PSYC 304: Midterm 3
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
transcranial magnetic stimulation
briefly turns off part of brain using magnetic field coil to study what happens when there are deficits - makes “virtual lesions”
disrupting voltage firing of local cells - magnetic pulses stimulates the nerve cells
influences brain activity
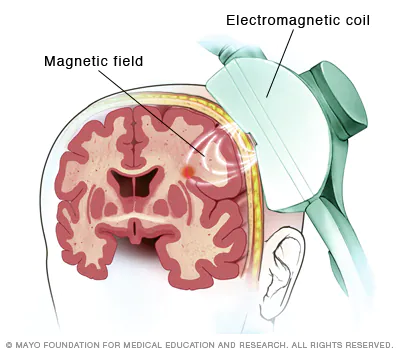
transcranial magnetic stimulation positives and negatives
positives: improves symptoms of MDD, OCD, migraines and smoking addictions, noninvasive
negatives: expensive, not a lot facilities, minor uncomfortable neuro side effects (headaches, spasms, dizziness)
morris water maze
rat is put into a pool with opaque water and a hidden platform. time for rat to find the platform in the pool is measured many times - time to find the platform gradually decreases
assesses spatial learning and the hippocampus (memory)
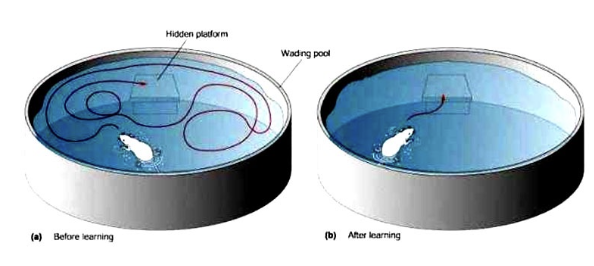
morris water maze positives and negatives
positives: reliable, requires less training, no special motivation required
negatives: can be stressful, may not be specific to spatial learning or memory, rodents may just float there
5-choice serial reaction time task
rat identifies which one of the 5 holes lights up - if they stick their nose in the right hole, they get a reward
assesses attention, accuracy, motor impulsivity
measures what happens when light flash shortens and impulsivity when rats are punished for picking a hole before light flashes
conditioning (rats get faster)
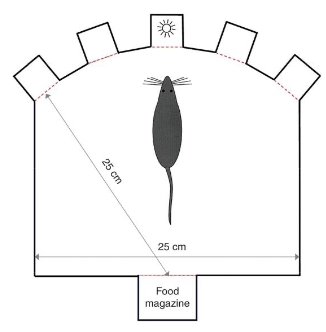
5-choice serial reaction time task positives and negatives
positives: tests multiple abilities, flexible
negatives: time-intensive training, individual variation, difficult to isolate one motor function
forced-swim test
rodent is placed into a pool where they can’t escape - measures how fast they give up swimming
measures depression, antidepressant medication efficacy
forced swim test positives and negatives
advantages: easy to perform, sensitive to antidepressants
negatives: learn that if they give up, they will be taken out of the pool so the giving up does not really measure poor mood; stressful for the animal
why use animal models?
they truly model human behaviours
mammalian brain similarity - have same divisions, similar organization (frontal cortex is smaller, cerebral hemisphere is a lot smaller)
cognition is sophisticated - able to do many things
types of animal models
morris water maze
5-choice serial reaction time task
forced-swim test
conditioning
T-maze
potential routes to administer drugs to animals
intramuscular
intravenous
subcutaneous
intraperitoneal
intraventricular
intramuscular
injections in muscles, like the shoulder (enters the bloodstream quickly)
can leave a lot of soreness in small animals
commonly used for medication administration
intravenous
injections into veins through catheters
used for drug self-administration studies, replacing fluids, replenishing blood volume
subcutaneous
insertion of medications beneath the skin (cutis, below dermis and epidermis) by injection or infusion
intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption (faster than intradermal injections), medication that can’t be taken orally
ex. insulin, live vaccines
intraperitoneal
injection of a substance into body cavity (peritoneum)
most often for animals, preferred when large amounts of blood replacement fluids are needed or problems prevent use of intravenous injection
chemo for some cancers, infant peritoneal dialysis
intraventricular
injections into ventricles
bypasses blood-brain barrier to central nervous system
in animals, used to study effects of drugs, plasmid DNA, viral vectors in central nervous system
in humans, treats spinal muscular atrophy, chemo in gliomas, drugs for long-term pain
best ways to test drugs on animals?
