4.1 The role of marketing
Introduction
- Marketing: management task that links the business to the customer by identifying and meeting the needs of customers profitably it does this by getting the right product at the right price to the right place at the right time.
- Involving some related management functions such as:
- Market research: process of evaluating the feasibility of a new product/service, through research conducted directly with potential consumers. This method allows organizations/businesses to discover their target market, collect and document opinions and make informed decisions.
- Distribution: spreading the product throughout the marketplace such that a large number of people can buy it.
- Product design: process of imagining, creating and iterating products that solve users’ problems or address specific needs in a given market.
- Customer service: direct one-on-one interaction between a consumer making a purchase and a representative of the company that is selling it.
- Pricing: method of determining the value a producer will get in the exchange of goods/services. Simply, pricing method is used to set the price of producer’s offerings relevant to both the producer and the customer.
- Packaging: covering the product itself so that it is protected from damage, leakage, dust, pollution, contamination etc.
- Advertising: means of communication in which a product, brand or service is promoted to a viewership in order to attract interest, engagement and sales.
Market characteristics
Market size: total level of sales of all producers within a market.
Market growth: percentage change in the total size of a market (volume or value) over a period of time.
Ease of entry: lack of barriers for the establishment of new competitors in a market.
Homogeneous products: goods that are physically identical or viewed as identical by consumers.
Segmentation: dividing a market into distinct groups of consumers who share common tastes and requirements.
Target marketing: focusing marketing activity on particular segments of the market.
Mass marketing: selling to the whole market using a standardized product and the same marketing activities.
Consumer good: tangible physical product marketed to end users (consumers).
Consumer service: intangible provision of an activity to end users (consumers).
Marketing approaches
Market orientation: outward-looking approach basing product decisions on consumer demand, as established by market research.
Product orientation: inward-looking approach that focuses on making products that can be made or have been made for a long time and then trying to sell them.
Social (societal) marketing considers not only the demands of consumers but also the effects on all members of the public (“society”) involved in some way when firms meet these demands.
Market share and market leadership
Market share: percentage of sales in the total market sold by one business.
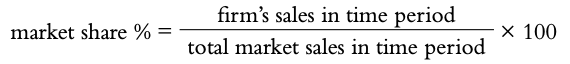
Market leadership: when a business has the highest market share of all firms that operate in that market.
Marketing objectives
- Marketing objectives: goals set for the marketing department to help the business achieve its overall objectives.
- For-profit organizations
- Non-profit-making organizations