BIO Final 2023
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
A. small and nonpolar
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane by simple diffusion?
A. small and nonpolar
B. large and hydrophobic
C. large and polar
D. cations and anions
E. monosaccharides such as glucose
C. 2
In the energy investment phase of glycolysis, how many ATP molecules are expended for every molecule of glucose?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
D. Pyruvate is decarboxylated and reduced into ethanol
In alcohol fermentation, when compared to aerobic respiration, what is the primary difference regarding the fate of pyruvate?
A. Pyruvate is decarboxylated and oxidized to acetyl-CoA
B. Pyruvate directly enters the citric acid cycle
C. Pyruvate is unable to be formed through glycolysis
D. Pyruvate is decarboxylated and reduced into ethanol
E. Pyruvate is oxidized into lactic acid
E. A substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein would also block the transport of glucose
If a membrane protein in an animal cell in the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions into the cell, which of the following is most likely true?
A. The sodium ions and glucose are both moving against their electrochemical gradient
B. ATP is required for glucose and sodium ions to enter the cell by facilitated diffusion
C. Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell
D. Potassium ions move across the same gradient as sodium ions
E. A substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein would also block the transport of glucose
E. Breakdown of Pyruvate
You are studying a mutated cell that has a defect in aerobic respiration. In the presence of oxygen, you determine that the cell produces a large amount of a 3-Carbon molecule that builds up in the cytosol and that it is making only a small amount of ATP. Which part of aerobic respiration is most likely impacted by the mutation?
A. Citric Acid Cycle
B. Oxidative Phosphorylation
C. Fermentation
D. Glycolysis
E. Breakdown of Pyruvate
E. hypotonic, enter, expand
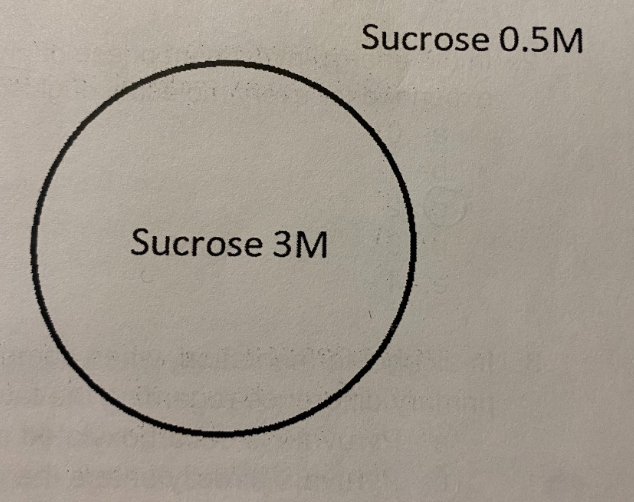
In the picture to the right, the concentration of sucrose (an impermeable molecule) inside and outside of the cell are shown. Use the picture to answer the question:
The solution is _______ compared to the cell, meaning water will _______the cell and the cell will ________
A. hypertonic, enter, expand
B. hypotonic, leave, shrink
C. hypertonic, leave, expand
D. hypotonic, enter, shrink
E. hypotonic, enter, expand
C. To prevent the over-accumulation of metabolic pathway products
What is the primary purpose of feedback inhibition regulation in a metabolic pathway?
A. to increase the rate of flux through the metabolic pathway
B. To promote the enhanced synthesis of metabolic pathway products
C. To prevent the over-accumulation of metabolic pathway products
D. To convert catabolic pathways into anabolic pathways
E. All of the Above
B. The molecule’s chemical bonds and their strengths
What is the primary factor that determines the amount of energy stored within a molecule in the form of chemical potential energy?
A. The temperature at which the molecule is stored
B. The molecule’s chemical bonds and their strengths
C. The molecule’s color and transparency
D. The molecule’s size and shape
E. The number of electrons in the molecule
A. Develop a drug that is an irreversible inhibitor of adenylyl cyclase
A pharmaceutical company wishes to develop a drug that will dull the sense of smell in hypersensitive individuals. Their goal is to prevent the depolarization of the olfactory receptor neuron. This depolarization occurs when Cl- ions diffuse out of the cell through a Ca2+ gated Cl- channel, based on the cell signaling pathway outlined in the figure. What would be an effective drug development approach?
A. Develop a drug that is an irreversible inhibitor of adenylyl cyclase
B. Develop a drug that prevents GTP hydrolysis to GDP in a G-Protein
C. Develop a drug that is a competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase
D. Develop a drug that permanently opens the Ca2+ gated Cl- channel
E. All of the above strategies would be effective in preventing depolarization
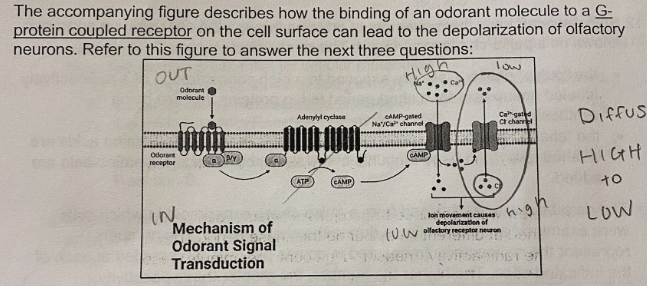
E. Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations are higher outside of the cell, Cl- concentrations are higher inside of the cell
Based on the figure, what are the relative concentrations of Na+, Ca2+, and Cl- inside vs. outside the cell prior to binding the odorant molecule
A. Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations are higher inside the cell, Cl- concentrations are higher outside of the cell
B. Na+ and Cl- concentrations are higher inside of the cell, Ca2+ concentrations are higher outside of the cell
C. Na+, Ca2+, and Cl- concentrations are all higher outside of the cell
D. Na+, Ca2+, and Cl- concentrations are all higher inside of the cell
E. Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations are higher outside of the cell, Cl- concentrations are higher inside of the cell
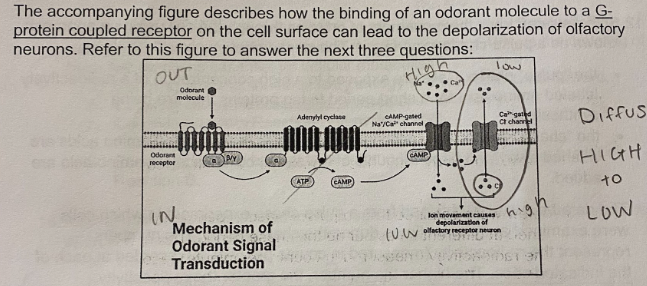
E. All of the Above
Based on the pathway, what would be an effective way to turn the signaling pathway off?
A. Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP on the G-protein
B. Release of the odorant molecule from the G-protein coupled receptor
C. Hydrolysis of cAMP to AMP by phosphodiestrase
D. Closing of the Ca2+ gated channel
E. All of the above
D. The mitochondria; post-translational sorting signal
What is the primary destination of the proteins that are being produced and what sorting signal is involved in this process?