multiple doses - saline → low → medium → high
within-subjects design - test all conditions with one animal
placebo = vehicle (saline)
invasive electrophysiological recording methods
intracellular unit recording
extracellular unit recording
multiple-unit recording
invasive EEG recording
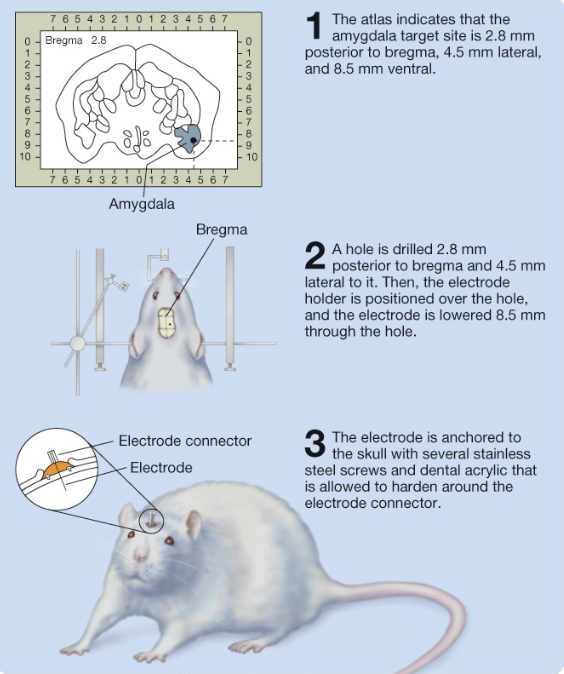
stereotaxic surgery
procedure that uses 3D coordinate equipment to precisely locate and treat targets inside the body
used for creating lesions, optogenetics, electrodes - allows accurate placement
employs stereotaxic atlas (brain structure records for a specific animal) and instruments (helps to precisely locate brain sections)
bregma = reference point
stereotaxic surgery positives and negatives
positives: fewer risks because there are no surgical incisions, minimizes damage in hard-to-reach places
negatives: small errors can be more impactful, shape of cerebellum can make surgery difficult in medulla and upper spinal cord
lesion types
chemical - excitotoxic lesions
selective chemical lesions
reversible lesions
chemical - excitotoxic lesions
neurons damaged by over-activation of glutamate receptors
spreads out evenly over a specific area, too much excitation can destroy neurons
used to test drug treatments, neurotrophic factors, fetal neuronal grafts
Selective neurochemical lesions
Target specific cells in the brain, not entire areas
6-hydroxydopamine, 5, 7-dihydroxytriptamine (targets serotonin and its receptors)
