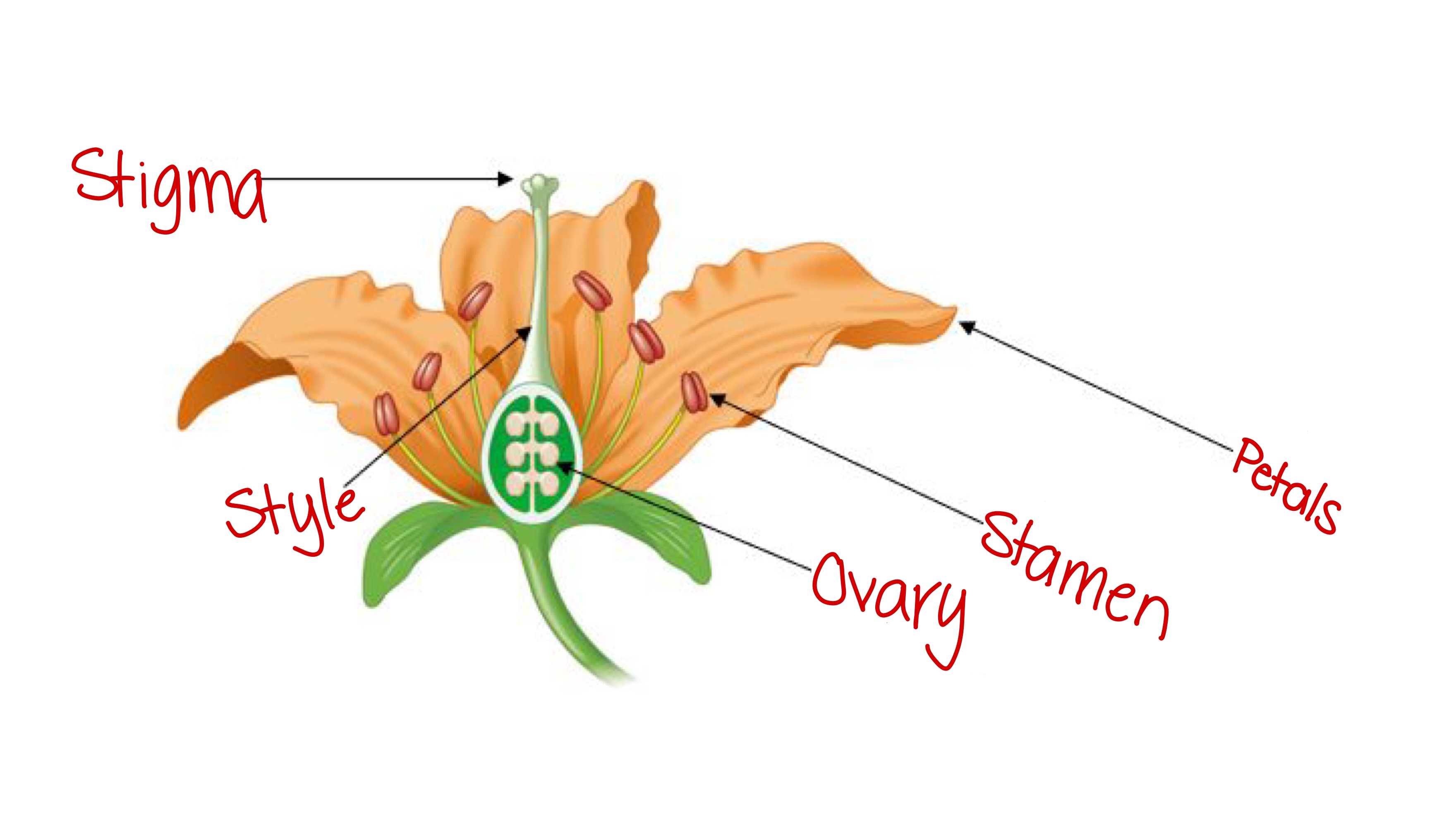
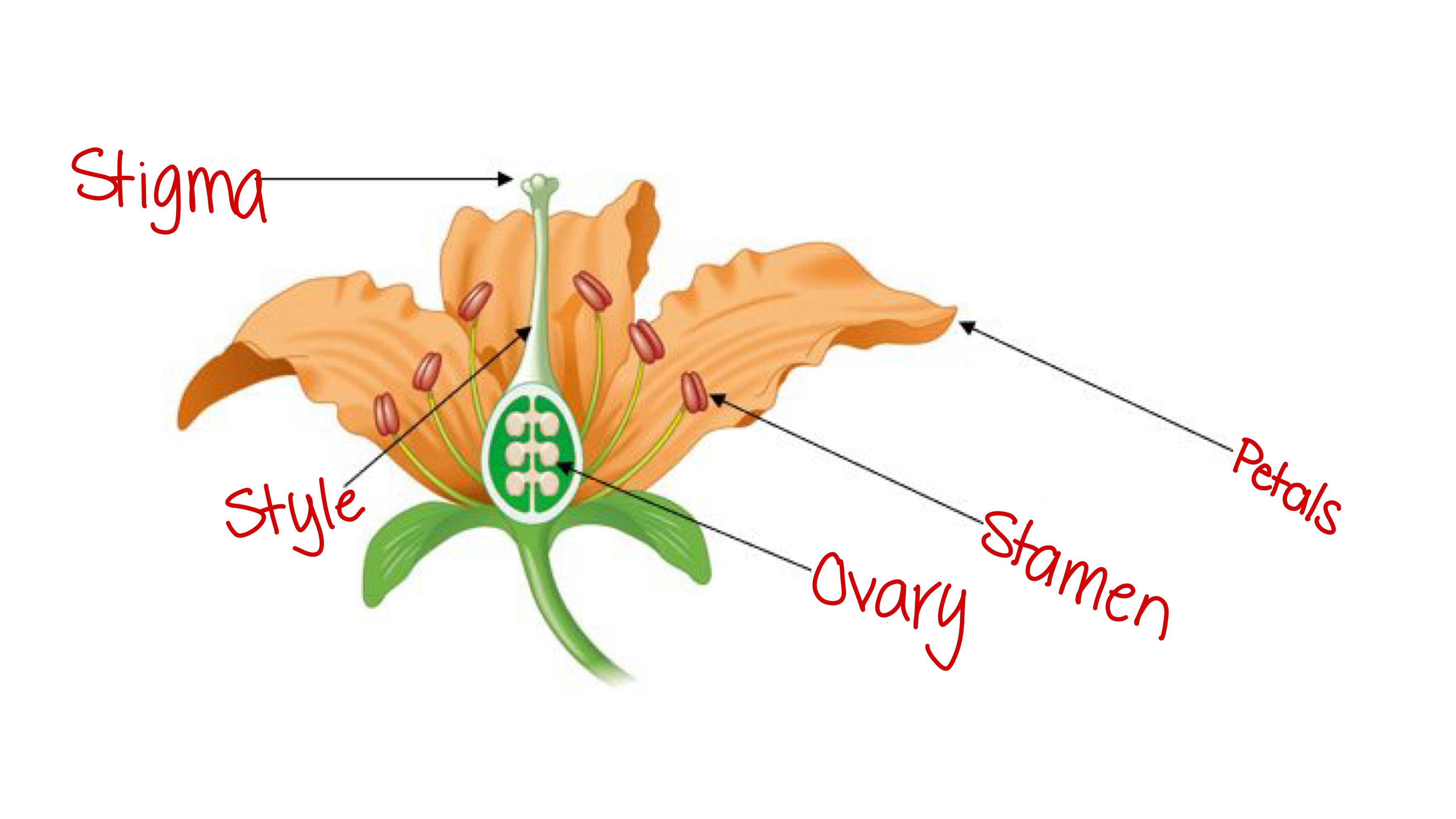
Petals (angiosperm)
