AP Human Geography AMSCO Unit 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
population distribution
the arrangement or spread of people living in a given area
population density
Number of individuals per unit area
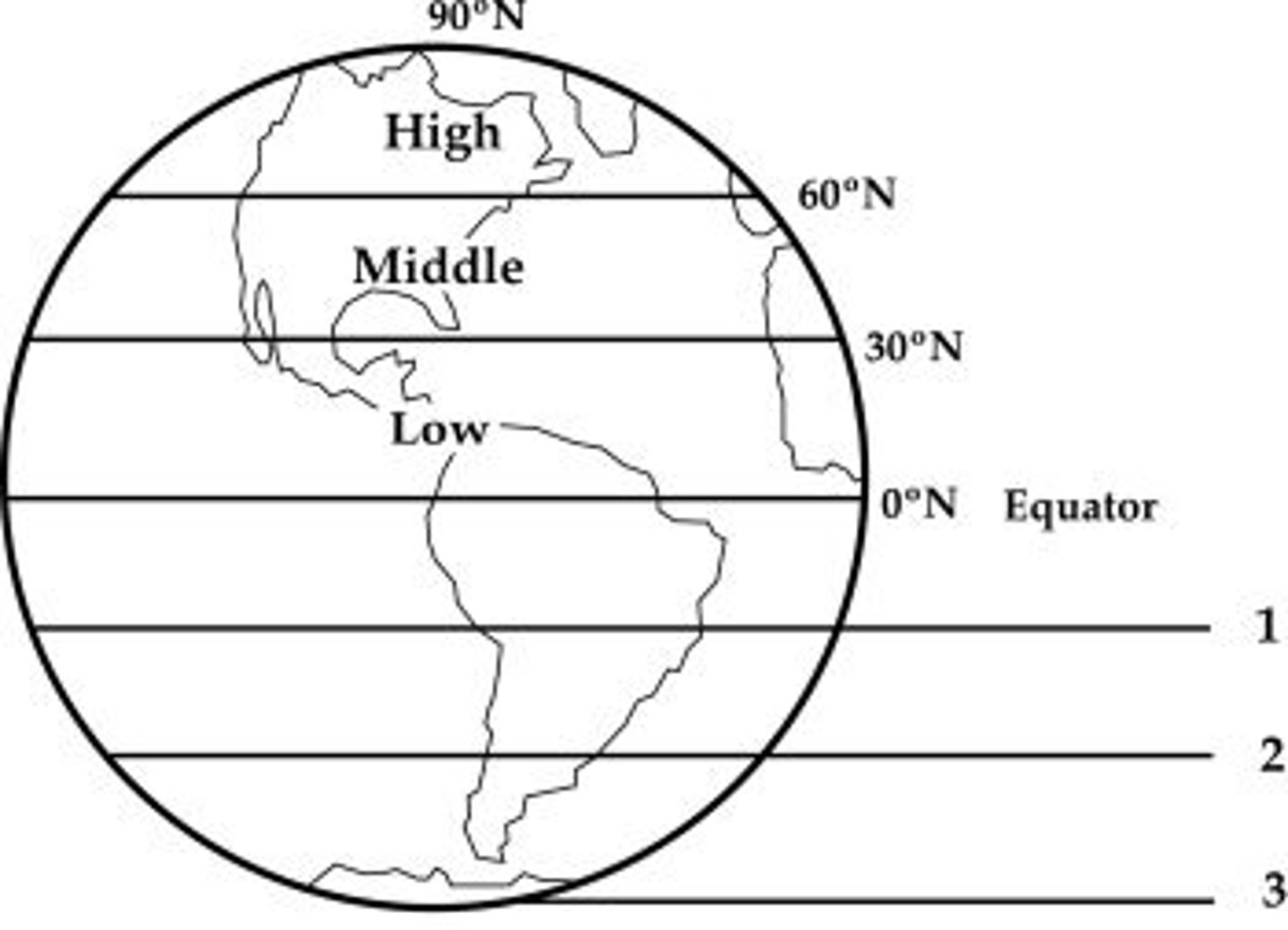
midlatitudes
Between 30 N and 60 N and 30 S and 60 S
social stratification
the division of society into groups arranged in a social hierarchy
arithmetic population density
The total number of people divided by the total land area

physiological population density
The number of people per unit area of arable land
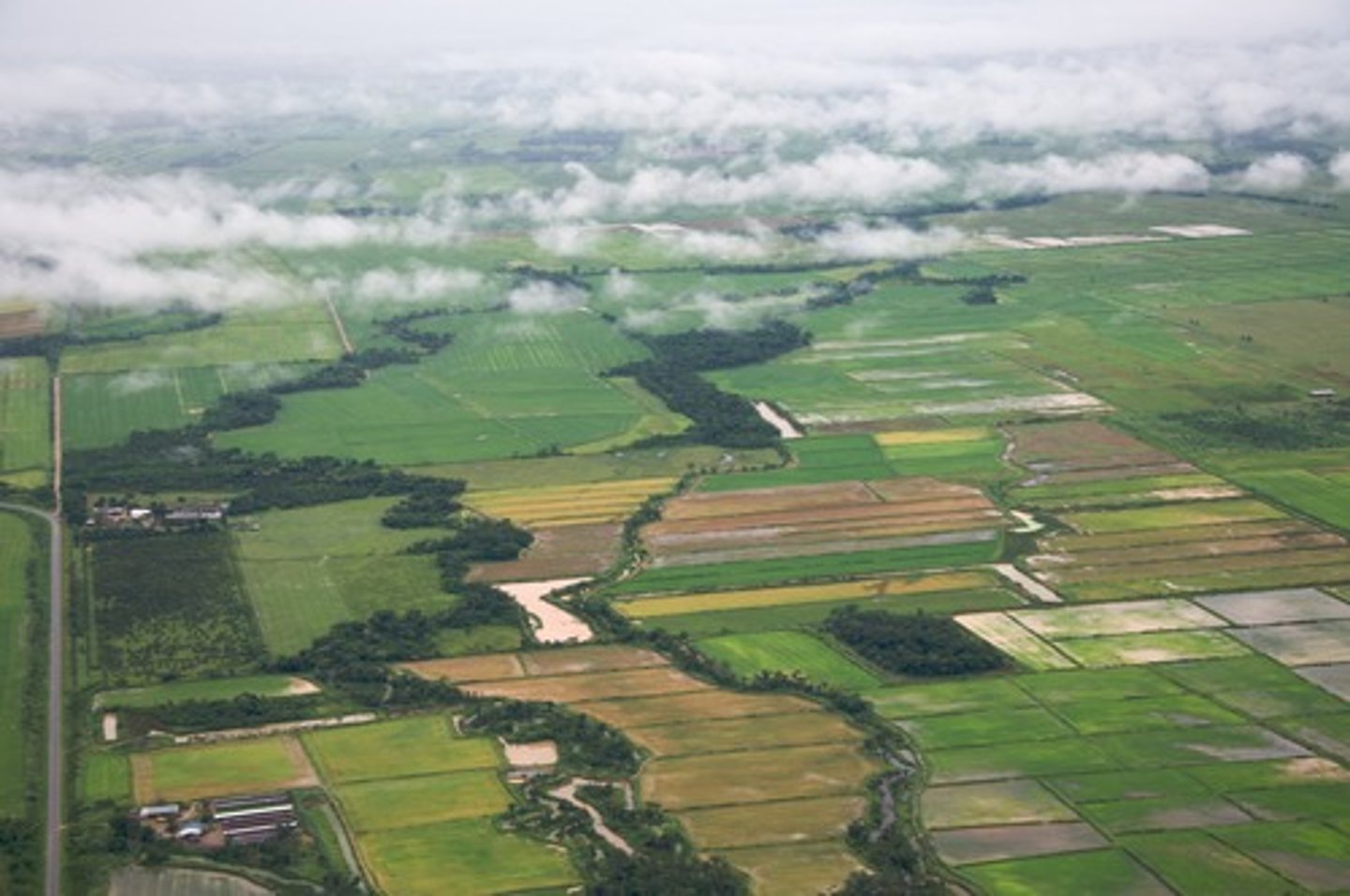

