Paper 2 - Summary
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/214
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:01 PM on 6/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
1
New cards
What is the function of a red blood cell?
Carries oxygen
2
New cards
Why do red blood cells have a biconcave shape?
Increase surface area so they can carry more oxygen
3
New cards
Why don’t red blood cells have a nucleus?
More space to carry oxygen
4
New cards
What is the red pigment in red blood cells called?
Haemoglobin
5
New cards
What element does haemoglobin contain?
Iron
6
New cards
What is the function of haemoglobin?
Oxygen binds to it
7
New cards
What is the haemoglobin called when it is carrying oxygen?
Oxyhaemoglobin
8
New cards
What is the haemoglobin called when it is not carrying oxygen?
Deoxyhaemoglobin
9
New cards
What is the function of platelets in the blood?
Clot blood
10
New cards
Name the liquid part of the blood that everything else floats in.
Plasma
11
New cards
What are the substances carried in the blood?
* Oxygen
* Glucose
* Amino acids
* Carbon dioxide
* Hormones
* Urea
* Protein
* Glucose
* Amino acids
* Carbon dioxide
* Hormones
* Urea
* Protein
12
New cards
Which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Arteries
13
New cards
Is the blood under high or low pressure in the artery?
High
14
New cards
Why do arteries contain thick layers of muscle?
Strengthen them
15
New cards
Why do arteries contain elastic fibres?
To allow recoil
16
New cards
Which blood vessels carry substances to the organs?
Capillaries
17
New cards
Why are capillaries narrow?
They can squeeze between the gaps between cells (every cell gets substances)
18
New cards
Why do capillaries have permeable walls?
So substances can diffuse in and out
19
New cards
How many cells thick is a capillary wall?
1
20
New cards
Which substances are carried to cells in capillaries?
* Oxygen
* Glucose
* Amino acids
* Glucose
* Amino acids
21
New cards
What substances are removed from cells by capillaries?
* Carbon dioxide
* Urea
* Urea
22
New cards
Which blood vessels carry blood back to the heart?
Veins
23
New cards
Is blood pressure high or low in the veins?
Low
24
New cards
Why do veins have valves?
Prevent backflow
25
New cards
Do veins have a small or big lumen?
Big
26
New cards
Why do veins have a big lumen?
Helps blood flow
27
New cards
What is a double circulatory system?
Heart pumps blood to the lungs and to the rest of the body
28
New cards
Where does the right side of the heart pump blood to?
Lungs
29
New cards
Which specific blood vessel carries blood from:
heart → lungs
heart → lungs
Pulmonary artery
30
New cards
Which specific blood vessel carries blood from:
lungs → heart
lungs → heart
Pulmonary vein
31
New cards
Which specific blood vessel carries blood from:
heart → organs
heart → organs
Aorta
32
New cards
Is the aorta a vein or an artery?
Artery
33
New cards
Which specific blood vessel carries blood from:
organs → heart
organs → heart
Vena cava
34
New cards
Is the vena cava a vein or an artery?
Vein
35
New cards
When blood goes:
pulmonary vein → heart
Which part of the heart does it enter after?
pulmonary vein → heart
Which part of the heart does it enter after?
Left atrium
36
New cards
Where does blood flow to after the left atrium?
Left ventricle
37
New cards
What does blood pass through in between:
left atrium → left ventricle
left atrium → left ventricle
Atrio-ventricular (AV) valves
38
New cards
Which blood vessel does the blood enter after the left ventricle?
Aorta
39
New cards
What does blood pass through in between:
ventricle → artery
ventricle → artery
Semi-lunar valves
40
New cards
What blood vessels does blood enter when it passes through the organs?
Capillaries
41
New cards
Which substances transfer to cells from the blood inside the capillaries?
* Oxygen
* Glucose
* Amino acids
* Glucose
* Amino acids
42
New cards
Which substances leave cells and go into the capillaries?
* Carbon dioxide
* Water
* Urea (from liver)
* Water
* Urea (from liver)
43
New cards
Which blood vessel does blood enter when:
capillaries → heart
capillaries → heart
Vena cava
44
New cards
Where does the blood go after the vena cava?
Right atrium
45
New cards
Where does blood flow after the right atrium?
Right ventricle
46
New cards
Where does blood flow after the right ventricle?
Pulmonary artery
47
New cards
Which side of the heart has a thicker wall?
LeftWh
48
New cards
Why does the left side of the heart have a thicker wall than the right?
Blood needs to be pumped a further distance, so it is pumped at a higher pressure
49
New cards
What is cardiac output?
