Unit 2: Plants for Food, Fibre, and Adaptations
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the primary uses of plants by humans?
used for food, fibre, environmental benefits, and medicine.
What is fibre in the context of plants?
tissue of plants derived from the stem, leaves, seeds, and roots.

What percentage of the world's food supply is based on seven crops?
75%.
List the seven crops that form the basis of most of the world's food supply.
Wheat, rice, maize (corn), potatoes, barley, cassava, and sorghum.
What is cassava and where is it commonly grown?
a sweet, chewy root vegetable commonly grown in Africa, Asia, and South America.
What products are derived from the cocoa tree?
Chocolate.

What are the uses of cotton?
is used for clothing, plastics, and papers.

How does flax compare to cotton in terms of strength?
2-3 times as strong as cotton.

What are some historical uses of hemp?
Hemp was used for making sails, ropes, and the first Bible was printed on hemp.

What are the advantages of hemp?
can be harvested in one year, its paper can be recycled 7 times, it is not eaten by most insect pests, and it chokes out weeds.
What are some medicinal plants and their uses?
White willow bark is used for aspirin (pain relief), opium poppies for morphine (strong pain killer), and cinchona trees for quinine (malaria prevention).
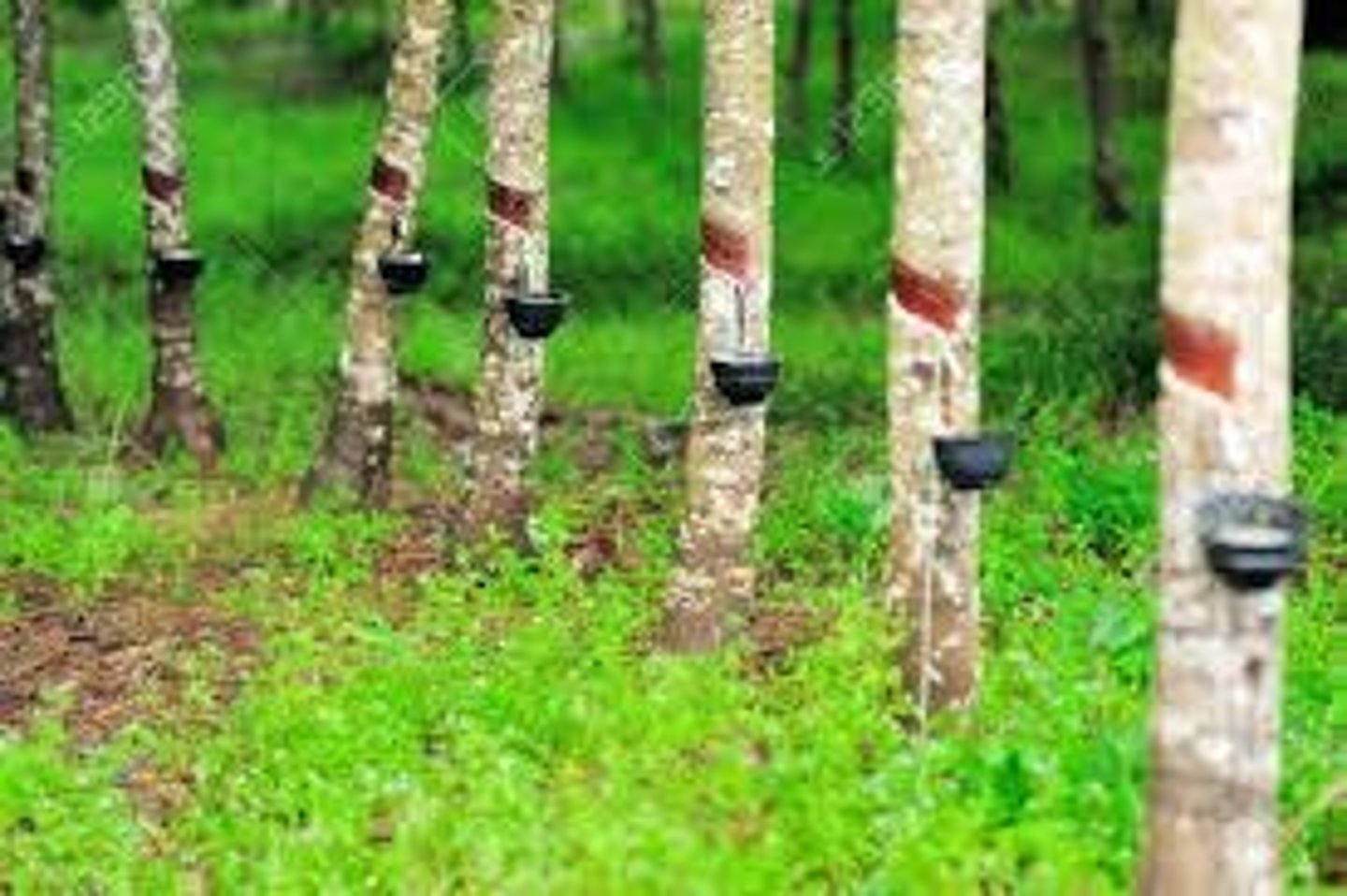
What are the uses of rubber trees?
