IB Biology HL - A2.2: Microscopy
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
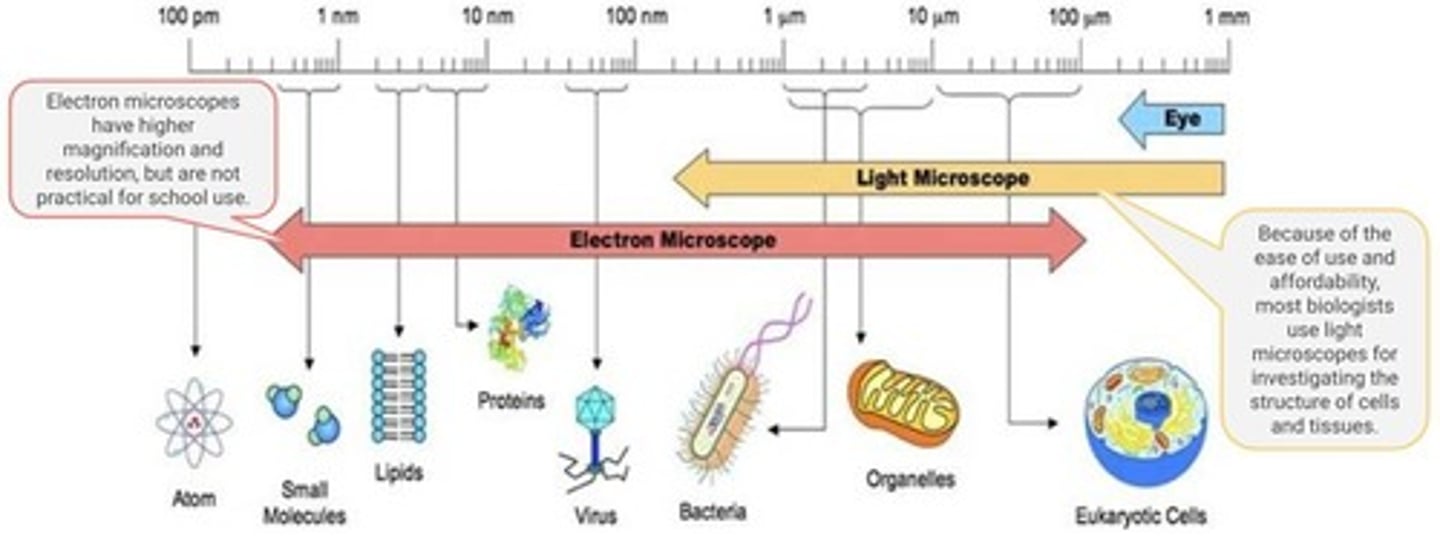
Microscopy
Technique for magnifying small objects.
Magnification
Size increase of an object compared to actual size.
Resolution
Smallest distinguishable detail in an image.
Compound Light Microscope