Protective; open and expose reproductive parts, attract animals to aid in reproduction
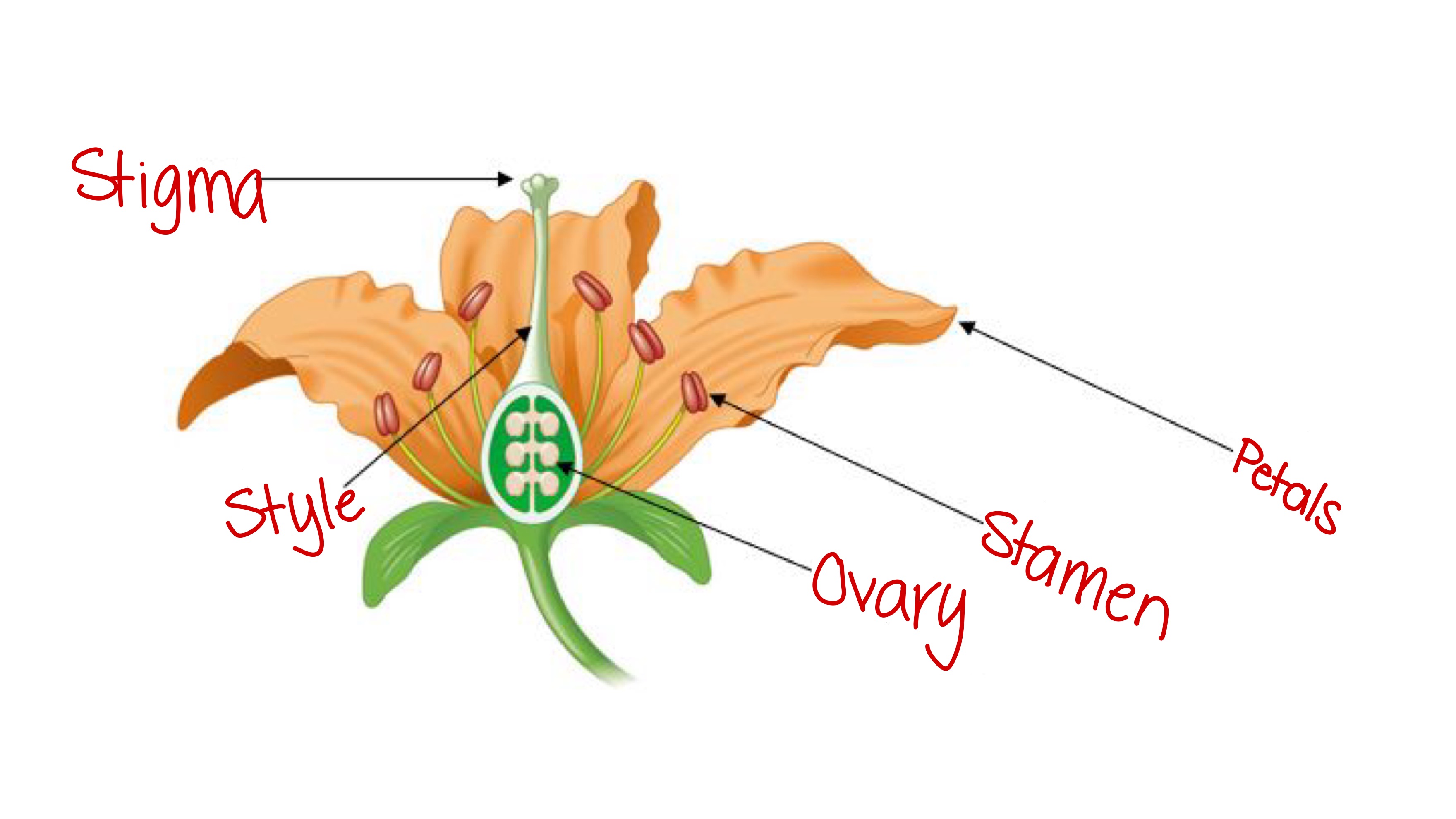
Stamen (angiosperm)
The male reproductive part of a flower, has a filament to lift up the top part, which holds pollen.
