Chapter 9: Molecular Structure of DNA and RNA
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What is Molecular Genetics?
The study of DNA structure and function at the molecular level
Dramatic advances in techniques and approaches have?
Greatly expanded our understanding of molecular genetics, transmission genetics, and population genetics
A large extent of our genetics come from?
The molecular structure of DNA and RNA
What are the 2 nucleic acids?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), and its molecular cousin RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Who first identified Nucleic Acids?
Friedrich Miescher in 1869 in waste surgical bandages
What did Miescher name the substance in waste surgical bandages?
Nuclein
What is Nuclein?
Material from the nucleus of a cell
What did research later show about DNA and RNA?
That DNA (and RNA) release H+ in water and therefore are acids
What did DNA and RNA come?
Nucleic Acids
What are DNA and RNA?
Large macromolecules with several levels of complexity
What do Nucleotides form?
The repeating unit of nucleic acids
What are nucleotides linked to?
Linked to form a linear strand of RNA or DNA
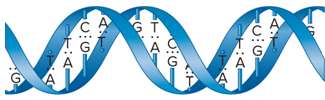
In DNA, how is a double helix formed?
Two strands can interact to form a double helix
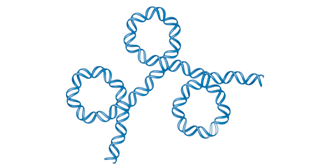
What causes the 3-D structure of DNA?
From folding and bending of the double helix.
Interaction of DNA with proteins produces chromosomes within living cells
What do nucleotides look like?
What does a single strand look like?

What does a double helix look like?
What does a three-dimensional structure look like?
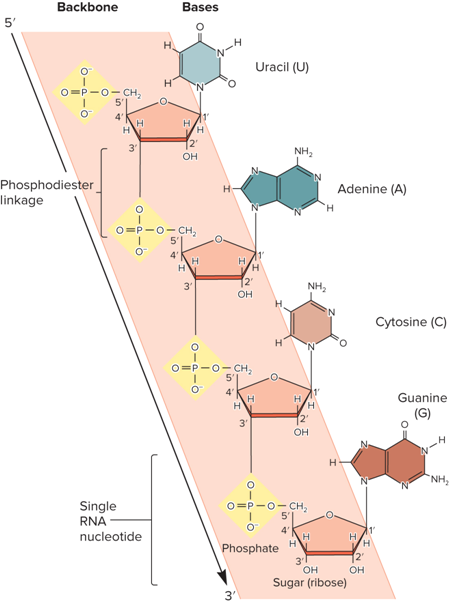
What is a nucleotide?
The repeating structural unit of DNA and RNA
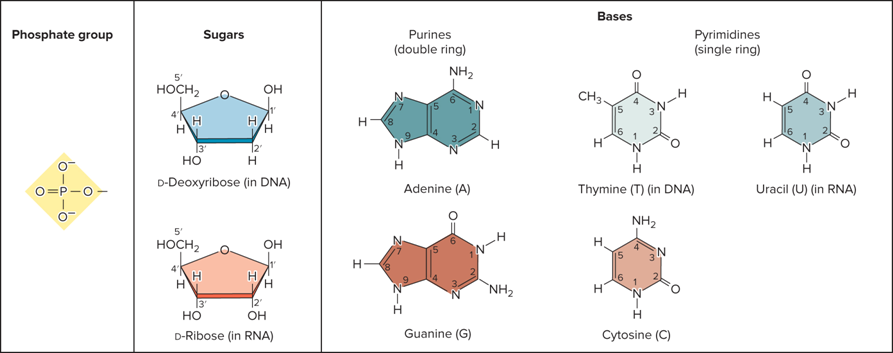
What are the 3 components of a nucleotide?
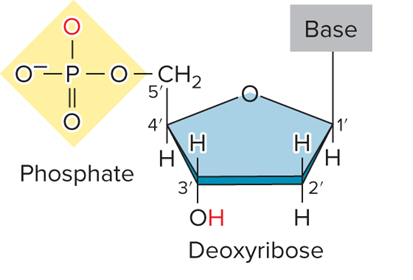
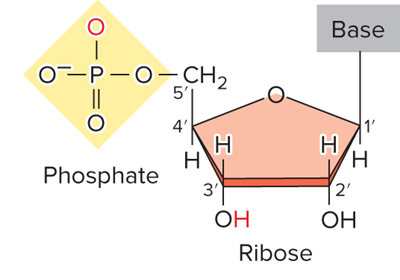
A phosphate group
A pentose sugar
A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base
What pentose sugar is in RNA?
Ribose
What pentose sugar is in DNA?
Deoxyribose
What do the components of nucleotides look like?
What does figure 9.5, DNA structure look like?
What does figure 9.5, RNA structure look like?
What is a nucleoside made of?
