cestoda I (tapeworms)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
cestode body composition
scolex - head
may be armed with spines
neck - regenerative region; continuously generates proglottids
strobila - segmented part of the body
proglottid - individual segment
note: each proglottid has its own reproductive capacity
cestode infection site
intestines (adult in definitive host; larval forms can go to a variety of locations)
cestode general characteristics
no digestive system; feed through “tegument” (selective uptake of nutrients)
hermaphroditic
immature proglottid
does not contain any sexual organs
mature proglottid
contains male and female sex organs
gravid proglottid
mature and can produce eggs
each has male and female portion
genital pore
common external opening of male & female reproductive system
can be lateral, medial, or bilateral depending on species
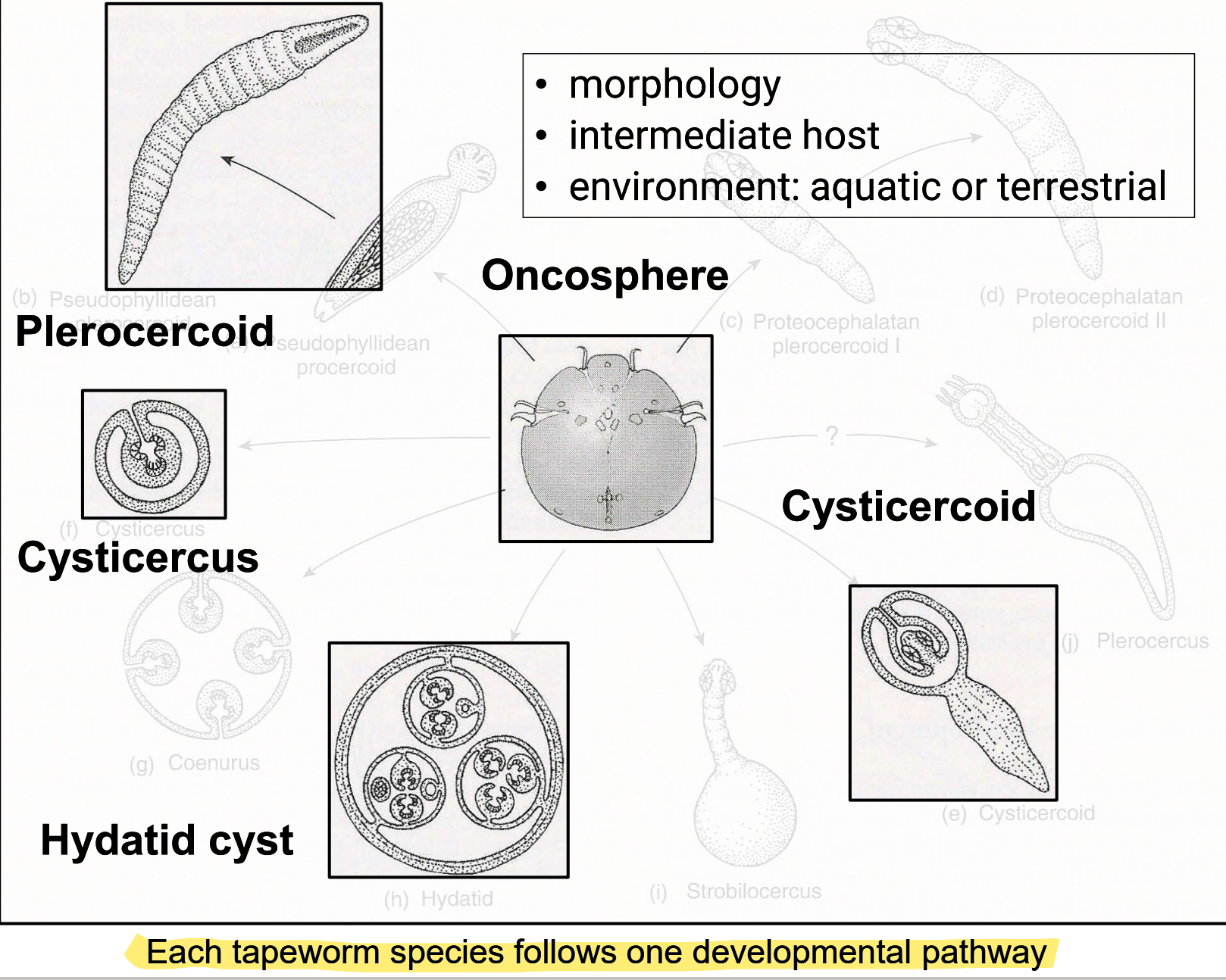
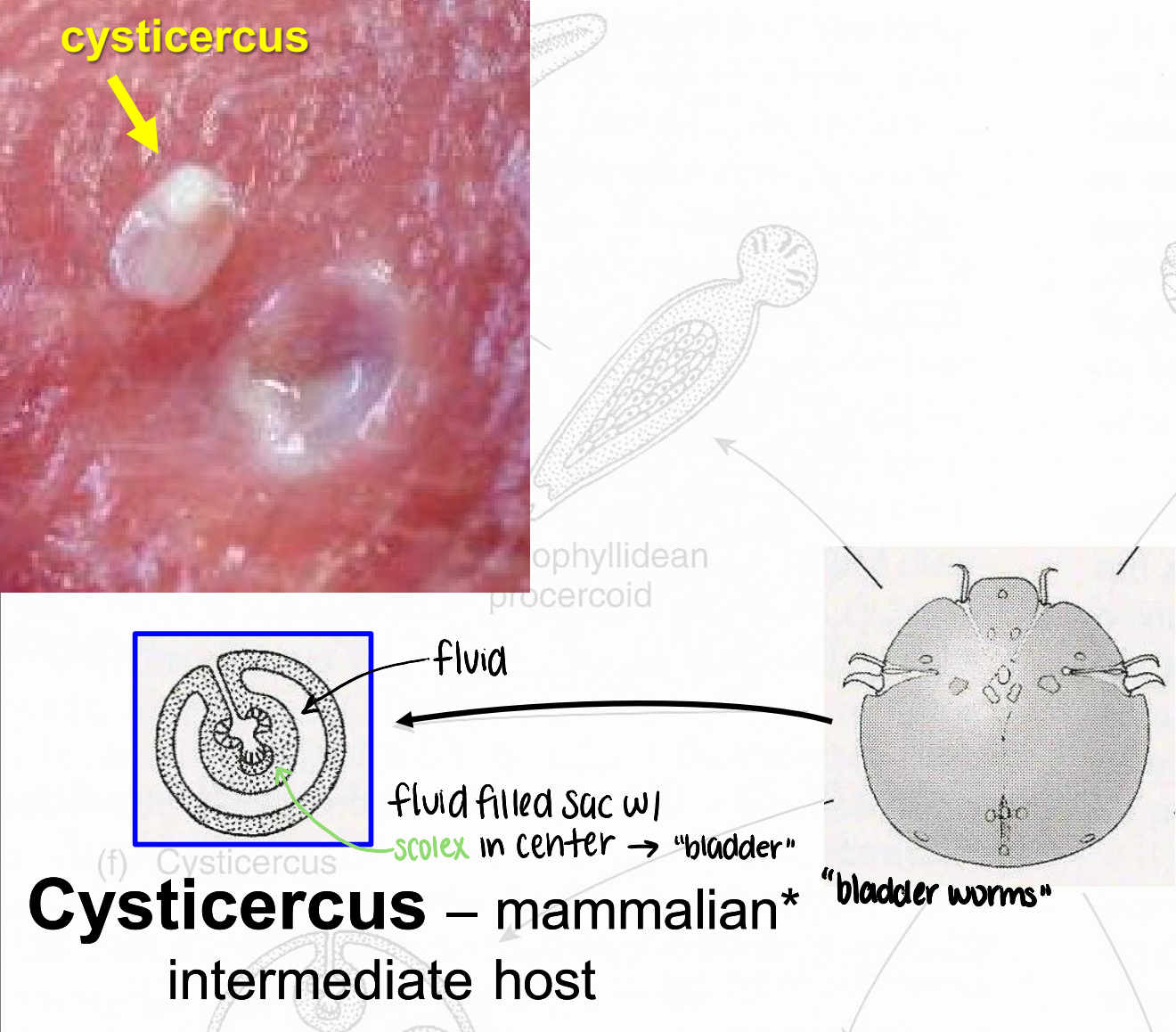
metacestode
cestode larval stage
lives within intermediate host
infection site: body tissues/cavities
species-dependent migration
variety of different morphologies, depending on species
each tapeworm species follows one developmental pathway
major source of pathology!
