CMS III Final: EM
1/211
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
In which cases is air transport used?***
critically ill pts when ground transport would take too long/terrain is difficult
which ER should you go to if a pt is in cardiac or respiratory arrest?
ALWAYS go to CLOSEST facility → can transfer after
inappropriate (not accepting) transfer is a violation of which law?
EMTALA → prohibits ERs from refusing to examine and tx pts with emergency med condition
what is indirect communication?
paramedic operates under medical director's standard operating procedure manual/training
what is direct communication?
once care is established with receiving facility, the care of the patient can be directed by the ER doc
which decontamination zone: hospital area where arriving pts without decontamination are held?***
hot zone → also area of spill/chemical release
which decontamination zone: area where decontamination and medical stabilization occurs?***
warm zone***
which decontamination zone: area to which fully decontaminated pts are transferred?***
cold zone
which class of bioterrorism agents is the highest risk?
class A → smallpox, anthrax, plague, botulism
which class of bioterrorism agents are moderately easy to disseminate but have less potential for causing widespread illness/death?
class B → west nile virus, hep A, ricin toxin, salmonella, E. coli
which class of bioterrorism involves agents that could emerge as future threats?
class C → flu, SARS, rabies, MDR-TB, yellow fever, tick borne hemorrhagic fever
what is the treatment for anthrax?
cipro
what is the DOC for brief procedures requiring a local block?
lidocaine
which local anesthetics have longer duration of action?
bupivacaine, mepivacaine
what should be documented prior to administering a block?
Neurovascular status
which type of block is used for procedures on digits, hands, and feet?
peripheral nerve block → requires less total LA med → site of delivery is less painful than local infiltration
what does severe pain during needle insertion indicate?
contact with nerve → withdraw and reposition
which nerves are blocked in a foot block?
at least 2 → posterior tibial, sural, saphenous, peroneal
what is a CI for digital block?
compromise of digit's blood supply
what are hematoma blocks useful for?
isolated closed fracture reduction → not as effective as IV regional (Bier's) block but good when IV block is CI
which type of block involves lidocaine w/o epi being infiltrated in the fx cavity around the periosteum?
hematoma block
which type of block involves IV infusion of LA distal to inflated pneumatic tourniquet?
IV regional block (Bier's) block
What is Bier's block used for?
fx reductions
large lacs
FB removal
what are the CI to a Bier's block?
- PVD/Raynaud's
- sickle cell
- cardiac conduction abnormalities
- HTN
- cellulitis
- children <5
should you rely on non-self report pain measurement to determine severity of pain?
no, use self-report also
HOWEVER → non-self report is used in children, pts with difficulty communicating, non-verbal patients (can also use visual analog scale for these pts)
when should opioids be withheld for pain management?
resp depression <10 breaths/min
what is the primary tx of acidosis in shock?
reverse underlying cause → do not give bicarb unless acidotic
what is a common presenting sx of sepsis in elderly pts?
AMS
what are the 4 clinical goals of sepsis treatment?****
1. blood cultures BEFORE abx
2. lactate before 90 mins
3. IV abx before 60 min
4. 30 ml/kg of IV fluids before 180 mins
what is the triad of cardiogenic shock?
sustained hypotension
chest pain
AMS
MCC is MI***
what are the treatments for cardiogenic shock?
PCI or CABG → thrombolytics if PCI/CABG not available
PCI within 90 mins
who may be resistant to epinephrine? What should you give?
people on BBs → give glucagon
which dx is characterized by hypotension and bradycardia with warm/dry skin?
neurogenic shock
only shock w/ warm/dry skin!!
what is the tx for neurogenic shock?
atropine and IVF
what term describes a heavy, prolonged menstrual flow?
menorrhagia
what term describes bleeding occuring between menstrual periods?
metrorrhagia AKA irregular periods
what term describes heavy bleeding at irregular intervals?
menometrorrhagia
at what point is bleeding considered post-menopausal bleeding?
at least 6 months to 1 yr after cessation of cycles
what term describes lack of menstruation for 6+ months? what is the MCC?
amenorrhea → pregnancy is MCC
what should always be ordered in the case of abnormal uterine bleeding?
urine/serum hCG (pregnancy test) followed by US***
which type of abortion involves loss of pregnancy <20 wks or fetus weighing <500g?
spontaneous abortion
which type of abortion occurs in the 1st trimester and is related to bloody discharge or bleeding WITHOUT cervical dilation?
threatened abortion ***→ MC
which type of abortion involves vaginal bleeding AND cervical dilation?
inevitable abortion
which type of abortion involves passage of only parts of the fetus?
incomplete abortion
which type of abortion involves passage of ALL fetal tissue?
complete abortion
before 20 wks
which type of abortion involves fetal death <20 wks without passage of any fetal tissue for 4+ weeks after?
missed abortion
which type of abortion involves infection at any stage?
septic abortion → something is retained in the uterus leading to infection
what are the long term effects of PID?
tubular factor infertility (TFI)***
what is the treatment for PID?
inpatient = cefoxitin PLUS doxy or rocephin PLUS doxy
outpatient = rocephin PLUS doxy AND metronidazole
where is the MC site of ectopic pregnancy?
fallopian tube
how should you r/o ovarian torsion?
pelvis/transvag US with doppler***
what dx should you suspect in a pt with abnormally high b-hCG levels?
gestational trophoblastic disease
what is the 1st line tx for N/V during pregnancy (NVP) and hyperemesis gravidarum?
IV fluids***
is abdominal pain present in NVP and hyperemesis gravidarum?
NO → suggests another dx (GI)
if a pregnant pt presents with painless bright red bleeding, what should you avoid?
placenta previa → avoid digital and speculum exams
eclampsia can occur up to ___ weeks after delivery
6
what is the MCC of mitral stenosis?
rheumatic heart disease***
if a pt presents with syncope, chest pain, and dyspnea, what would you expect the murmur to sound like?