Volume of blood pumped out the heart per minute
50
New cards
What is the equation for cardiac output?
heart rate (bpm) × stroke volume
51
New cards
Why do organs need glucose and oxygen?
Aerobic respiration
52
New cards
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
oxygen + glucose → carbon dioxide + water + energy
53
New cards
What is the balanced, symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
6O₂ + C₆H₁₂O₆ → 6CO₂ +6H₂O + energy
54
New cards
Is energy made or released during respiration?
Released
55
New cards
Where does aerobic respiration take place in the cells?
Mitochondria
56
New cards
Which type of cells contract during exercise?
Muscle cells
57
New cards
What do muscle cells use in order to contract?
Energy
58
New cards
What process releases energy inside muscle cells?
Aerobic respiration
59
New cards
What substances do muscle cells need in order to respire?
* Oxygen
* Glucose
* Glucose
60
New cards
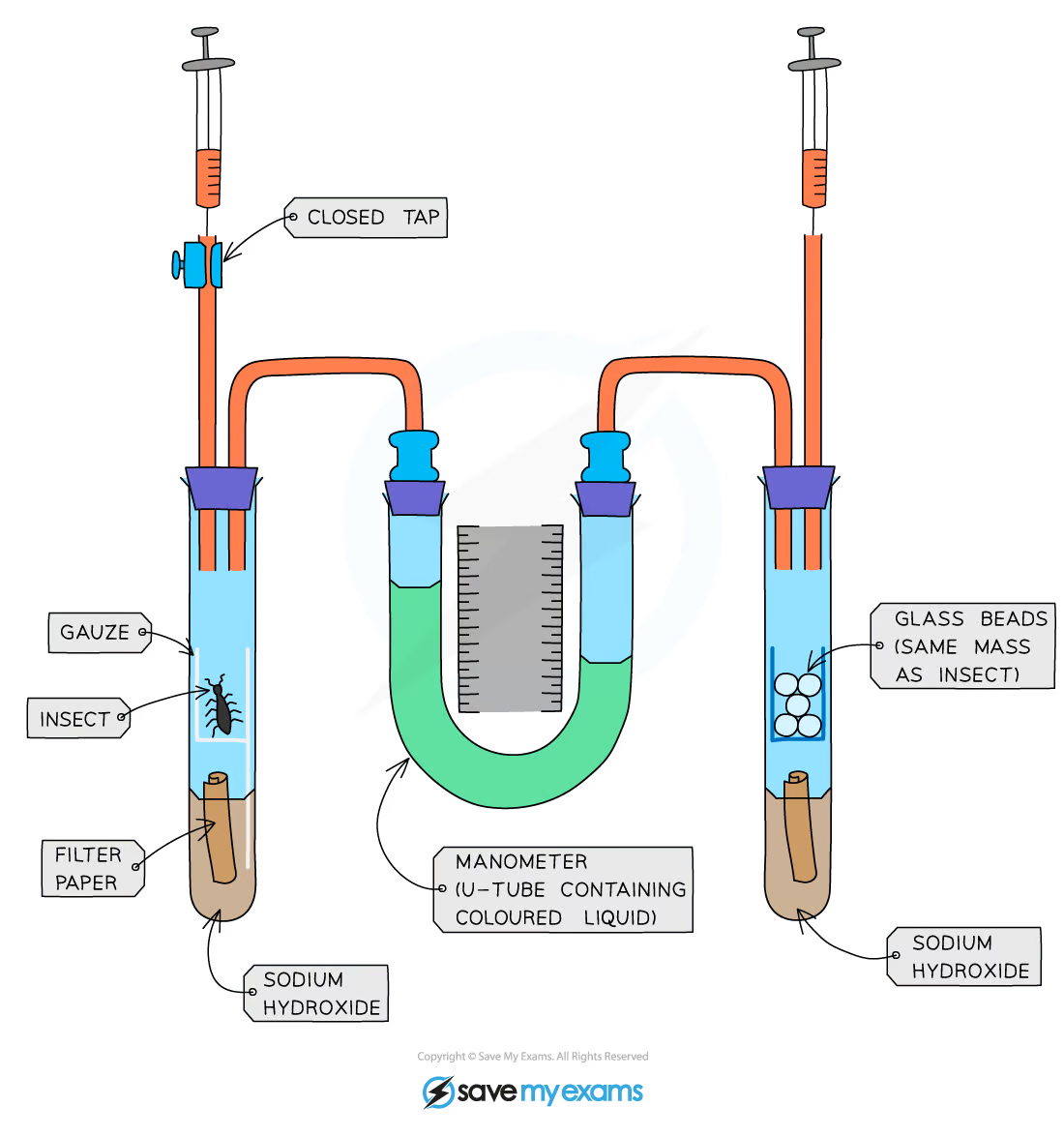
What is this piece of equipment called?