used to produce tires for cars, planes, and spacecraft.

What are the functions of plant roots?
absorb water and minerals, support and anchor the plant, and store food.
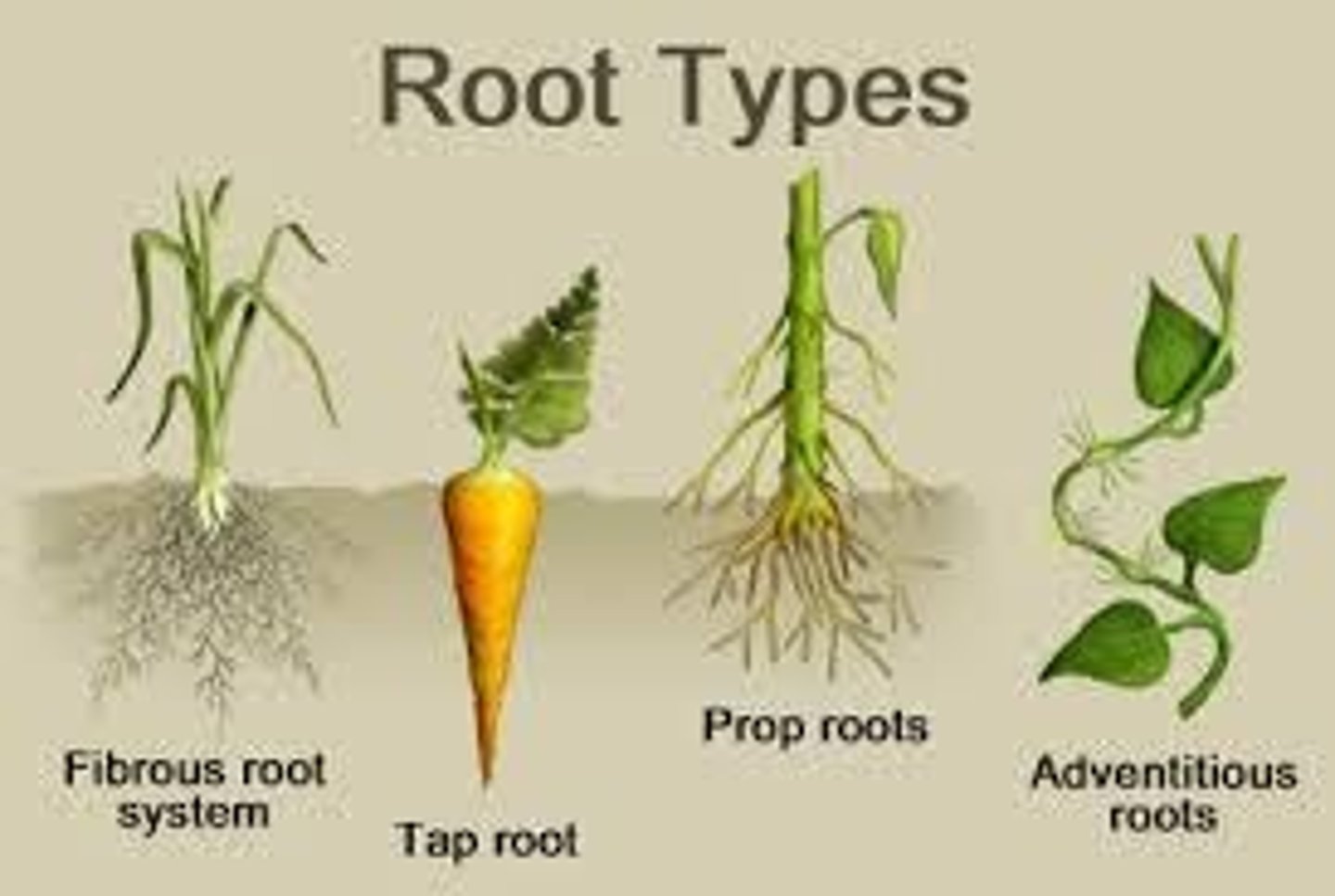
What are the two main types of root systems?