study brain function - indicates neuronal and axonal loss or dysfunction
Reversible Lesions
temporary inactivations of certain brain regions
place a cannulae in brain to directly inject drug to specific brain region
within-subjects: each rat can be case and control
ex. baclofen + muscimol (GABA agonist, temporarily inhibit)
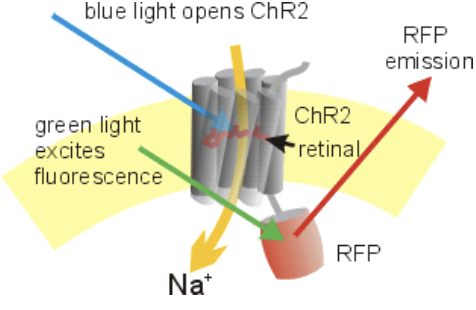
optogenetics
uses light to control activity of cells, tissues, organs with high temporal and spatial resolution
light-gated ion channels (channelrhodopsins) - open with light, triggers APs
use system-specific transcription factors (proteins expressed in only one area)
can be used for recording/mapping and manipulation
positives and negatives of optogenetics
positives: spatial and temporal resolution, can manipulate specific genes, noninvasive
negatives: expression patterns are limited, can stimulate tegmental area, can cause widespread changes, inefficient
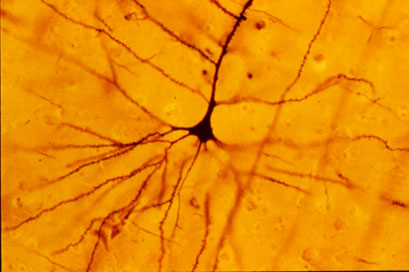
golgi stain
silver staining technique that is used to visualize nervous tissue under light microscopy
see neurons in clear detail
characterize structure of different types of neurons
takes a long time and is very inconsistent
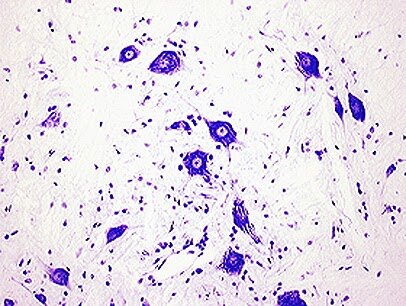
nissl/cresyl violet stain
stains nissl, or the rough ER of a cell - gives cytoplasm a mottled appearance
useful for distinguishing neurons and glia from one another, study arrangement of neurons
detail of the neurons is not captured