AS → harsh systolic ejection murmur
syncope = AS!!
if a pt presents with chest pain or other cardiac symptoms, what should be ordered within 10 mins?
EKG!
what lab should you order with sus MI?
troponin
what is the TOC for MI?
PCI within 90 mins
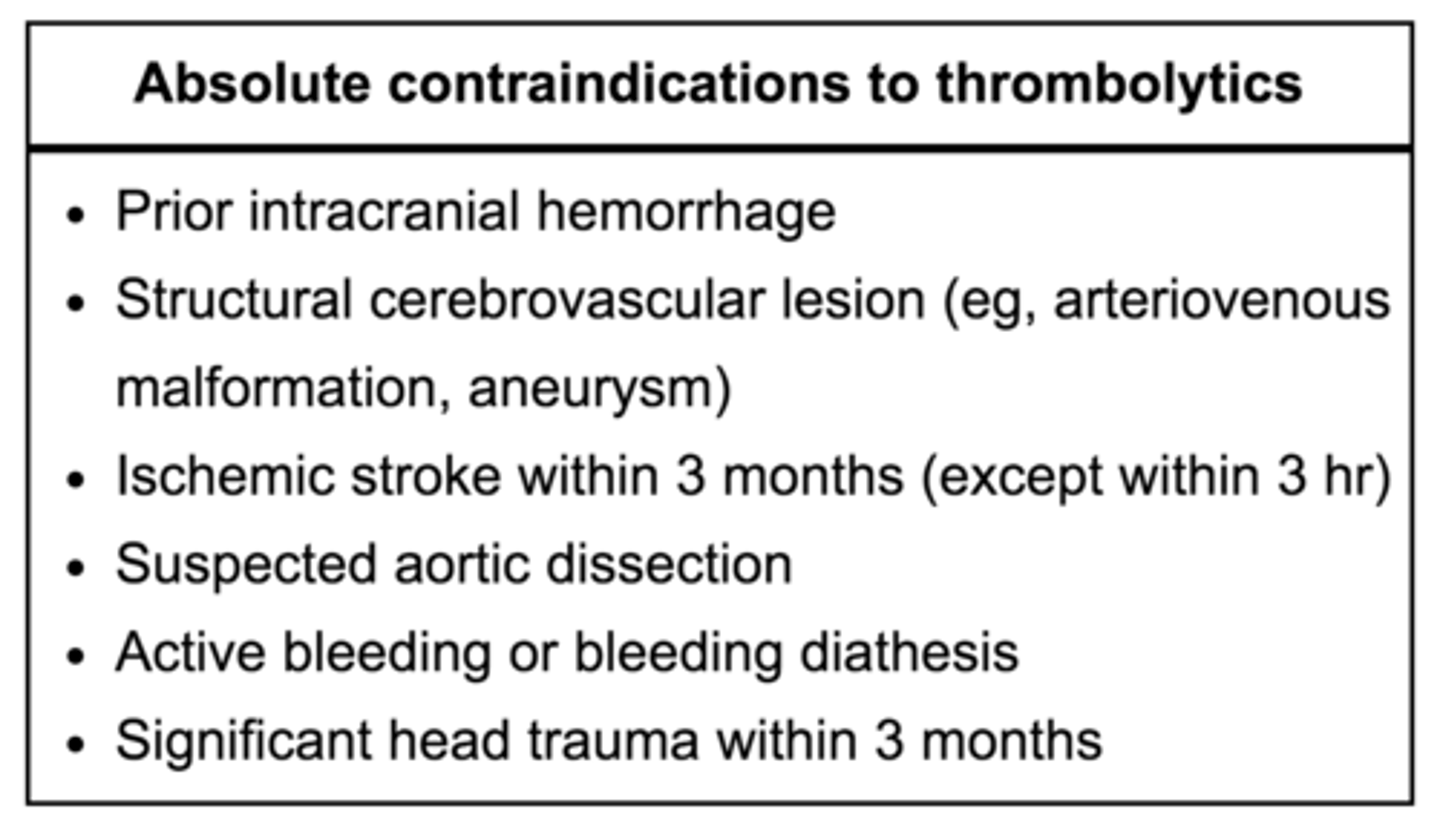
what are the absolute CI for thrombolytic tx for MI?**
- hx of brain bleed
- hx of ischemic stroke within 3 months
- cerebral vasc. malformation or primary/metastatic brain cancer
- s/sx of aortic dissection
- active bleed (not menses)
- closed-head/facial trauma within 3 months
what tx is indicated in MI if ischemia is too severe and they no longer qualify for PCI?
CABG
which type of angina is relieved with rest?
stable
what is the presentation of unstable angina?***
- new onset exertional angina
- angina inc. in frequency/duration
- refractory to Nitroglycerin
- may have ST depression
which type of angina occurs primarily at rest?
prinzmetal → triggered by smoking d/t coronary vasospasm
why should you treat prinzmetal angina like an MI?
ST elevation makes it impossible to differentiate from AMI
if a pt presents with dyspnea, orthopnea, PND, and cough with pink frothy sputum, what should you order?
CHF → BNP!!!** and echo
what dx do you suspect when a pt complains of sharp precordial/retrosternal chest pain that radiates to the back or left arm?
pericarditis***
what are the signs of pericarditis?
pericardial friction rub → pt sitting and leaning forward
diffuse ST elevation and PR depression
what is the initial test of choice for pericarditis?
echo (TEE) → helps dx tamponade or effusion
which dx causes severe ripping or tearing pain in the back, chest, or abdomen?