Taproot and fibrous roots.
Describe taproot systems.
has a main root that reaches deep into the ground with numerous smaller roots branching from it.
What is diffusion in the context of plant roots?
the movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration.
What is osmosis?
a type of diffusion where water moves from a high concentration to a low concentration through a differentially permeable membrane.
What is a differentially permeable membrane?
that allows some materials to pass through while keeping others out.
What are examples of edible roots?
Carrots, beets, turnips, radishes, and parsnips.
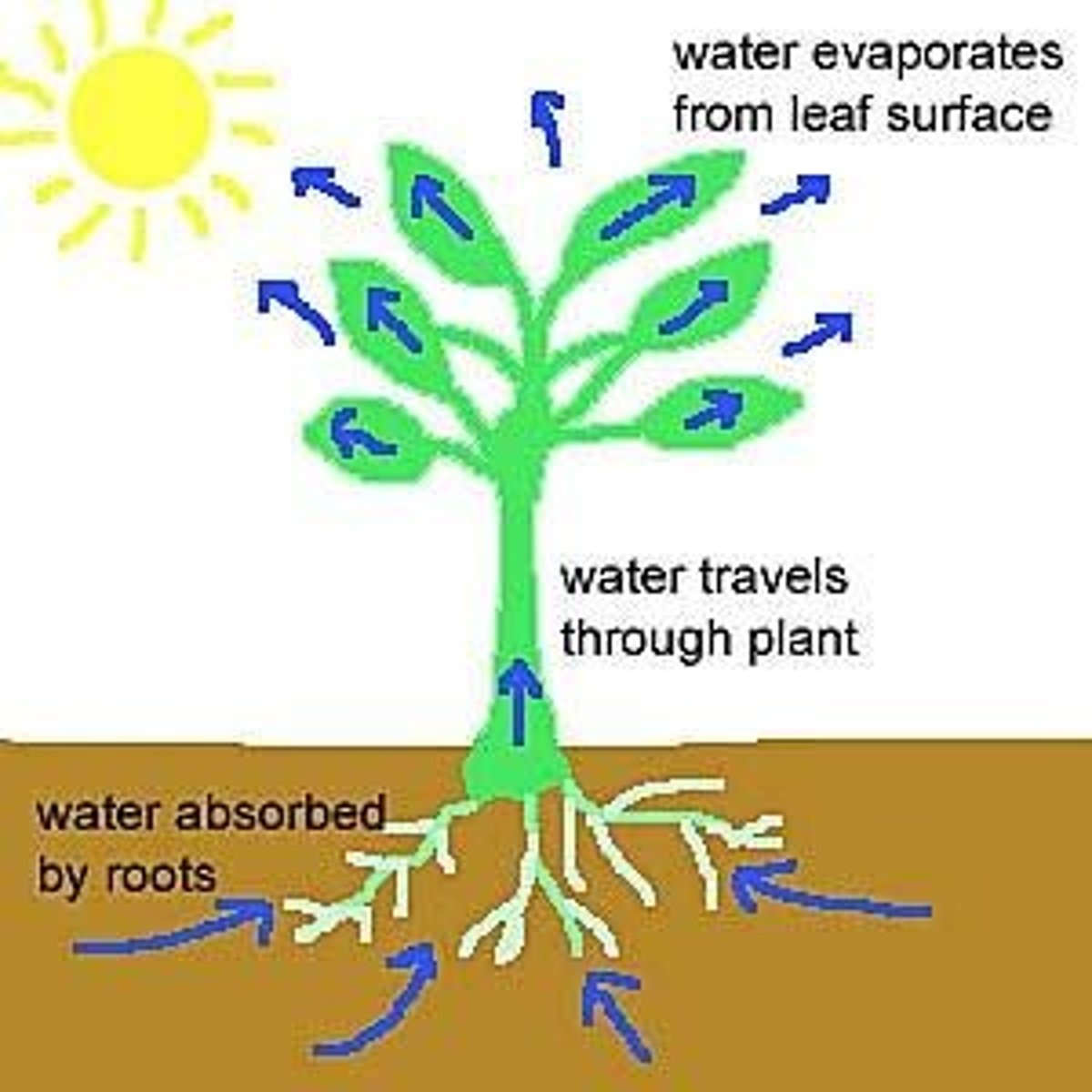
What role do roots play in water and nutrient absorption?
increase surface area through root hairs to absorb water and nutrients effectively.