Uses multiple lenses to magnify light objects.

Electron Microscope
Uses electron beams for high-resolution imaging.
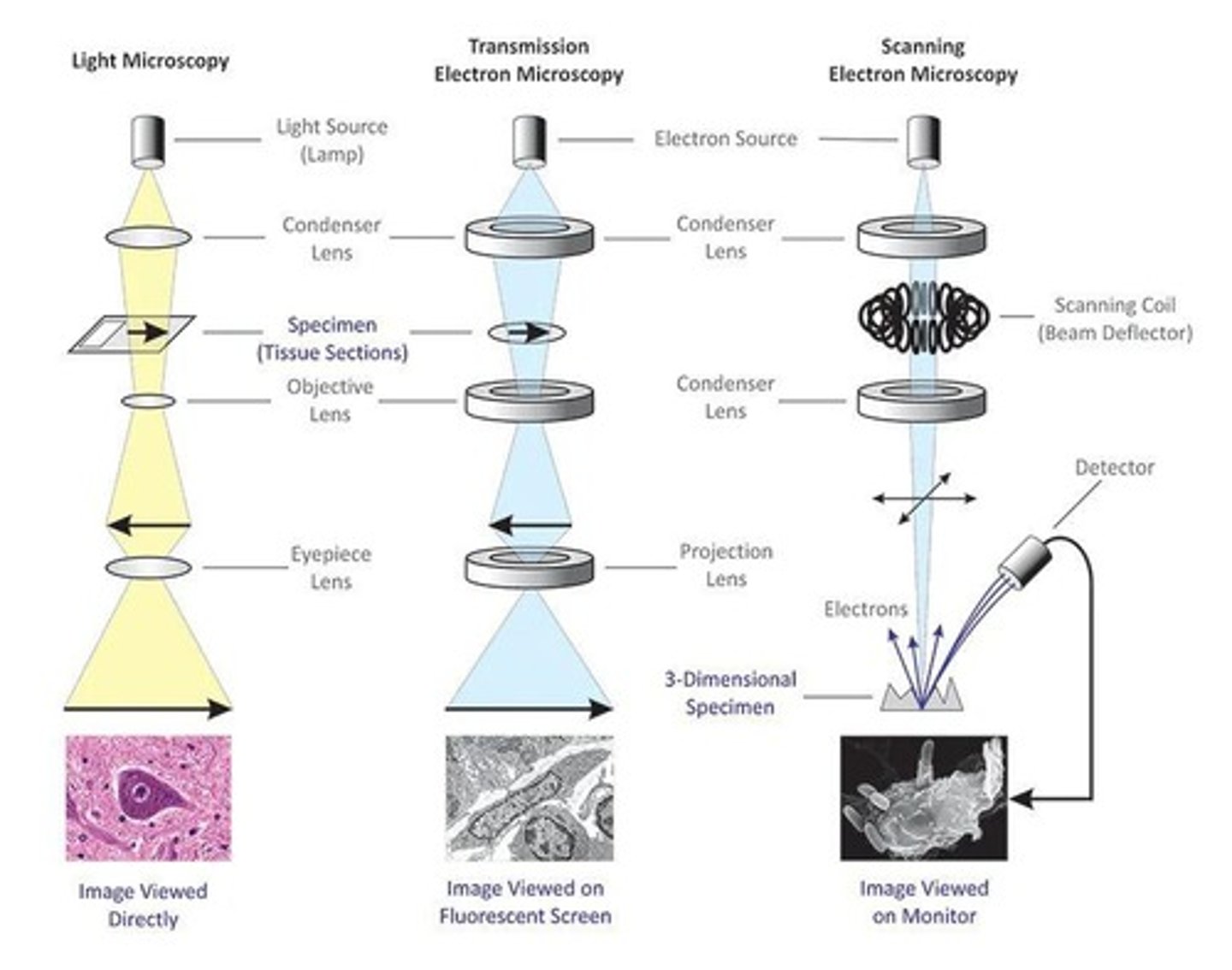
Transmission Electron Microscope
Visualizes internal structures of specimens.
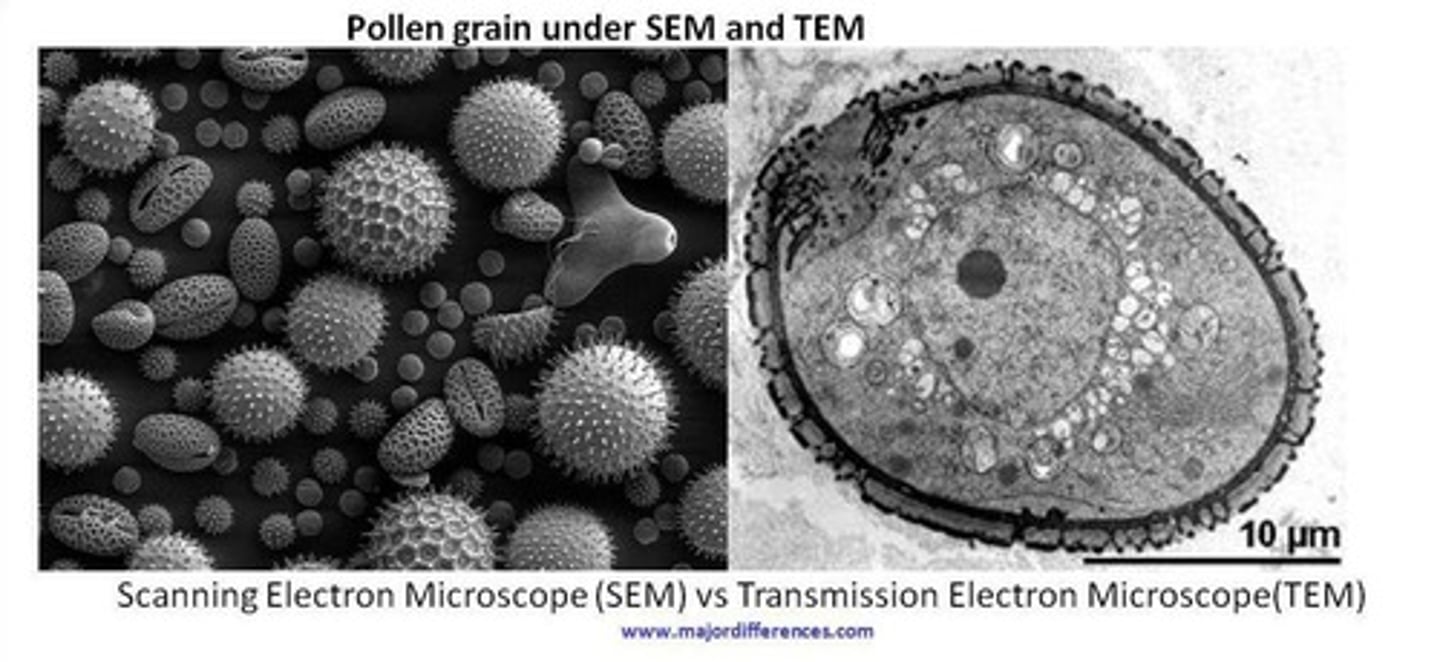
Scanning Electron Microscope
Visualizes surface details of specimens.