aortic dissection***
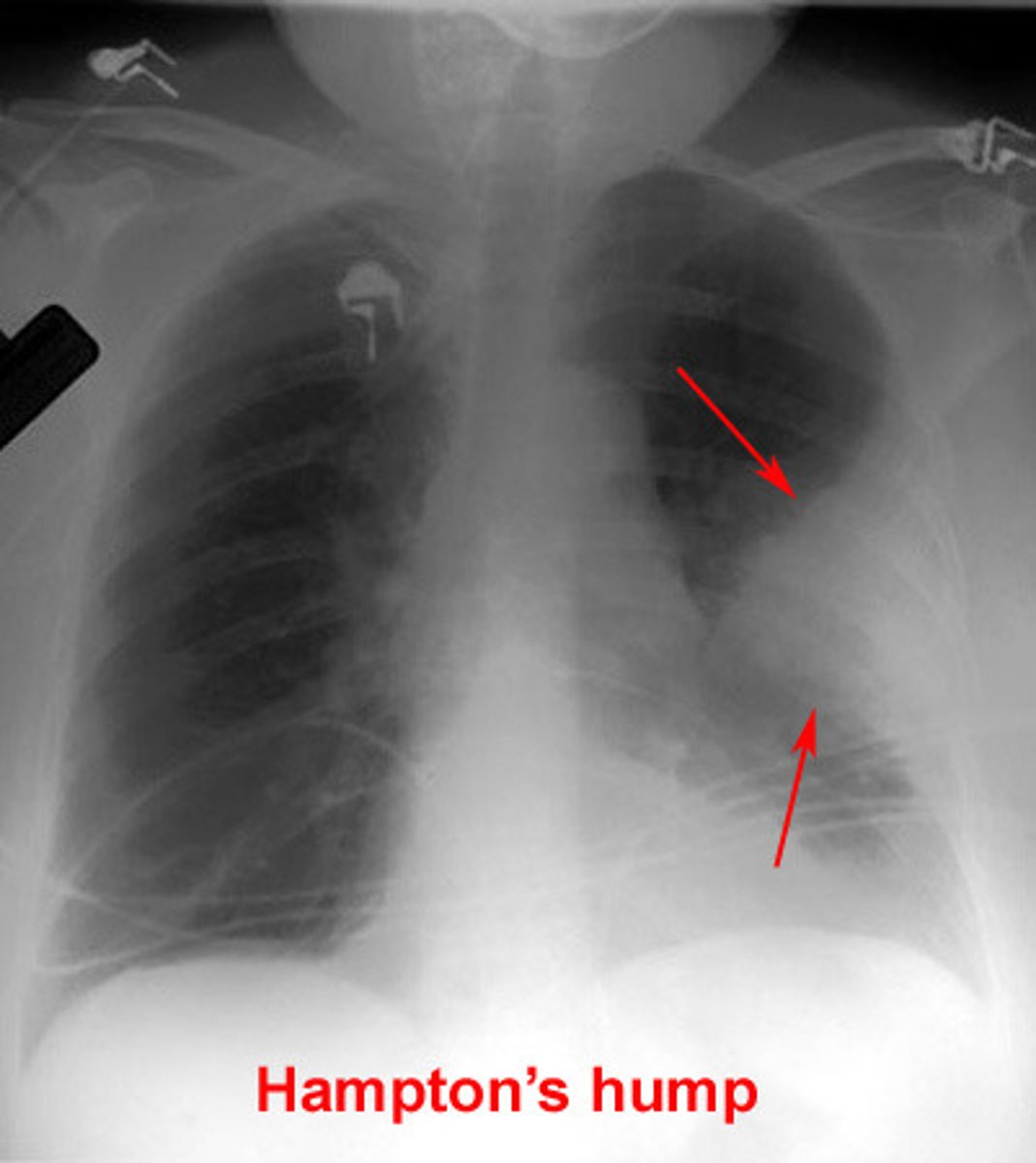
what is the gold standard for dx of pulmonary embolism? what lab can be ordered?
CTA***
D-dimer
what may CXR show in pulm embolism?
westermark sign
hampton's hump
fleischner sign
MAP should be lowered by no more than ___% in the first hr of HTN treatment?
20%***
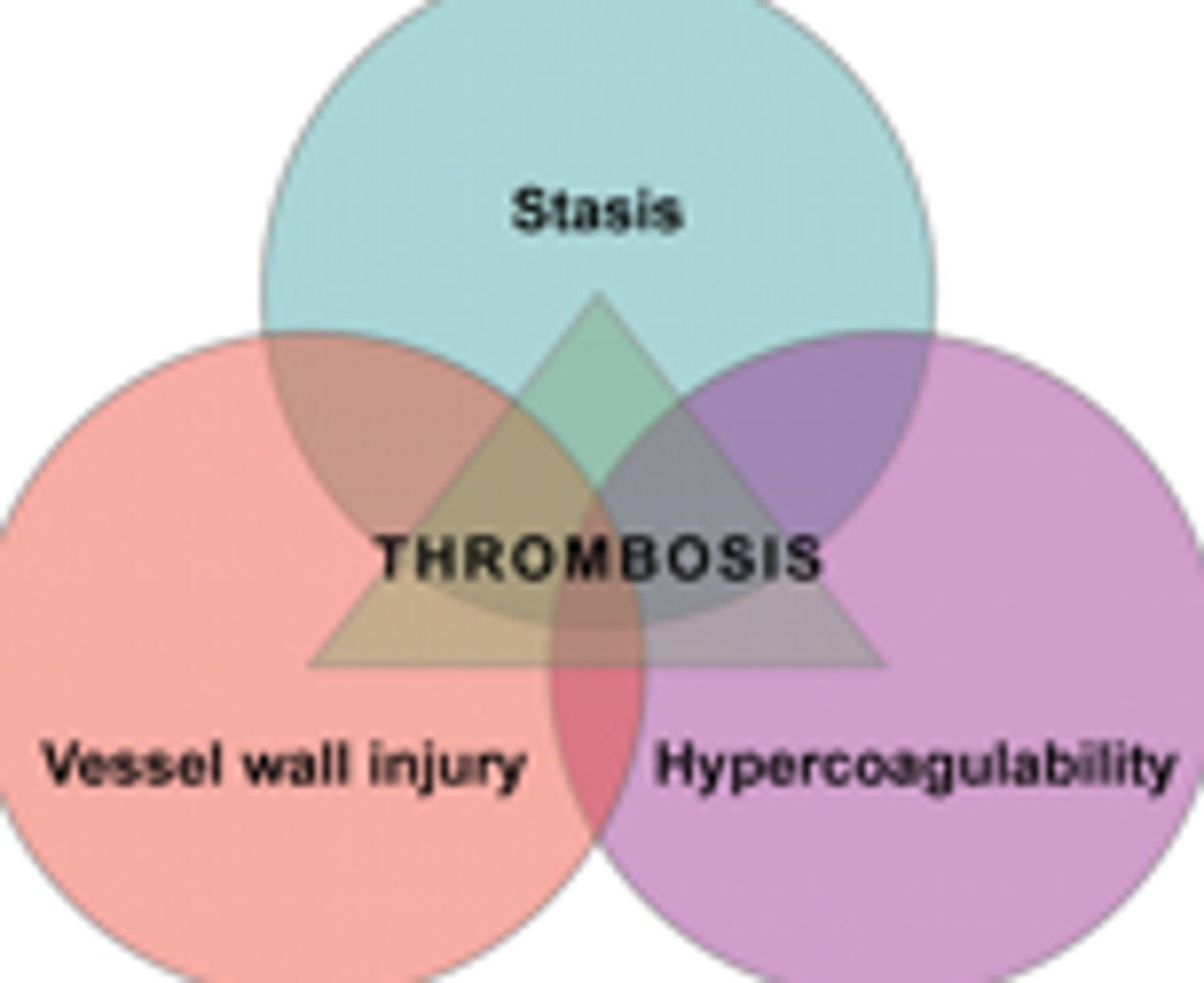
which triad: venous stasis, vessel wall injury, hypercoagulable?
