AMINO ACIDS
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Glycine, Gly, G
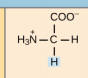
Alanine, Ala, A
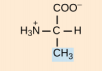
Valine, Val, V
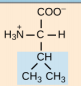
Leucine, Leu, L
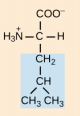
Methionine, Met, M
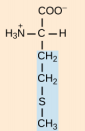
Isoleucine, Ile, I
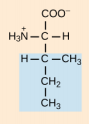
Serine, Ser, S
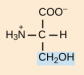
Threonine, Thr, T
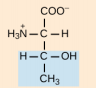
Cysteine, Cys, C
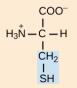
Proline, Pro, P
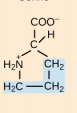
Asparagine. Asn, N
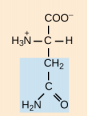
Glutamine, Gln, Q
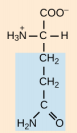
Lysine, Lys, K
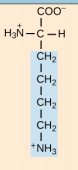
Arginine. Arg, R
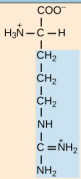
Histidine, His, H
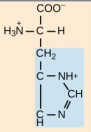
Aspartate, Asp, D
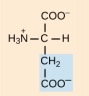
Glutamate, Glu, E
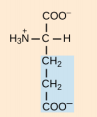
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
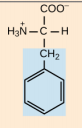
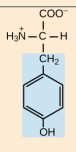
Tyrosine. Tyr, Y
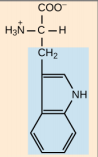
Tryptophan, Trp, W
Proteins
are polymers that are assembled from amino acid monomers that have been linked together.
amino group and a carboxylic acid group.
Each amino acid contains an
peptide bonds
Amino acids are coupled together by amide linkages, also called
polypeptides, proteins.
Chains comprised of fewer than 40 or 50 amino acids are often called while still larger chains are called
L-amino acids
Naturally occurring amino acids are
L- amino acid
The amino acid is an ______ if the amino group is on the left.
D- amino acids
______have the amino group placed on the right.
Hydrophobic amino acids
Have nonpolar side chains that interact very weakly with water
Hydrophobic amino acids
Most have aliphatic chains
Hydrophobic amino acids
Almost always located in the interior of a protein molecule where they can avoid interactions with water
Polar amino acids
Contain H-bonding groups and thus, can interact with water
Polar amino acids
Can be found on the waterexposed surface of proteins
Charged amino acids
Side chains are virtually always charged under physiological conditions
Charged amino acids
Located on the protein's surface
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
gives the relationship between the pKa of an acid and the pH of the solution. It also says whether an acid, based on its pKa , will be protonated or deprotonated at a certain pH value.
Deprotonated
when placed in a solution whose pH is higher than the acid’s pKa
❑ Protonated
when placed in a solution whose pH is lower than the acid’s pKa
TRUE
Amino acids are weak polyprotic acids. True or False
amphoteric
Amino acids are also said to be ______because they will react with either acids or bases.
The isoelectric point (pI) of a molecule
is the pH at which the molecule carries no net electric charge