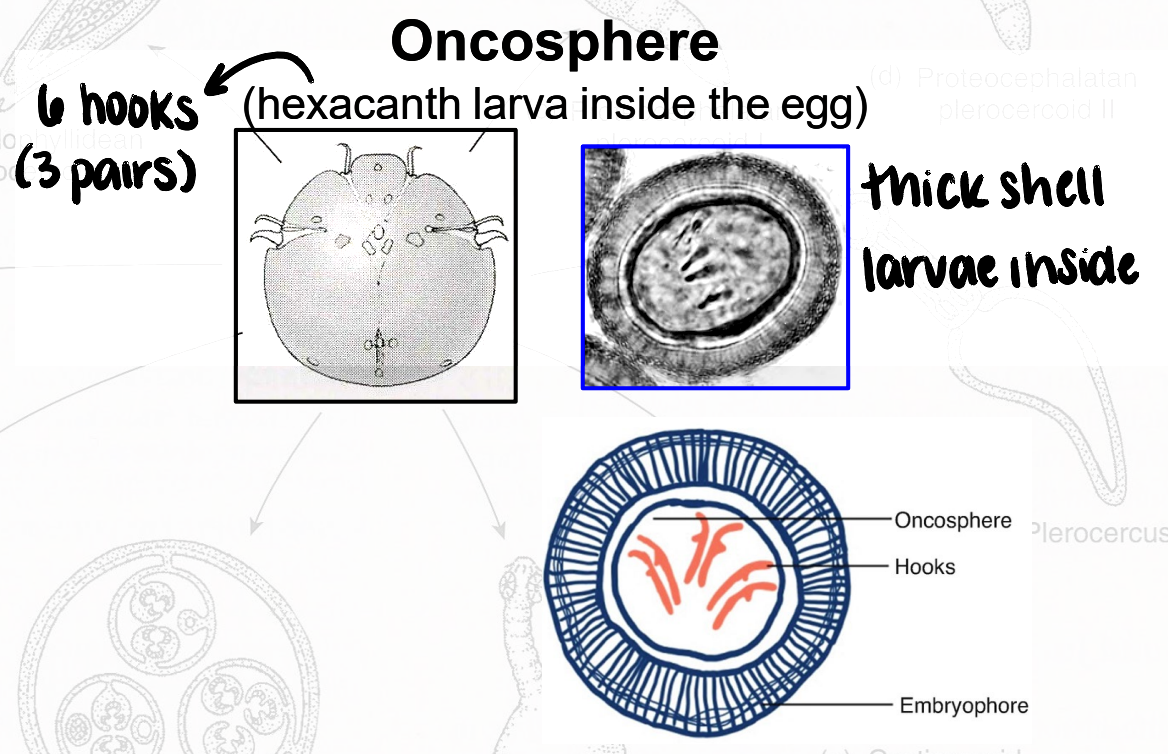
oncosphere
thick-shelled egg containing hexacanth larva
hexacanth → 6 hooks (3 pairs)
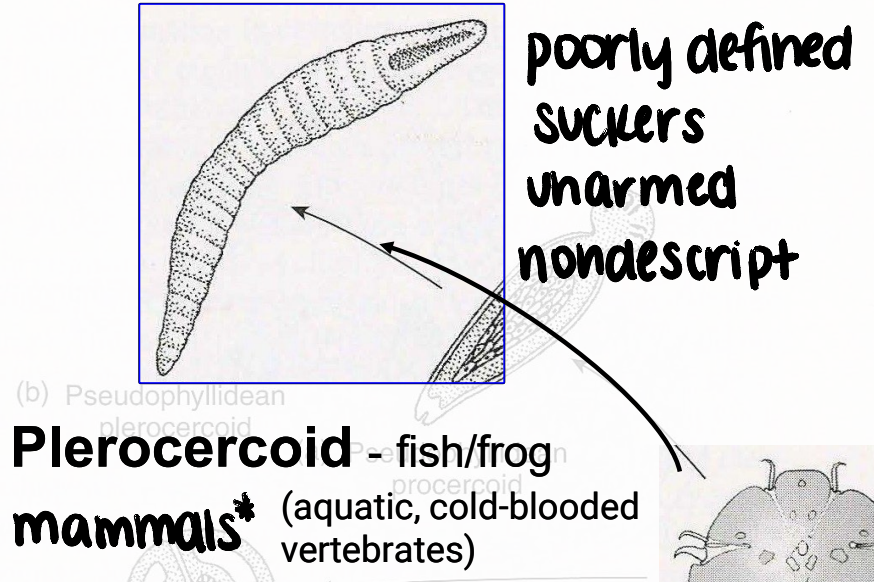
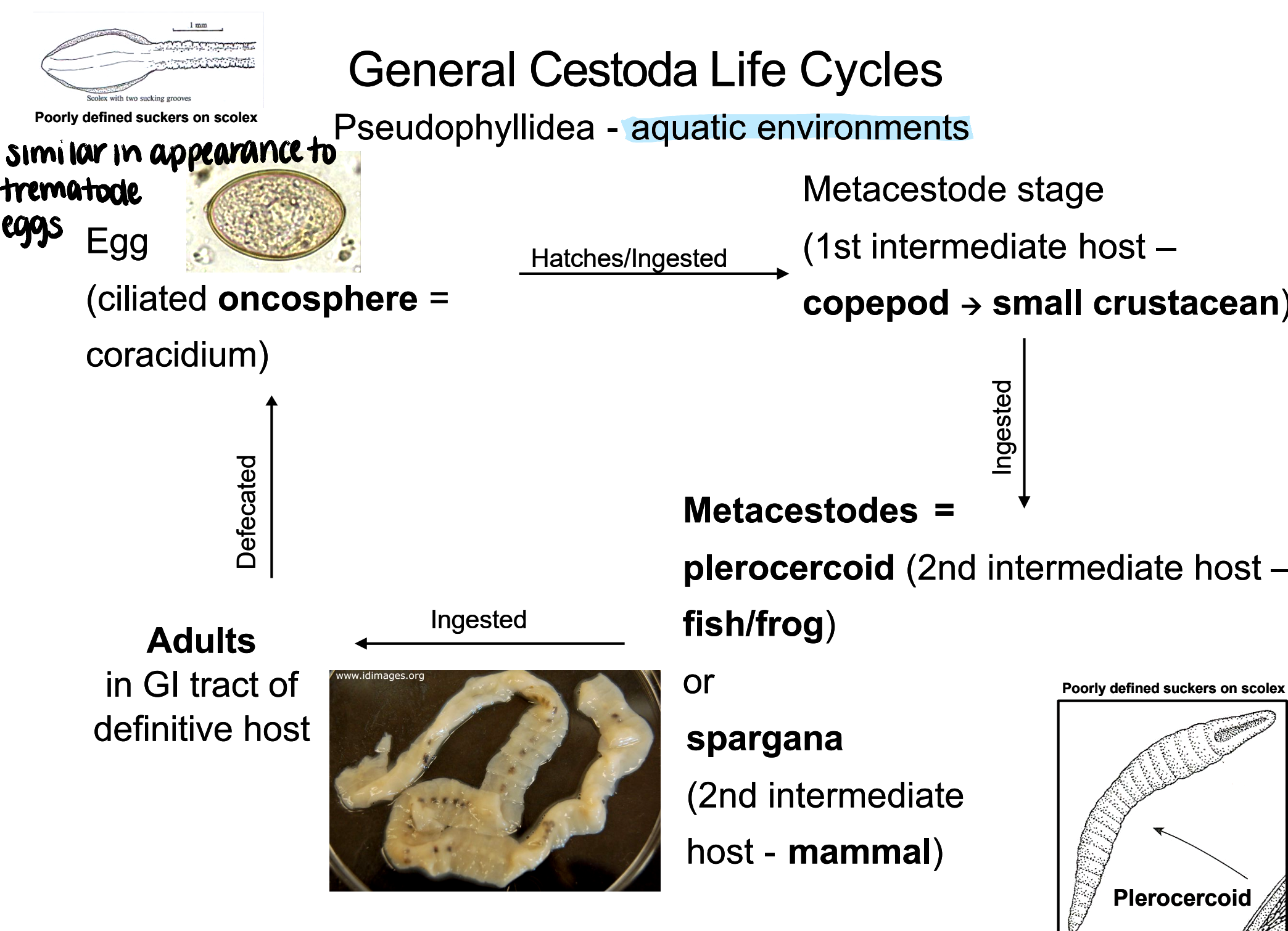
plerocercoid
metacestode that infects fish/frogs (aquatic, cold-blooded vertebrates)
can also infect mammals, including humans
poorly defined suckers, unarmed, nondescript
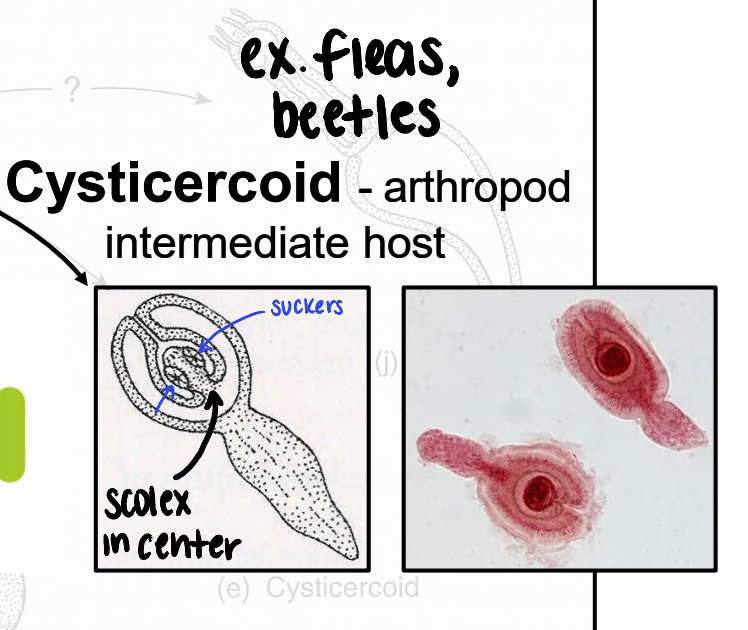
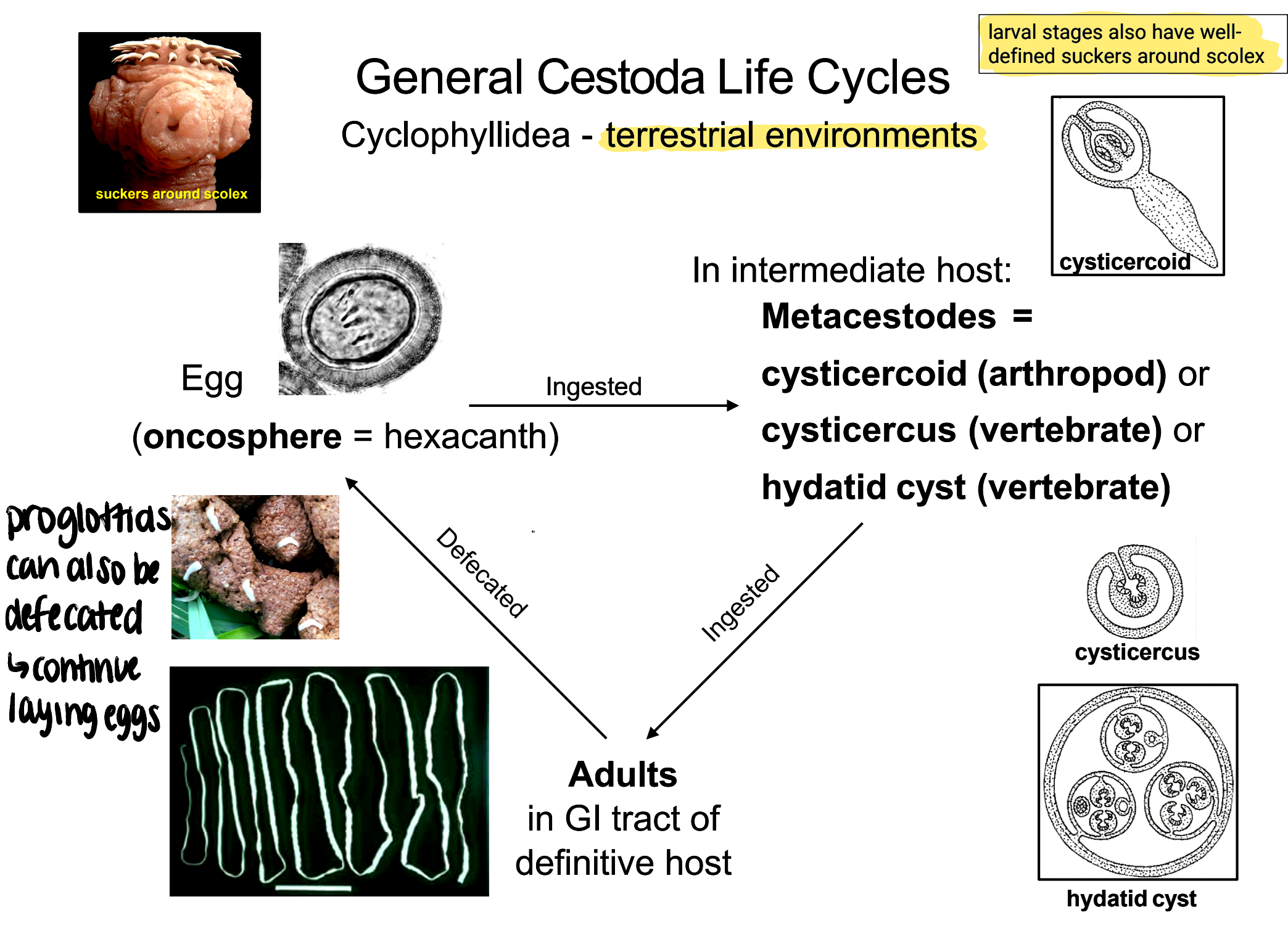
cysticercoid
metacestode that infects arthropod intermediate host (ex. fleas, beetles)
cysticercus
metacestode that infects mammalian intermediate host (can include humans)