virchow → DVT
if a pt with sus DVT has a positive D-dimer, what should you order to confirm?
Duplex US (doppler)
what is the MCC of cardiac tamponade?
malignancy
which triad: JVD, hypotension, muffled heart sounds?
beck triad → cardiac tamponade
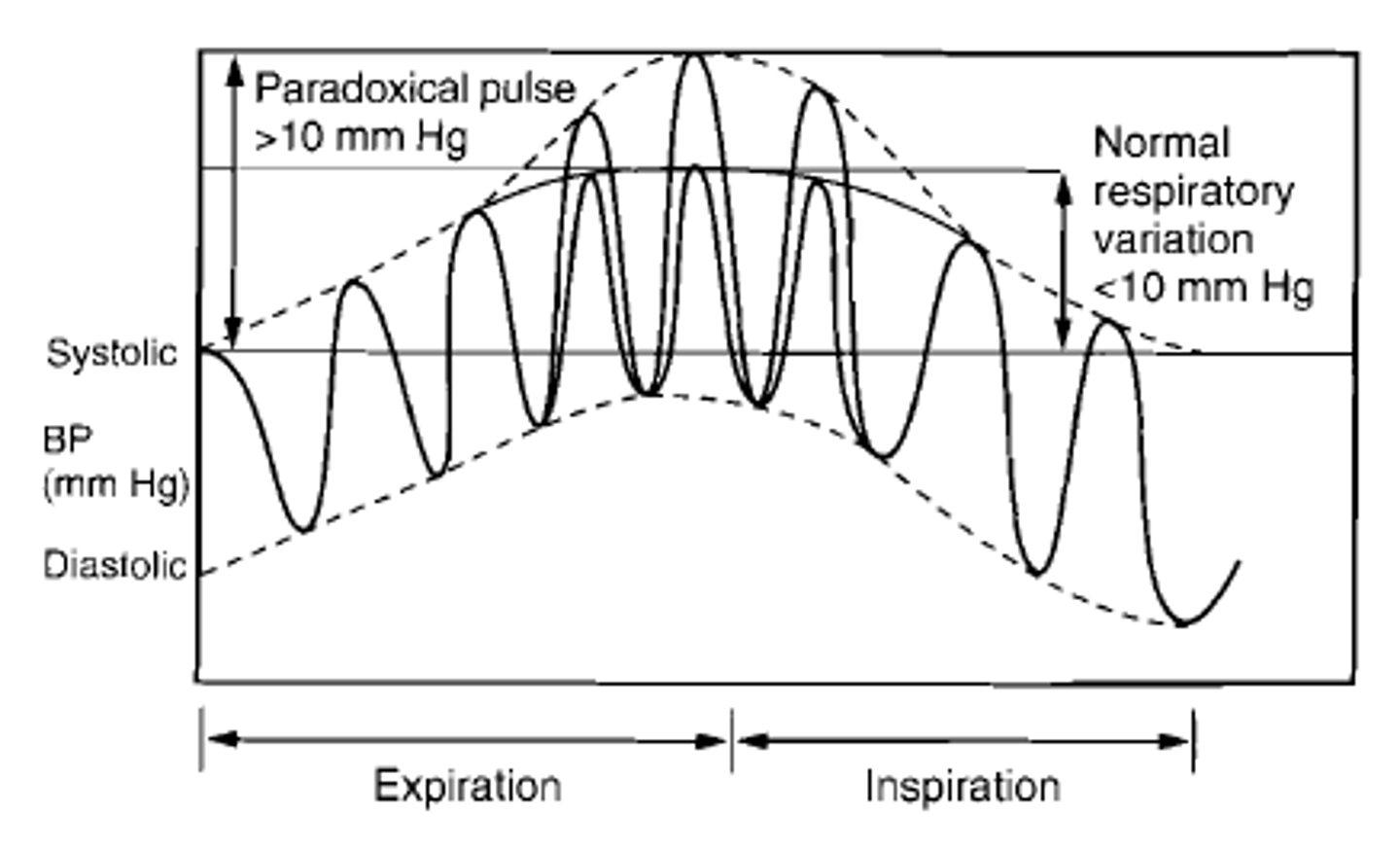
pulsus paradoxus is commonly found in which dx?