Respirometer
61
New cards
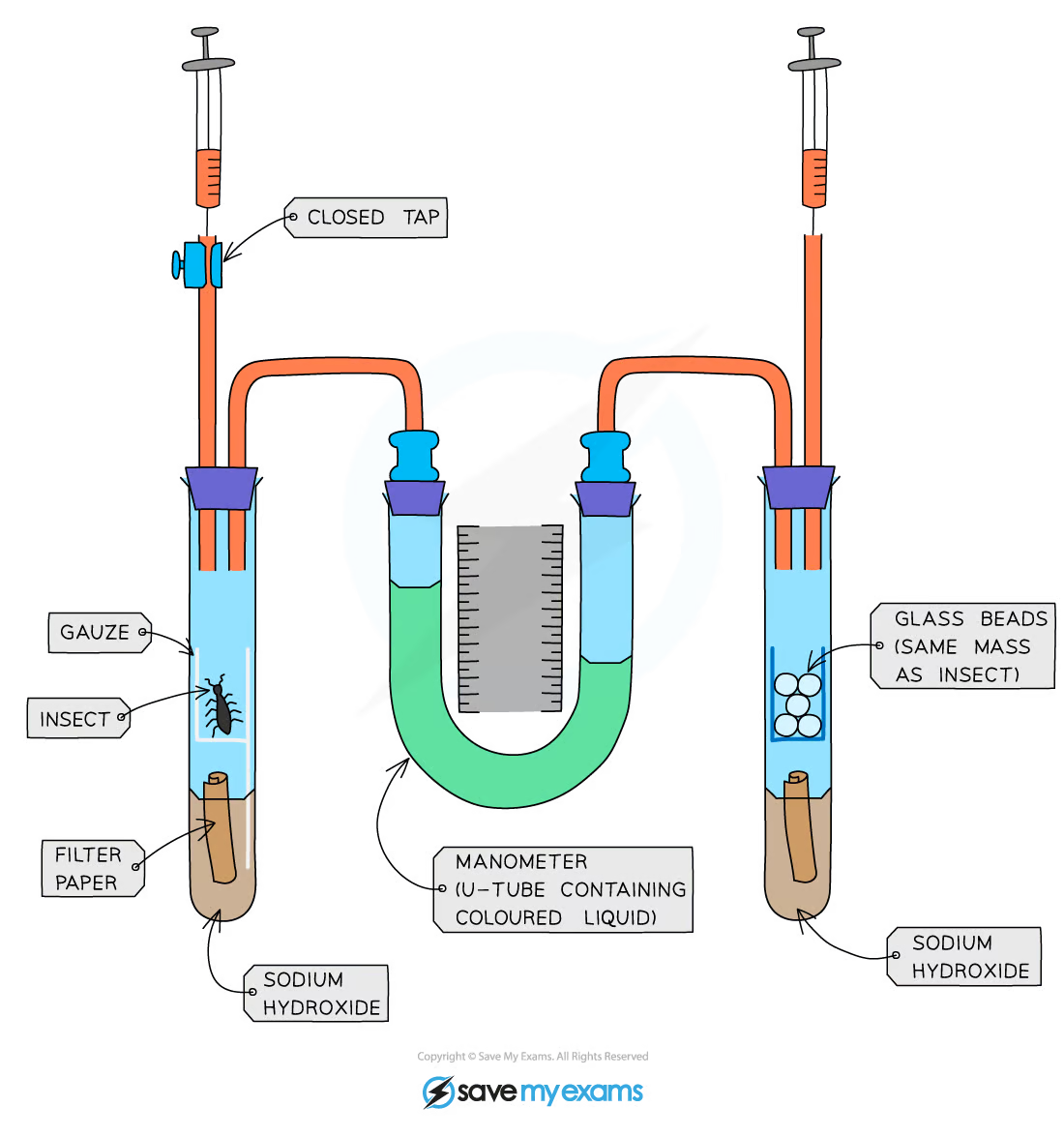
What is this piece of equipment used for?