fibre stains
Luxol-fast blue (LFB) and Toluidine blue
observe myelin and white matter, stains tissue rich in DNA and RNA
green fluorescent protein
protein found in jellyfish and inserted into mammal brains to track gene expression and protein targeting - can track cells fate
very stable and can be visualized in live cells, so dynamic behaviour can be observed
types of stains
golgi stain
nissl/cresyl violet stain
fibre stains
green fluorescent protein
neuroimaging
captures brain structure and function - can’t definitively determine causality
non-invasive
static neuroimaging
stationary representation of the brain, measures brain’s intrinsic functional architecture - doesn’t measure activity
X-Ray
CT
MRI
DTI (form of MRI)
doesn’t capture fundamental differences in brains (Younger vs. older brains, high vs. low SES)
x-rays
use invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, organs
help diagnose tumours, bone injuries
fast, cost-effective, visualize bones, noninvasive
radiation exposure, can’t really visualize soft tissues, don’t know what is actually going on
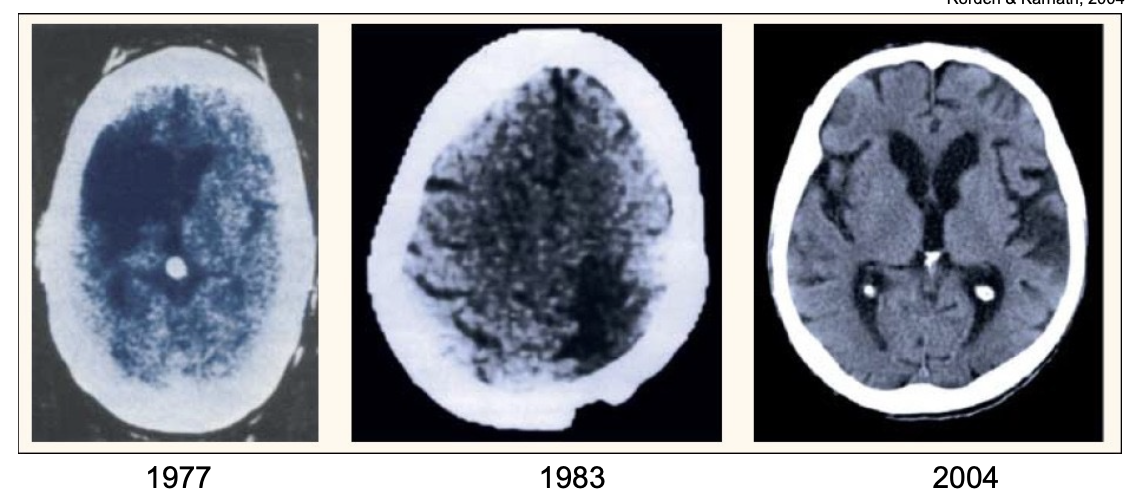
CAT/CT scan
computerized axial tomography scan, noninvasive imaging using X-rays creating detailed pictures of inside of the body
type of X-ray
scanner takes multiple images of the brain from different angles, which are then set to a computer - analyzes radiation absorption patterns