cardiac tamponade→ tx with pericardiocentesis
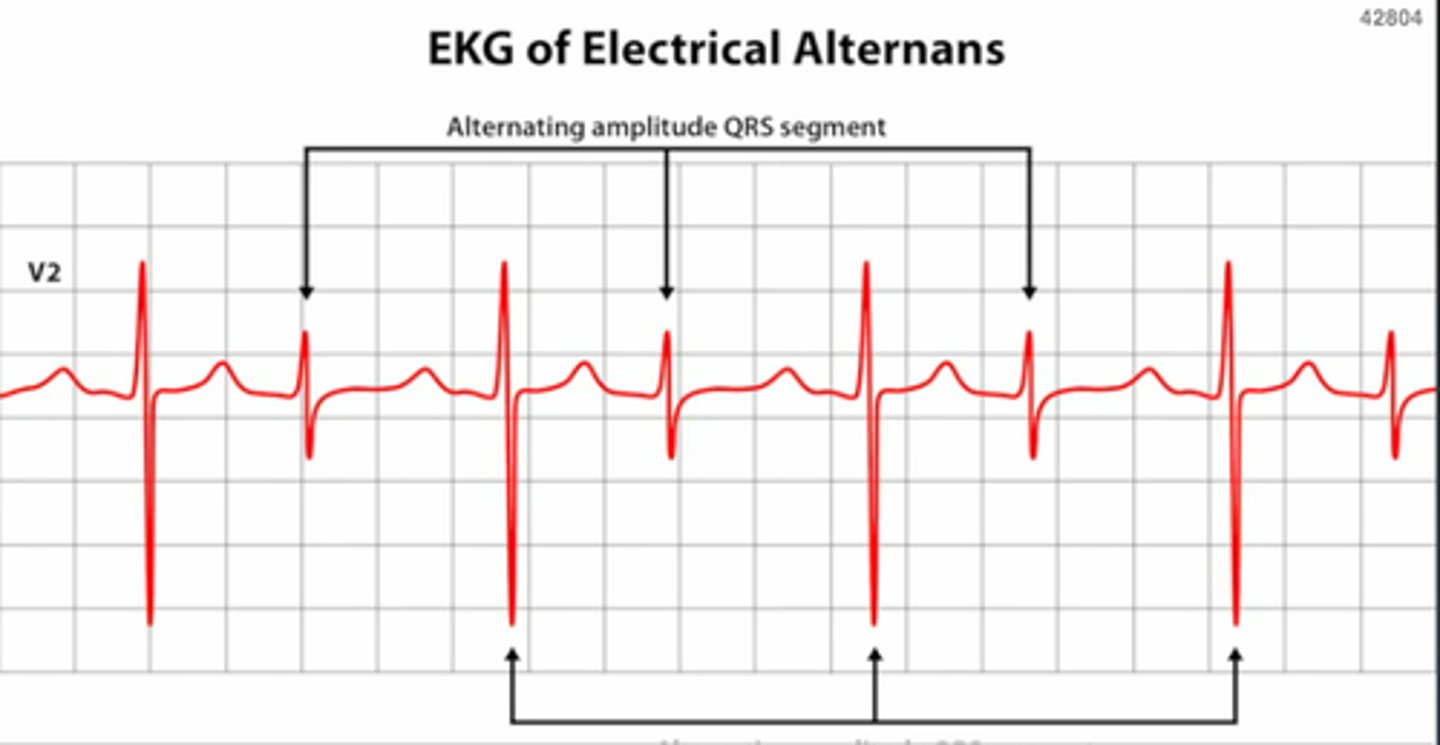
electrical alternans is pathognomonic for which dx?
cardiac tamponade
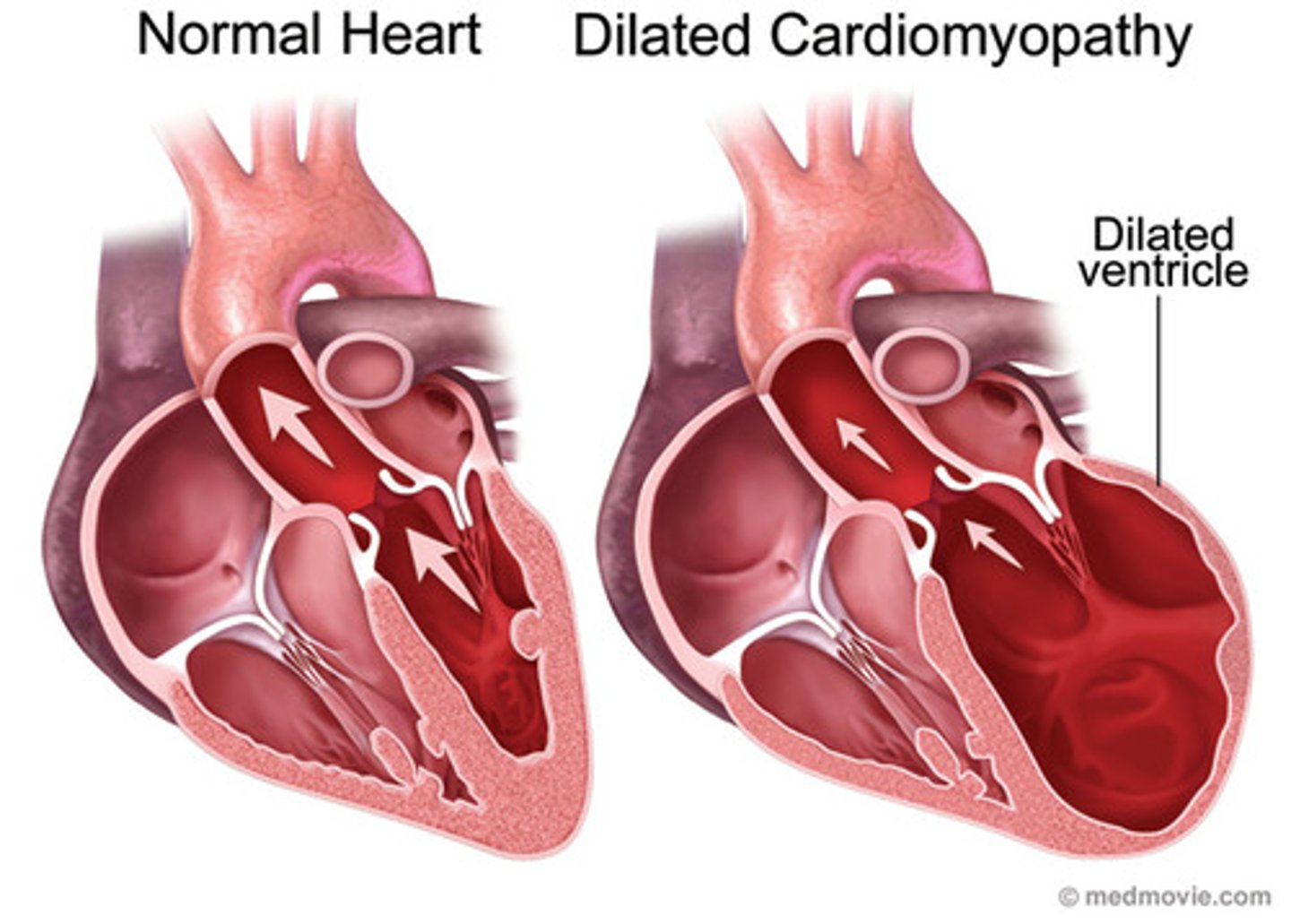
which cardiomyopathy: sx of CHF, enlarged cardiac silhouette on CXR, LVH and LA enlargement on EKG?