Base and Sugar
What are 2 examples of a nucleoside?
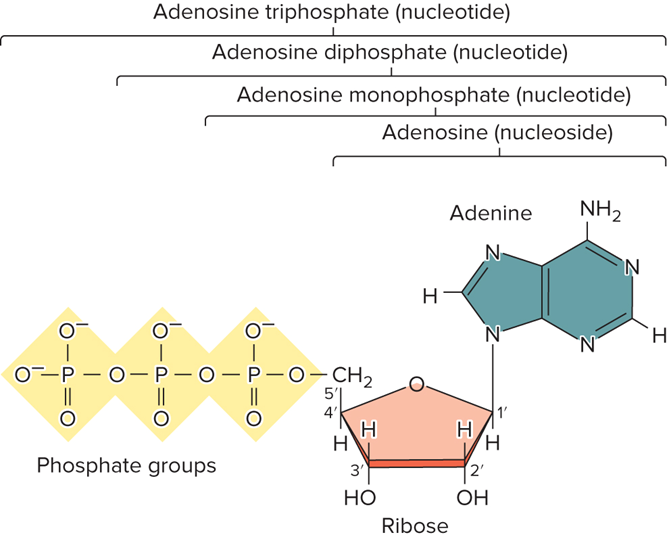
Adenine + ribose= Adenosine
Adenine + deoxyribose= Deoxyadenosine
What is a nucleotide made of?
Base, sugar and phosphate(s)
What are 3 example of nucleotides?
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
What do the units of Nucleic Acid Units look like?
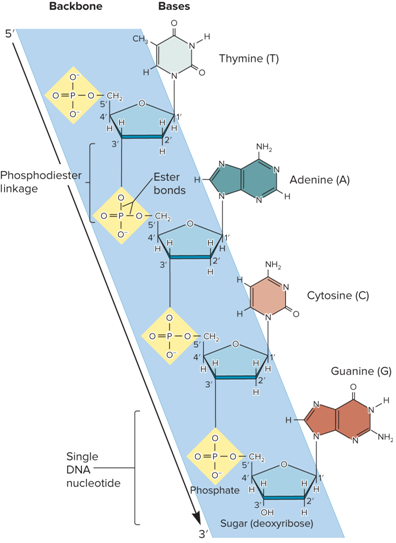
In a DNA strand, nucleotides are linked together by?
Covalent bonds (called ester bonds)
What is a Phosphodiester Linkage?
A phosphate connects the 5’ carbon of one nucleotide to the 3’ carbon of an adjacent nucleotide
What directionality does a DNA strand have?
Has 5’ to 3’directionality
In a strand, all sugar molecules are oriented in the same?
Direction
Phosphates and sugar molecules form what?
The backbone of the nucleic acid strand
The bases project?
From the backbone
What do Nucleotides that are linked in strands look like?
In 1953 who elucidated the double helical structure of DNA?
James Watson and Francis Crick
What 3 scientists provided the scientific framework for their breakthrough ?
Linus Pauling
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Erwin Chargaff
Who performed x-ray diffraction of DNA fibers?
Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin worked in same laboratory as?
Maurice Wilkins
Why did Rosalind Franklin use X-ray diffraction?
To study wet fibers of DNA
Why is a diffraction pattern interpreted?
To provide information concerning the structure of a molecule
What does X-ray diffraction of wet DNA fibers look like?
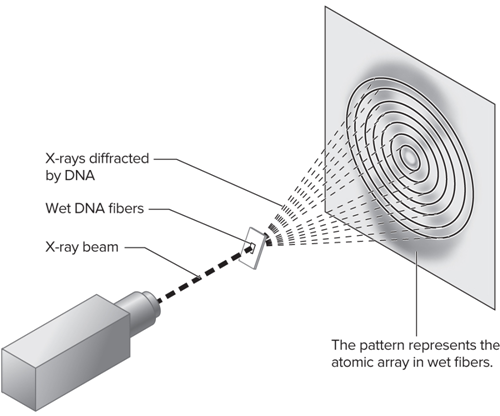
What did Franklin make?
Made marked advances in X-ray diffraction techniques with DNA
What 3 structural features of DNA did Franklins diffraction pattern suggest?
Helical
More than one strand
10 base pairs per complete turn
What was the purpose of Franklin’s results?
These findings were instrumental in solving the structure of DNA; her results were shared with Watson and Crick, presumably without her knowledge
What did Erwin Chargaff pioneer?
Many of the biochemical techniques for the isolation, purification and measurement of nucleic acids from living cells
What did Chargaff know about DNA?
Contained four bases
What are the four bases of DNA?
A
G
C
T
What did Chargaff analyze?
The base composition of DNA isolated from many different species
What was Chargaff’s rule?
Percent of adenine = percent of thymine
Percent of cytosine = percent of guanine
What did Watson and Crick used to elucidate the structure of DNA?
