Psych 101 -- exam 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Before his railroad accident which damaged his frontal lobe, Phineas Gage personality was ____________________ but after the accident he was___________________
reliable and efficient, unreliable and irreverent and obstinate
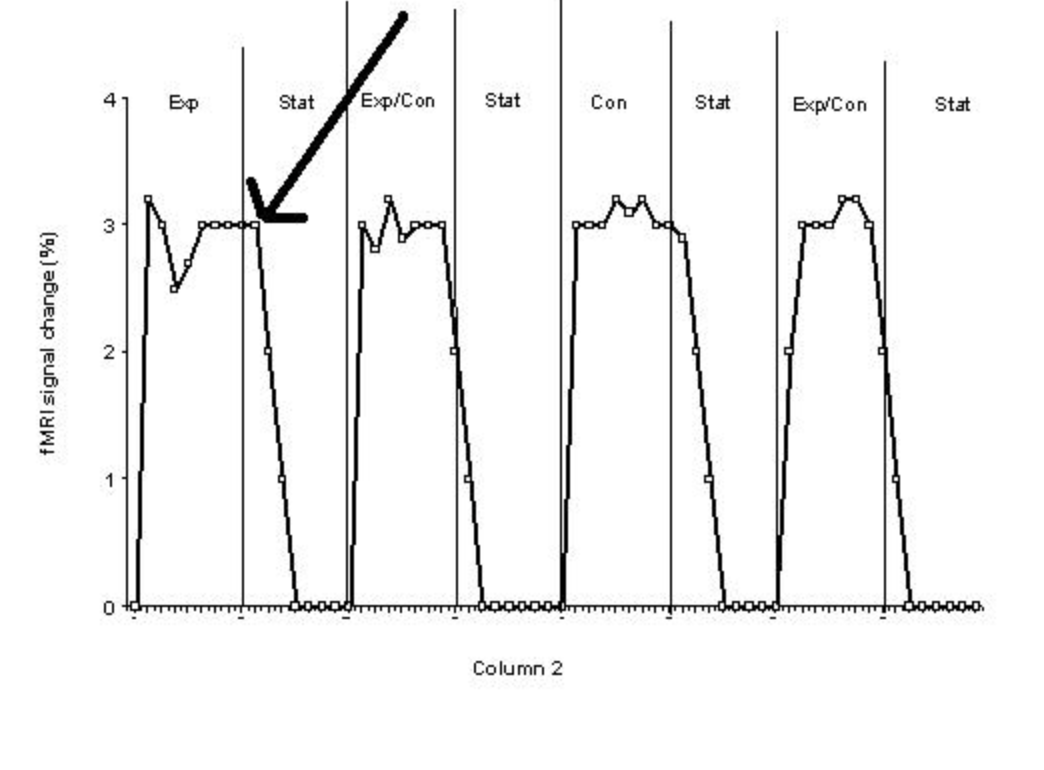
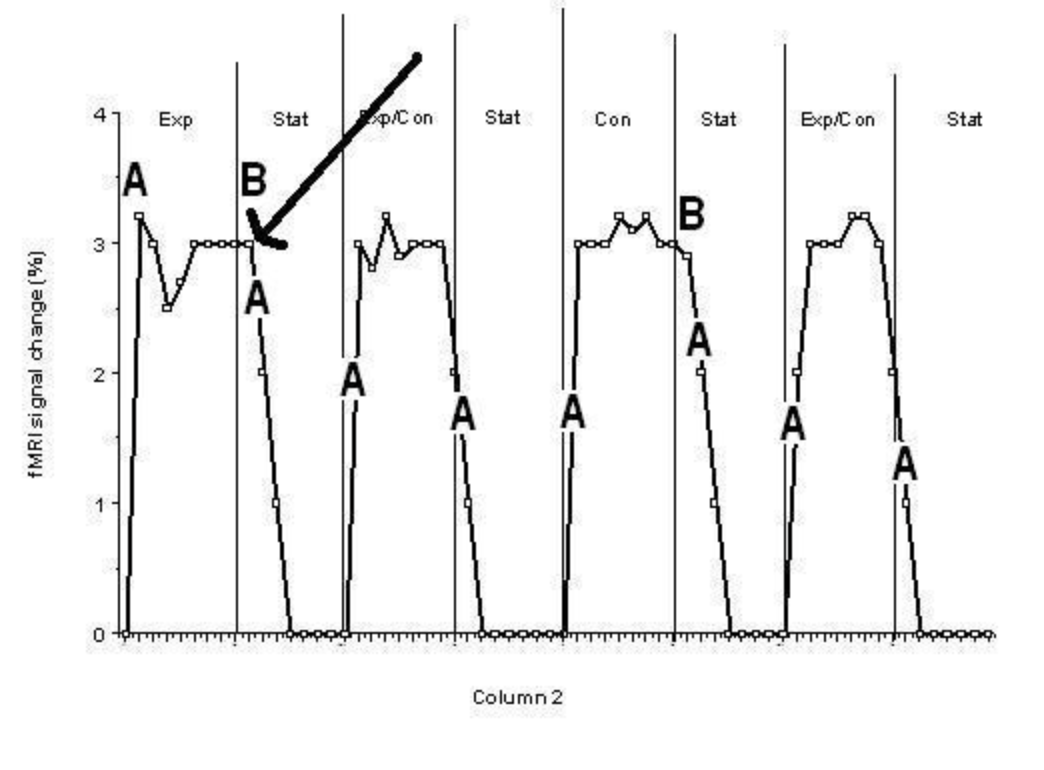
Consider the graph above showing the brain activity in the motion processing area (3 points)
A) Label/circle one part of the graph that is due to the hemodynamic lag (1).
