Bio 5
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
B15,B16,B17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
asexual vs sexual reproduction definitions
asexual - o process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent
sexual - a process involving the fusion of the nuclei of 2 gametes to form a zygote and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
advantages of asexual reproduction
faster reproduction
consistent offspring
energy efficient
no need for pollination (for crops)
disadvantages of asexual reproduction
no genetic diversity
vulnerable to disease
haploid vs diploid
haploid - nuclei of gametes - 23 chromosomes
diploid - nucleus of zygote - 46 chromosomes
advantages + disadvantages of sexual reproduction
Advantages -
increased genetic diversity
less vulnerable to disease
Disadvantages -
slower process
requires the fusion of 2 gametes
species definition
a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring
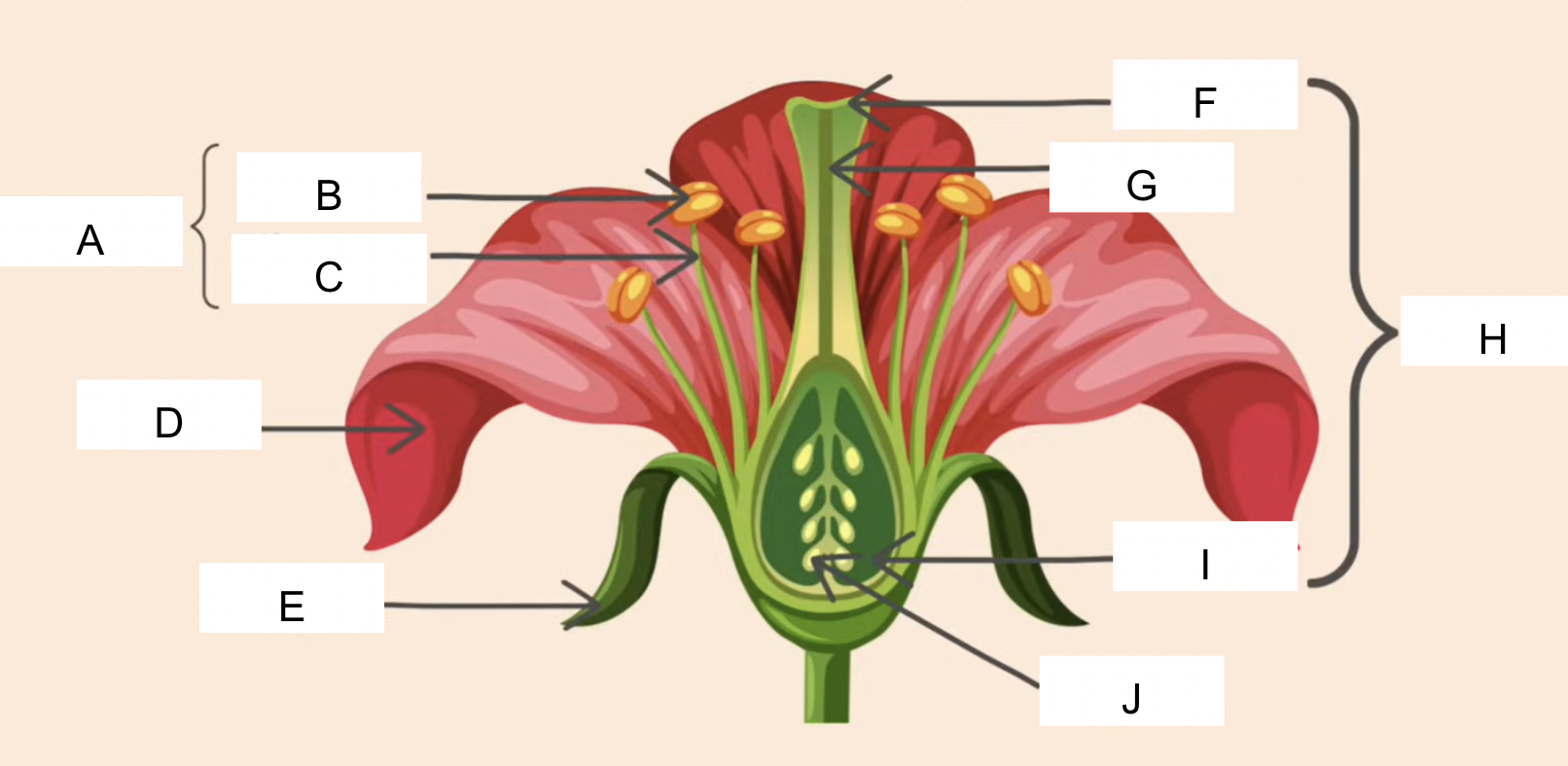
label
A - Stamen
B - Anther
C - filament
D - petal
E - Sepal
F - Stigma
G - Style
H - Carpel
I - Ovary
J - Ovules
functions of the anther, filament, stigma, style
anther - contains pollen (male sex cell)
filament - supports the anther
stigma - the sticky surface that catches pollen
style - links stigma to ovary
functions of the petal, speal, ovary, ovules
petal - brightly colored in insect pollinated flowers to attract insects
sepal - protects the unopened flower
ovary - protects ovum (female sex cell)
ovules - found inside ovary and contains female sex cell
pollination definition
the transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma
fertilization - flowers
occurs when a pollen nucleus fuses with a nucleus in an ovule
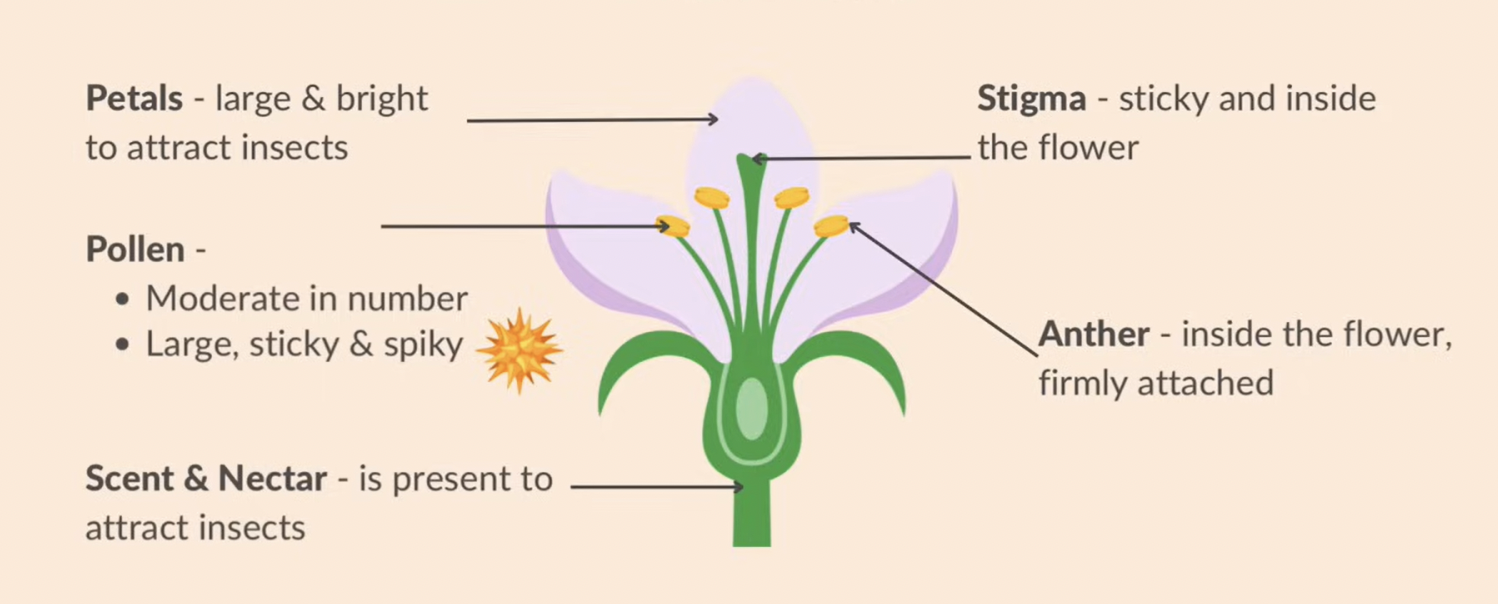
structural adaptations of insect pollinated flowers
large + bright petals to attract insects
moderate number of pollen + large, sticky and spiky
scent + nectar is present to attract insects
stigma is sticky and inside the flower
anther is inside the flower and firmly attached
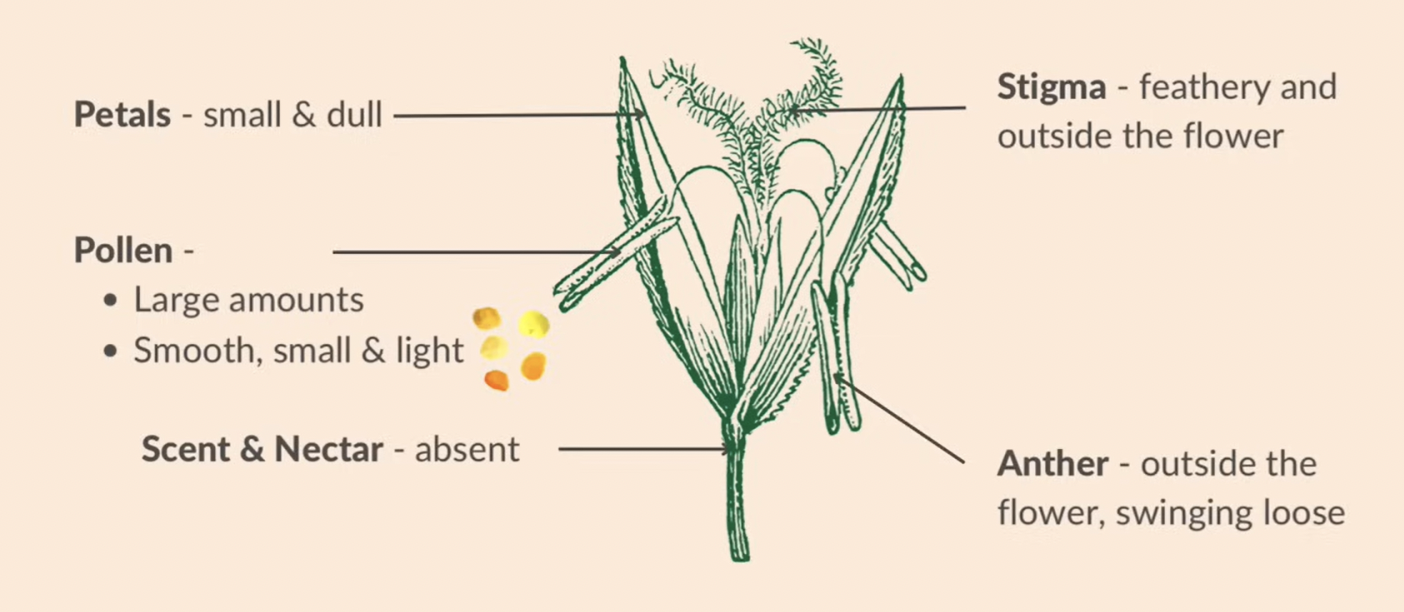
structural adaptations of wind pollinated flowers
small + dull petals
large amounts of pollen + smooth, small and light
scent + nectar is absent
a feathery stigma outside the flower
an anther outside the flower swinging loose
factors that affect the germination of seeds
oxygen - for respiration to release energy for growth
water - causes seed to expand and activates enzymes within embryo to initiate growth