A. The endomembrane system; cotranslational sorting signal
B. The endoplasmic reticulum; post-translational sorting signal
C. The cytosol; no sorting signal
D. The mitochondria; post-translational sorting signal
E. The protein is secreted from the cell; cotranslational sorting signal
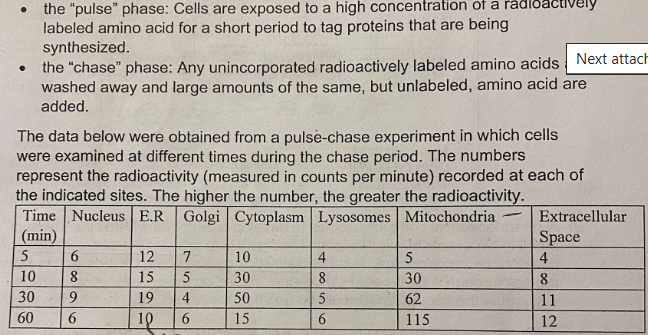
B. Chemiosmosis
Through which process does ATP synthase produce ATP?
A. Substrate-level phosphorylation
B. Chemiosmosis
C. The reduction of ADP in the electron transport chain
D. The transfer of electrons from O2 to NADH
E. Electrons flowing down their concentration gradient
A. NAD+ is converted to NADH, while G3P is oxidized to 1,3-BPG
In one of the early steps in the energy liberation phase of glycolysis, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) is converted to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG) and NAD+ is converted to NADH. What most accurately describes the changes that occur during this chemical reaction?
A. NAD+ is converted to NADH, while G3P is oxidized to 1,3-BPG
B. NAD+ is oxidized to NADH, while G3P is reduced to 1,3-BPG
C. NADH is reduced to NAD+, while G3P is oxidized to 1,3-BPG
D. NADH is oxidized to NAD+, while G3P is reduced to 1,3-BPG
E. NAD+ is neither converted nor reduced in this reaction, it remains unchanged
A. Coupling provides the necessary energy to drive Reaction B forward.
In a metabolic pathway, Reaction A is highly exergonic, while Reaction B is highly endergonic. The cell couples these two reactions together. Why is the coupling of these two reactions essential for cellular metabolism?
A. Coupling provides the necessary energy to drive Reaction B forward.
B. Coupling allows Reaction A to proceed spontaneously
C. Coupling prevents Reaction B from occurring
D. Coupling increases the speed of Reaction B
E. Coupling provides energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of Reaction B
C. The lysosome
A protein is being synthesized in the rough ER of a plant cell. What is a possible final destination for this protein?
A. The mitochondria
B. The nucleus
C. The lysosome
D. The chloroplast
E. ALL of the above
E. Facilitated Diffusion
Glucose diffuses slowly through the artificial phospholipid bilayer. The cells lining the small intestine, however, rapidly move large quantities of glucose from the glucose-rich-food into their glucose-poor cytoplasm. Using this information, which transport mechanism is most probably functioning in the intestinal cells?
A. Simple Diffusion
B. Secondary Active Transport
C. Primary Active Transport
D. Exocytosis
E. Facilitated Diffusion
A. Catabolic Pathways
What is the name used to describe the type of metabolic pathways that involve the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process?
A. Catabolic Pathways
B. Anabolic Pathways
C. Deconstructive Pathways
D. Energy harvesting pathways
E. Feedback pathways
C. 8
A total of 4 glucose molecules complete glycolysis. What would be the NET production of ATP?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 12
E. 16
B. It will be on the side facing the ER lumen
The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER, what side of the ER membrane will the ATP binding site be on?
A. It will be on the cytosolic side of the ER
B. It will be on the side facing the ER lumen
C. It could be facing in either direction because the orientation of proteins is scrambled in the Golgi apparatus.
D. It doesn’t matter, because the pump is not active in the ER
A. i only
A total of 2 glucose molecules have begun to undergo aerobic cellular respiration. The cell has made a NET total of 4 ATP and 4 NADH, what phases of cellular respiration have been completed?
i. Glycolysis ii. breakdown of pyruvate iii. citric acid cycle iv. oxidative phosphorylation
A. i only
B. i and iii
C. i and ii
D. i,ii, and iii
E. iii only
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation
How is ATP produced through fermentation?
A. Chemiosmosis
B. Dephosphorylation
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation
D. Oxidative phosphorylation
E. Production of FADH2
C. Phospholipids and proteins
Which of the following types of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane?
A. Phospholipids and cellulose
B. Nucleic acids and proteins
C. Phospholipids and proteins
D. Proteins and cellulose
E. Glycoproteins and cholesterol
A. Acetyl CoA would not be able to enter the citric acid cycle
A cell becomes mutated, and its mitochondria no longer produce any oxaloacetate. How would this affect the breakdown of glucose within the cell?
A. Acetyl CoA would not be able to enter the citric acid cycle
B. A net gain of 4 ATP would be produced since oxidative phosphorylation cannot be completed
C. The cell would be unable to generate any ATP from glucose
D. The cell would stop producing CO2 from glucose
E. All of the above
B. Gene expression
In a laboratory experiment, you are investigating the effects of a specific drug on cell communication pathways. You observe that this drug inhibits the phosphorylation of signal transduction proteins. Which of the following cellular processes is most likely to be impacted by this drug’s actions?
A. Membrane permeability
B. Gene expression
C. Cellular respiration
D. Endocytosis
E. DNA replication
E. An endoplasmic reticulum
All of the following are part of the prokaryotic cell cycle except:
A. DNA
B. A cell wall
C. A plasma membrane
D. Ribosomes
E. An endoplasmic reticulum
C. The maximum velocity or rate at which an enzyme-catalyzed reaction proceeds at saturating substrate concentrations
What does the term “Vmax” represent in enzyme kinetics?
A. The initial rate of the reaction
B. The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum
C. The maximum velocity or rate at which an enzyme-catalyzed reaction proceeds at saturating substrate concentrations
D. The maximum enzyme concentration in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
E. The pH at which the enzyme exhibits maximum activity
D. The ΔG is negative and is unrelated to the activation energy barrier
Consider an Exergonic chemical reaction. how does the ΔG value relate to the energy activation barrier of the reaction?
A. The ΔG value is negative, which lowers the activation energy barrier
B. The ΔG value is positive, which raises the activation energy barrier
C. The ΔG value depends on whether the activation energy barrier is negative or positive
D. The ΔG is negative and is unrelated to the activation energy barrier
E. The ΔG value dictates the rate of the chemical reaction, while the activation energy barrier dictates whether the reaction is favorable
E. Substrate-level phosphorylation couples a highly exergonic reaction to promote the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
In cellular respiration, what is the primary role of substrate-level phosphorylation?
A. Substrate-level phosphorylation involves the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and is often coupled with endergonic reactions
B. Substrate-level phosphorylation primarily occurs during oxidative phosphorylation
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation is the primary method of synthesizing ATP into the mitochondria.