arable
Suitable for growing crops

carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support

agricultural population density
Number of farmers per unit of arable land

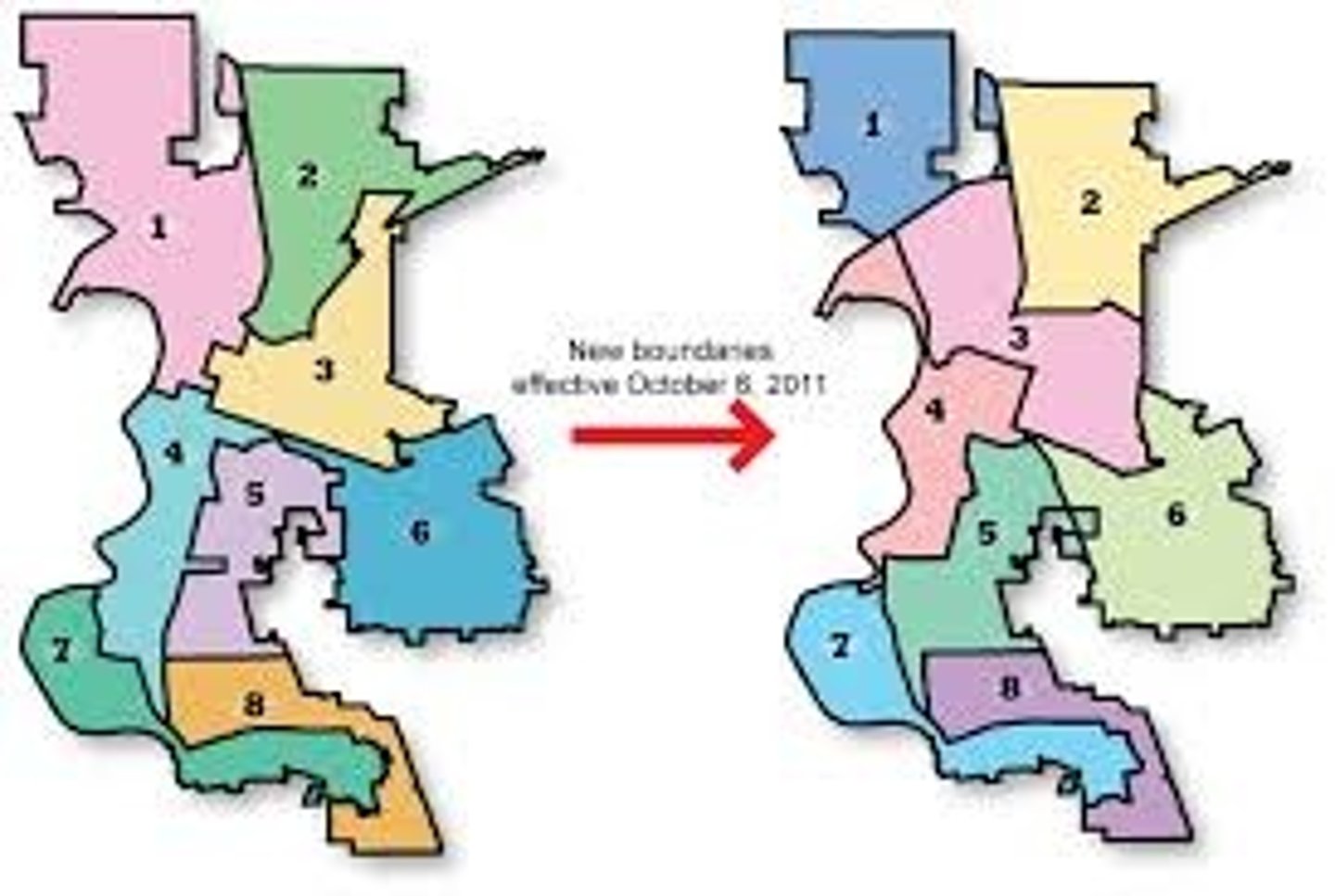
redistricting
The drawing of new electoral district boundary lines in response to population changes.
overpopulation
too many people in an area relative to the resources and level of technology available