B) Label/circle all parts of the graph where the subject experiences the motion after-effect (1)
C) Consider where the arrow is pointing to on the graph. What problem/limitation of fMRI is related to this point on the graph?
(1) Hint: the answer is NOT the hemodynamic lag
C) FMRI shows activity, but does not say what activity means
What is the main advantage of EEG?
Great temporal resolution
What are some strengths of positron emission tomography?
Decent spatial resolution, can track specific chemical processes in brain by radioactively tagging (e.g. glucose)
What are two strengths of fMRI?
Spatial resolution, non-obtrusive
Someone touches my cheek and it feels like someone is touching my thumb--what kind of injury did I have and what happened to my brain after that injury?
I lost my thumb and my brain reorganized.
My wife and I both suffered brain damage to our left hemispheres. I am 3 times as likely as my wife to have ________________ -- this impairment is when a person has difficulty ___________________ (1 point total).
aphasia, naming things
________% of hemispatial neglect patients have right hemisphere damage and ___________ % of hemispatial neglect patients have left hemisphere damage.
86,7
There are 400 people in a room--300 right handed people and 100 left handed people. These people are drawn from the general population and therefore have typical probabilities of left and right hemisphere dominance processing for language. If I pick a person at random from this room and determine that they have the right hemisphere as the dominant language processing center, what is the probability that this person is right handed?
0.5
What is it called when people are not aware of the deficits due to brain damage?
Anosognosia
In class, we discussed a parametric fMRI that was used to study what cognitive function?
Working Memory
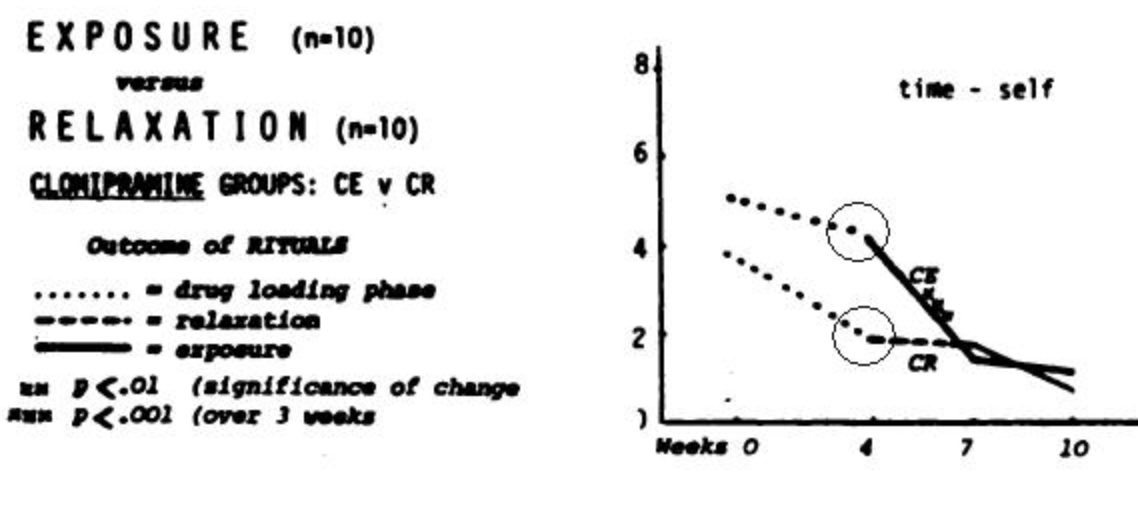
In the graph, what is the cause for the difference between the values graphed in the two areas circled?