D. Substrate-level phosphorylation can only take place under anaerobic conditions
E. Substrate-level phosphorylation couples a highly exergonic reaction to promote the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
C. The catabolism of proteins, carbs, and fats all rely on the presence of oxygen
****What can you determine from the diagram?
A. Cells require 3 completely independent pathways to break down proteins, carbs, and fats
B. Fatty acids can serve as an input for glycolysis
C. The catabolism of proteins, carbs, and fats all rely on the presence of oxygen
D. Pyruvate is an intermediate that is only formed from the breakdown of carbs
E. Glycerol cannot be used to make ATP under aerobic conditions
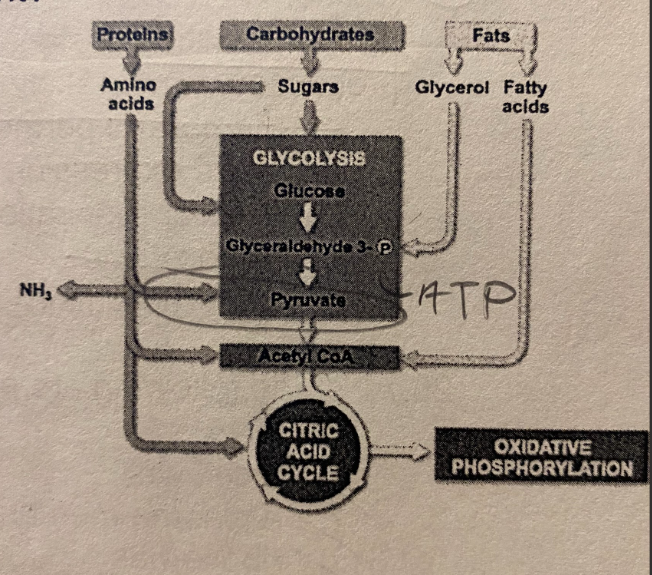
D. Oxidative Phosphorylation
In an experiment to determine the relative importance of the 4 pathways in cellular respiration, a researcher selectively inhibits the activity of the mitochondrial inner membrane proton pumps associated with the electron transport chain. As a result, which of the following processes would be most directly affected?
A. Glycolysis
B. Breakdown of Pyruvate
C. Citric Acid Cycle
D. Oxidative Phosphorylation
E. Energy Liberation Phase
B. Smaller cells can readily exchange materials with the environment
What is one significant advantage of cells maintaining a small size?
A. Smaller cells can store more genetic information
B. Smaller cells can readily exchange materials with the environment
C. Smaller cells can maintain stronger control over metabolism
D. Smaller cells have a greater capacity for movement
E. Smaller cells can replicate more rapidly
A. Cytosol
The first 18 amino acids of a newly translated cytochrome oxidase enzyme, one of the members of the ETC, serve as a sorting signal for protein receptors on the mitochondria. These amino acids form an a-helix with positively charged amino acids on one face and nonpolar amino acids on the opposite face. If this sequence is altered so that the a-helix of the sorting signal is comprised entierly of polar amino acids are distributed equally on both faces of the signal peptide, where will you likely find this protein?
A. Cytosol
B. Mitochondrial Matrix
C. Mitochondrial Inner Membrane
D. Golgi Apparatus
E. Plasma Membrane
B. A decrease in the pH of the intermembrane space
In oxidative phosphorylation, the proton gradient is established across the inner mitochondrial membrane. If a substance is added that inhibits the function of ATP synthase, what would be the effect?
A. An increase in the pH of the intermembrane space
B. A decrease in the pH of the intermembrane space
C. An increase in the pH of the mitochondrial matrix
D. No change in the pH of the intermembrane space or the mitochondrial matrix
C. Plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytosol
The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells if often much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells. What is the most reasonable explanation for this observation?
A. Plant cells are capable of having a much higher surface-to-volume ratio than animal cells
B. Plant cells have a much more highly convoluted (folded) plasma membrane than animal cells
C. Plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytosol
D. Animal cells are more spherical, while plant cells are elongated
E. The basic functions of plant cells are very different from those of animal cells
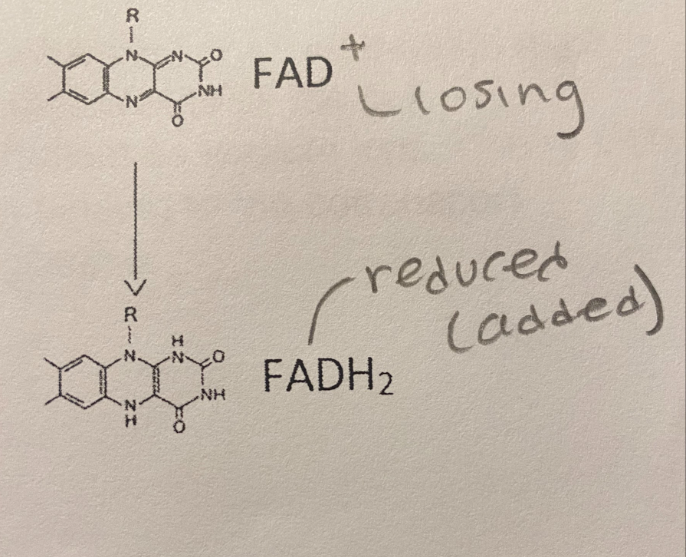
B. The oxidizing agent; reduced
In the reaction illustration to the right, FADS is _______ and FADH2 is _________.
A. Reduced; the oxidizing agent
B. The oxidizing agent; reduced
C. Oxidized; the oxidizing agent
D. The reducing agent; oxidized
E. The reducing agent; reduced
A. The inhibitor is competitive
In a biochemical experiment, an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is evaluated in the presence of an inhibitor. The researchers notice that increasing the concentration of the substrate leads to a gradual recovery of the reaction rate, until the enzyme ultimately fully recovers its activity. What can you conclude about the nature of this inhibitor based on this observation?
A. The inhibitor is competitive
B. The inhibitor is a substrate
C. The inhibitor is non-competitive
D. The inhibitor is irreversible
E. The inhibitor is an enzyme
B. It adheres to the second law because it is impossible to convert all the energy into useful work, and some energy will be lost as heat
A car engine converts chemical energy from gasoline into mechanical work to move the vehicle. In this process, some of the energy is lost as heat. How does this situation relate to the law of thermodynamics?
A. It violates the first law because energy cannot be converted from one form to another
B. It adheres to the second law because it is impossible to convert all the energy into useful work, and some energy will be lost as heat
C. It adheres to the second law because energy loss as heat is a characteristic of all energy conversions
D. It violates the first law because energy is lost in the process
E. It adheres to the second law because energy transformations are always 100% efficient
E. Lysosome
In animal cells, hydrolytic enzymes are packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles functions in this compartmentalization?
A. Central Vacuole
B. Peroxisome
C. Mitochondria
D. Chloroplast
E. Lysosome
C. discovery science
The method of scientific inquiry that describes natural structures and processes as accurately as possible through careful observation and analysis of data is known as….