temperature - increases rate of germination, the enzyme catalyzed reaction temperature-dependent, up to an optimum
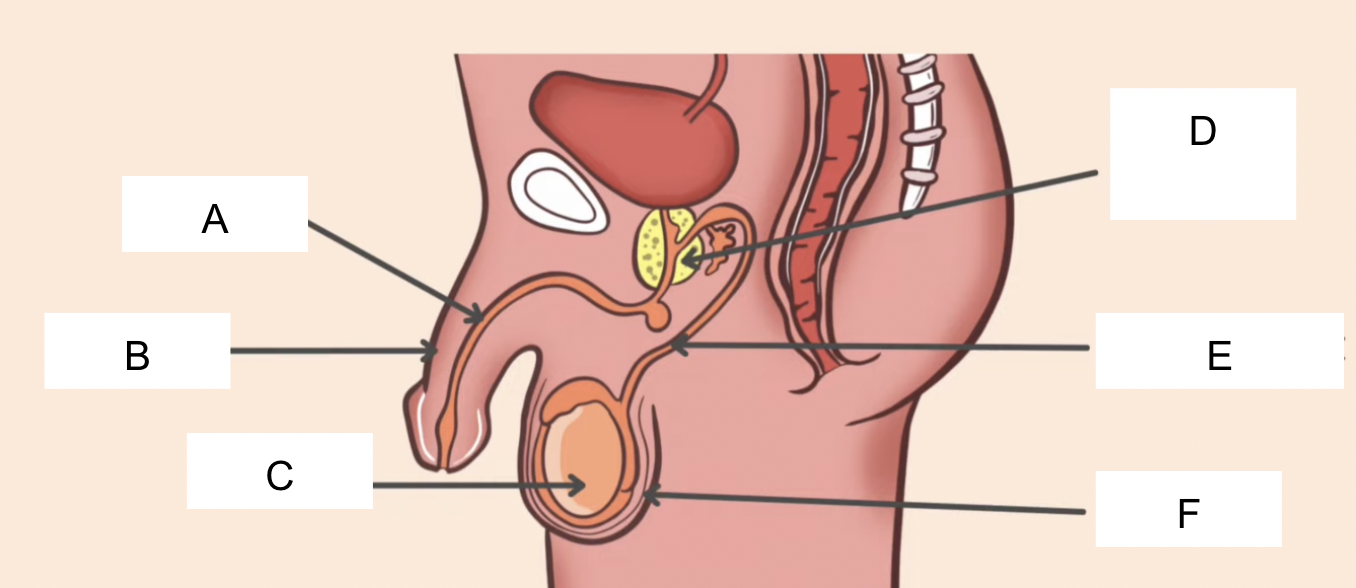
label
A - urethra
B - penis
C - testes
D - prostate gland
E - sperm duct
F - scrotum
state the functions of the male reproductive system : urethra, penis, testes, prostate gland, sperm duct, scrotum
urethra - tube which allows excretion of urine and semen from the body
penis - passes urine out of the body + allows semen to pass into the vagina
testes - produces sperm (male gamete) and testosterone (hormone)
prostate gland - secretes nutriative fluid which combines with sperm to form semen
sperm duct - tube that carries sperm from the testes to the urethra
scrotum - holds the testes outside the body to keep it colder than body temp.