fluid filled sac with scolex in center → “bladder worms”
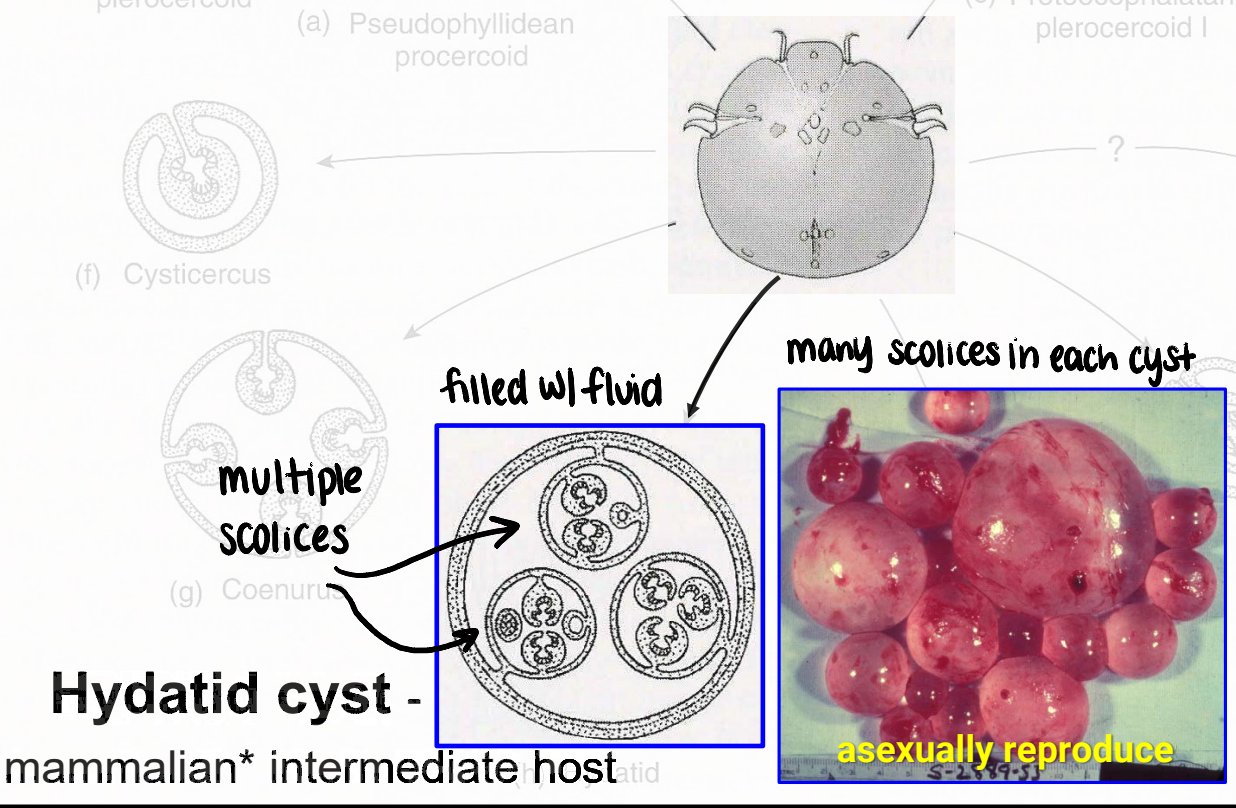
hydatid cyst
metacestode that infects mammalian intermediate host (can include humans)
filled with fluid
many scolices in each cyst
can asexually reproduce
cestodiases pathology
adults in definitive host
generally little pathology; commonly asymptomatic
heavy infections: GI pain/discomfort, diarrhea, constipation, disruption of proper digestion/nutrition
metacestodes in intermediate host
major source of pathology
varies with intensity and tissue location
economic importance → production loss, condemnation of meat
cestodiases diagnostics
adult
definitive diagnosis: eggs/proglottids in feces