A. experimental science
B. hypothesis-based science
C. discovery science
D. quantitative science
E. qualitative science
A. Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge
Nitrogen (N) is much more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of the following statements is correct about the atoms in ammonia (NH3)?
A. Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge
B. The nitrogen atom has a strong positive charge
C. Each hydrogen atom has a slight negative charge
D. The nitrogen atom has a partial positive charge
E. There are covalent bonds between the hydrogen atom
D. The strength of evidence against the null hypothesis
In the context of hypothesis testing, what does the p-value represent?
A. The probability of a successful experiment
B. The level of confidence in the research findings
C. The effect size of the experiment
D. The strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis
E. The precision of the measurement instrument used
E. Drawing a conclusion
In a biology laboratory experiment, students investigate the effect of different temperatures on the growth of a particular plant species. After analyzing the results, they determine that the plants grow best at a constant temperature of 25 Celsius. Which step of the scientific method does this finding directly relate to?
A. Formulating a hypothesis
B. Designing the experiment
C. Collecting and recording data
D. Communicating the results to peers
E. Drawing a conclusion
C. 10
How many molecules are needed to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long?
A. 12
B. 11
C. 10
D. 9
E. 8
A. the H of one water molecule and the O of another water molecule
An example of a hydrogen bond is the bond between…
A. the H of one water molecule and the O of another water molecule
B. the Na+ and Cl- in salt
C. The two hydrogen atoms in a molecule of hydrogen gas
D. the Ca2+ and Cl- in CaCl2
E. the C and H in methane (CH4)
A. Proteins
What macromolecule is composed of amino acids that are connected by a peptide bond?
A. Proteins
B. Carbohydrates
C. Nucleic Acids
D. Lipids
E. None of the Above
C. Molecules of this type are usually at room temperature
Which of the following statements is true regarding the molecule illustrated below?
A. It is a saturated fatty acid
B. It is a triglycerol
C. Molecules of this type are usually at room temperature
D. A and B only
E. A,B, and C
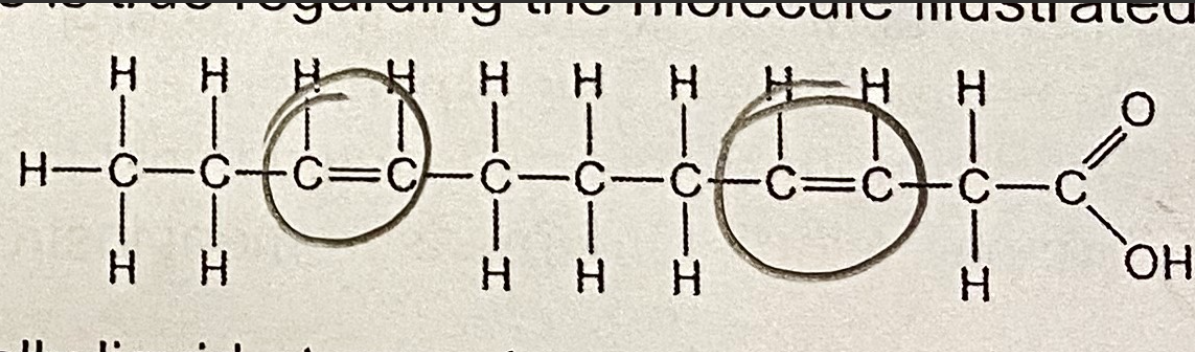
D. Atomic Number: 12, Mass Number: 25, Charge: +2
An atom has 12 protons, 13 neutrons, and 10 electrons. Determine the atomic number, the mass number, and the electric charge of this atom.
A. Atomic Number: 12, Mass Number: 13, Charge: +1
B. Atomic Number: 13, Mass Number: 25, Charge: +1
C. Atomic Number: 13, Mass Number: 12, Charge: +1
D. Atomic Number: 12, Mass Number: 25, Charge: +2
E. Atomic Number: 25, Mass Number: 12, Charge: +2
C. 40
If a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
A. 10
B. 20
C. 40
D. 80
E. impossible to tell from the information given
A. pH=2
From the selections below, which solution has the highest concentration of H+ ions?
A. pH=2
B. pH=4
C. pH=7
D. pH=10
E. pH=14
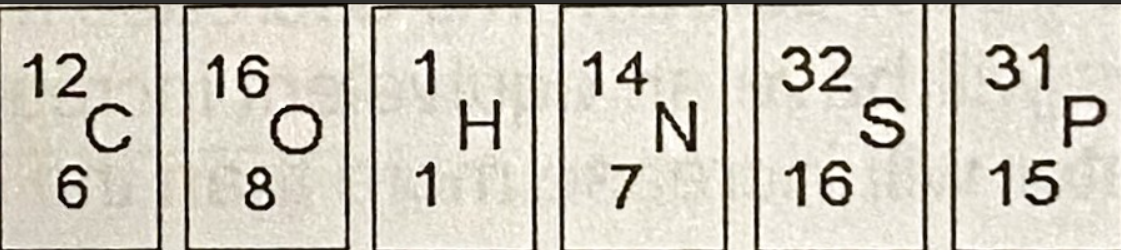
A. Sulfur
Based on the electron configuration determined from the figure, which of these elements would exhibit chemical bonding behavior most like that of oxygen?
A. Sulfur
B. Carbon
C. Hydrogen
D. Nitrogen
E. Phosphorous
B. 5
How many electrons does nitrogen have in it’s valence shell?
A. 2
B. 5
C. 7
D. 8
E. 14
E. Hydrogen bonds in water raise its heat capacity. This prevents extreme temperature changes in aquatic habitats.
How do the hydrogen bonds in water impact the ability of aquatic environments to support life?
A. Hydrogen bonds in water make it very difficult for salts to dissolve in water. This keeps ocean salt concentrations low enough to support life.
B. Hydrogen bonds in water create a low surface tension. This allows surface nutrients to flow into underwater aquatic ecosystems.
C. Hydrogen bonds in water cause it to evaporate at much lower temperatures than other liquids. This leads to rapid temperature changes that promote nutrient upswelling.
D. The presence of hydrogen bonds in water enables it to freeze more quickly than other solvents. This supports life in cold aquatic environments.
E. Hydrogen bonds in water raise its heat capacity. This prevents extreme temperature changes in aquatic habitats.
B. The pH of the water will decrease more than the buffer solution.
A lab researcher has two solutions at their bench; one is a solution of buffer and the other is a solution of pure water. Unfortunately, the label was worn off these two bottles and they must now devise and experiment to determine which is which. They add equivalent volumes of strong hydrochloric acid to each solution, and then measure the change in pH. What do you predict will happen in this experiment?
A. The pH of the buffer solution will increase more than the water
B. The pH of the water will decrease more than the buffer solution
C. The pH of the buffer solution will decrease more than the water
D. Both solutions will have an equivalent increase in pH
E. The pH of water will increase more than the buffer solution.
A. covalent bond
What type of chemical bond is responsible for linking amino acids together in a protein’s primary structure?
A. Covalent bond
B. Ionic bond
C. Hydrogen bond
D. Van Der Waals bond
E. Hydrophobic bond
D. C18H32O16
The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking 3 glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions?