age-sex composition graph
another name for a population pyramid
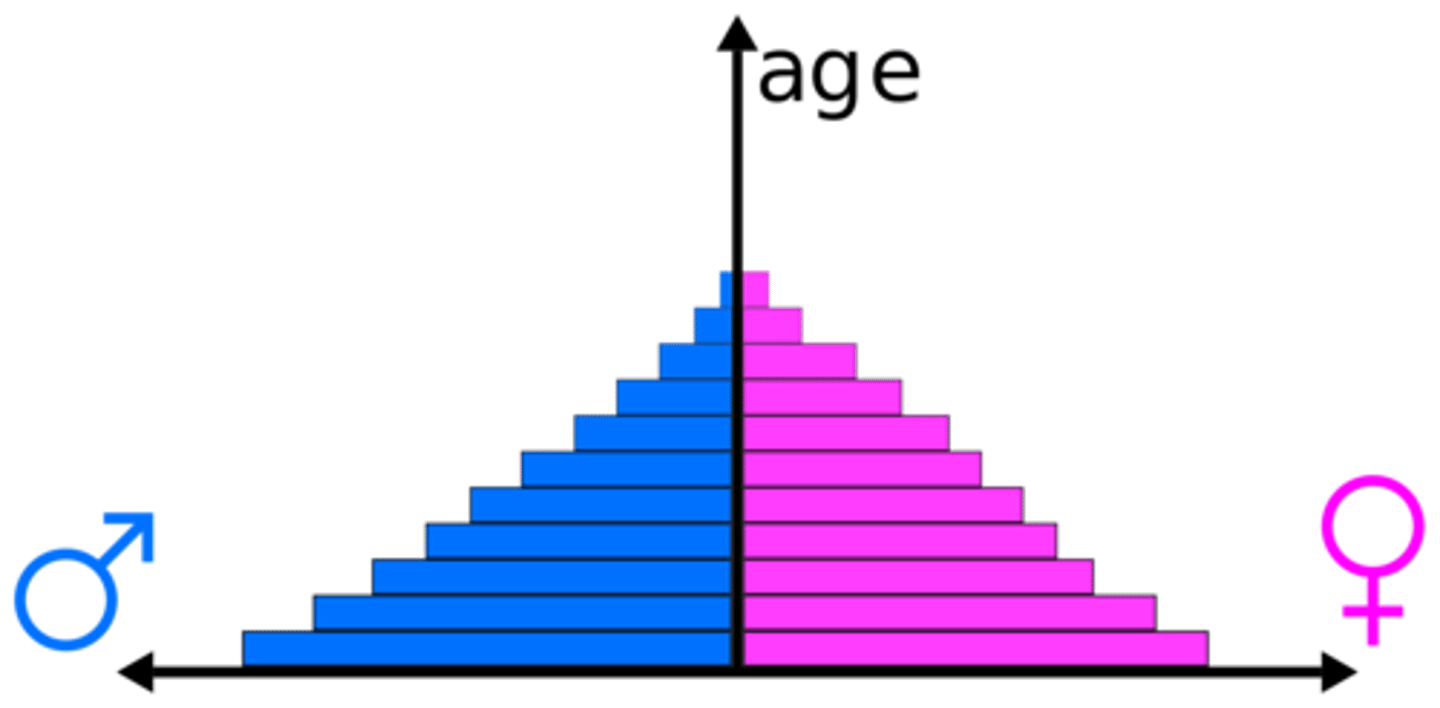
population pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
cohort
A group of individuals of the same age.

birth deficit
slow down of birth caused by war and separation of the sexes during conflict
baby boom
a temporary marked increase in the birth rate, especially the one following World War II.

baby bust
after a baby boom; any period marked by a greatly decreased birth rate.
echo
the children of a baby boom, another bulge in the pyramid 25-40 years after the baby boom
dependency ratio
the ratio of the number of people under 15 and over 64 years to those 15-64 years of age

potential workforce
society's expected labor force, age 15-64

dependent population
those who rely on the working population for support e.g. the young and elderly

crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.

anti-natalist policies
gov't policies to reduce Total Fertility Rate; China and India-- one child policy (young and rapidly increasing population)

pro-natalist policies
Policies that either encourage births; paid time off after birth, day care stipends, tax incentives

life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live

infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of infants under age 1 per 1,000 live births per year