Chargaff’s rule/data
What was Watson and Crick looking to do?
To solve the structure of DNA
What did Watson and Crick try to do?
To build ball-and-stick models that incorporated all known experimental observations
What 2 observations did Watson and Crick make?
Sugar-phosphate backbone on the outside
Bases projecting toward each other
What was the previous and prior observation of Watson and Crick?
Previous; Considered a structure in which bases form H bonds with identical bases in the opposite strand
Prior; This was incorrect
What were examples of identical bonds and bases forming H bonds with them?
A to A
T to T
C to C
G to G
What did Watson and Crick find out about hydrogen bonding?
Realized that the hydrogen bonding of
A to T was structurally similar to that of C to G, prompting further modeling with AT and CG interactions between the two DNA strands
The final double helical model by Watson and Crick was?
Consistent with all known data about DNA structure
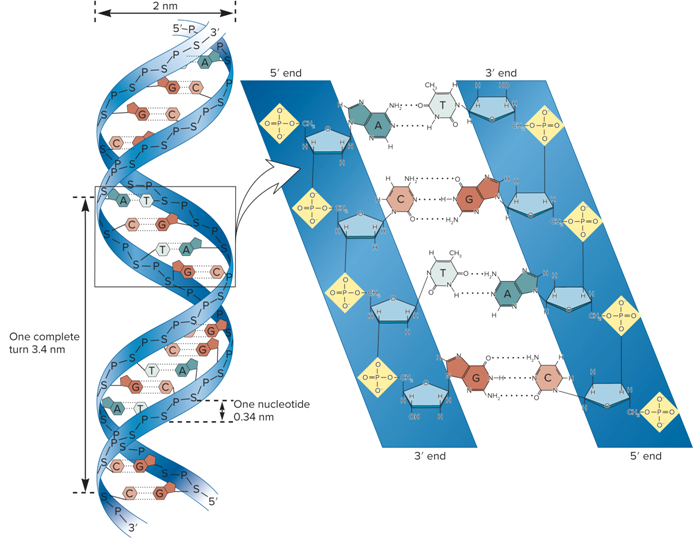
What is the structure of the DNA double helix?
Two strands are twisted together around a common axis
There are 10 base pairs (bp) and 3.4 nm per complete turn of the helix
The two strands are antiparallel
One runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction and the other 3’ to 5’
The helix is right-handed
As it spirals away from you, the helix turns in a clockwise direction
What are 4 key features of the structure of the DNA double helix?
Two strands of DNA form a right-handed double helix.
The bases in opposite strands hydrogen bond according to the AT/GC rule.
The 2 strands are antiparallel with regard to their 5’ to 3’ directionality.
There are ~10.0 nucleotides in each strand per complete 360° turn of the helix.
What is the double-helical structure of DNA stabilized by?
Hydrogen bonding between complementary bases
Base Stacking
What are the two complementary bases?
A bonded to T by two hydrogen bonds
C bonded to G by three hydrogen bonds
What is Base Stacking?
Within the DNA, the bases are oriented so that the flattened regions are facing each other
What does the Stabilization of the Double Helix look like?
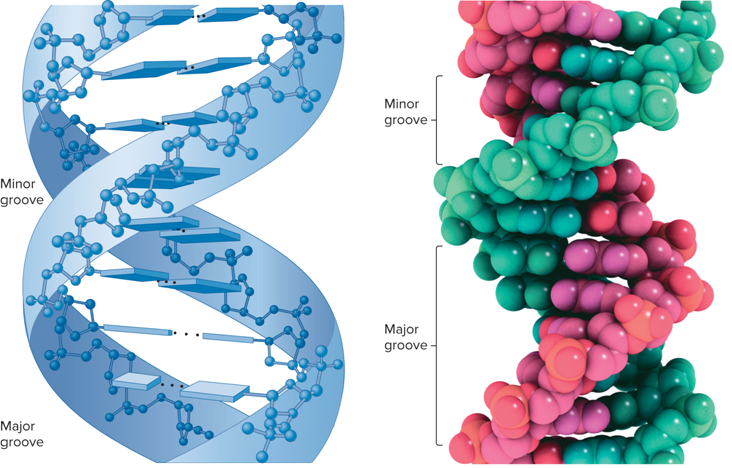
What are the 2 asymmetrical grooves on the outside of the helix?
Major groove
Minor groove
How do certain proteins bind within these grooves?
They can thus interact with a particular sequence of bases
What do Grooves on the DNA double helix look like?
DNA forms what?
Alternative Types of Double Helices
What can the DNA double helix form?