A. C18H36O18
B. C18H30O15
C. C6H10O5
D. C18H32O16
E. C18H10O5
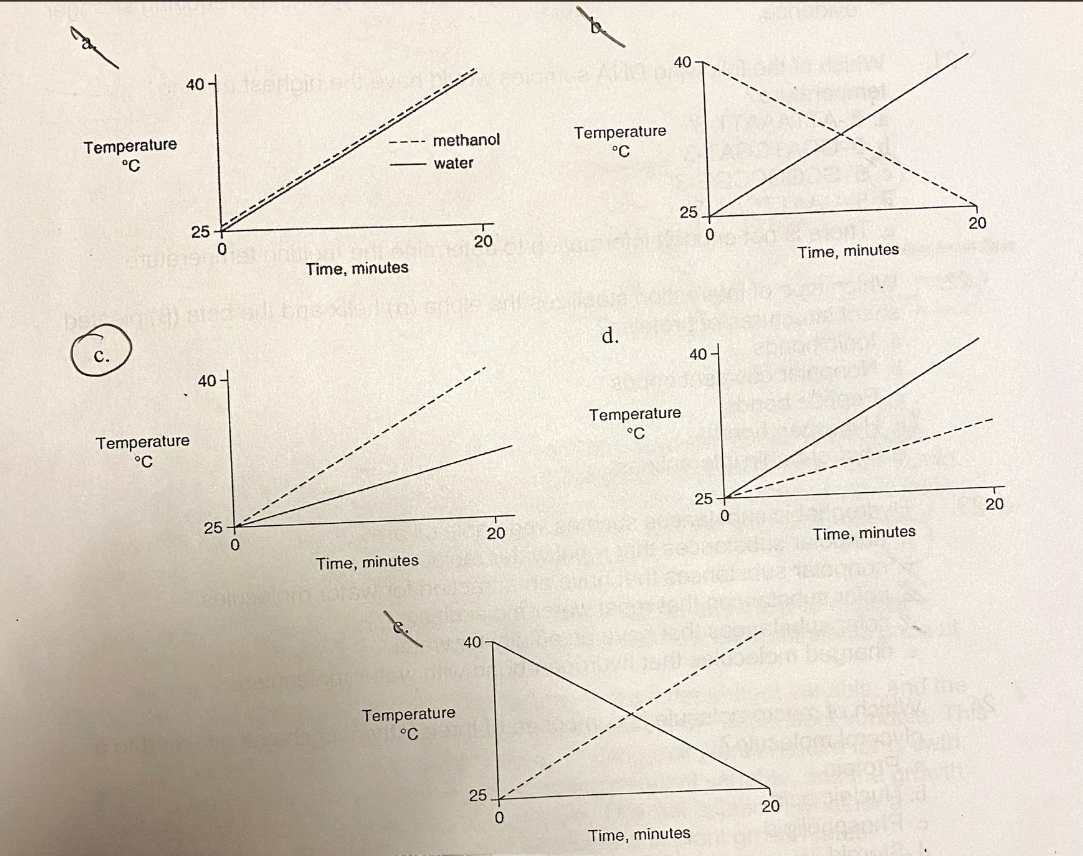
C.
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. Most of the covalent bonds of methanol molecules are non-polar, so there are less hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules compared to water. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and methanol?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
A. A long chain saturated fatty acid
Which of the following fatty acids is likely to have the highest melting temperature (convert from solid to liquid at the highest temperature)? **long chain = 16 carbons; short chain = 6 carbons
A. A long chain saturated fatty acid
B. A short chain saturated fatty acid
C. A short chain unsaturated fatty acid with 3 cis double bonds
D. A long chain monosaturated fatty acid with a single double bond
E. A short chain unsaturated fatty acid with trans double bonds
C. It would decrease the power of the test to detect significant events
What would be the impact of lowering the p-value from the standard threshold of 0.05 to 0.01 in a hypothesis test?
A. It would make it easier to reject the null hypothesis, requiring less evidence
B. It would have no effect on the hypothesis test’s outcome or conclusions
C. It would decrease the power of the test to detect significant events
D. It would increase the effect size in the study
E. It would make it more difficult to reject the null hypothesis, requiring stronger evidence
C. 5’-GCGGCCCG-3’
Which of the following DNA samples would have the highest melting temperature?
A. 5’-ATTAAATT-3’
B. 5’-GGATCGAT-3’
C. 5’-GCGGCCCG-3’
D. 5’-GAATTCAT-3’
E. There is not enough information to determine the melting temperature
D. Hydrogen bond
Which type of structure stabilizes the alpha and beta pleated sheet structures of proteins?
A. Ionic bonds
B. Nonpolar covalent bonds
C. Peptide bonds
D. Hydrogen bond
E. Hydrophobic interactions
A. Nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are…
A. Nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
B. Nonpolar substances that have an attraction for water molecules
C. Polar substances that repel water molecules
D. Polar substances that have an affinity for water
E. Charged molecules that hydrogen-bond with water molecules
E. Triacylglycerol
Which macromolecule is composed of 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule?
A. Protein
B. Nucleic Acid
C. Phospholipid
D. Steroid
E. Triacylglycerol
A. 0
A solution has a [H+] ion concentration of 1 M. What is the pH of this solution?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 7
D. 14
E. 15
E. All of the Above
Chymotrypsin is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes a peptide bond any time it encounters a phenylalanine, tryptophan, or tyrosine residue. About 10% of the sequence for hemoglobin is made up of these residues. Based on this information, which what level of hemoglobin protein structure will be impacted by treating it with chymotrypsin?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
E. All of the Above
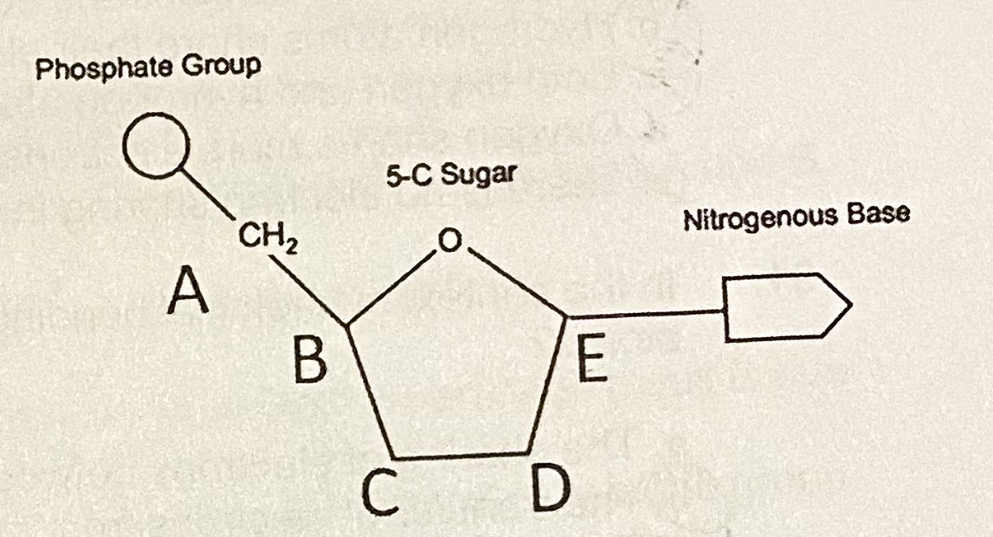
D. D
Which position of the nucleotide will tell you if you are looking at DNA or RNA?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
C. The amount of sunlight exposure is the independent variable, and the growth rate of the plant is the dependent variable. This will establish whether a correlation exists between sunlight exposure and plant growth rates.