dilated
echo shows chamber enlarged
which cardiomyopathy: DOE, syncope, systolic ejection murmur, LVH and LA enlargement on EKG, and disproportionate septal hypertrophy on echo?
HOCM
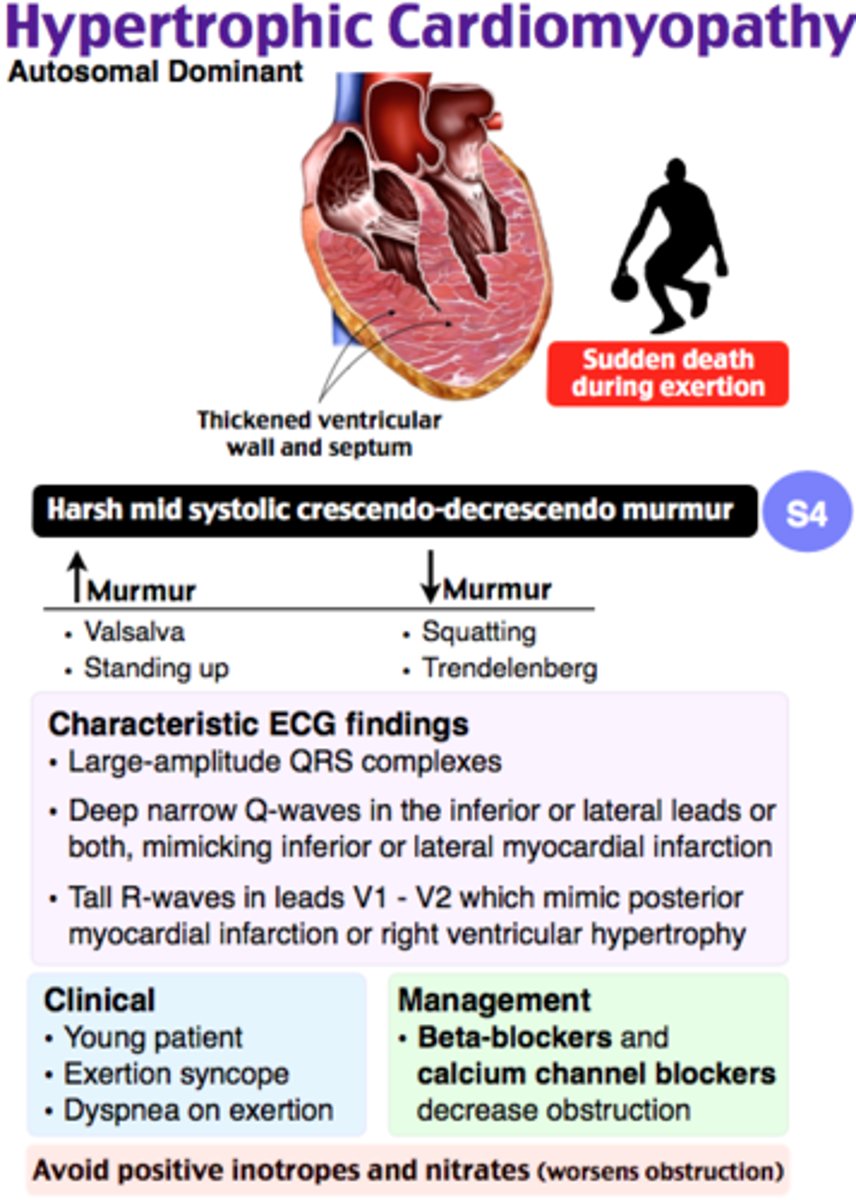
what is the mainstay of tx for HOCM?
