Psych Unit 3
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:57 AM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
1
New cards
A nerve cell/neuron
the basic building blocks of the nervous system. We have tens of billions of neurons in the human brain.
Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by a chemical signal from a neighboring neuron
Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by a chemical signal from a neighboring neuron
2
New cards
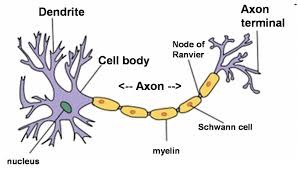
How a neuron works
- Dendrites receive neurotransmitters
- They send the info to the cell body
- The cell body sends it to the axon, which has a myelin sheath (insulating fatty layer that speeds transmission)
- The info travels to axon terminals
- The terminals release the info to other neurons
- The process is repeated
- They send the info to the cell body
- The cell body sends it to the axon, which has a myelin sheath (insulating fatty layer that speeds transmission)
- The info travels to axon terminals
- The terminals release the info to other neurons
- The process is repeated
3
New cards
Types of neurons
Sensory Neurons
Motor Neurons
Interneurons
Motor Neurons
Interneurons
4
New cards
Sensory Neurons (afferent)
Take information from the senses to the brain. Ex: pencil poke game with the arm
5
New cards
Interneurons
Shortcut/reflex. They make it to the brain eventually but the spinal cord processes them first. Ex: when the doctor hits your knee with a hammer and it moves.
6
New cards
Motor Neurons(Efferent Neurons)
Take information from brain to the rest of the body. Ex: you stub your toe, so your brain sends pain signals to your toe
7
New cards
How a Neuron Fires
It is an electrochemical process.
A neuron fires an impulse when it receives a signal from a sense receptor (pressure, heat) or when stimulated by chemical messages from neighboring neuron
This impulse is called the action potential, and is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
A neuron fires an impulse when it receives a signal from a sense receptor (pressure, heat) or when stimulated by chemical messages from neighboring neuron
This impulse is called the action potential, and is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
8
New cards
The All-or-None Response
- The idea that either the neuron fires or it does not
- There is no part-way firing.
- Like a gun
- A tap is differentiated from a punch bc more neurons will fire or fire more quickly
- There is no part-way firing.
- Like a gun
- A tap is differentiated from a punch bc more neurons will fire or fire more quickly
9
New cards
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired. Just like how you can't flush a toilet twice in a row
10
New cards
Steps of Action Potential
- Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse (the small gap between two neurons, where nerve impulses are relayed)
- Reached its threshold(is there enough there to fire)- then fires based on the all-or-none response.
- Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Axon is negative at rest). Because potassium is inside and sodium is outside.
The mixing of + and - ions (called depolarization) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Na) while closing the original portal. The time it takes for the negative ions to recharge is the refractory period.
- Process continues down the axon to the axon terminals.
- Terminal buttons turn electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoot the message to the next neuron across the synapse.
- Reached its threshold(is there enough there to fire)- then fires based on the all-or-none response.
- Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Axon is negative at rest). Because potassium is inside and sodium is outside.
The mixing of + and - ions (called depolarization) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Na) while closing the original portal. The time it takes for the negative ions to recharge is the refractory period.
- Process continues down the axon to the axon terminals.
- Terminal buttons turn electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoot the message to the next neuron across the synapse.
11
New cards
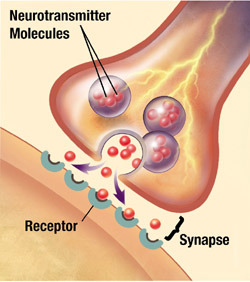
how neurons communicate
axon terminals release neurotransmitter from sacs called vesicles, neurotransmitter enters synapse, neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits
then reuptake: where the sending neuron absorbs excess neurotransmitters molecules (they make more neurotransmitters than they need)
then reuptake: where the sending neuron absorbs excess neurotransmitters molecules (they make more neurotransmitters than they need)
12
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
MUSCLE ACTION, LEARNING
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory. With Alzheimer's disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate.