used for: assessing for brain tumours/other lesions, detect clots in the brain, guide biopsies of brain tissue
can’t easily resolve white vs. grey matter, easy to implement but not useful for research
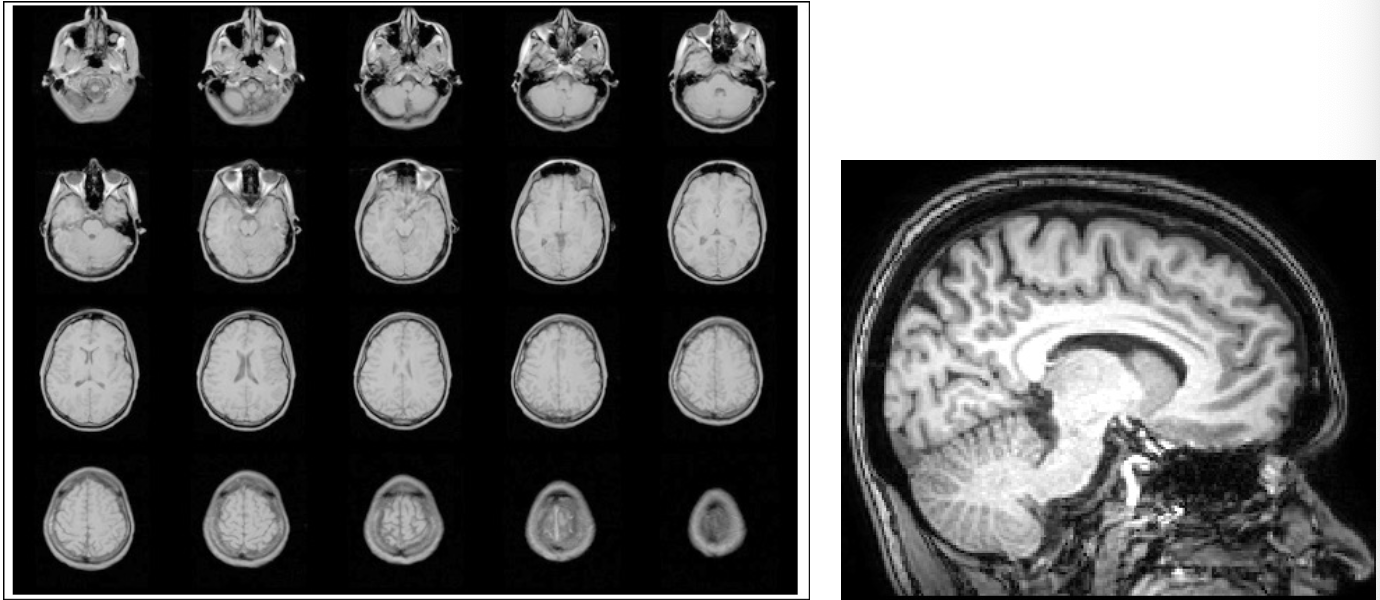
MRI scan
uses a large magnet and pulses of radio waves to scan 3D images of the brain (measured in voxels), producing images of brain structures - noninvasive
detailed images
electric current passed through coiled wires to create a magnetic field - sends and receives radio waves
more accurate than CT scans - examines macrostructure and microstructure, detects abnormalities
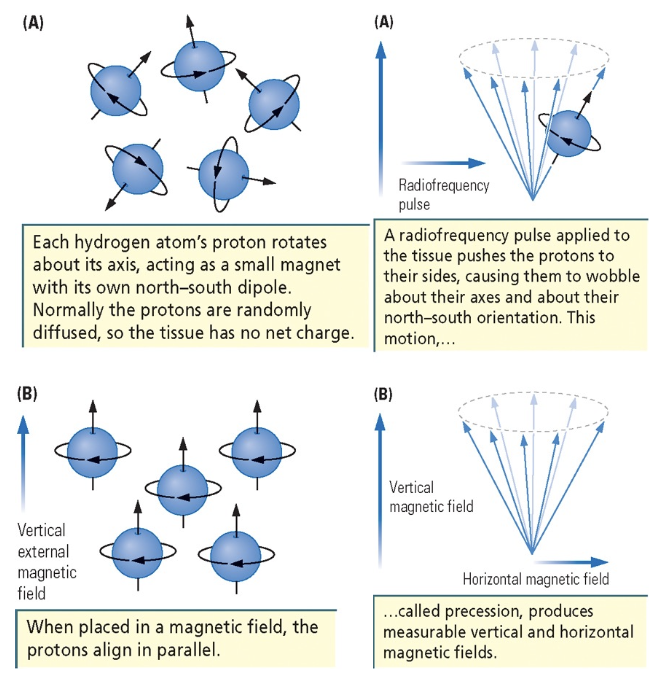
how does an MRI scan work?
each hydrogen atom’s proton rotates about its axis with its own north-south dipole - normally protons are randomly diffused
when placed in a magnetic field, protons align in parallel
radio frequency pulse applied to tissue pushes protons to their sides, causing them to wobble about their axes
this motion is caused precession, which produces measurable vertical and horizontal fields
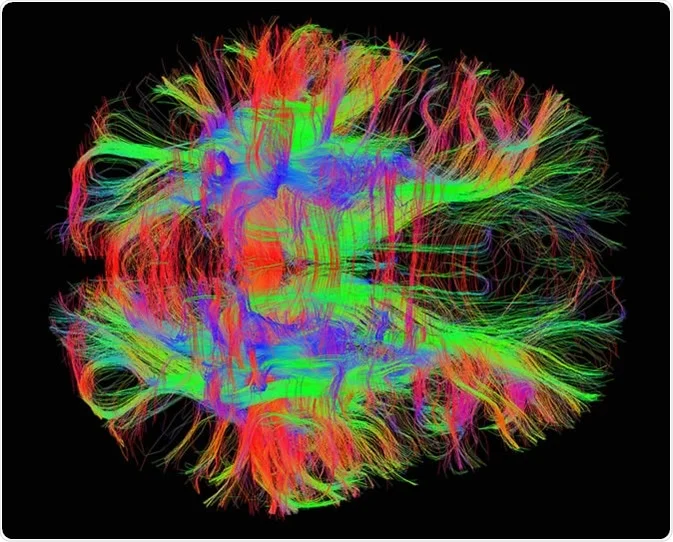
DTI scan
type of MRI that measures the movement of water molecules in tissue to create detailed images of brain and spinal cord
difference in how water moves parallel to and perpendicular to nerve fibres (diffusion anisotropy)
detailed images of brain’s white matter, direction of diffusion flow (identifies injuries and abnormalities)
Diagnoses stroke, brain tumours, MS, TBIs, concussions