history/clinical signs
larvae
clinical signs, serology, imaging
visual ID at surgery, necropsy, or slaughter
cestodiases treatment
anthlemintics - available adulticides
praziquantel, epsiprantel, niclosamide
albendazole → larvacide
treat definitive hosts to stop transmission
avoid contact/ingestion of intermediate hosts
cyclophyllidea
terrestrial cestodes
distinct suckers around scolex
taenia, echinococcus, dipylidium, mesocestoides, moniezia, anoplocephala
pseudophyllidea
aquatic cestodes
poorly defined suckers on scolex
diphyllobothrium, spirometra
cyclophyllidea general life cycle
oncosphere eggs/proglottids passed in feces → eggs ingested by intermediate host → develop to metacestode stage (cysticercoid, cysticercus, or hydatid cyst) → infected intermediate host ingested by definitive host → adult worms in GI of definitive host
pseudophyllidea general life cycle
coracidium (ciliated oncosphere egg) passed in feces → hatch/ingested by 1st intermediate host (copepod) → metacestode infects 2nd intermediate host (plerocercoid - fish/frog or spargana - mammal) → 2nd intermediate host ingested by definitive host → adults in GI tract of definitive host
diphyllobothrium definitive hosts
dog, cat, human
diphyllobothrium intermediate hosts (2)
1st = copepod (ex. plankton)
2nd = fish (ex. perch, walleye)
plerocercoid
diphyllobothrium diagnostic stage
eggs in feces
similar in appearance to trematode eggs
operculated
spirometra definitive hosts
dog, cat
spirometra intermediate hosts
1st = copepod
2nd:
frogs (plerocercoid)
rodents, dogs, humans, etc. (spargana)
spirometra diagnostic stage
eggs in feces; more likely to float than diphyllobothrium
pseudophyllidean cestodiases pathology
adults (in definitive host)
little pathology unless numerous
GI disturbance (diphyllobothrium, spirometra)
anemia due to B12-deficiency (diphyllobothrium; specific strain in Great Lakes)
metacestodes (in intermediate host)
infection by spirometra plerocercoid → sparganosis (serious!)