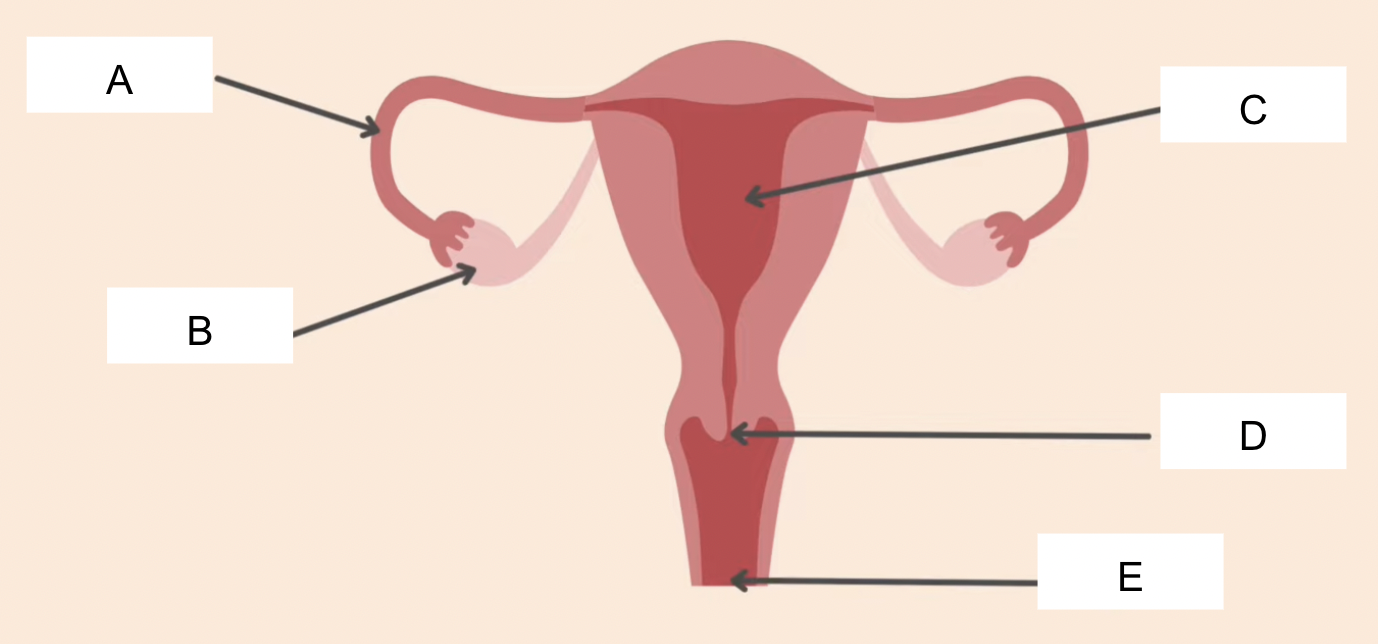
label
A - oviduct
B - ovary
C - uterus
D - cervix
E - vagina
state the functions of the female reproductive system : oviduct. ovary, uterus, cervix, vagina
oviduct - place where fertilization takes place, connects the ovary to the uterus,
ovary - where egg cells (female gametes) are produced
uterus - place where fetus develops
cervix - ring of muscle that keeps the fetus in place during pregnancy
vagina - entry point for penis
adaptive features of sperm
mitochondria to provide energy for movement
flagellum to swim towards the egg cell
enzymes in the acrosome to break down the protective layer around an egg
adaptive features of egg cells
jelly coat that changes after fertilization(to prevent multiple sperm from entering the egg)
cytoplasm containing energy stores to support early development after fertilization
compare female + male sex cell in terms of structure, size, motility and number
sperm - small, head region + flagellum, can move, many produced
egg - large, round cell with jelly coating, can’t move on its own, only released once a month
role of testosterone in males
growth of penis + testes
growth of facial + body hair
muscles develop
voice deepens
testes start to produce sperm
role of oestrogen in females
breasts develop
body hair grows
hips get wider
menstrual cycle begins
menstrual cycle
ovaries release an ovum every 28 days
uterus lining thickens in preparation for embryo implantation
if ovum is not fertilized uterus lining breaks down
the unfertilized egg cell together with the old uterus lining are passed out of the vagina
menstrual cycle changes in uterus and ovaries from day 0-28
0 - menstruation - ovary - follicle
7 - maturing follicle
14 - uterus lining builds up + ovulation (follicle releases egg)