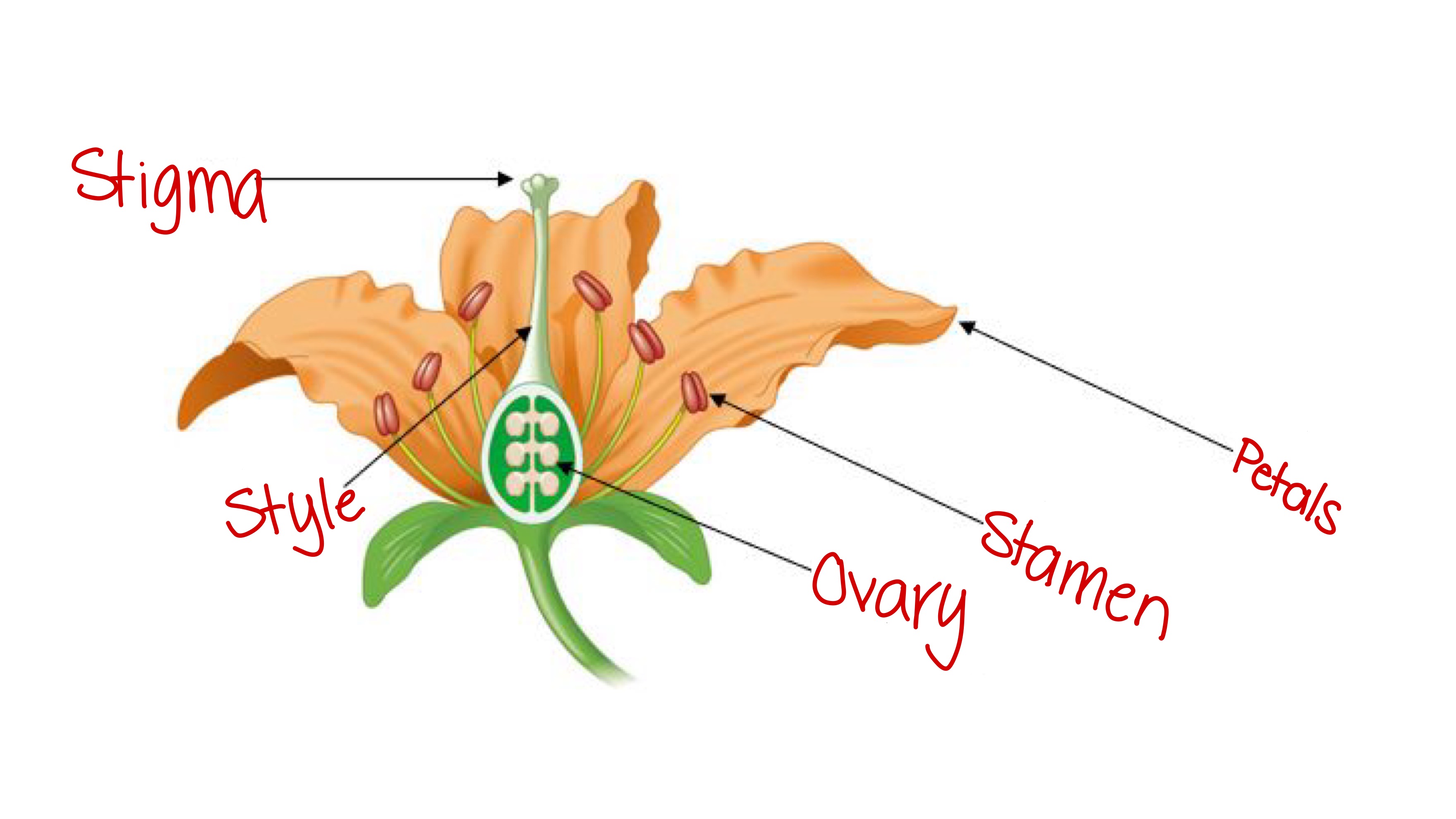
Stigma (angiosperm)
Female part of the flower; the sticky part of a flower that holds onto pollen grains and opens them to expose sperm.
T/F: Pollen grain makes the cells that create the tube needed for the sperm to reach the egg.
True
Carpel (angiosperm)
The female reproductive structure of a flower; consists of the ovary, style, and stigma.