Measuring respiration rate
62
New cards
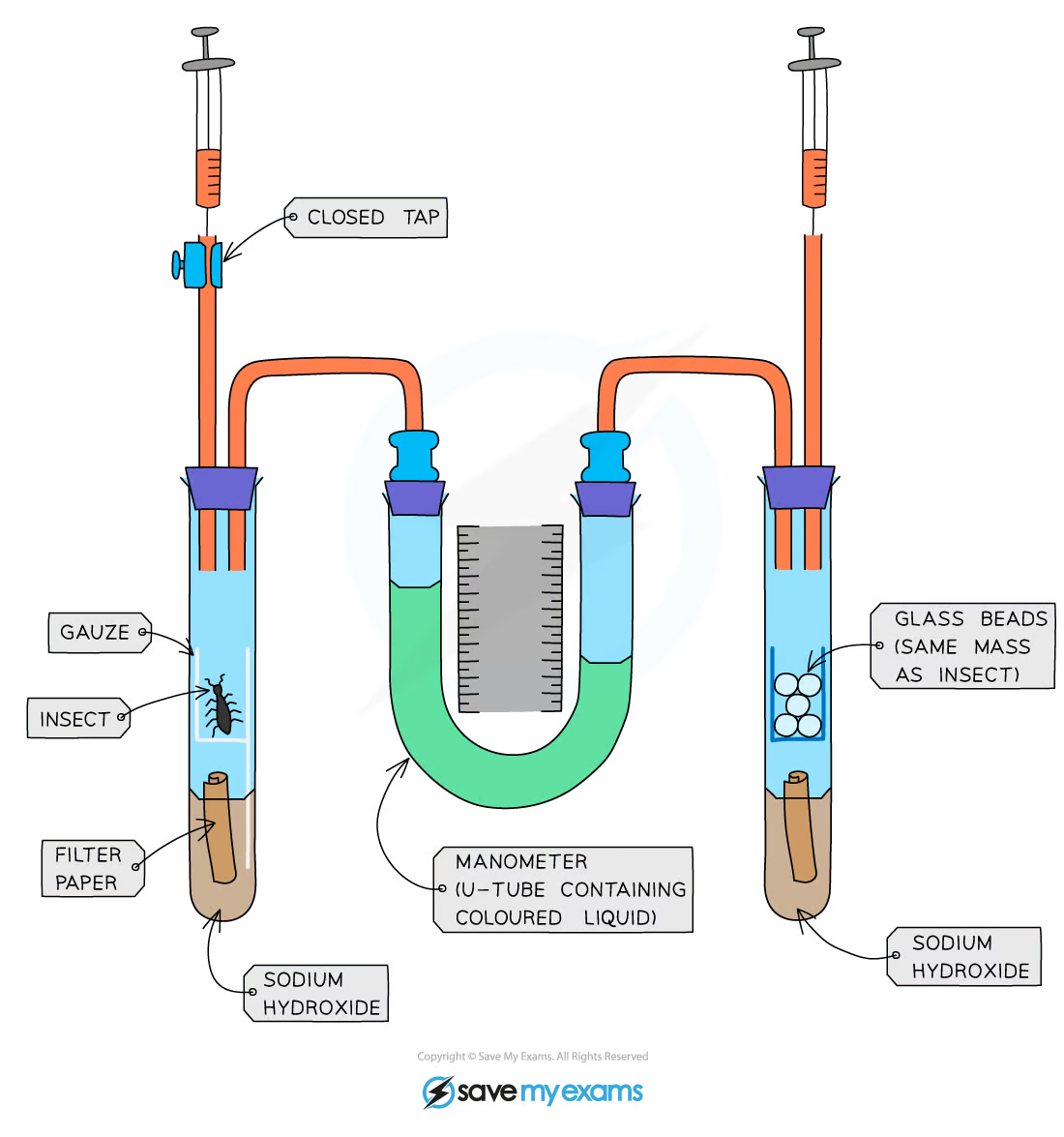
What gas will the insects be using when respiring in the tube?
Oxygen
63
New cards

What gas will the insects be producing when respiring in the tube?