What are some environmental benefits of plants?
use carbon dioxide and give off oxygen, form the base of food webs, provide shelter, clean and filter water, and prevent soil erosion.
What are the three main functions of the stem in plants?
1) Transport water and nutrients between the leaves and the roots. 2) Provide support for the plant. 3) Food storage.
What is the role of xylem in plants?
carries water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
What is the role of phloem in plants?
carries sugar from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
What is photosynthesis?
is the process by which plants make their own food from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight energy, converting it into chemical energy (sugar).
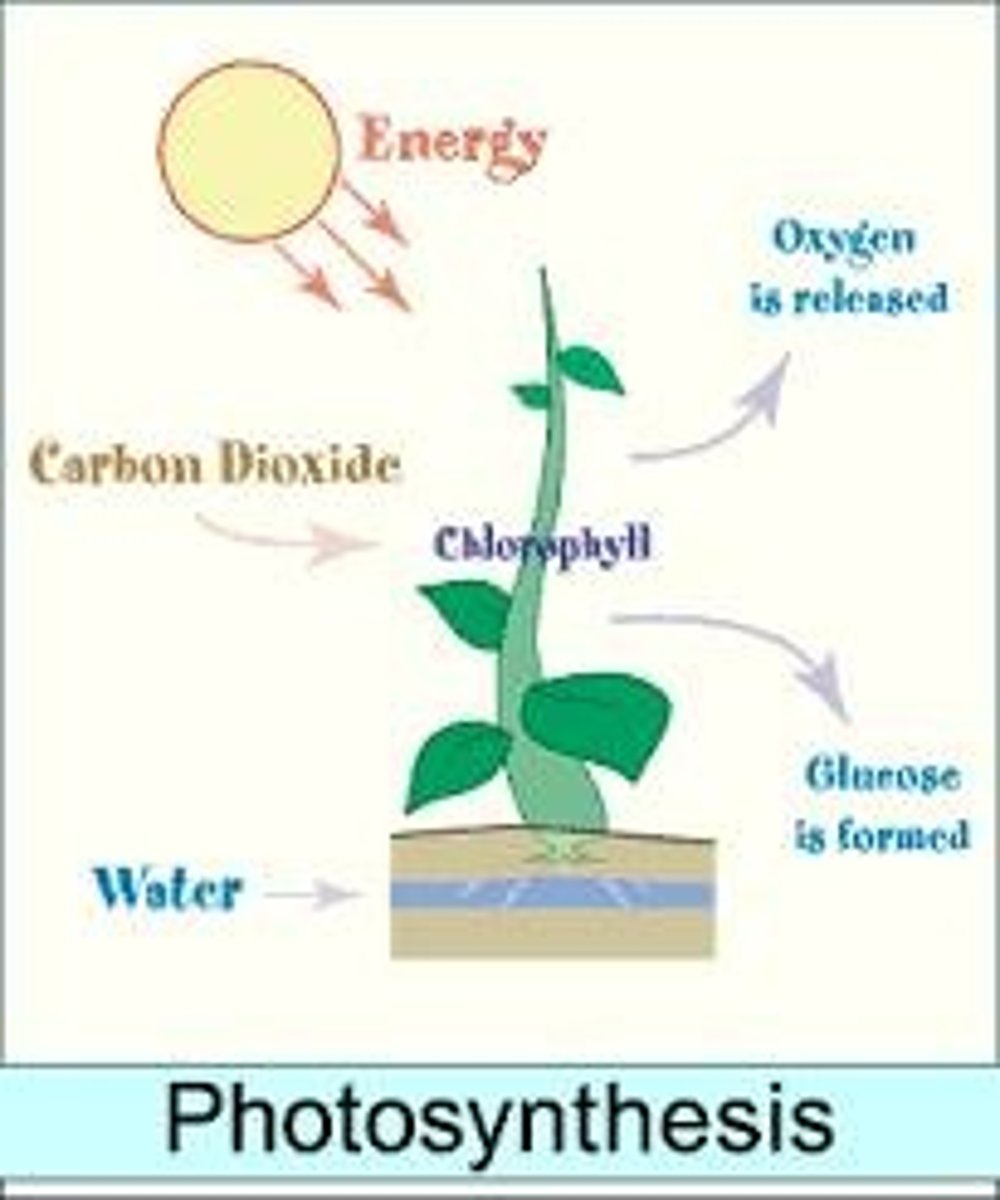
What is the equation representing photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O + Sunlight + nutrients + chlorophyll → sugar + O2.