demographic transition model
a model of how the size of a population changes as a country develops its economy
1) High Stationary
2) Early Expanding
3) Late Expanding
4) Low Stationary
5) Declining
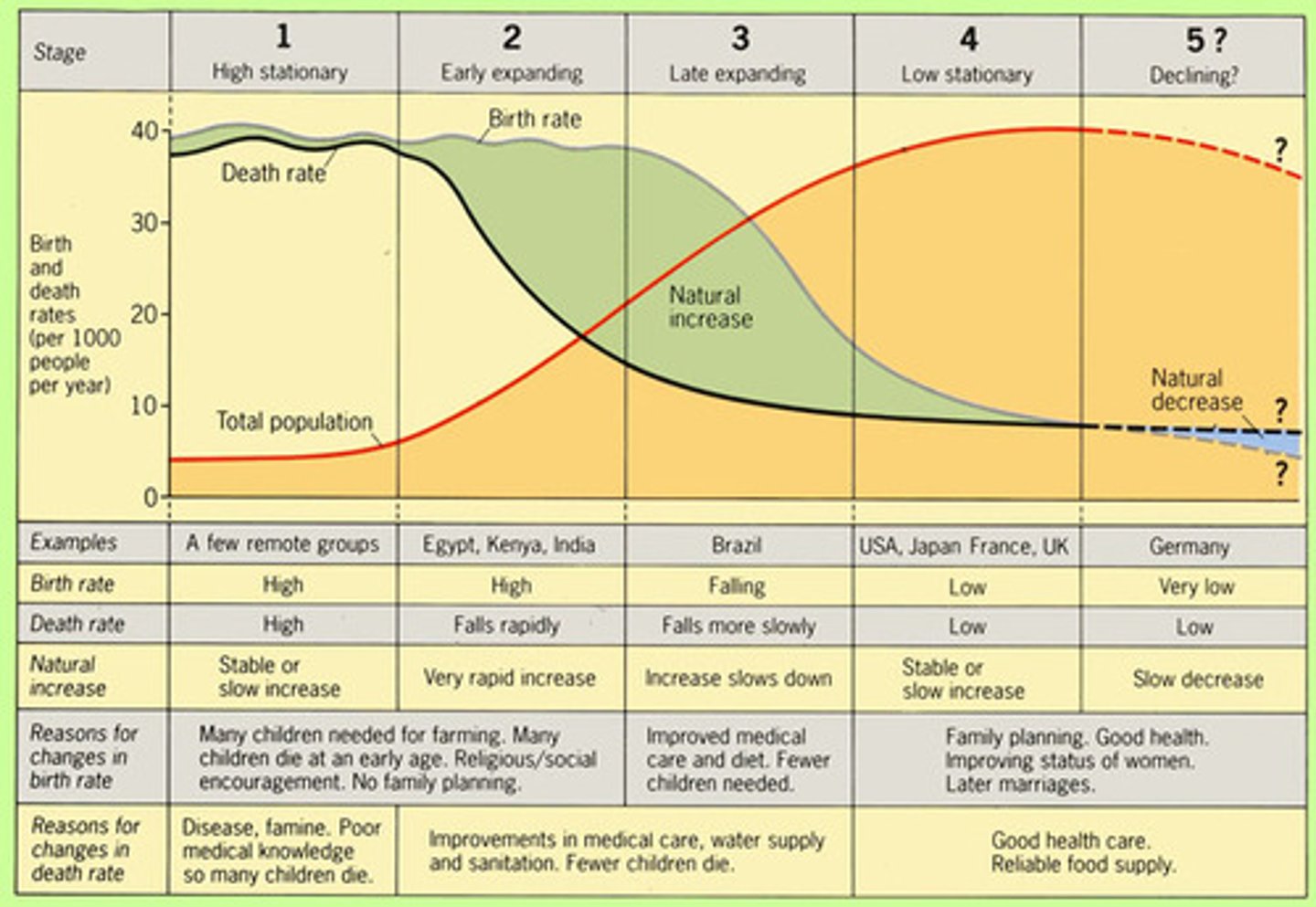
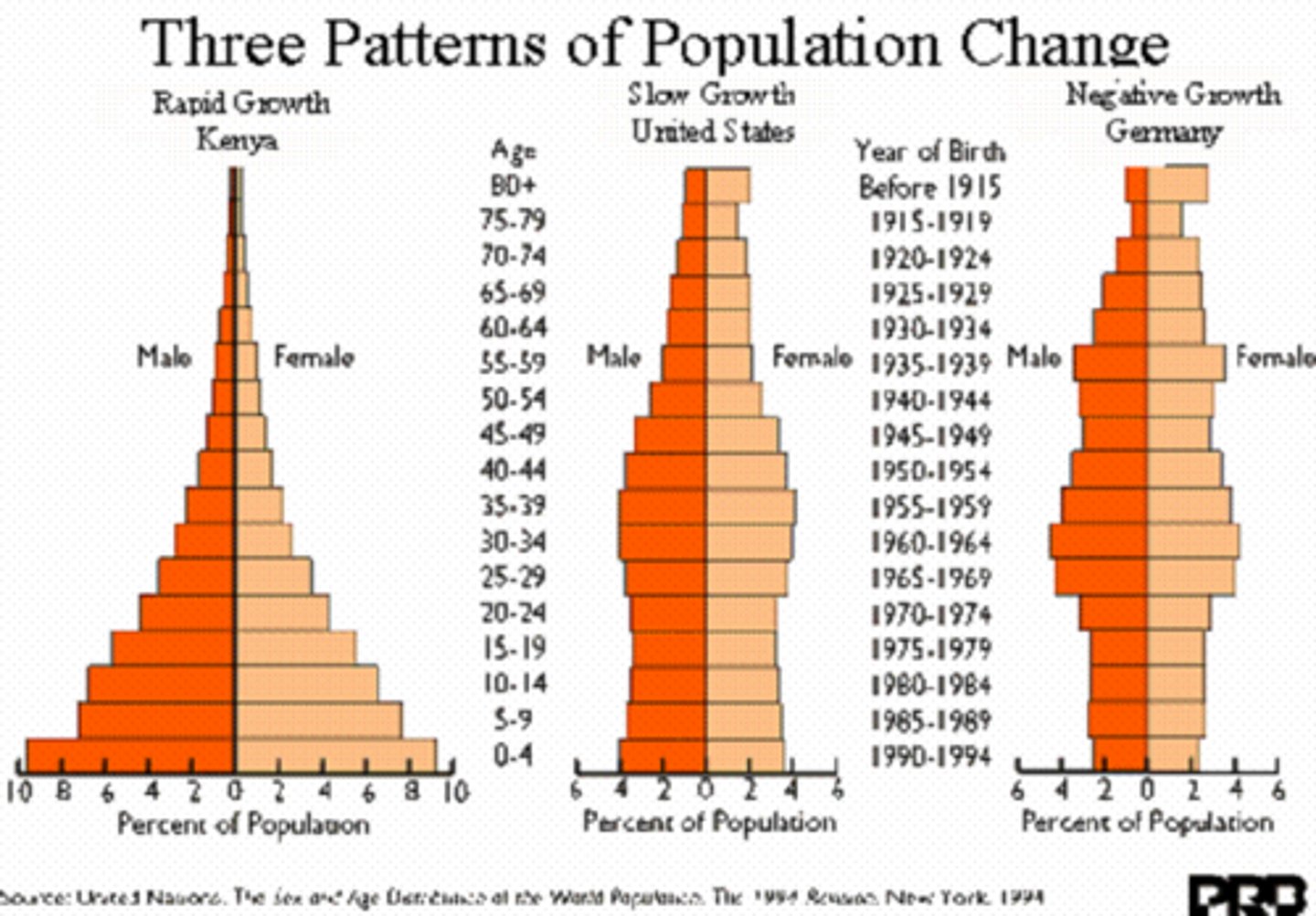
expansive population pyramid
large births, die off fast, under developed/developed country