BBs
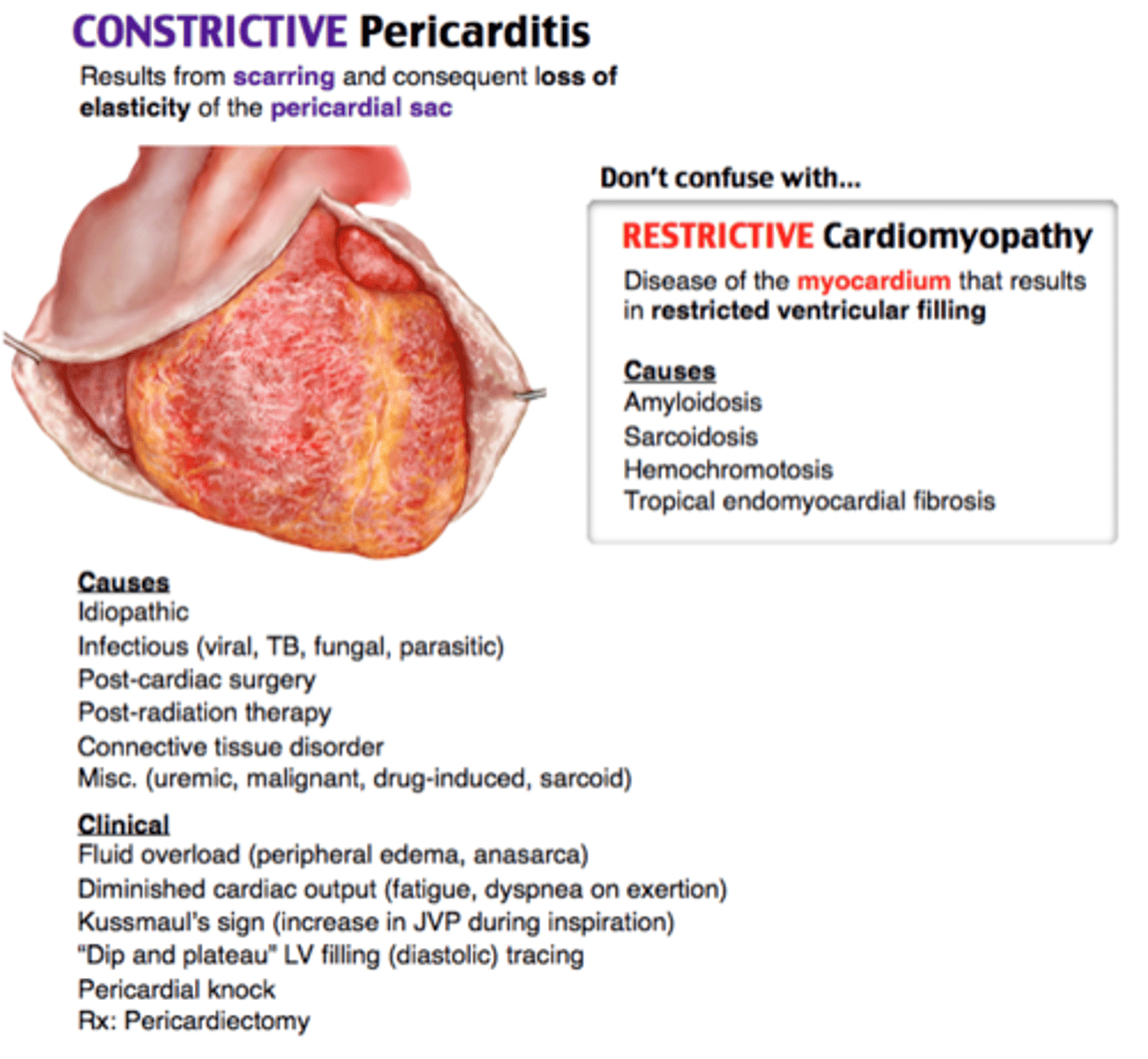
in which cardiomyopathy is S3 ALWAYS present, S4 common, JVD, and Kussmaul sign?***
restrictive → also see R CHF sx
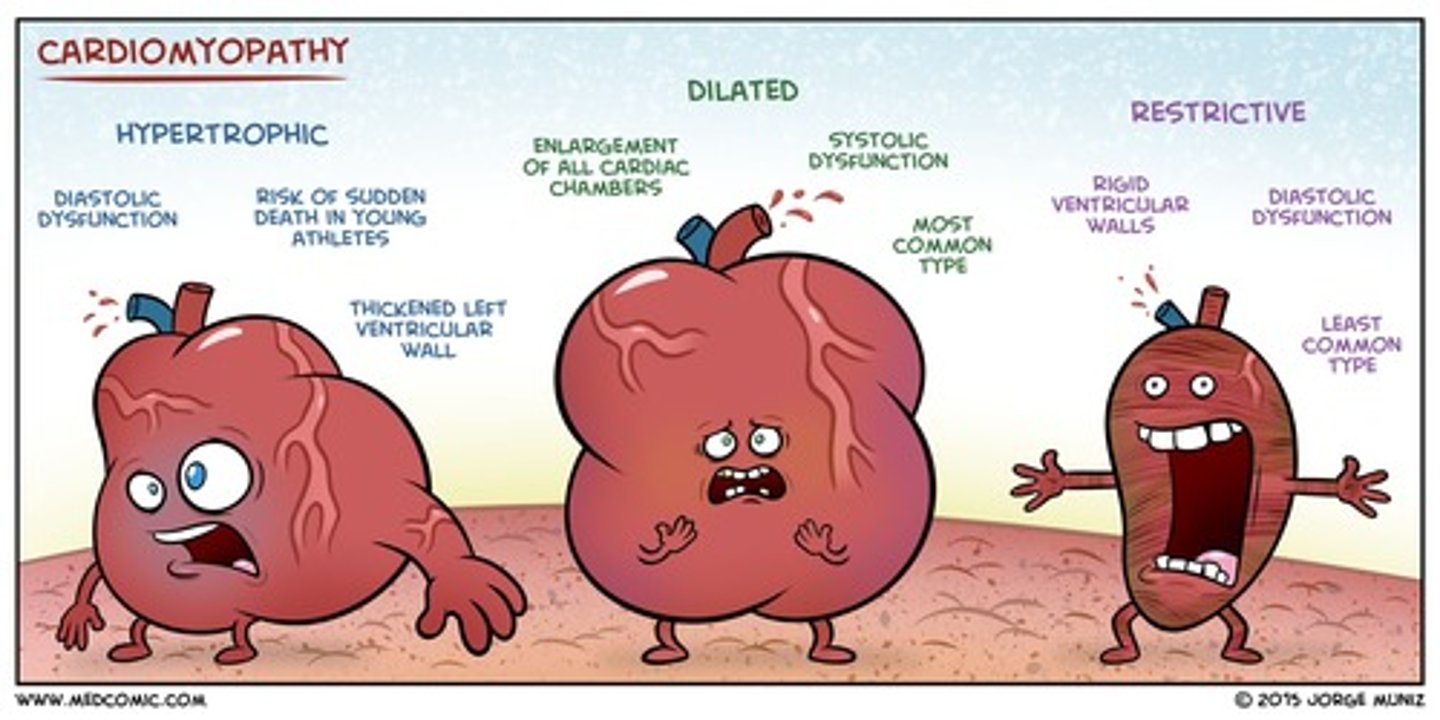
what are the s/sx of restrictive/constrictive pericarditis?