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory. With Alzheimer's disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate.
13
New cards
Dopamine
PLEASURE
influences movement (more involuntary like tremors), learning, attention, and emotion. Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease
influences movement (more involuntary like tremors), learning, attention, and emotion. Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease
14
New cards
Serotonin
DEPRESSION
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression. Some antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels.
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression. Some antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels.
15
New cards
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal; undersupply can slow you down and decrease your alertness
16
New cards
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
CALMING
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
17
New cards
Glutamate
MEMORY
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (which is why some people avoid MSG in food)
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (which is why some people avoid MSG in food)
18
New cards
Agonists
drugs that increase the action of a neurotransmitter, acts like a neurotransmitter
19
New cards
Antagonists
drugs that block the function of a neurotransmitter
20
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
21
New cards
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
22
New cards
Somatic nervous system (part of the peripheral)
controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
23
New cards
autonomic nervous system (part of the peripheral)
Automatic actions of your organs and glands
24
New cards
sympathetic (part of the peripheral)
arousing Ex: fight or flight
25
New cards
Parasympathetic (part of the peripheral)
calming
26
New cards
Neural network
fire together, wire together
refers to interconnected neuron cells that work together as a team. The brain learns by modifying certain connections in response to feedback
refers to interconnected neuron cells that work together as a team. The brain learns by modifying certain connections in response to feedback
27
New cards
endocrine system
Secretes hormones
Slower than neurotransmitters, but last longer. They are transmitted through blood.
Ex: your friend steps on your foot, your neurotransmitters give you immediate pain, but you feel anger towards your friend slightly after and it lasts for a few minutes
Slower than neurotransmitters, but last longer. They are transmitted through blood.
Ex: your friend steps on your foot, your neurotransmitters give you immediate pain, but you feel anger towards your friend slightly after and it lasts for a few minutes
28
New cards
Thalamus
sensory switchboard, processes every sense other than smell
29
New cards
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing
30
New cards
Brainstem
oldest part of the brain, newer parts are built on top of this, automatic survival functions
31
New cards
Reticular formation
controls arousal
32
New cards
Cerebellum
Processes coordinates voluntary movement and balance
33
New cards
Amygdala
FEAR AND AGRESSION
linked to emotion
linked to emotion
34
New cards
Hippocampus
learning and memory
35
New cards
Hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
reward center, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal
reward center, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal
36
New cards
pituitary gland
Master gland, works with hypothalamus
37
New cards
cerebral cortex
Outside of the brain, control an information-processing center of the brain
38
New cards
Cerebrum
beefy portion of the brain
39
New cards
frontal lobe
higher order thinking (what makes us human)
40
New cards
parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch/body position
41
New cards
occipital lobe
receives visual information
42
New cards
temporal lobe
receives auditory information
43
New cards
motor cortex
left hemisphere section controls movement of the right side of the body and right hemisphere section controls movement of left side of the body
44
New cards
sensory cortex
area at front of parietal lobe that registers and processes the senses
45
New cards
association areas
not included in primary motor or sensory function, but involved in higher mental functions
46
New cards
Wernicke's Area
language comprehension. Carl Wernicke established it
47
New cards
Broca's area
controls speech. Paul broca established it
48
New cards
Plasticity
brain's ability to reorganize itself, higher in younger people to overcompensate for damage
49
New cards
corpus callosum
connects the left and right brain hemispheres half way down
might be severed because of frequent seizures (epilepsy)
might be severed because of frequent seizures (epilepsy)
50
New cards
Opposite hemispheres
- control opposite sides of the body- Right side/Right visual field → left hemisphere- Left Side/Left Visual Field → Right hemisphere
51
New cards
Left hemisphere
Analytical thoughts
Math/ScienceLanguage/Speech
Controls more important functions than right hemisphere
controls speech
brocas area
Math/ScienceLanguage/Speech
Controls more important functions than right hemisphere
controls speech
brocas area
52
New cards
Right hemisphere
Emotion
Artsy
facial recognition
Artsy
facial recognition
53
New cards
biological psychology
a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
54
New cards
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
55
New cards
limbic system
EMOTIONS
neural system composed of the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus
neural system composed of the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus
56
New cards
endorphins
pain control and pleasure. Ex: will help soothe a runner's achy muscles
57
New cards
nerves
bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
58
New cards
Reflex
an automatic response to a sensory stimulus
59
New cards
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
60
New cards
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
61
New cards
Lesion
tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue
62
New cards
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
Ex: may help identify the cause of certain symptoms - such as seizures or memory problems
Ex: may help identify the cause of certain symptoms - such as seizures or memory problems
63
New cards
CT
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body
Ex: to assess brain tumors
Ex: to assess brain tumors
64
New cards
PET scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task. Basically shows pathway
Ex: looks for disease or injury in the brain
Ex: looks for disease or injury in the brain
65
New cards
MRI
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer generated images of soft tissue.