Any number of variables can be manipulated in a scientific. If you wished to investigate the effect of sunlight exposure on plant growth, how would you appropriately design that experiment? Choose the answer that best identifies the independent variable, the dependent variable, and the best explanation of how these contribute to the goal of the experiment?
A. The type of plants used is the independent variable, and the rate of plant growth is the dependent variable. This will reveal how different plants grow at different rates.
B. The amount of sunlight exposure per day is the independent variable, and the height of the plants at the end of the experiment is the dependent variable. This will determine whether sunlight is the only thing that plants require for growth.
C. The amount of sunlight exposure is the independent variable, and the growth rate of the plant is the dependent variable. This will establish whether a correlation exists between sunlight exposure and plant growth rates
D. The height of the plants at the end of the experiment is the independent variable, and the nitrogen content of the soil is the dependent variable. This will determine whether nitrogen content causes plants to grow faster.
E. The temperature of the soil is the independent variable, and the sunlight exposure is the dependent variable. This will determine whether plant growth responds to soil temperature rather than sunlight exposure
B. Condensation/dehydration reaction, resulting in a peptide bond
In the formation of a bond between two amino acids, what type of chemical reaction occurs, and what is the resulting bond that is formed by this reaction?
A. Condensation/dehydration reaction, resulting in a glycosidic bond
B. Condensation/dehydration reaction, resulting in a peptide bond
C. Hydrolysis reaction, resulting in a glycosidic bond
D. Hydrolysis reaction, resulting in a peptide bond
E. Condensation/dehydration reaction, resulting in a phosphodiester bond
B. Hydrogen atoms share their electrons unequally with oxygen
In a molecule of water, the oxygen atom forms a covalent bond with 2 hydrogen atoms. How are electrons shared in this bond?
A. Oxygen shares its electrons equally with both hydrogen atoms
B. Hydrogen atoms share their electrons unequally with oxygen
C. Both oxygen and hydrogen toms lose electrons to form the bond
D. Oxygen shares more electrons with one hydrogen atom than the other
E. There is no electron sharing in a covalent bond
A. The sharing of electrons between 2 atoms
In the context of chemical bonding, what defines a covalent bond between 2 atoms?
A. The sharing of electrons between 2 atoms
B. The transfer of electrons from one atom to another
C. The attraction between oppositely charged ions
D. The formation of a crystal lattice structure
E. The exchange of protons between atoms
C. Secondary
A 100 amino acid protein is made up of only one amino acid: the uncharged and polar amino acid Serine. What is the highest level of protein structure that this protein can achieve?
A. None
B. Primary
C. Secondary
D. Tertiary
E. Quaternary
B. The carboxyl group of the first monomer is connected by a peptide bond to the amino group of the second monomer
How are the first 2 monomers of a protein connected?
A. the amino end of the first monomer is connected by a peptide bond to the carboxyl end of the second monomer
B. The carboxyl group of the first monomer is connected by a peptide bond to the amino group of the second monomer
C. The 3’ end of the first monomer is connected by a glycosidic bond to the 5’ end of the second monomer
D. The 5’ end of the first monomer is connected by a phosphodiester bond to the 3’ end of the second monomer
E. The carboxyl group of the first monomer is connected by a glycosidic bond to the amino group of the second monomer.
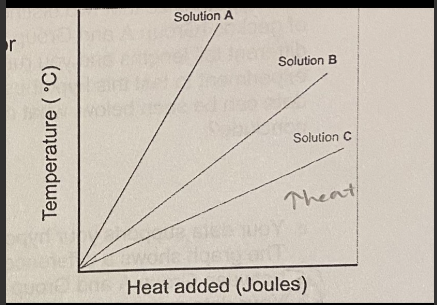
C. Solution C can form more hydrogen bonds than solutions A and B
3 pure solutions (A, B, C) are heated and their temperatures are monitored. The figure illustrates the temperature change for each of these solutions as a function of the amount of heat added. What can you conclude about solution C relative to solutions A and B?
A. Solution C is the most non-polar of the 3 solutions
B. Solution C must have a higher atomic mass than solutions A and B.
C. Solution C can form more hydrogen bonds than solutions A and B
D. Solution C has a lower heat capacity than solutions A and B
E. Solution C must contain a greater number of hydrogens than solutions A and B
A. Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested or some other factor
Why is it important for an experiment to include a control group?
A. Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested or some other factor
B. The control group is the group that the researcher is in control of; it is the group in which the researcher predetermines the nature of the results
C. The control group provides a reserve of experimental subjects
D. A control group is required for the development of an “if,then” statement
E. A control group assures that an experiment will be repeatable
E
How are the first 2 monomers of a nucleic acid connected?