Fluorescent Stains
Bind to molecules, emitting light when excited.
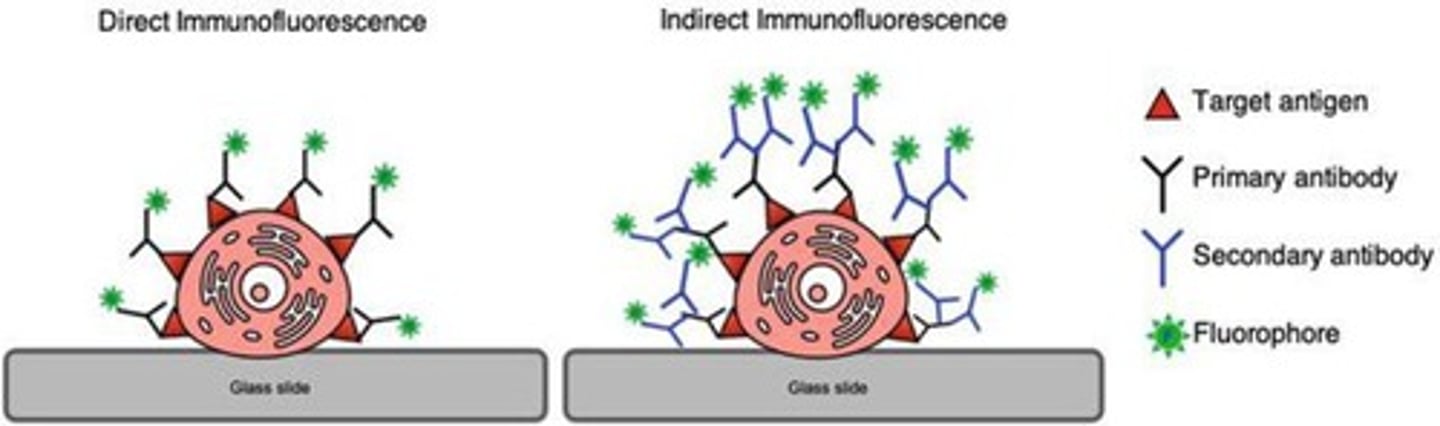
Immunofluorescence
Uses antibodies to visualize specific proteins.
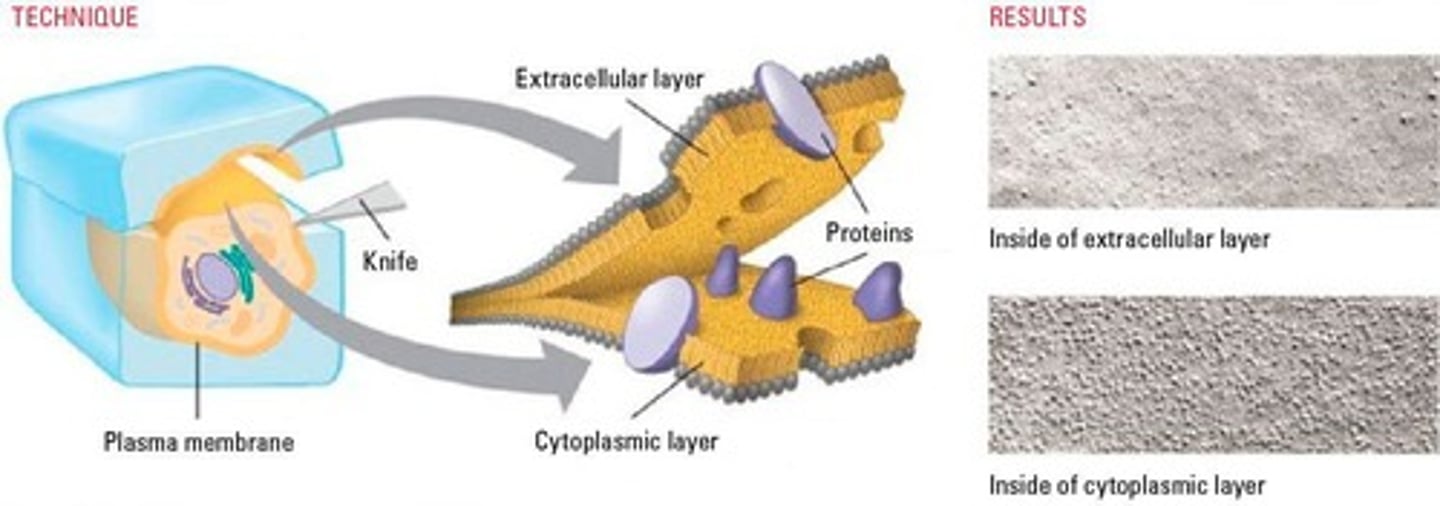
Freeze-Fracture Electron Microscopy
Preserves cell surfaces by fracturing frozen specimens.