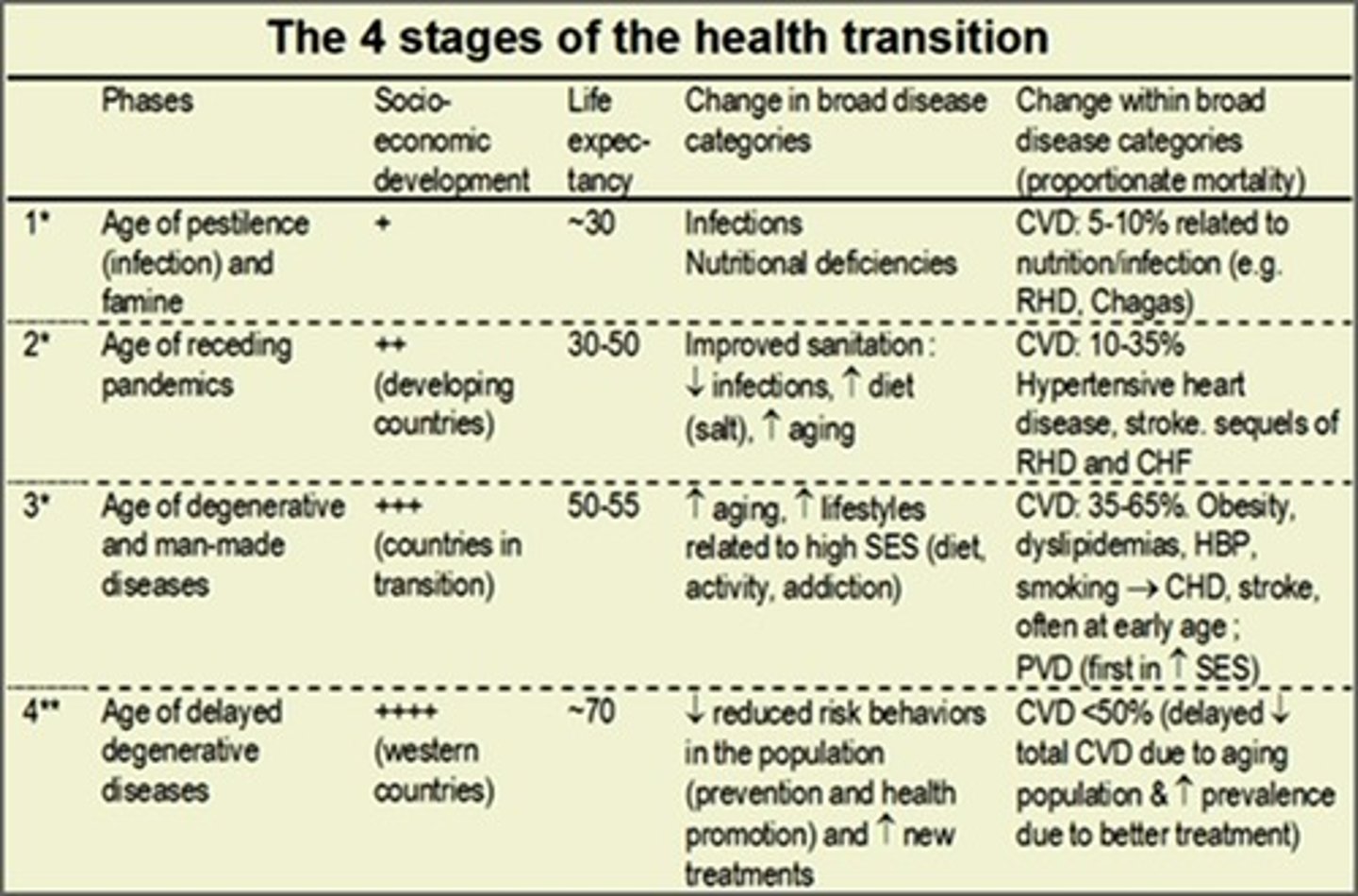
epidemiological transition model
distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
1) Pestilence and Famine 2)Receding Pandemics 3) Degenerative and Human-Made Diseases 4) Delayed Degenerative Diseases 5) Reemergence of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
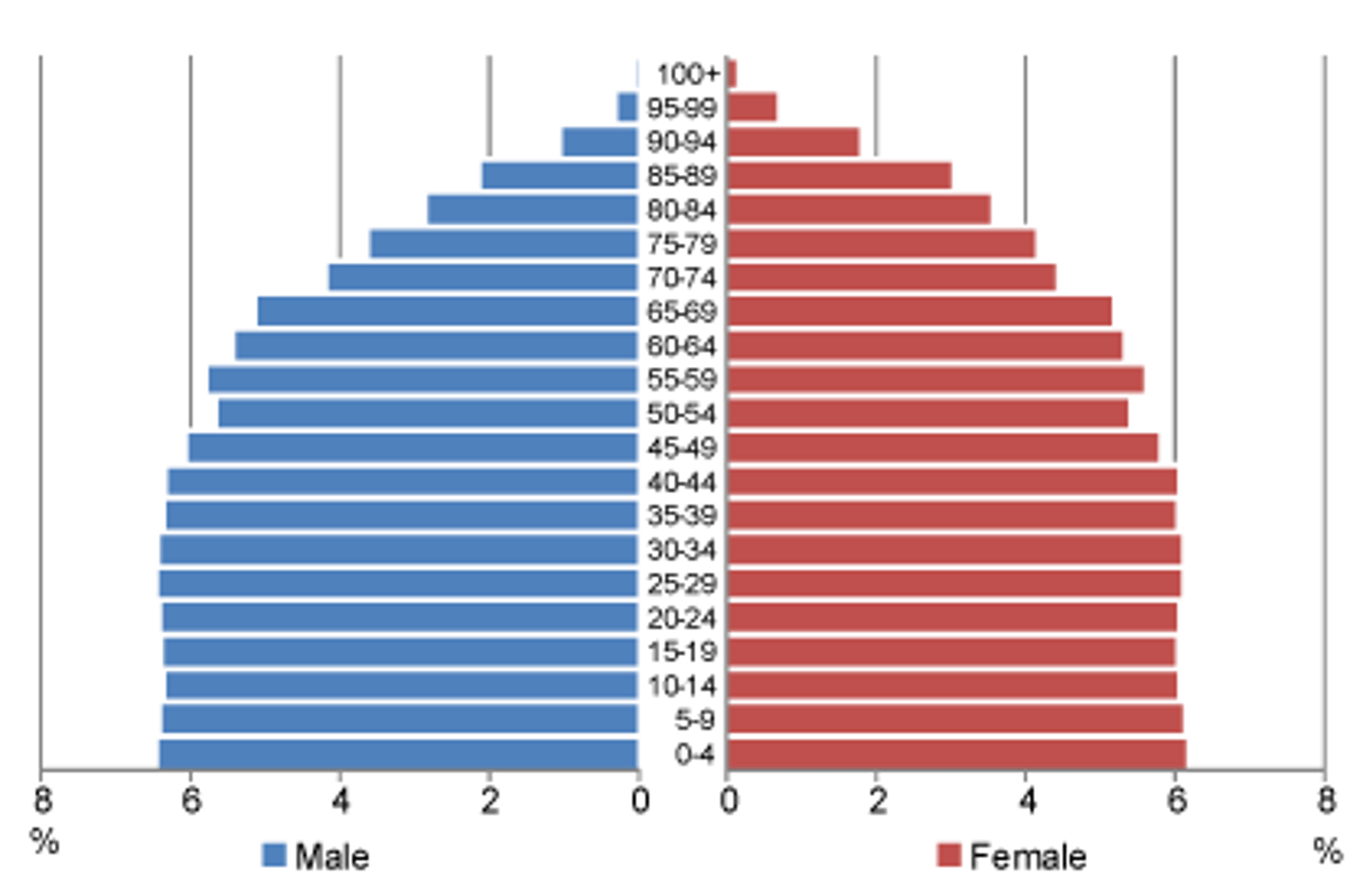
stationary population pyramid
births and deaths are about the same, Japan and Russia
crude death rate
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.