A. The carboxyl group of the first monomer is connected by a peptide bond to the amino group of the second monomer.
B. The 3’ end of the first monomer is connected by a glycosidic bond to the 5’ end of the second monomer
C. The 5’ end of the first monomer is connected by a phosphodiester bond to the 3’ end of the second monomer.
D. The carboxyl group of the first monomer is connected by a glycosidic bond to the amino group of the second monomer
E. The 3’ end of the first monomer is connected by a phosphodiester bond to the 5’ end of the second monomer.
E. You reject your hypothesis. The data is not statistically significant
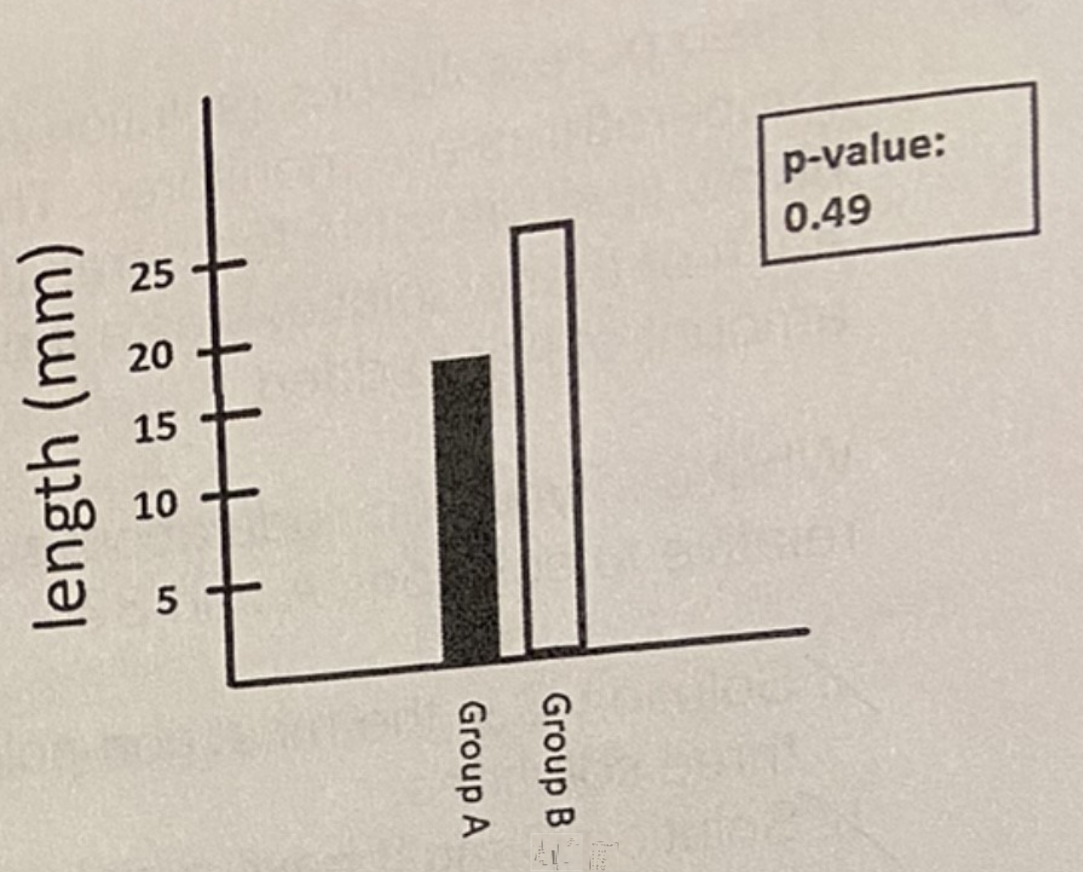
You hypothesize that 2 distinct groups of geckos (Group A and Group B) have different tail lengths and you run an experiment to test this hypothesis. Your data can be seen below, what can you conclude?
A. Your data supports your hypothesis. The graph shows a difference between Group A and Group B
B. Your data supports your hypothesis. The data is statistically significant
C. You reject your hypothesis. The graph shows a difference between Group A and Group B
D. More information is needed to reach a conclusion.
E. You reject your hypothesis. The data is not statistically significant.
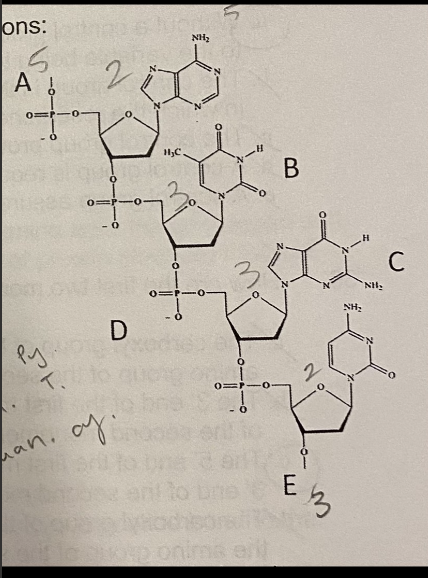
A. A
Which letter shows the 5’ end of the nucleic acid?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
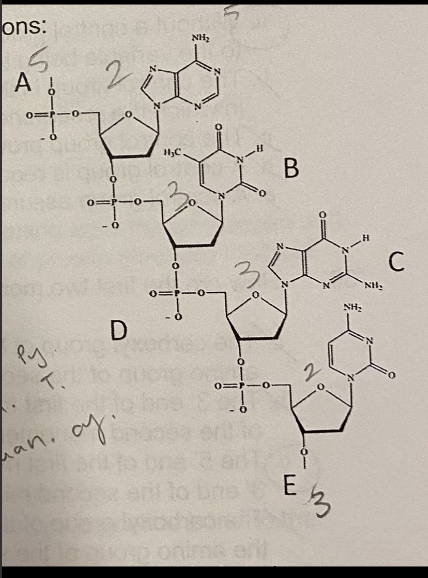
B. Pyrimidine, purine
The nitrogenous base indicated by letter B is a ______, and will most likely pair with ________.
A. Pyrimidine, pyrimidine
B. Pyrimidine, purine
C. Purine, purine
D. Purine, pyrimidine
E. Depends on if we are talking about DNA or RNA
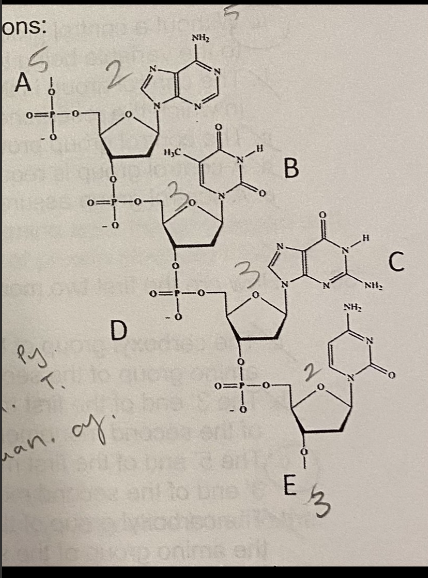
D. 10
How many hydrogen bonds will be present in this strand when it binds to its complement?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 10
E. 12
B. DNA helicase
Which molecule is responsible for separating double-stranded DNA into single strands?
A. DNA primase
B. DNA helicase
C. Topoisomerase
D. DNA ligase
E. single-stranded binding proteins
D. GG or Gg
Which of the following is a possible genotype of a good egg (one that has a gold shimmer)
A. GG
B. Gg
C. gg
D. GG or Gg
E. GG or gg

C. Heterozygous
One Oompa Loompa is working with a goose that lays both good eggs and bad eggs. What is the best description for the genotype of this goose?
A. Homozygous dominant
B. Homozygous recessive
C. Heterozygous
D. Hemizygous
E. A test cross would have to be performed to find out
A. anaphase I
What stage of meiosis is responsible for pulling apart homologous chromosomes?
A. anaphase I
B. anaphase II
C. metaphase II
D. prophase II
C. metaphase I
E. Metaphase of meiosis II
The following diagram illustrates a diploid cell with 12 chromosomes. In what phase of cell division is this cell?
A. Prophase of meiosis II
B. Metaphase of mitosis
C. Metaphase of meiosis I
D. Anaphase of mitosis
E. Metaphase of meiosis II
B. X-linked recessive
What mode of inheritance does the pedigree most likely suggest?