Variability
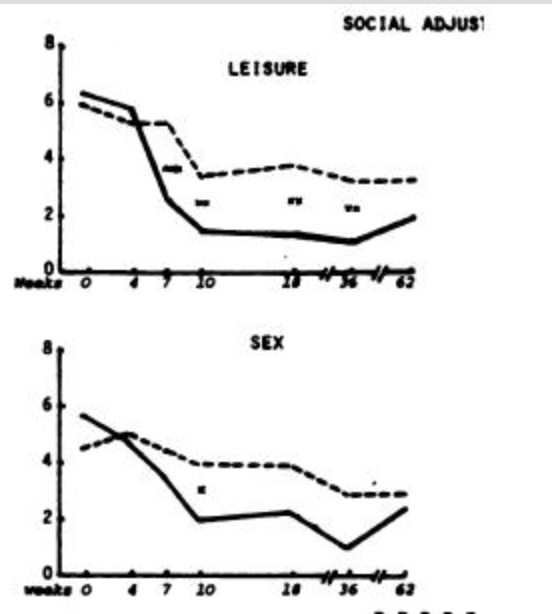
Why are there more asterisks (indicating lower p-values) in the leisure graph (top) than the sex graph (bottom) even though the mean values are generally the same? Be as specific as possible.
Less variability in the leisure graph
In the drug study on the effects of Clomipramine, what effects did the Clomipramine have on compulsive behavior for patients who were not depressed?
None
An experimenter assigns subjects to either a drug or placebo condition without telling them their condition. Is it always possible to keep subjects from guessing if they are in the drug condition or in the placebo condition? Why or why not?
No, higher rates of side effects with drug may allow subjects to guess they are in drug condition.
Give an example from class of a false equivalence
Tea party vs occupy
57 states versus 50- second brain freeze
Give four examples of biased samples that people use in everyday life. Only the first four answers will be graded.
Early dating
Fighting with someone you love
Job interviews
Inspirational speeches (Steve Jobs)
Politicians
What were the results of the study on bias in the media?
The media is biased slightly to the left (liberal)
Besides laziness, name two reasons why people are persuaded by biased sample.
Confirmation bias
Social affiliation
According to what we learned in class, what percent of people have an anxiety disorder? (Answers 5% or less from the correct answer will get credit)
18.1
What is the name of the brain structure that processes fear and fear related stimuli?
Amygdala
Describe a set of distracters that will allow me to find a target Waldo (a character with a red striped shirt) using a parallel search?
When the distracters are all in black and white.
Who has higher rates of anxiety, men or women? Explain why the answer may be misleading.
Women have higher diagnosed rates, but women seek out more treatment so it is hard to know the real rates.
Phobias can be grouped into three different categories. Besides 'situational' phobias, what are the other two categories? Only the first two answers will be graded.
Mutilation and animals
Name four common methods used to study infant perception? Only first four answers will be graded.
Dishabituation, visual preference, eye tracking, EEG
To determine if a young infant is red-green color blind, we can show the infant a screen that is colored red until the infant _________________, then we show the infant a screen colored green and if the infant ___________________, then we know they can distinguish red from green.
Gets bored, starts looking more,
Babies selectively attend to what kind of visual stimuli at birth?
Faces
Which will a white baby look at more?
A) blobs that have the same color as the average color of a white face
B) blobs that have the same color as the average color of a black face
They will not look at either one more than the other
In the study that used preferential looking to show that males are better at mental rotation than females, how old were the participants? Be specific in terms of years and/or months.
5 months
Bob has OCD. He is shown two objects and asked to ignore the one presented in red ink. A truck is presented in red ink.
Sam does not have OCD. He is shown two objects and asked to ignore the one presented in red ink. A truck is presented in red ink.
Later that day, Sam and Bob are both presented with a truck and asked to name it. Who will name it faster? Why ?
Bob, less negative priming
____________% of people have some obsessive thoughts and___________ % of people have minor compulsive behaviors.
80-90.
50-60.
Besides organizing, name four types of compulsions. Only first 4 answers are graded.
Checking, repeating, mental compulsions, washing
Exposure with response prevention is the treatment for what disorder?
OCD
If X is the % of people who will have an indifferent reaction after unilateral brain damage to the left hemisphere, and Y is the % of people who will have an indifferent reaction after unilateral brain damage to the Right hemisphere, then what is X+Y?
49