Ex: look for bleeding and swelling in the brain
Ex: look for bleeding and swelling in the brain
66
New cards
fMRI (functional MRI)
A technique for revealing bloodflow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function.
67
New cards
glial cells (glia)
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
may play a role in learning and thinking
may play a role in learning and thinking
68
New cards
somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
69
New cards
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
70
New cards
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them
71
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language)
72
New cards
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
73
New cards
environment
every external influence
74
New cards
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
75
New cards
identical twins
twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms. monozygotic, same-sex only
76
New cards
fraternal twins
twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment. same or opposite sex. dizygotic
77
New cards
molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
78
New cards
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. ex: height has a 90% heritability score
79
New cards
interaction
the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as environment) depends on another factor (such as heredity)
80
New cards
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
81
New cards
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
82
New cards
who we share dna with
share 96% of dna with gorillas
share 99.9% with other humans
share 99.9% with other humans
83
New cards
1959 Russian Fox story
30 males, 100 females mated, then kept only tamest of bunch. mated the tame bunch. 40 years later, new breed of fox
84
New cards
Why is casual sex more accepted by men? (when avg women and men asked strangers for sex tn, 75% of men agreed, almost no women)
sperm is cheap, eggs are not
85
New cards
What do men want?
healthy, young, waist 1/3 narrower than hips
86
New cards
what do women want?
wealth, power, security
87
New cards
twin studies
dr. bouchard, whether or not they are raised in same environment, they are very alike in many ways
88
New cards
placental arrangement
can determine how similar twins are
- most of the time they share a placenta
- 1/3 of the time, two separate placentas, can create differences, one can get more nutrients than the other
- most of the time they share a placenta
- 1/3 of the time, two separate placentas, can create differences, one can get more nutrients than the other
89
New cards
Roger Sperry
In the early 1960s, Sperry and colleagues, including Michael Gazzaniga, conducted extensive experiments on an epileptic patient who had had his corpus collosum, the "bridge" between the left and right hemispheres of the brain, split so that the connection was severed
90
New cards
Michael Gazzaniga
worked w sperry
studied split brain patients; showed that left/right hemispheres have different functions
studied split brain patients; showed that left/right hemispheres have different functions
91
New cards
superchiasmatic nucleus
group of neurons in hypothalamus that makes us drowsy at different times of the day/night
92
New cards
William James
thoery of emotion. emotion arises in response to external events
93
New cards
Ernest Hilgard
believed hypnosis invovles not only social influences but also a special state of dissociation
94
New cards
Types of environmental influence
- parents
- prenatal
- experience
- peer influence
- culture
- gender
PPEPCG
- prenatal
- experience
- peer influence
- culture
- gender
PPEPCG
95
New cards
as we age
IQ becomes more aligned w bio influence, less w the environment
Explore top notes
Unit 11: The Industrial Revolution and Imperialism. The division of the world - Point 5
Updated 1069d ago0.0(0)
Unit 11: The Industrial Revolution and Imperialism. The division of the world - Point 5
Updated 1069d ago0.0(0)