More detailed than standard MRI - shows actual nerve tract
helpful for white matter disorders - schizophrenia, psychopathy
dynamic/functional neuroimaging
captures ongoing neuro processes like blood flow through imaging technique that captures sequential images
PET
fMRI
rsfcMRI
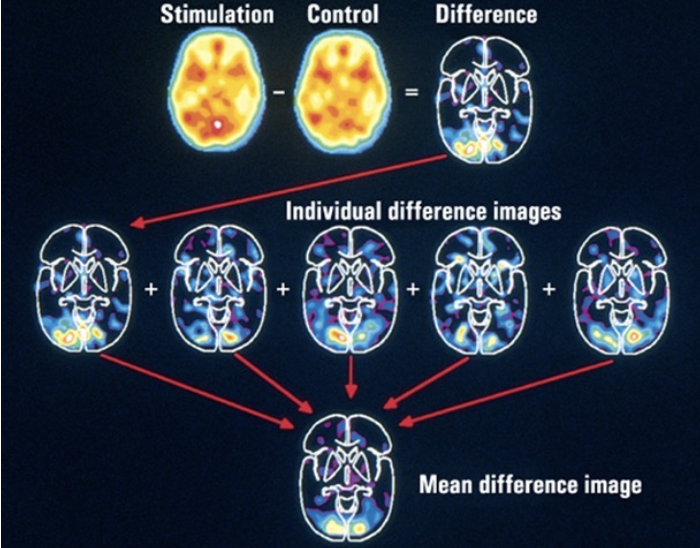
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
nuclear imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to visualize/measure metabolic activity of cells in tissues and organs
uses a very tiny amount of radio-labelled cocaine, parts of the brain with the most dopamine light up the most
need multiple sessions to subtract baseline from experimental condition
PET advantages and disadvantages
advantages: useful for targeting specific systems (ex. DA)
disadvantages: very expensive, temporally slow, poor spatial resolution
fMRI
non-invasive brain imaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow
oxygenated blood vs. deoxygenated blood - more oxygenated blood should be going to more active areas (BOLD response)
see a curve in brain activity called hemodynamic response - after 6 seconds, there is a peak in oxygenated blood
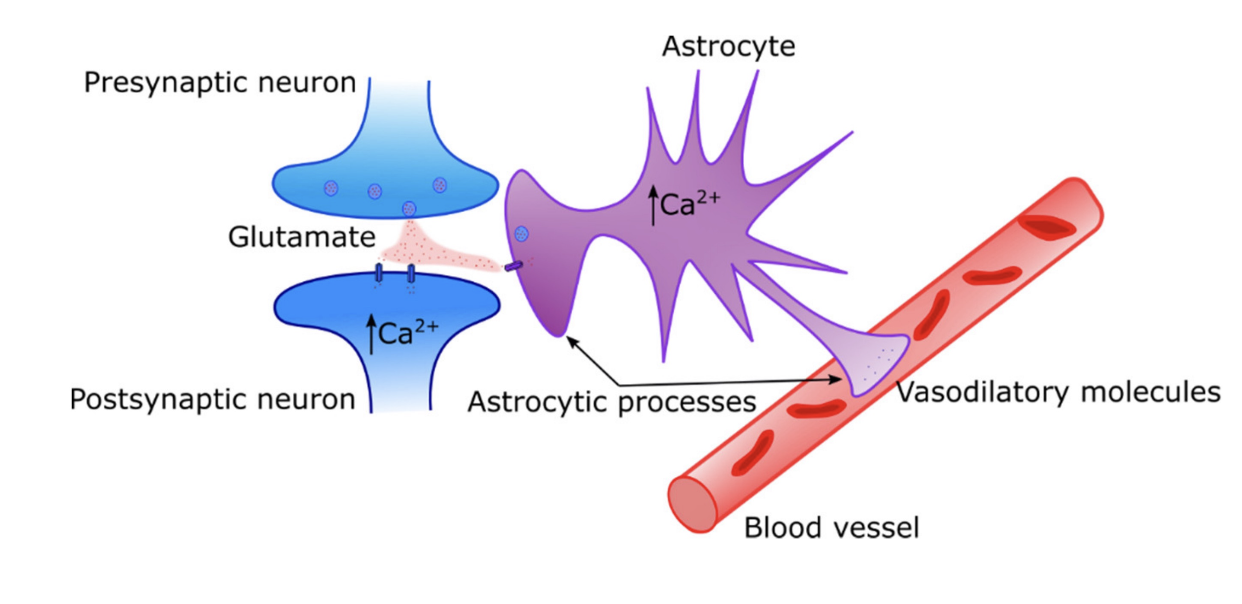
fMRI BOLD response
blood-oxygen-level-dependent signal, reflects changes in brain blood flow and blood oxygenation
astrocytes are causing differences in blood - causes an increase in calcium and dilates the blood vessels = increase in blood flow