Different types of secondary structure
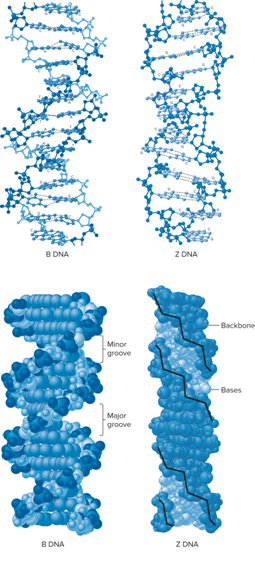
What is the predominant form found in living cells?
B DNA
What DNA can form under certain conditions?
Z DNA double helices
What are characteristics of Z DNA?
Left-handed helix
12 bp per turn
Its formation is favored by
Alternating purine/pyrimidine sequences, at high salt concentrations (for example GCGCGCGCGC)
Cytosine methylation, at low salt concentrations
Negative supercoiling
May play a role in transcription and chromosome structure
Recognized by cellular proteins
May alter chromosome compaction
What is the comparison of B DNA and Z DNA?
B DNA: Bases relatively perpendicular to the central axis
Z DNA: Bases substantially tilted relative to the central axis
Sugar-phosphate backbone follows a zigzag pattern
What does the comparison of B DNA and Z DNA look like?
What are the 2 exceptions that the primary structure of an RNA strand is much like that of a DNA strand?
RNA uses Uracil as a base, instead of Thymine
RNA uses Ribose with 2’ OH, instead of Deoxyribose
How many nucleotides do RNA strands have?
Typically several hundred to several thousand nucleotides in length
How many strands in RNA synthesis is used as a template?
One
What does RNA structure look like?
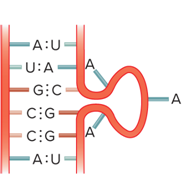
Even though RNA is usually single-stranded, RNA molecules can form?
Short double-stranded regions
What is the secondary structure of RNA?
Short double-stranded regions
What are the secondary structure due to?
Complementary base-pairing
What are the complementary base-pairing in RNA?
A and U
C and G
Complementary base pairing allows short regions to?
Form a double helix
What does RNA double helices typically do?
Are right-handed
Have 11 to 12 base pairs per turn
Are different types of RNA secondary structures possible?
Yes
What does a Bulge loop look like in a RNA molecule?
What does a Internal loop look like in a RNA molecule?
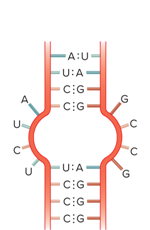
What does a Multibranched loop look like in a RNA molecule?
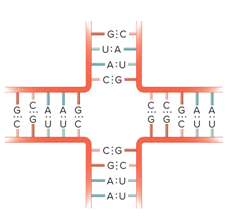
What does a Stem loop look like in a RNA molecule?
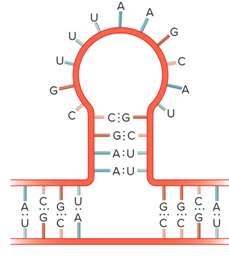
What does the structure of a Transfer RNA look like?
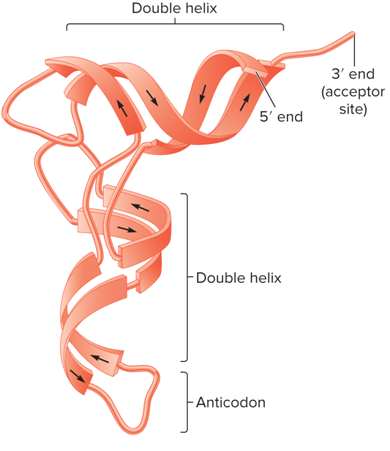
What are 2 factors that contribute to the tertiary structure of RNA?
Base-pairing and base stacking within the RNA itself
Interactions with ions, small molecules and large proteins
Concept: Explain why the mouse in part (d) (Live type R+ dead type S died?
In this experiment, the type R bacteria had taken up genetic material from the heat-killed type S bacteria, which converted the type R bacteria into type S. This enabled the bacteria to proliferate within the mouse and kill it
Concept: What was the purpose of adding RNase or protease to a DNA extract?
RNase or protease was added to a DNA extract to rule out the possibility that small amounts of contaminating RNA or protein were responsible for converting the type R bacteria into type S
Textbook 9.1: In the experiment of Avery, Mcload, and McCarty, the addition of RNase or protease to a DNA extract?
Allowed the conversion of type R bacteria into type S bacteria
Textbook 9.2: Going from simple to complex, which of the following is the proper order of the structure of DNA?
Nucleotide, DNA strand, double helix, chromosome
Concept: Which of these components of nucleotides are not found in DNA?
Ribose and uracil
Textbook 9.3: Which of the following could be the components of a single nucleotide found in DNA?
Deoxyribose, phosphate and thymine
Textbook 9.3: A key difference between the nucleotides found in DNA and those in RNA is that?
Those in DNA have deoxyribose, and those in RNA have ribose
Those in DNA have thymine and those in RNA have uracil