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy
Freezes samples to prevent ice crystal formation.
Optical Sectioning
Obtains sharp images at different depths.
Micrograph
Photograph taken through a microscope.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
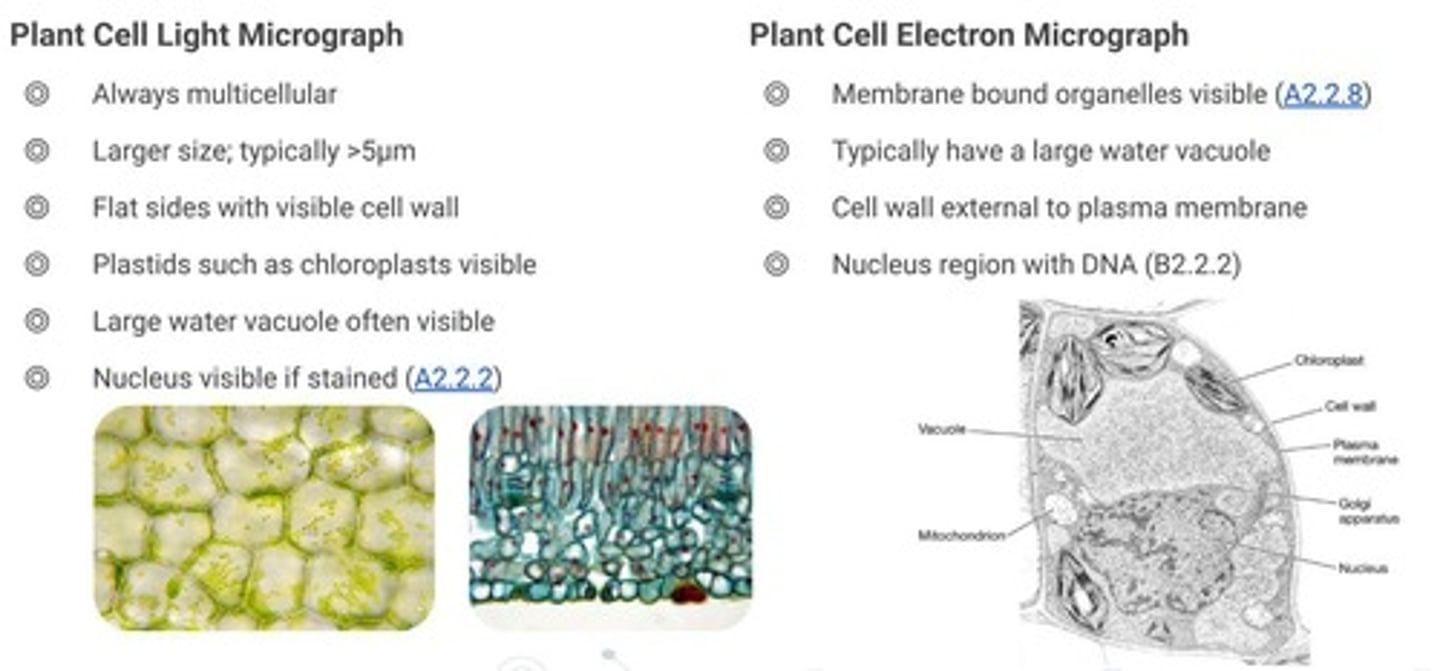
Plant Cells
Eukaryotic cells with cell walls and chloroplasts.
Animal Cells
Eukaryotic cells without cell walls.
Cell Structure
Arrangement and organization of cellular components.
Microscopy Lab Guide
Resource for drawing rules in IB Biology.
Dynamic Processes
Changes occurring in live cells over time.
High-Resolution Images
Detailed images revealing fine structural features.
Cell Types Identification
Recognizing cell types from micrographs.
Ultrastructures
Detailed structures within cells visible via microscopy.