What is the function of stomata in leaves?
are small openings that allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to exit the leaves.
How do guard cells function in relation to stomata?
regulate the opening and closing of stomata to control gas exchange.
What is respiration in plants?
is the process by which plants release CO2 and take in O2, occurring at night and slower than photosynthesis.
What is transpiration?
is the loss of water from a plant through evaporation, helping to move water up the stem via osmosis.
What is selective breeding in plants?
involves choosing specific plants with desired characteristics to reproduce.
What are the two types of plant reproduction?
1) Sexual reproduction, which involves specialized seeds and fruits from two plants. 2) Asexual/Vegetative reproduction, which occurs from roots, stems, or leaves of a parent plant.
What is an advantage of asexual reproduction in plants?
allows for the rapid production of genetically identical plants.
What is layering in plant reproduction?
involves bending a branch of a parent plant to the ground and covering it with soil to encourage root growth.
What is grafting in plant reproduction?
is the process of attaching a branch from one tree to another to promote growth.
What are cones in seed plant reproduction?
parts of trees with woody scales; female cones contain ovules, and male cones produce pollen.
What is pollination?
is the process of pollen traveling to the female cone for fertilization.
What is the main job of flowers in plant reproduction?
attract insects that help spread pollen to other plants.
What are the main parts of a flower?
1) Stamen (male part), 2) Pistil (female part), 3) Petals (often brightly colored), 4) Sepals (green parts underneath the flower).
What are the three main parts of the pistil?
1) Stigma (sticky tip that catches pollen), 2) Style (tube connecting stigma and ovary), 3) Ovary (holds the ovule).
What are the two parts of the stamen?
1) Filament (the stalk), 2) Anther (tip that produces pollen).
What are the two parts of a stamen?
Filament (the stalk) and Anther (tip, produces pollen).
What are the three steps of pollination?
1) Pollen grain lands on the stigma. 2) A pollen tube grows down the style into the ovary and enters an ovule. 3) A sperm travels down the pollen tube to attach to the egg.
What is formed once a plant is pollinated?
A seed, which contains a tiny living plant called an embryo surrounded by food.
What is fruit in botanical terms?
A growing ovary of a plant that swells and protects the seeds until they are ripe.
How are seeds dispersed?
can be carried by animals and insects, by winds or water, or planted by humans using machines.
What is germination?
The development of a seed into a new plant.
What are the five main factors that affect soil development?
1) Parent material 2) Vegetation 3) Landscape 4) Climate 5) Time.
What is parent material in soil development?
The mineral (non-organic) matter from which the soil is developed, such as rock or clay.
How does vegetation influence soil development?
determines the amount and type of organic material in/on the soil and protects it from erosion.
What role does landscape play in soil development?
It affects drainage, with some soils being well-drained and others being saturated.
How does climate influence soil development?
determines the types of plants that grow and how fast organic material decomposes.
What is humus?
A dark soil rich in nutrients that holds water well.
What are the four key types of decomposers in healthy soil?
1) Bacteria 2) Fungi 3) Microscopic actinomycetes 4) Earthworms.
What is the role of bacteria in healthy soil?
They actively break down dead material.
What nutrients do healthy plants require?
Nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, sulfur, calcium, magnesium.
What is salinization?
Salty water caused by too little vegetation and too much water.
What is a solution to salinization?
Replanting areas so that water cannot dissolve the salt and leave it behind.
What causes soil erosion and loss of organic material?
Too much cultivating mixed with water and wind.
What are three solutions to soil erosion?
1) Leaving a root system in place 2) Zero tillage 3) Crop rotation.
What is zero tillage?
A farming practice that minimizes soil disturbance.
What are shelterbelts?
Rows of trees or shrubs planted to protect crops from wind and erosion.
What is crop rotation?
The practice of alternating the crops grown on a particular piece of land to improve soil health.
What defines a pest?
Any organism that humans find annoying or harmful.
What characteristics make dandelions successful weeds?
Powerful roots, broad leaves, super seeds, adaptability, and chemical weapons.
What are introduced or exotic species?
Species not common to an area, often without natural enemies.
What are some problems associated with chemical pest control?
Bioaccumulation, poisoning of non-target species, and pest resistance to chemicals.
What is organic food?
Food grown without the use of pesticides or chemical fertilizers.