Carbon dioxide
64
New cards
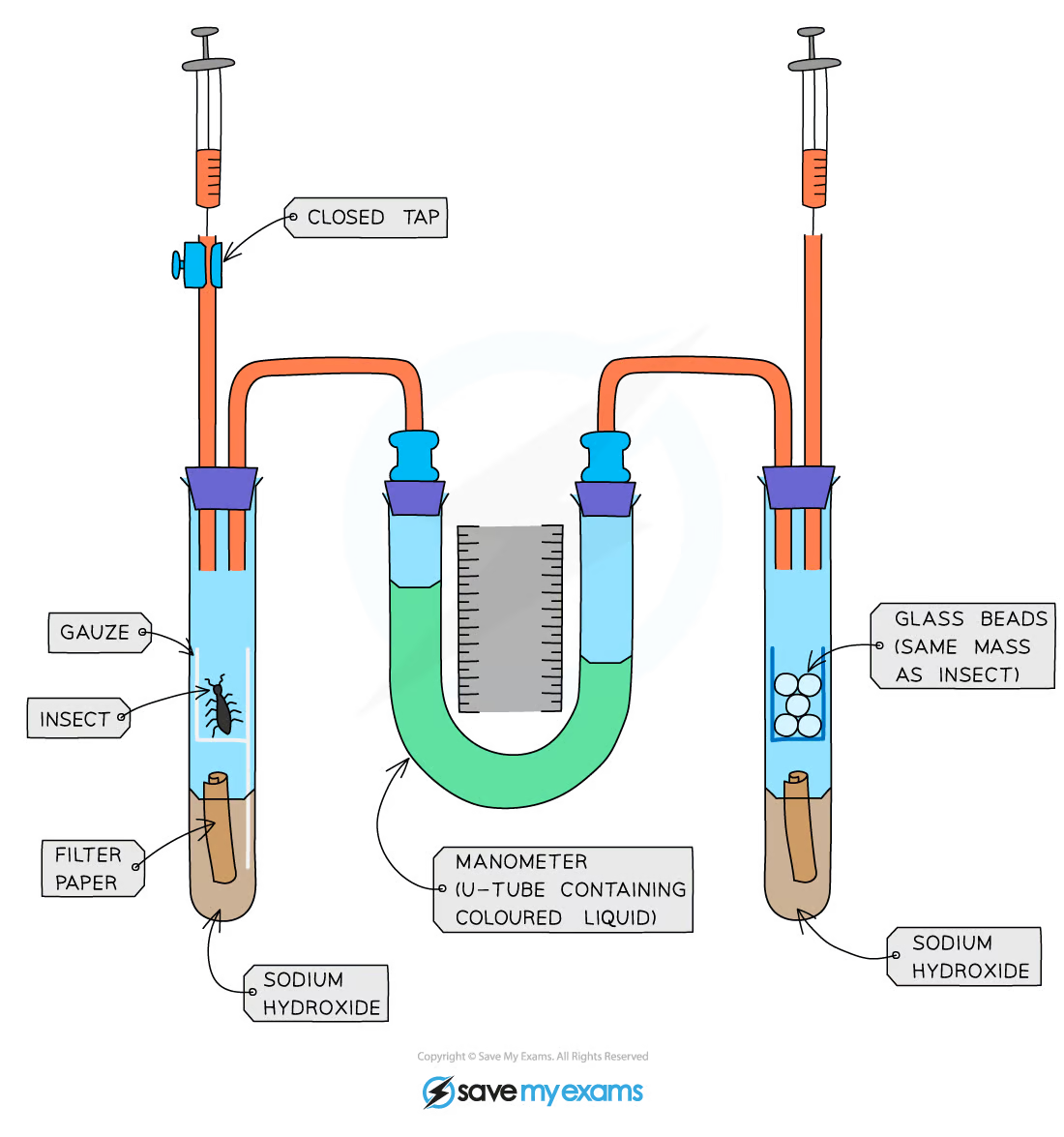
Which chemical absorbs carbon dioxide so that we can identify how much oxygen the insects are using up during this experiment?
