MOD 6 - Late Effects of Radiation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
late effects
stochastic, meaning the effects are increased with dose but the severity isn’t
occurs with low doses exposures over a prolonged time (whole/partial body)
opposite for late effects (type)
early effects which are deterministic (dose increase will increase chance of occurrence as well as severity)
break down of late effects
genetic
somatic
stochastic
carcinogenesis
teterogenesis
late tissue rxn / deterministic
fibrosis
sterility/fertility
cataractogenesis
carcinogenesis and late effects
almost negligible to non-existent as there is no evidence of increased risk
indistinguishable from normally occurring cancers
two main non-threshold risk models
non-threshold linear model
non-threshold linear quadratic model
Linear Non-Threshold Dose-Response Model
suggests that no dose should be completely safe and appropriate consideration of the risk vs benefit of the exposure needs to justify even small doses
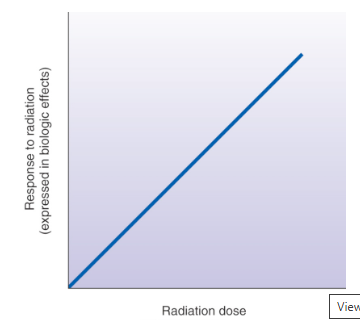
Linear Non-Threshold Dose Model appropriation
suits high-dose whole body population (not individuals) exposure response information satisfactorily
exaggerates the actual risk at low doses typical to medical imaging and partial body exposures
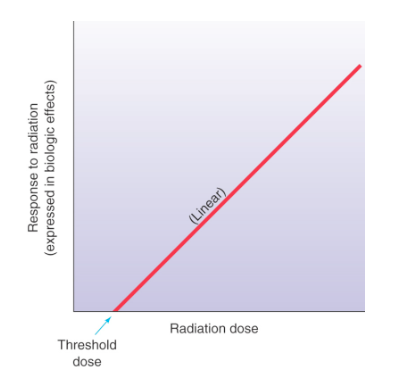
Linear Threshold Dose Response Model
proposes the existence of a threshold exposure below which there is no risk of a response
consideration for Linear Threshold Dose Response Model
an exact threshold value has not been established due to lack of sufficient life time data
not accepted practice to disregard the possibility of a potential small dose stochastic effect
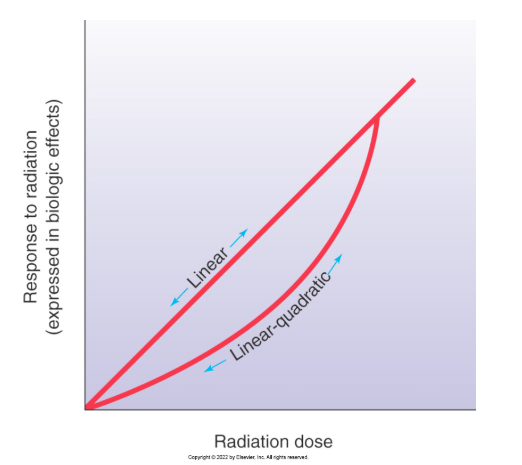
Linear Quadratic Dose-Risk Model
what
best application
rate of change in response is different at different doses unlike the LNT where damage/risk was proportional to dose
best applies for risk or leukemia and breast cancer
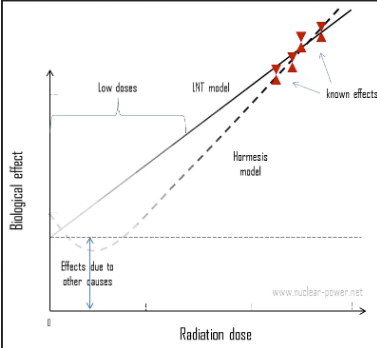
Radiation Hormesis Dose-Risk Models
suggests a beneficial effect of low-dose exposure creating up regulation in cellular activity, but still being investigated
populations with known low dose exposures to radiation (5-50 mSv) have reduced cancer death rates
purpose of non-threshold dose risk models
to better estimate the potential risk, due to the stochastic nature of low dose late effects
why are late effects hard to differentiate
since low dose exposures manifest as late effects months - years
not uniquely identifiable as ARS
where were late effect data extrapolated from
lower dose exposures in populations resting in peripheral regions of nuclear events
medical radiation exposures are
low dose
partial body
low LET (sparsely ionizing)
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
promotes minimizing exposure to meet the diagnostic task rather than striving for high IQ
effect of cumulative low dose exposure
while evidence suggests that infrequent low dose has negligible cumulative effect compared to a single equivalent higher dose; because of ALARA and risk vs. benefit thinking, we limit the cumulative exposure of individuals and populations
eg. stochastic late effects
leukemia
cancers
eg. late tissue reactions
cataractogenesis
organ atrophy
fibrosis
impaired fertility
sterility
late tissue reactions are
deterministic, meaning the chance of occurrence and severity increases with dose
radio sensitivity of the eyes is dependent on what
with age
higher age = less radiosensitivity
leukemia’s latent / at risk period
between 2-7 years
up to 20 years
influence of radiation source and damage
radiation source effects the body differently even when the dose is the same
dose response models
risk models that correlate the early and late effects
Late Effects of radiation on Fetus
inhibited growth
intellectual disability
microcephaly
genital deformities
sensory organ damage
birth abnormalities and medical imaging tests
rate is not increased with medical imaging tests, but abnormality may be more pronounced
Vancouver annual background equivalent
1.3 mSv
Genetic Effects
effects that are manifested in future generations, this effect has been proven on mice and fruit flies, however, it is still inconclusive to humans
Why is genetic effects still in consideration
because radiation exposure damage causes recessive genetic mutations (the mutation will only be passed down if the parents have the exact same recessive mutation)
genetic effects are interrelated with
the exposure to gonads rather than fetal exposure, which will alter the DNA or chromosomes of sperm/ova germ cells
why is it hard to differentiate genetic effects caused by radiation
due to other natural mutation causing factors such as viruses, chemicals and medications
most concerned late effect
cancer
late effects of low dose radiation have
limited to no incidence compared with non-exposed populations
chances of late effects manifesting are further influenced by
genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors
who has the highest risk of late effects
pediatrics and fetus
how much radiation will cause temporary male sterility
>2Gy
how much radiation will cause infertility of the ovaries
6Gy