21 - lining continues to build up + is maintained, corpus luteum - ovary
28 - corpus luteum breaks down if ovum is not fertilized, new cycle
sexually transmitted infection definition
an infection that is transmitted through sexual contact
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
a pathogen that causes an STI
HIV infection can lead to AIDS
how HIV affects immune system
HIV avoids being recognised by repeatedly changing its protein coat
the virus infects a certain type of lymphocytes
reduces the number of lymphocytes
decreases body’s ability to fight of infections → AIDS
how is HIV transmitted
unprotected sexual intercourse
sharing needles with an infected person
blood transfusions with infected person
from mother to fetus through placenta
from mother to baby via breast feeding
How to control the spread of STI’s
limiting the number of sexual partners
using condoms
getting tested if unprotected sex or sex with multiple partners has occurred
raising awareness through education programs
abstinence from sexual intercourse
using sterilized needles instead of sharing
chromosomes
made of DNA which contains genetic information in the form of genes
gene + allele definition
gene - a length of DNA that codes for a protein
allele - an alternative form of a gene
inhertience of sex
23rd chromosome pair - XX=female, XY=male
egg cells carries X
half of sperm carry X other Y
haploid vs diploid nucleus
haploid - single set of chromosomes
diploid - 2 sets of chromosomes
diploid cell
there is a pair of each type of chromosome
in human diploid cell - 23 pairs
mitosis
nuclear division giving rise to genetically identical cells
an exact replication of chromosomes occurs before mitosis
the copies of the chromosome separate, maintaining the chromosome number in each daughter cell