Sodium hydroxide
65
New cards
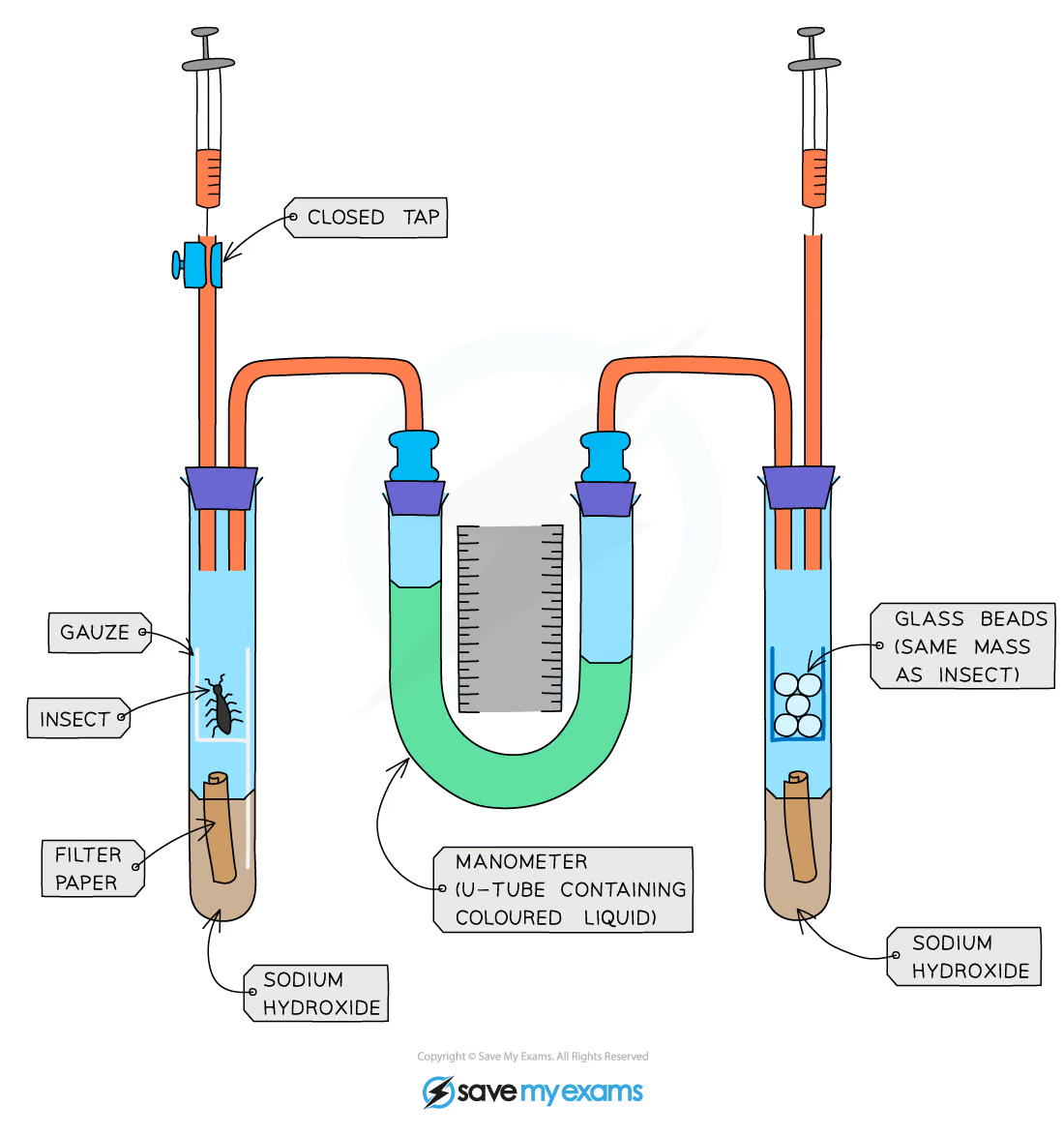
Which direction will the liquid move when the insects use up oxygen?
Left
66
New cards
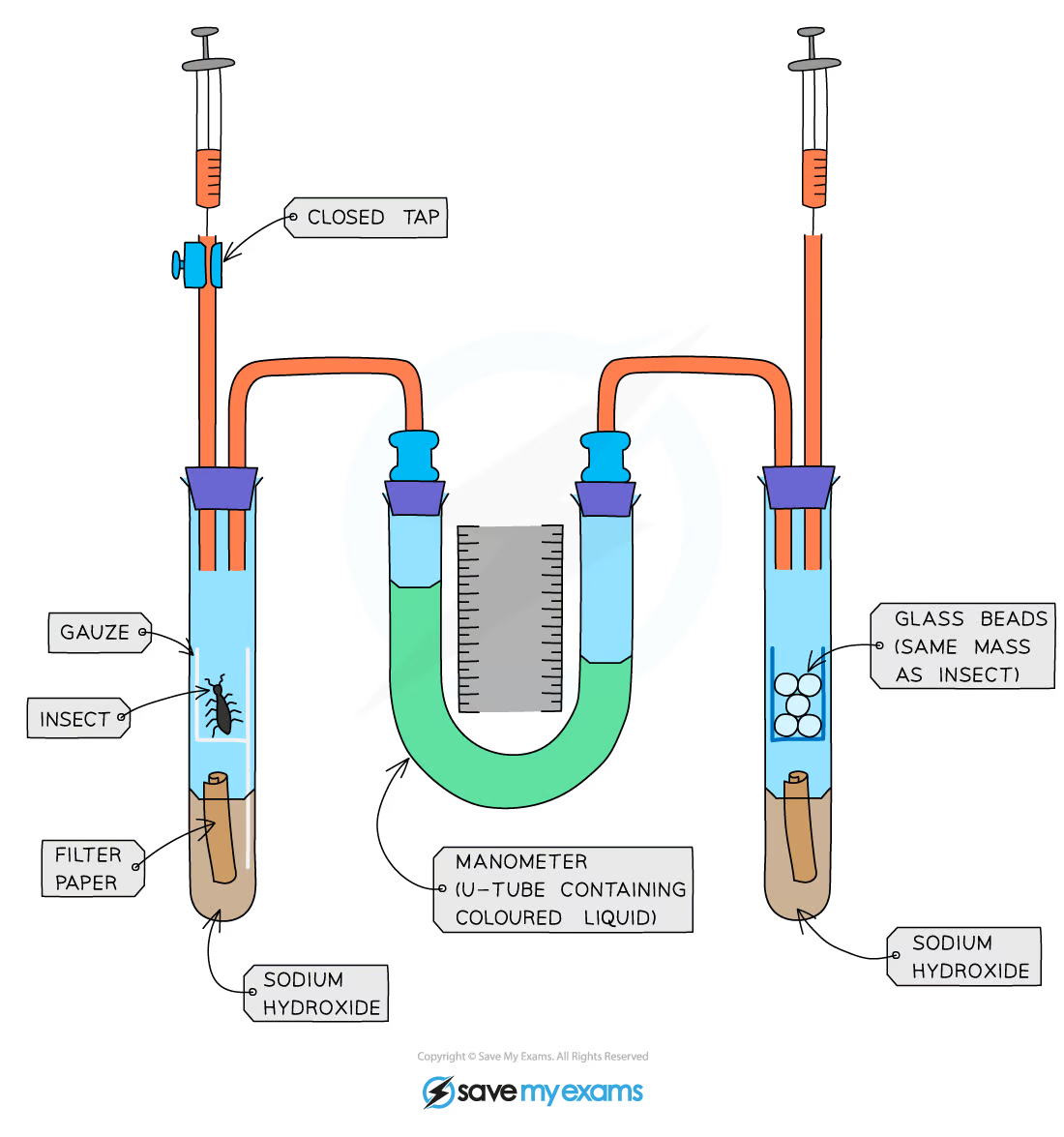
What is the equation for the rate that the liquid moves during the experiment?
distance ÷ time
67
New cards
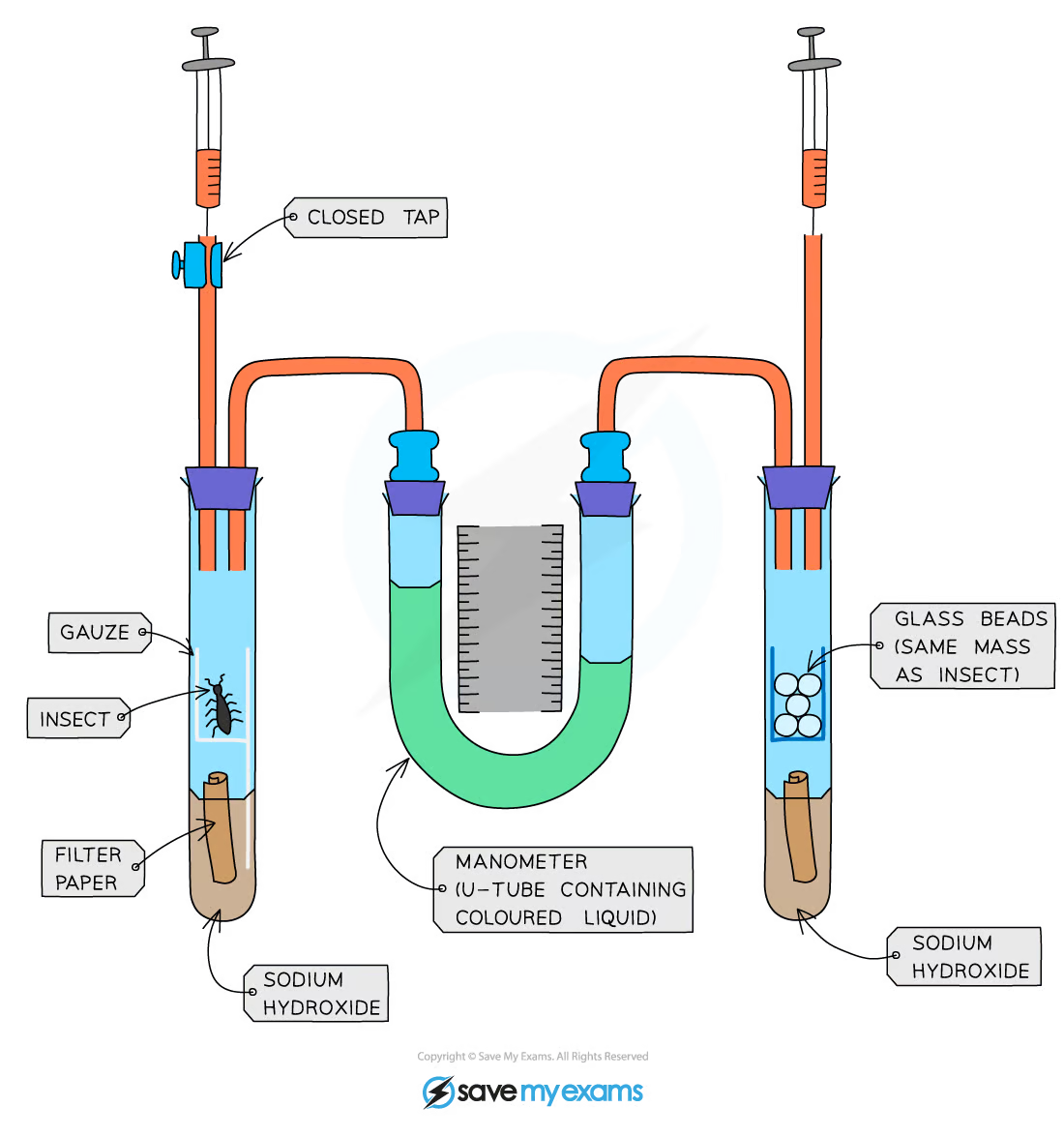
How should you ensure the insect’s safety when using a respirometer?
Don’t leave them in the tube too long (or they will run out of oxygen and die)
68
New cards
Which type of exercise results in muscle cells not being supplied with enough oxygen?
Vigorous exercise
69
New cards
What type of respiration do muscle cells do when they don’t have enough oxygen?
Anaerobic
70
New cards
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration?
glucose → lactic acid
71
New cards
What does a build-up of lactic acid cause?
Cramps
72
New cards
Do plants carry out respiration?
Yes
73
New cards
Why do plants have mitochondria?
Aerobic respiration
74
New cards
Are there times when plant cells do not get enough oxygen?
Yes
75
New cards
What type of respiration do plants do when they don’t get enough oxygen?
Anaerobic respiration
76
New cards