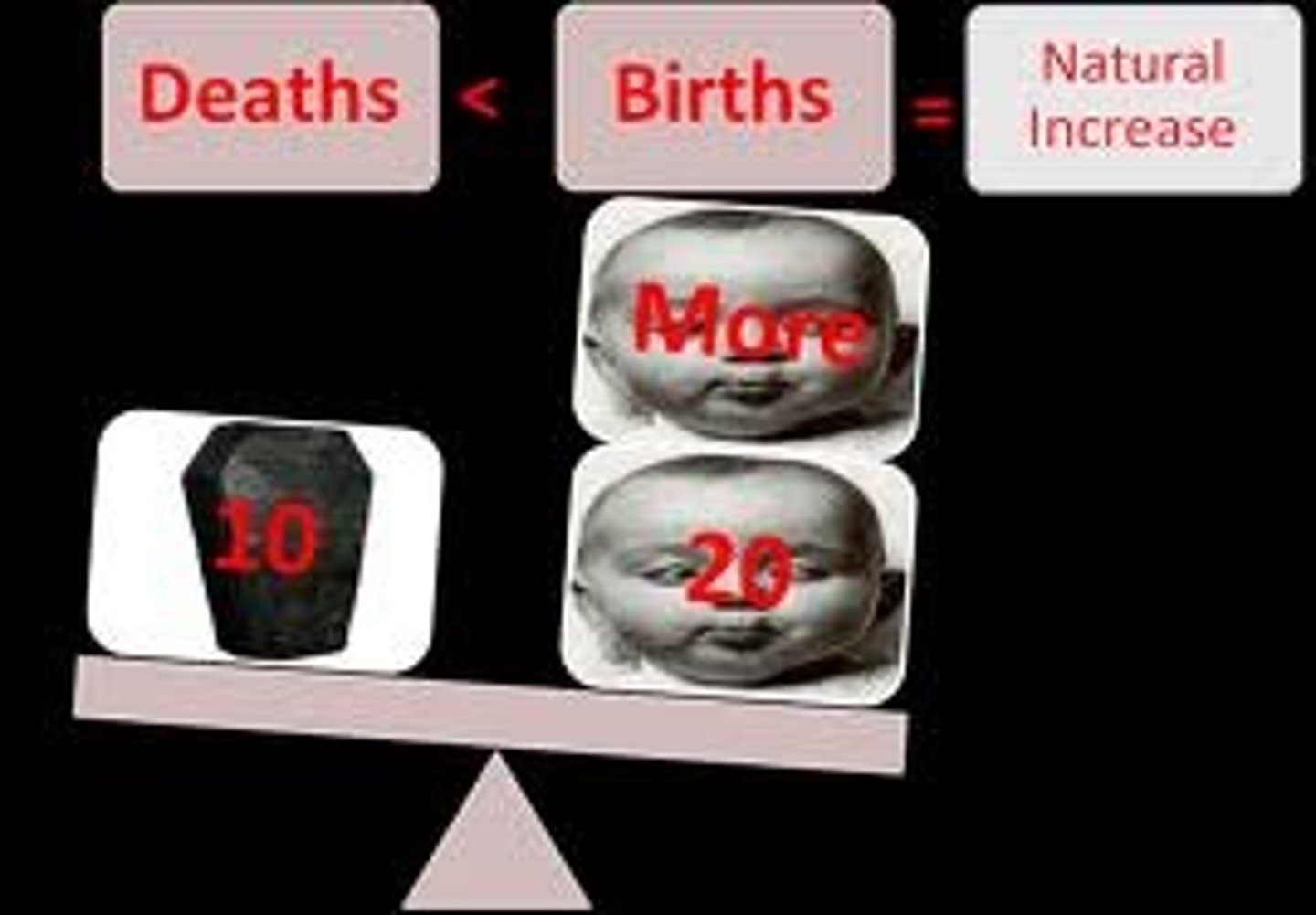
rate of natural increase
the birth rate minus the death rate expressed as a percentage
immigrants
People who settle in a country they weren't born in.

emigrants
a person who leaves a country or region to live elsewhere

demographic balancing equation
births - deaths + immigration - emigration
Malthusian Theory
the idea that population is growing faster than the food supply needed to sustain it
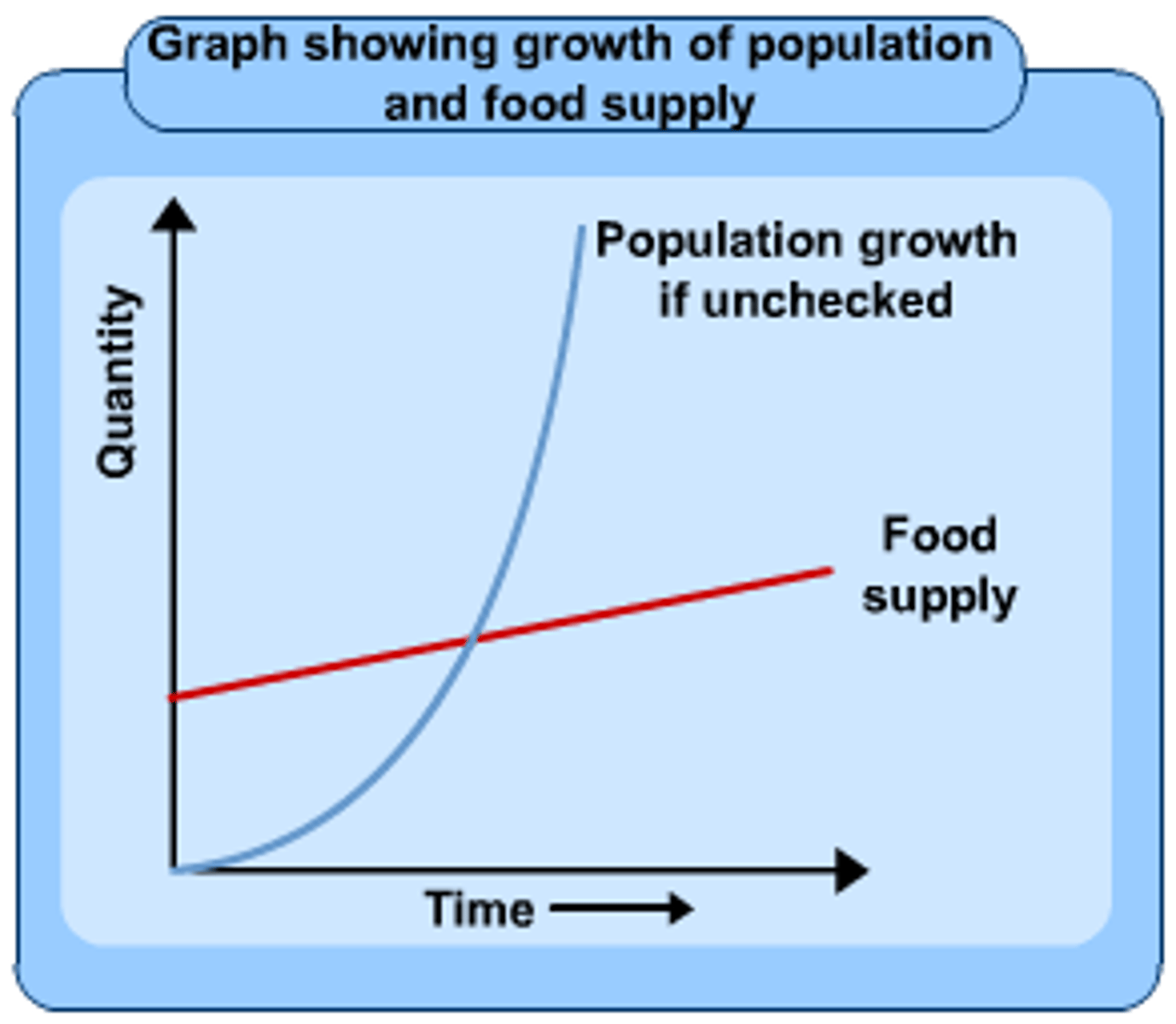
Neo-Malthusians
continued population growth will lead to depletion of non-renewable resources - adopted to more modern conditions
migration
the movement of people from place to place

voluntary migration
movement in which people relocate in response to perceived opportunity; not forced.

push factors
a factor that causes people to leave their homelands and migrate to another region

pull factors
something that encourages people to move to a new place

asylum
Shelter and protection in one state for refugees from another state

intervening obstacles
Any forces or factors that may limit human migration.

Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
(1) Most Migrants Go Only Short Distances. ...
(2) Migration Goes by Steps (Step-by-Step) ...
(3) Long-Distance Migrants Prefer to Go to Big Cities. ...
(4) Migration Flows Produce Counter-Flows. ...
(5) People from Urban Areas Migrate Less than Rural People.
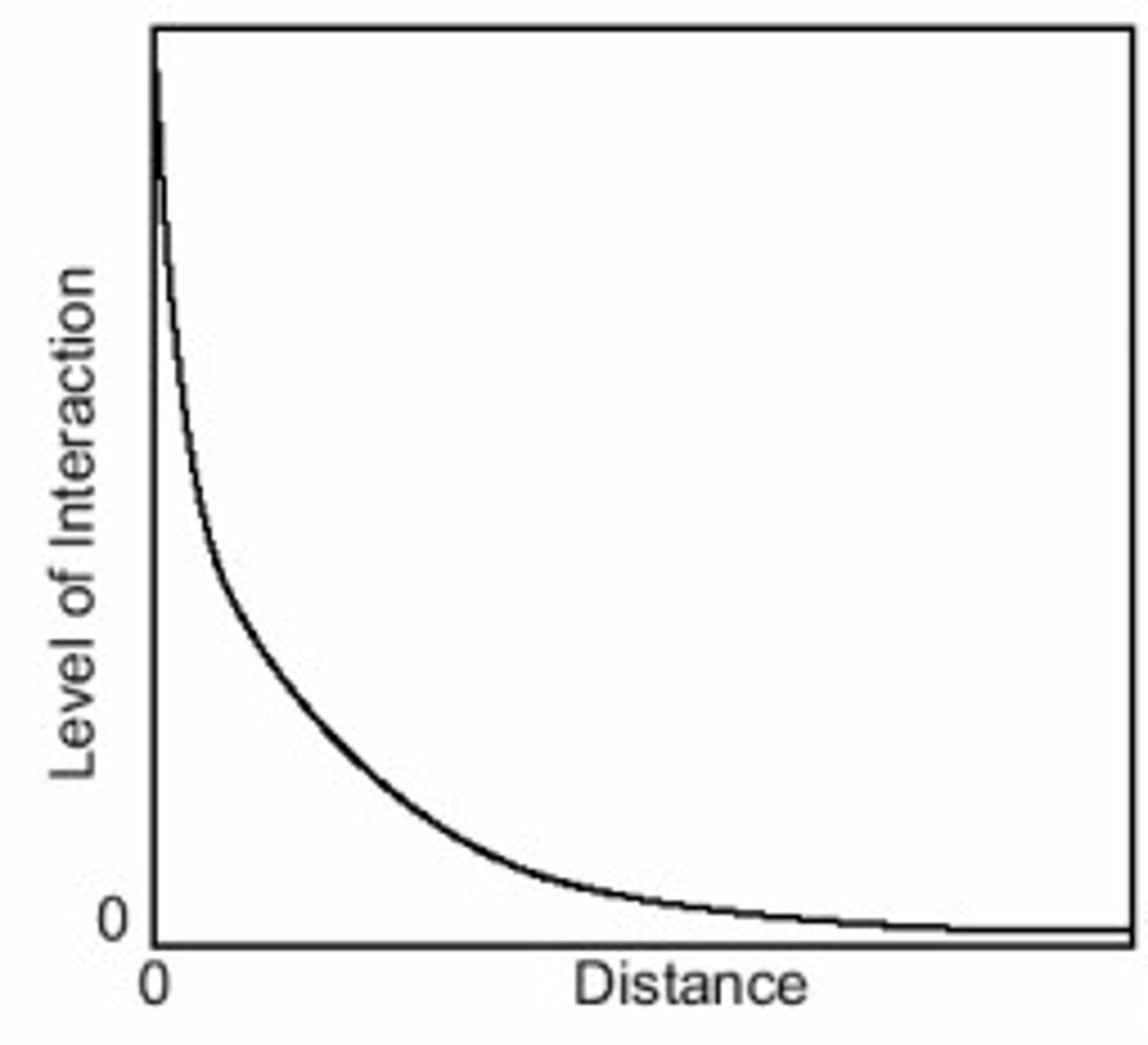
distance decay
The effects of distance on interaction, the greater the distance the less interaction
gravity model of migration
combines distance decay, greater pull of larger communities, and people are most likely to move from small communities to larger
step migration
migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages

counter migration
The return of migrants to the regions from which they earlier emigrated
return migration
The voluntary movements of immigrants back to their place of origin

forced migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate.