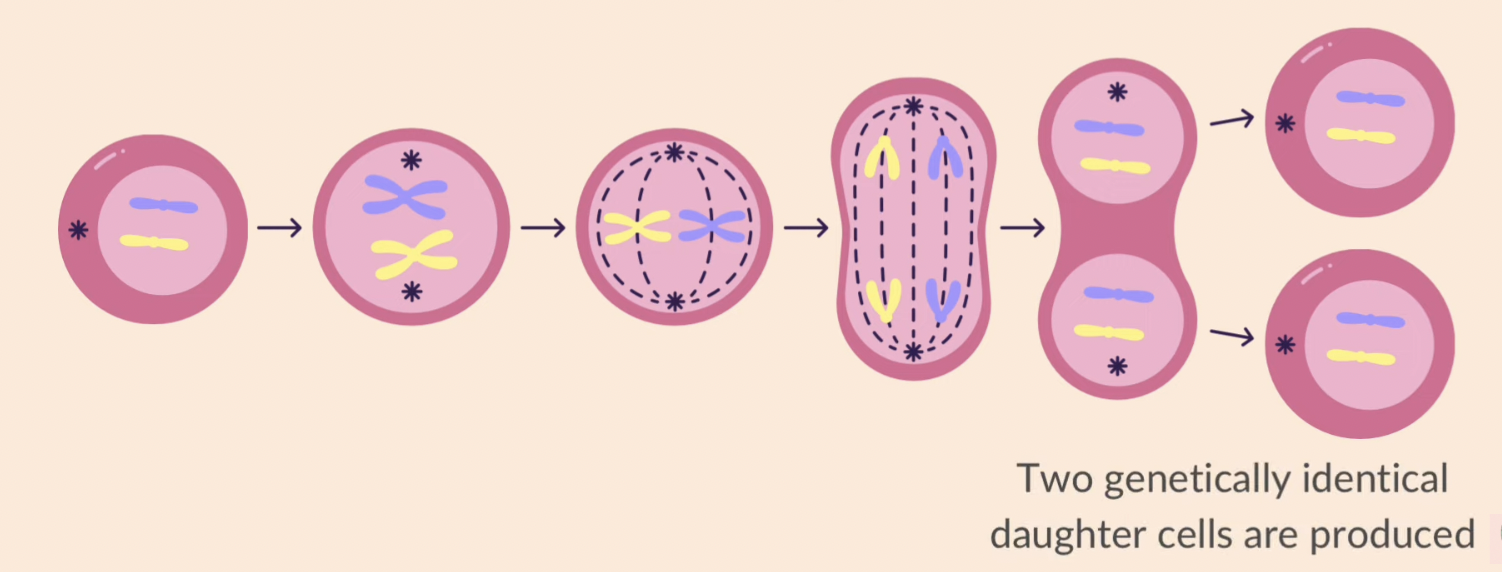
role of mitosis
growth + repair of damaged tissues
replacement of cells
asexual reproduction
meiosis
reduction division in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid resulting in genetically different cells
involved in the production of gametes
inheritance
the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation
genotype vs phenotype
genotype - the genetic makeup of an organism, including all of its genes + alleles
phenotype - the observable features of an organism
pure breeding
2 identical homozygous that breed together
heterozygous
having 2 different alleles of the same gene
no pure breeding
dominant vs recessive allele
dominant - an allele that is expressed if its is present in the genotype
recessive - an allele that is only expressed when there is no dominant allele of the gene present in the genotype
variation definition
differences between individuals of the same species
continuous vs discontinuous variation definitions
continuous - results in a range of phenotypes between 2 extremes(e.g body length)
discontinuous - results in a limited number of phenotypes with no intermediates (e.g blood type)
mutation
a genetic change
the way new alleles are formed - ionising radiation, certain chemicals
genetic vs phenotypic variation
genetic - the differences in genetics among individuals of the same species (e.g blood group, eye colour, gender, ability to roll tongue)
phenotypic - the variability of phenotypes within a population caused by either genetics or environment
what is genetic variation in populations caused by
mutation
meiosis
random mating
random fertilization
adaptive feature definition
an inherited feature that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment
natural selection
a process where within a population there is genetic variation and many offspring are produced
as these offsprings grow they face a struggle for survival (e.g competition for resources)
Individuals that are better adapted → higher chance of surviving + reproducing
these individuals pass on their alleles to the next generation leading to a gradual change in the population overtime
example of natural selection - bacteria
the development of strains of antibiotic resistant bacteria
selective breeding
humans choose individuals with desirable features which are then bred together to produce the next generation
from the new generation only individuals with the desired features are chosen
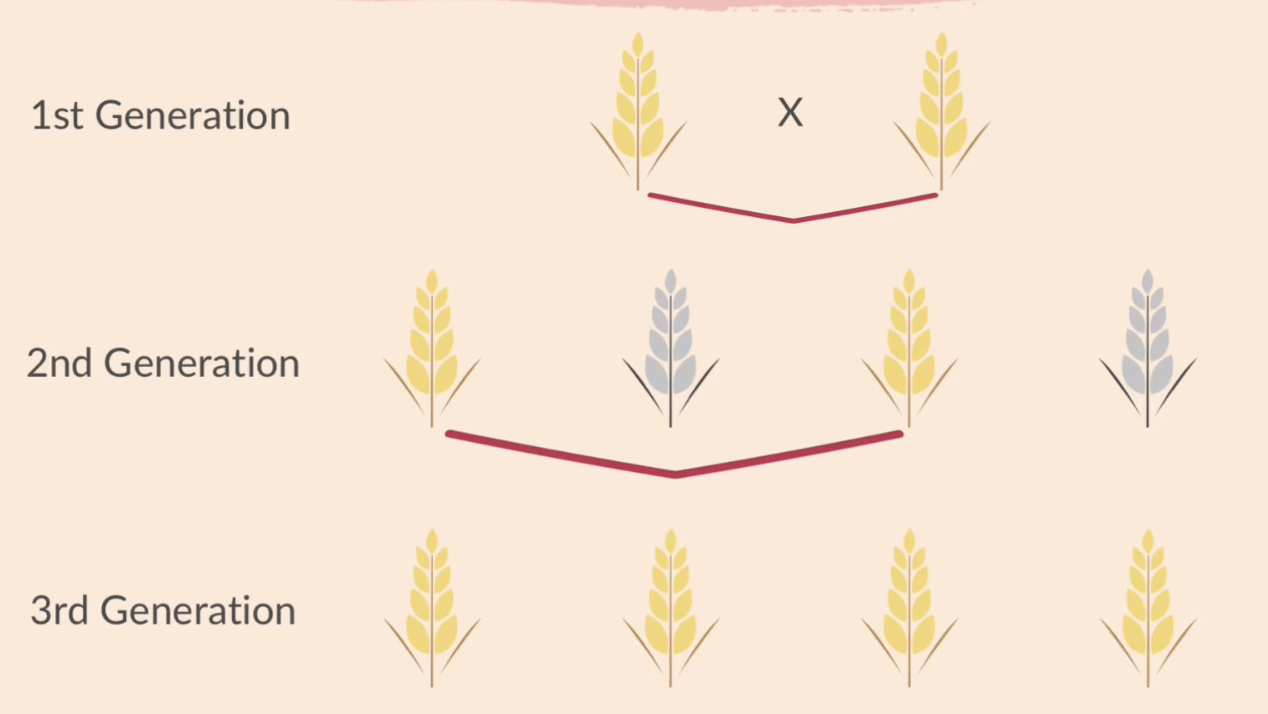
why do we do selective breeding in crop plants
disease resistance in food crops
increase crop yield
adaptation to challenging weather conditions
improvement in taste of fruits
cultivation plants with large/unique flowers
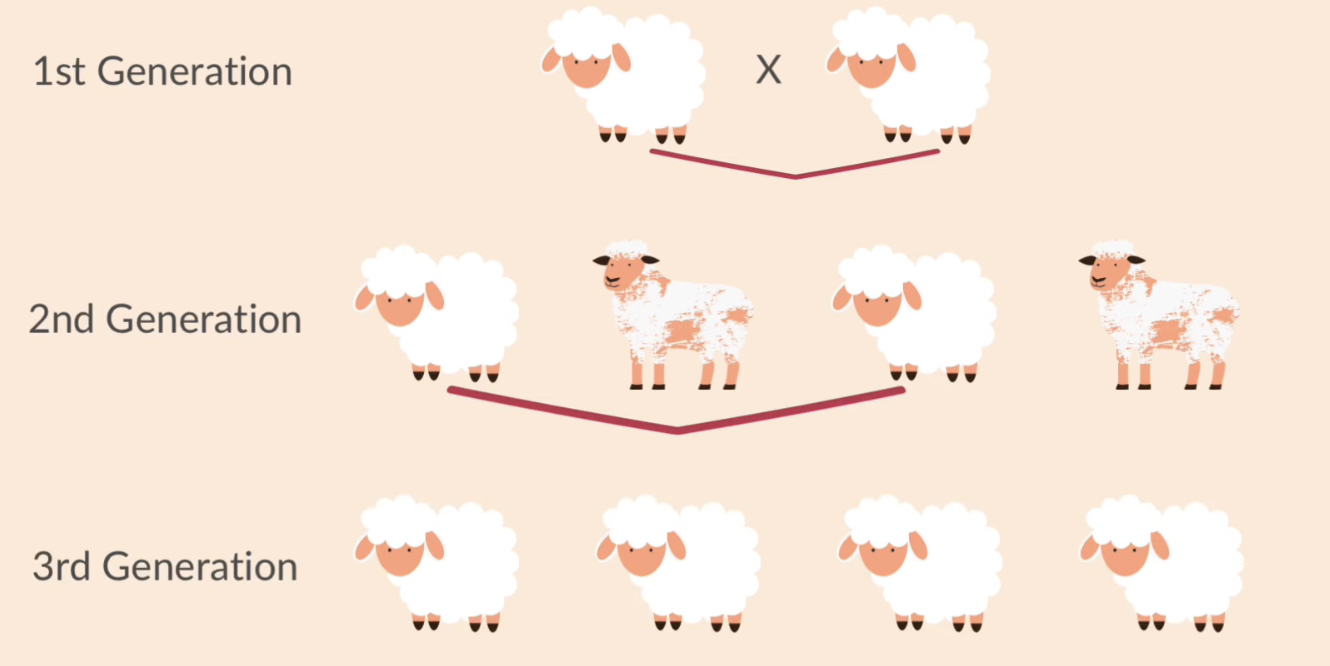
why do we use selective breeding on animals
cows, goats and sheep that produce large amounts of milk/meat
chickens that lay large eggs
domestic dogs with a gentle nature
sheep with good quality wool
horse with fine features + great speed
natural vs artificial selection
natural - occurs naturally, results in adaptations that increase chance of survival + reproduction in a specific environment, can lead to gradual change + diversification over time
artificial - occurs with human intervention, focuses on traits that are desirable to humans, can result in rapid changes in traits within a population
How to do a test cross
using the homozygous recessive in a cross to determine if parent is heterozygous or homozygous dominant