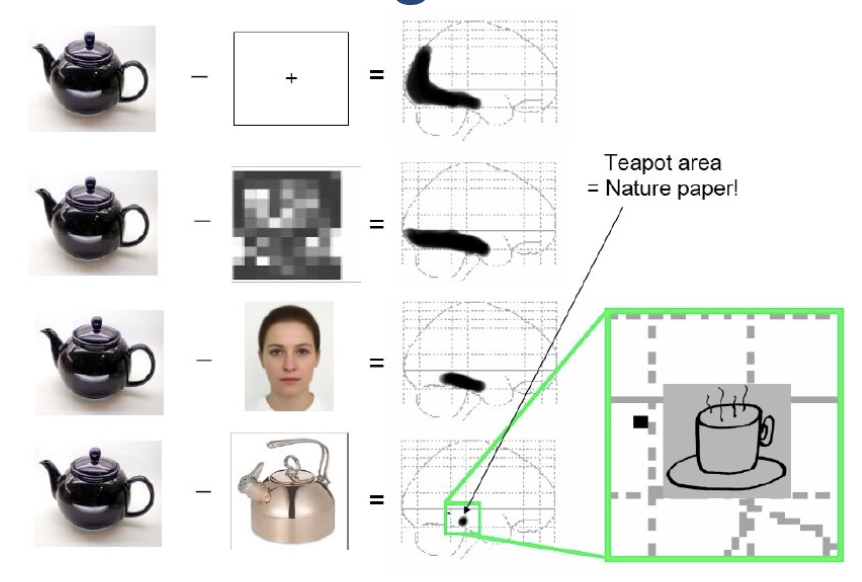
paired-image subtraction
technique that involves subtracting one image from another to highlight differences between them (position, colour, brightness, shape)
determine what is actually operating, not just baseline activity
quality of results depends on quality of your controls
as control gets more specific, activity in brain decreases
utilized with fMRI
event-related fMRI
do not need a specific control condition, just need many iterations of the same variables to measure one area of the brain - avoid paired image subtraction
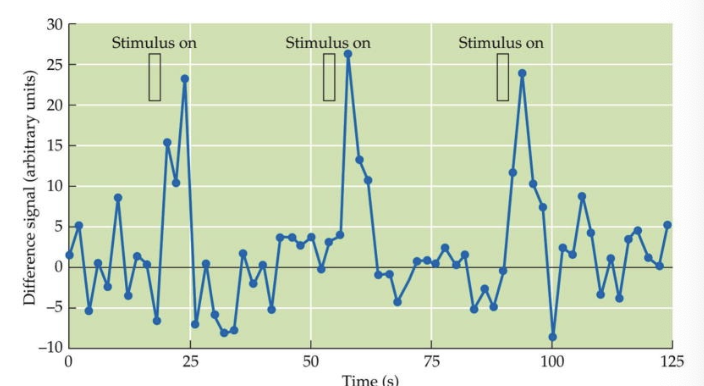
problems with interpreting fMRI studies?
spatial averaging: averages do not represent any individuals
spatial resolution: getting a millions neurons in one Voxel
temporal resolution not as fast as other methods
focuses on increases in activity and some regions are more active at rest
incorrect interpretations due to bold responses
anxiety and boredom confounds
psychoactive drugs (nicotine, caffeine) hard to control for
anticipatory hemodynamics shifting response earlier
low reliability
false positives
the heavy metal brain (Sun et al., 2017)
studying functional connectivity networks of heavy metal vs. classical music lovers - found significant differences, but if any study has significant sample size, differences will be significant
made poor assumptions about why brains were different, data not fitted to make assumptions about behaviour