internally displaced person
a refugee within his or her own country

refugees
People who flee to another country to escape mistreatment or disaster
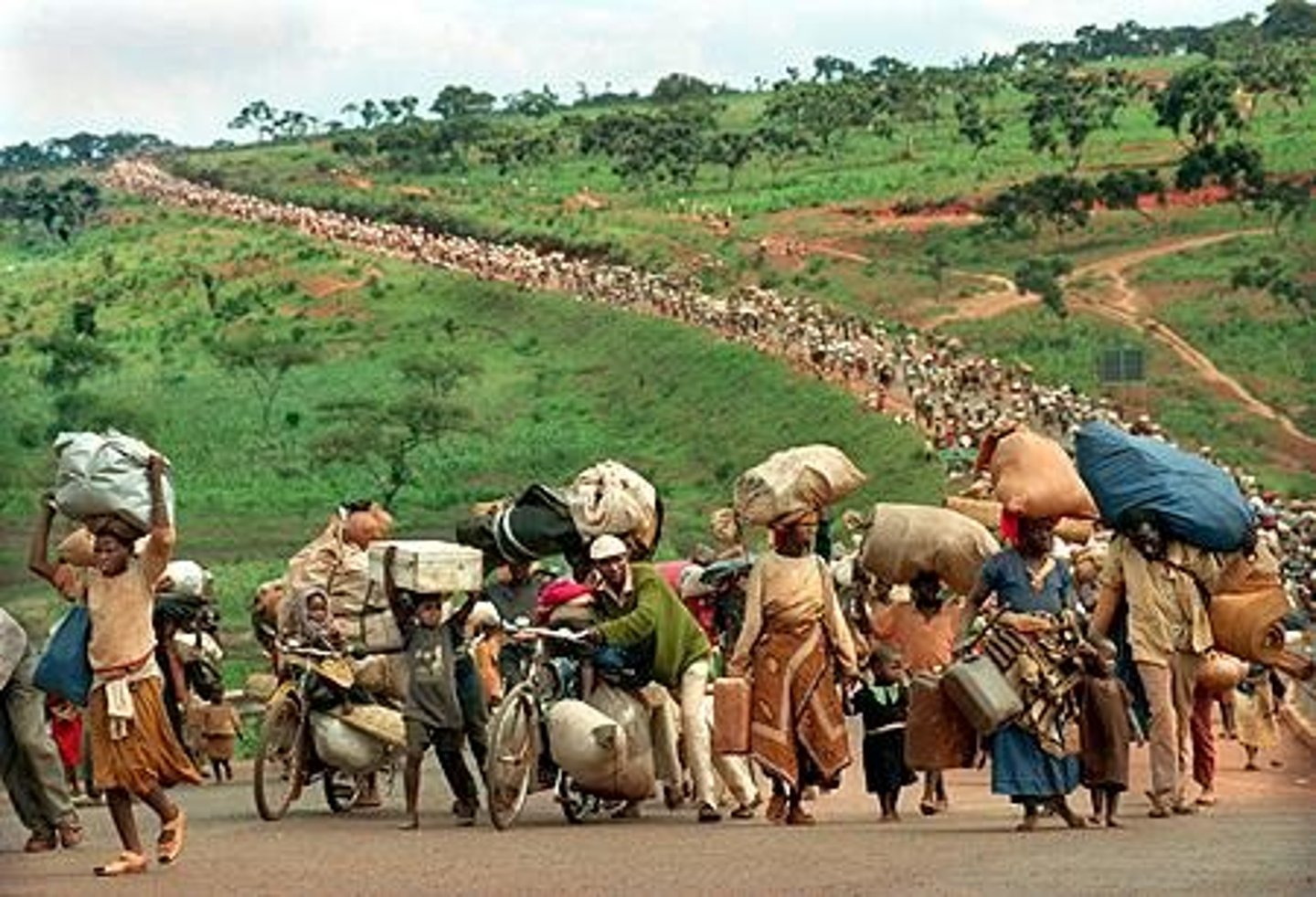

chain migration
migration that is caused by the feedback from people who have already immigrated
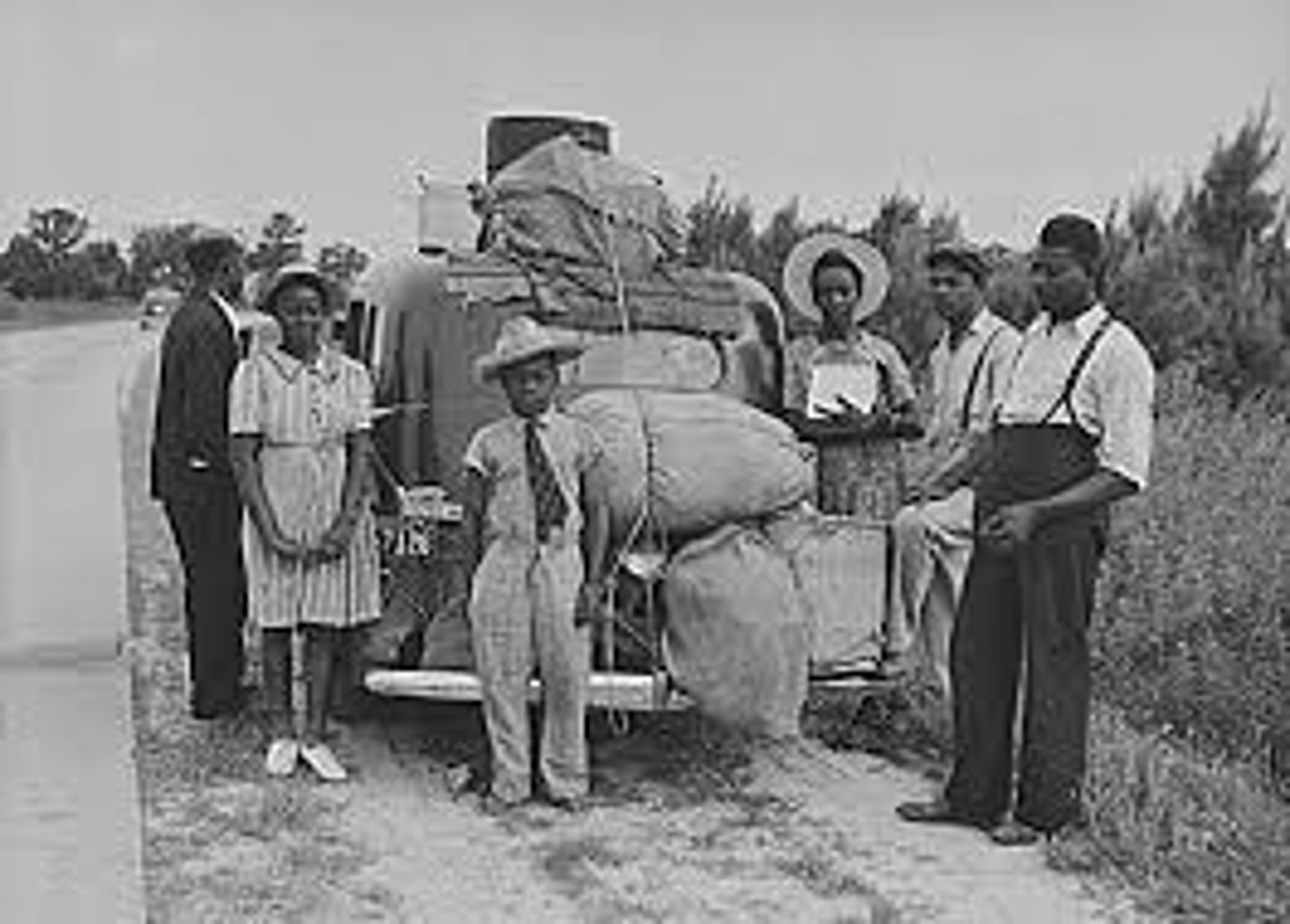

ethnic enclaves
Neighborhoods in which ethnically similar people settle

xenophobia
intense or irrational dislike or fear of people from other countries

brain drain
the loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries

remittances
When a foreigner sends money back to his or her home country.