Ovary (angiosperm)
The part of the flower that holds the egg and becomes the fruit after fertilization
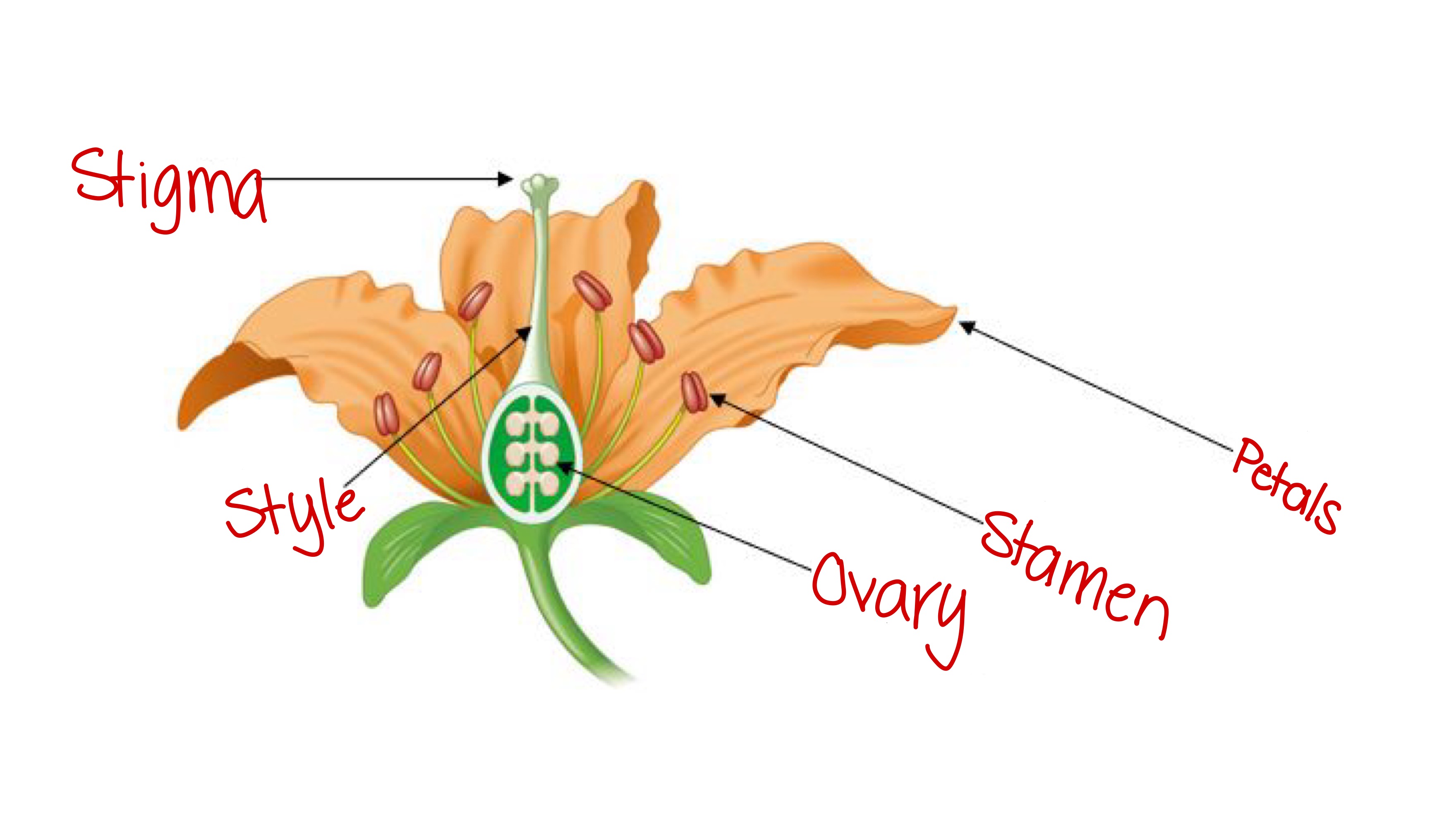
Style (angiosperm)
The slender stalk that connects the stigma to the ovary in a flower; sperm travels down to fertilize the egg.
Ovule (angiosperm)
The structure within the ovary that contains the egg and develops into a seed after fertilization.
Fruit (angiosperm)
Anything that grows from an ovary (tomatoes, peas)
How do animals help plants reproduce?
Help carry pollen from flower to flower
How do bees pollinate?
Pollen is attracted to hairs
How do hummingbirds pollinate?
They are attracted to nectar and transfer pollen between flowers as they feed; long beaks help reach flowers bees can’t
How does a moth pollinate?
Moths are attracted to night-blooming flowers due to their strong scents and transfer pollen while feeding on nectar; they have a long straw they can tuck under their chin.
How do bats pollinate?
Bats are attracted to flowers that bloom at night; they transfer pollen while feeding on nectar.
T/F: Mammals can pollinate.
True; rare, bats
T/F: Bats pollinate AND disperse seeds
True
Bats
sole pollinator of agave plants, eat fruits and disperse seeds, eat insects
Where is agave found and what is it used for?
The desert; tequila
What is the difference between pollination and fertilization?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part (getting on the stigma). Fertilization is when the egg and sperm unite, and the ovary grows.
Where do “helicopter” seeds come from?
maple trees
How are helicopters and dandelions dispersed?
Wind
What are the benefits of plants?
Food and oxygen; lumber and plants (gymnosperms)
What type of plants do nearly all of our food come from?