- gradual DOE
- dec. exercise tolerance
- pedal edema
- ascites
- LVD
- kussmaul sign
- pulsus paradoxus
- pericardial "knock" at apex
which dx shows low voltage QRS complexes and inverted T waves on EKG?
restrictive pericarditis
when should face sutures be removed?
3-5 days***
when should scalp sutures be removed?
7-10 days
when should trunk sutures be removed?
7-10 days
when should arm/leg sutures be removed?
10-14 days
when should joint sutures be removed?
14 days
what is the outpatient tx for diverticulitis?***
cipro and flagyl
how would you manually detorsion a testicle?
twisting outward and laterally***
bc most torsions twist inward/towards midline
what is a pt who vomits during intubation at risk for?
aspiration PNA***
how does an external thrombosed hemorrhoid appear?
bluish-purple discoloration**
if CXR shows mediastinal shift and tracheal deviation, what dx do you suspect?
tension PTX***
this is the CXR pic on the exam (not this exact one)
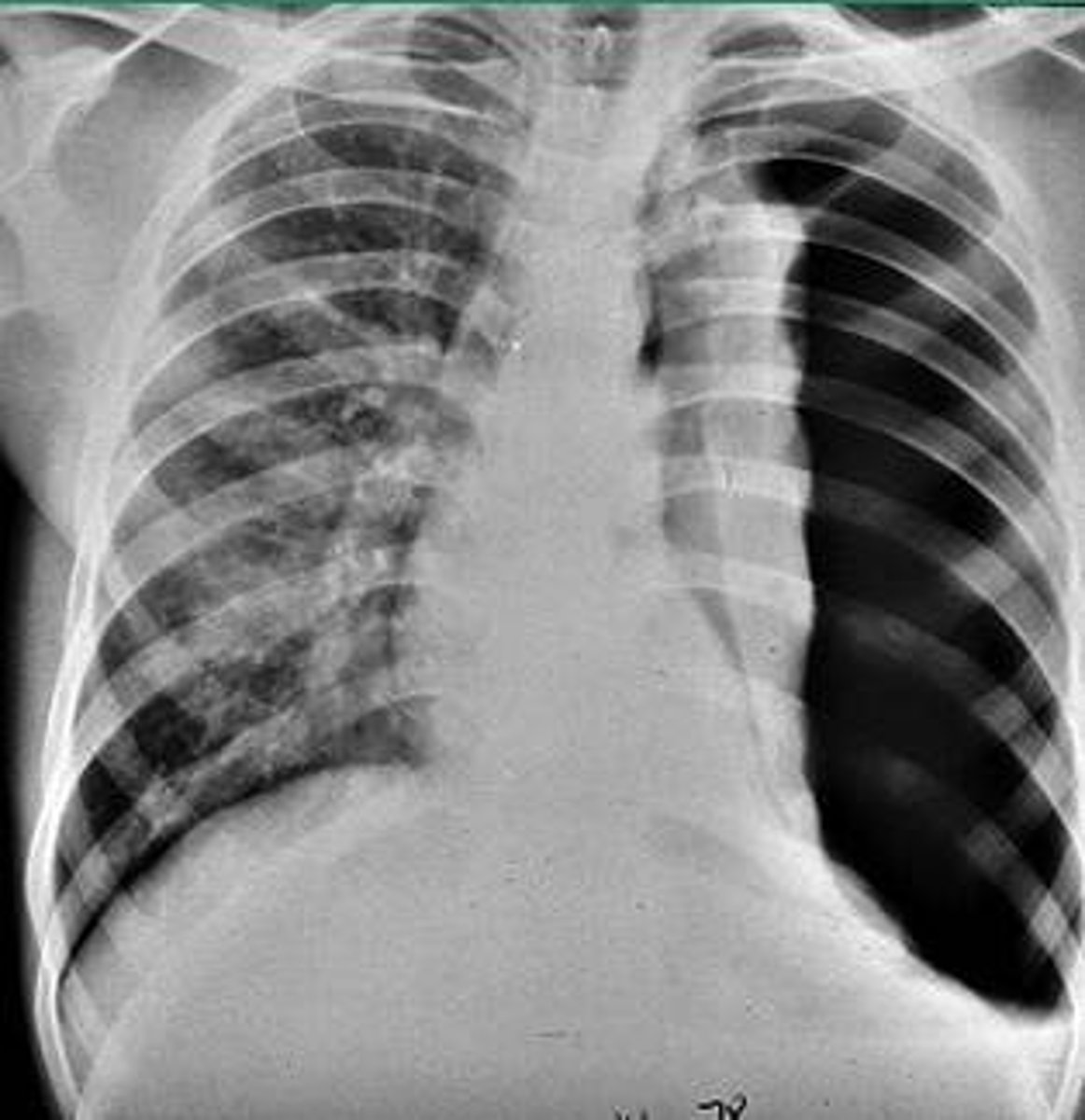
what are the s/sx of tension PTX?
hypotension
JVD
absent breath sounds
which lab is more accurate for dx of acute pancreatitis?
lipase >>> amylase
what is the order of tx for pancreatitis?***
NPO → fluids → pain control