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants?
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
77
New cards
Which organ monitors the concentration of glucose in the blood?
Pancreas
78
New cards
What hormone is released by the pancreas when the blood glucose concentration is higher than normal?
Insulin
79
New cards
Name the target organ/cells for insulin.
* Liver
* Muscle cells
* Muscle cells
80
New cards
How does insulin travel to the liver and muscle cells?
Blood
81
New cards
What does the liver do in response to insulin?
Takes it and stores it as glycogen
82
New cards
What hormone is released by the pancreas when blood glucose concentration is lower than normal?
Glucagon
83
New cards
Name the target organ for glucagon.
Liver
84
New cards
What does the liver do in response to the glucagon?
Breaks down glycogen back into glucose and puts it back into the blood
85
New cards
What else is the pancreas referred to as?
Endocrine gland
86
New cards
What causes type 1 diabetes?
Pancreas cannot make insulin
87
New cards
What is the main treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin injections
88
New cards
Where is insulin injected into when someone has type 1 diabetes?
Subcutaneous fat
89
New cards
What are changes in lifestyle people with type 1 diabetes can make?
* Eat more complex carbohydrates
* Exercise regularly
* Exercise regularly
90
New cards
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Liver and muscle cells aren’t as responsive to insulin
91
New cards
Can obesity cause type 2 diabetes?
Yes
92
New cards
What is the equation for BMI?
weight ÷ height
93
New cards
How does waist-to-hip ratio contribute to type 2 diabetes?
Ratio above 1.0 for men and 0.85 for women linked to increased risk
94
New cards
What is the equation for waist-to-hip ratio?
waist circumference ÷ hip circumference
95
New cards
State 2 treatments for type 2 diabetes?
* Healthy diet
* Regular exercise
* Regular exercise
96
New cards
Do some people with type 2 diabetes inject insulin?
Yes
97
New cards
State the endocrine for thyroxine.
Thyroid gland
98
New cards
How does thyroxine concentration affect metabolic rate?
As thyroxine concentration increases, metabolic rate increases
99
New cards
Which part of the brain monitors the concentration of thyroxine in the blood?
Hypothalamus
100
New cards
What hormone does hypothalamus release when thyroxine concentration is lower than normal?
TRH