A. Autosomal recessive
B. X-linked recessive
C. Y-linked recessive
D. Autosomal dominant
E. X-linked dominant
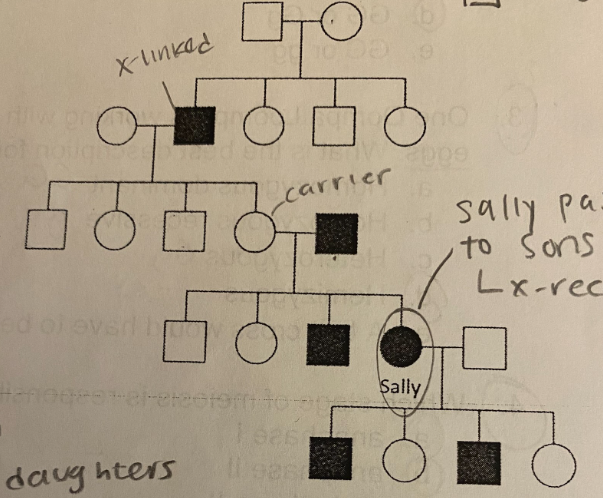
C. Homozygous recessive
What is Sally’s genotype?
A. Homozygous dominant
B. Heterozygous
C. Homozygous recessive
D. Hemizygous
E. Cannot be unambiguously determined
B. Treatment with RNAse will prevent bacterial transformation, while treatment with DNAse will have no effect.
In a hypothetical repetition of the Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty experiment where RNA is the transferring principle, which of the following outcomes is most likely to occur?
A. Treatment with DNAse will prevent bacterial transformation, while treatment with RNAse will have no effect.
B. Treatment with RNAse will prevent bacterial transformation, while treatment with DNAse will have no effect.
C. Treatment with RNAse and DNAse will both prevent bacterial transformation
D. Treatment with proteases will prevent bacterial transformation, while treatment with RNAse and DNAse will have no effect
E. Treatment with RNAse, DNAse, ad proteases will all prevent bacterial transformation
B. Guanine
Which purine base forms 3 hydrogen bonds when binding its complementary nucleotide base?
A. Cytosine
B. Guanine
C. Thymine
D. Uracil
E. Adenine
C. 16
In a species of plants, one individual has a diploid number of 10. If this plant undergoes the normal events of meiosis, how many possible ways can the homologous pairs of sister chromatids be arranged in meiosis I?
A. 4
B. 10
C. 16
D. 32
E. 64
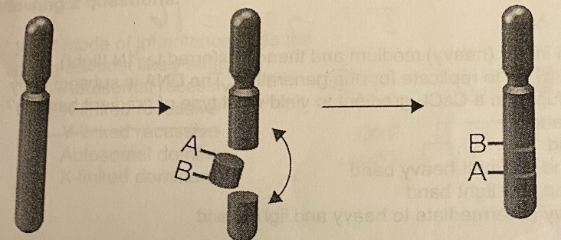
E. One half-heavy (intermediate to heavy and light) band
Bacteria are grown in 15N (heavy) medium and then transferred to 14N (light) medium and are allowed to replicate for one generation. The DNA is subsequently isolated and centrifuged in a CsCl2 gradient to yield what type of gradient band(s)?
A. One heavy band
B. One light band
C. One heavy and one half-heavy band
D. One heavy and one light band
E. One half-heavy(intermediate to heavy and light) band
D. It increases genetic diversity by creating new combinations of alleles
What is the significance of crossing over that occurs at the beginning of meiosis?
A. It leads to the formation of homologous chromosomes
B. It produces the kinetochore structure
C. It facilitates attachment of sister chromosomes to the spindle
D. It increases genetic diversity by creating new combinations of alleles
E. It results in the direct formation of diploid cells
E. Cell growth and protein synthesis
What is the primary function of the G1 phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
A. Formation of spindle fibers
B. Cell division
C. DNA replication
D. Preparation for mitosis
E. Cell growth and protein synthesis
D. Cyclins activate Cdks, leading to cell cycle progression
In the context of the eukaryotic cell cycle, how do cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) work together to regulate the progression of the cell cycle?
A. Cyclins inhibit Cdks, delaying cell cycle progression
B. Cdks inhibit cyclins, leading to cell cycle progression
C. Cyclins and Cdks have no regulatory role in the cell cycle
D. Cyclins activate Cdks, leading to cell cycle progression
E. Cdks activate cyclins, causing cell cycle arrest
E. Incomplete dominance
Suppose a true-breeding white-furred rabbit breeds with a true-breeding black-furred rabbit and all of their offspring have a phenotype of gray fur. What does the gene for fur color in rabbits appear to be an example of?
A. Codominance
B. Mosaicism
C. Disproportionate segregation
D. Complete dominance
E. Incomplete dominance
C. Inversion
How would the chromosomal mutation in this figure be classified?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Inversion
D. Simple translocation
E. Reciprocal translocation
D. 32 chromosomes at the end of G1, 32 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
If a diploid cell has n=16, how many chromosomes will it have at the end of the G1 phase, and how many pairs of sister chromatids will it have at the beginning of the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
A. 16 chromosomes at the end of G1, 32 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
B. 32 chromosomes at the end of G1, 64 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
C. 16 chromosomes at the end of G1, 16 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
D. 32 chromosomes at the end of G1, 32 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
E. 16 chromosomes at the end of G1, 32 pairs of sister chromatids at the beginning of G2
E. Deficiency in the kinetochore structure
In a sample of cells undergoing mitosis, a researcher observes that the spindle fibers form but that the chromatids do not separate during anaphase. What is a potential molecular explanation for this observed mitotic failure?
A. Overexpression of cyclins and Cdks
B. Excessive DNA replication during interphase
C. Mutations in the nuclear envelops proteins
D. Deficiency in microtubule assembly
E. Deficiency in the kinetochore structure
A.1
Which number on the figure below indicates the 5’ carbon of this nucleotide?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
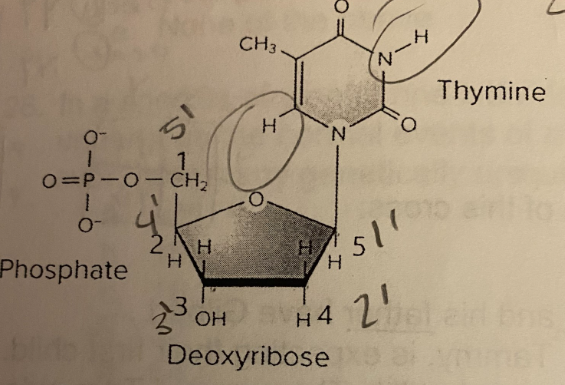
E. 24 chromosomes
Wheat is a hexaploid organism with a basic chromosome number of n=8. Wheat gametes are produced in meiosis through the same steps as outlined for diploid organisms. Based on this information, how many chromosomes are typically found in the gametes of wheat?
A. 2 chromosomes
B. 4 chromosomes
C. 8 chromosomes
D. 16 chromosomes
E. 24 chromosomes
B. X-O
In a controlled experiment, researchers discover a species that has males containing 12 autosomal chromosomal pairs and 1 sex chromosome and females containing 12 autosomal chromosomal pairs with 2 of the same sex chromosome. Which sex determination mechanism do these organisms most likely follow?
A. X-Y
B. X-O
C. Z-W
D. Y-Q
E. Haplodiploid