Angiosperms
Human benefits of plants
Main agriculture crops (wheat, rice, corn, soybeans), fruit, veggies, spices, coffee, tea, chocolate, hardwood lumber, fiber/clothing (cotton), culture (perfume, decoration, symbols of life, love, death), medicines
T/F: 25% of all pharmaceuticals are derived from plants.
True
What types of medicines come from plants?
Painkillers. cancer treatments, aspirin, caffeine
Examples of fungi
Mushrooms, molds, yeast
What is different about yeast as a fungus?
It is the only single-celled fungus, it uses asexual reproduction
Fungi
Most are multicellular, found in soil or water, heterotrophic
In what ways are fungi similar to plants?
Both have an aquatic protist ancestor and both have cell walls (fungi walls are made of chitin while plant walls are made of cellulose)
T/F: Fungi can grow up to 1 km each day.
True
Mushrooms
specialized mass of filaments; emerges from soil with rain only for reproduction, produce spores for reproduction
Puffballs
thin, brown, fungi outside of ground; release spores when thin layer is broken (stepped on or brushed against)
Nutrient acquisition
digest by excreting exoenzymes; then ingest by absorption; store food as glycogen
T/F: Fungi are the only organisms that digest outside of the body
True
Decomposers (fungi)
Break down cellulose and help recycle nutrients
Mycelia
The root structures of fungi, help with decomposition and nutrient cycling and forming the symbiotic relationships with plants (michorrizae)
Mycorrhizae
Symbiotic associations between fungi and plant roots that enhance nutrient absorption.
Symbiotic
live together
Mutualistic
Both organisms benefit
What are the benefits for fungi and a tree in a mycorrhizal relationship?
Fungi secretes enzymes that give the tree more nutrients through the roots; fungi receives sugars through photosynthesis
Lichen
A symbiotic association between fungi and algae; algae can live out of the water (grow on trees), fungi gets sugars from photosynthesis
T/F: Mycorrhizae is better for growth than chemical fertilizers.
True
Leaf cutter ants: mutualism between fungi, ants, and plants
Leaf cutter ants cultivate fungi, providing them with leaves while the fungi, in turn, serve as a food source for the ants. This relationship supports both the ants and the fungi in their growth and reproduction.
What is the symbiotic relationship between fungi and ruminant guts? (cows, goats, deer)
entire diet is full of fiber so they can’t get everything from food
Animals get more nutrients, fungi get a warm protective environment
How can you tell an animal is ruminant?
Their feet! Split hooves
How do cows get more nutrients?
Chewing cud; regurgitation
How do rabbits get more nutrients?
Eat feces
Parasitic fungus
A type of fungus that derives nutrients from a host organism, often harming it in the process. Symbiotic relationship (Still living together)
T/F: 80% of all plant diseases are caused by fungi.
True
Zombie fungus
Parasitic fungus that changes the host’s behavior once infected.
How does zombie fungus make hosts behave?
Travel higher t oproduce more spores, lockjaw until death, fungi takes over and releases spores
Human fungi
Ringworm, athlete’s foot, yeast infections
Athlete’s foot
fungal enzymes eat skin cells; caused by moisture
White-nosed bat syndrome
Fungus grows on face and wings of bats causing starvation; can result in 75-100% mortality
What are the general features of all animals?
Multicellular, heterotrophic organisms (have no cell walls); obtain nutrients by ingestion, diverse in morphology (form) and habitat (99% are invertebrates and mostly marine).
What are hox genes?
Specifically connected to embryonic development, specify where body parts are developed (limbs) and when/where genes are expressed.
morphology
means form
What is the ancestor of animals?
A protist; choanoflagellate
Evolution progression?
Sea > freshwater > land
Phylum
Animals
What are the 9 major phyla based on?
key characteristics and evolutionary advancements
Phylum porifera
Sponges; group of cells; all different shapes/sizes, little symmetry; named for pores; simple cellular organization, sedentary, many specialized cells, develop from embryo.
choanocyte “collar cell”
Cells found in sponges; have a main body, a collar, and tail; purpose is to obtain food; they create a current that moves water through pores and out of sponge to filter food from water.
Phylum Cnidaria
jellyfish, corals, anemones, and hydra; specialized structures and cells (stinging cells); active movement; radial symmetry
T/F: Coral and anemones are sedentary.
True