AP Psych Unit 2 Review
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Free Association
A method used in psychoanalysis where a person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind to explore the unconscious.
Unconscious
The part of the mind that holds thoughts, memories, and desires, we are unaware of but which influence behavior.
Id
The part of personality that operates on the pleasure principle-wants immediate gratification.
Ego
The part of personality that mediates between the i’d and reality, operating on the reality principle. (rational part)
Superego
The part of the personality that represents internalized ideals and provides standards for judgment.
Repression
Pushing painful memories out of awareness.
Regression
Returning to childlike behavior in stressful situations.
Reaction Formation
Behaving the opposite of true feelings.
Projection
Attributing your unacceptable thoughts to someone else.
Rationalization
Creating excuses to justify actions.
Displacement
Shifting feelings from the true source to a safer target.
Denial
Refusing to believe reality.
Sublimation
Redirecting unacceptable urges into socially acceptable activities.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
A projective test where people make up stories about pictures.
Rorschach Inkblot Test
A test using inkblots to analyze perceptions and emotions.
Self-Actualization
Fulfilling one’s potential and becoming the best version of yourself.
Unconditional Positive Regard
Accepting someone no matter what they do.
Big Five Personality Factors (OCEAN)
openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, neuroticism
Openness
high score: creative, imaginative, eccentric, and open to new experiences
low score: practical, conventional, and rational
Conscientiousness
high score: organised, self-directed and successful, but controlling
low score: spontaneous, careless, can be prone to addiction
Extroversion
high score: outgoing, enthusiastic and active; you seek novelty and excitement
low score: aloof, quiet and independent; you are cautious and enjoy time spent alone
Agreeableness
high score: trusting, empathetic and compliant, you are slow to anger
low score: uncooperative and hostile, finding it hard to empathize with others
Neuroticism
high score: prone to stress, worry, and negative emotions
low score: emotionally stable but can take unnecessary risks
Social Cognitive Perspective
Focuses on interaction between thinking and the environment.
Reciprocal Determinism
Behavior, personal factors, and environment all influence each other.
External Locus of Control
Believing outside forces control your fate.
Internal Locus of Control
Believing you control your own destiny.
Learned Helplessness
Giving up after repeated failures (“I will never be good at this”).
Self-Serving Bias
Attributing success to yourself and failure to outside forces.
High Self Efficacy
Belief in your ability to succeed.
Low Self Efficacy
Doubt in ability to succeed.
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE’s)
Traumatic events in childhood that impact developement.
Authoritarian Parenting Style
Strict, high expectations, low warmth.
Permissive Parenting Style
Lax rules, high warmth.
Authoritative Parenting Style
High expectations + high support
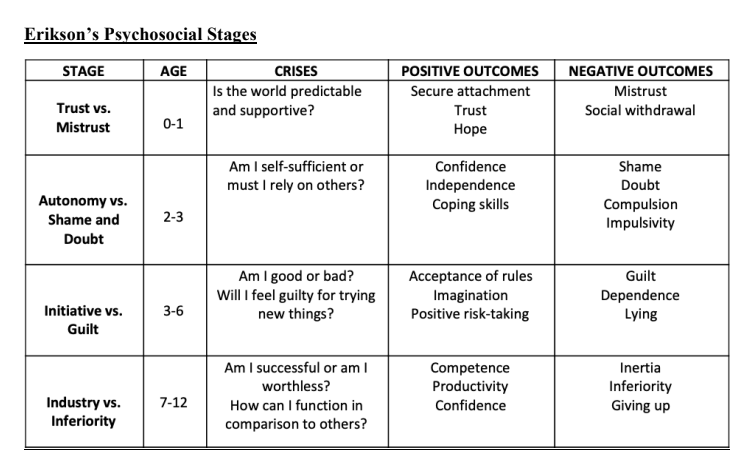
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages (ages 0-12)
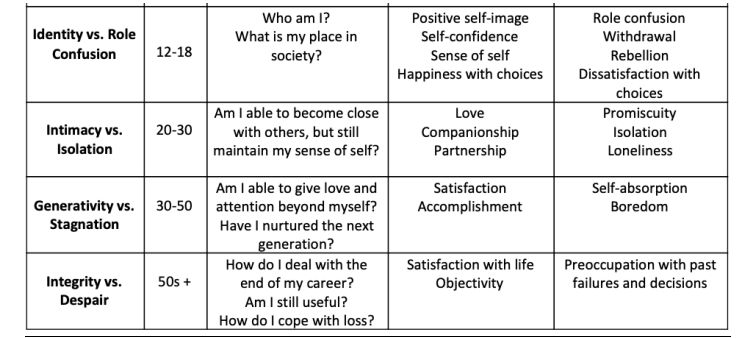
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages (ages 12-50+)
Attribution Theory
Explaining behavior by attributing it to internal (disposition) or external (situation) causes.
Fundamental Attribution Theory
Overestimating personality (internal factors) and underestimating the situation (external factors) when explaining the behavior of others.
Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon
Agreeing to a small request makes one more likely to to agree to a larger one.
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Discomfort from conflicting thoughts and behaviors, which motivate change. (You want to be healthy but don’t exercise regularly or eat a nutritious diet.)
Conformity
Adjusting behavior to match a group.
Normative Social Influences
Conforming to be liked or accepted.
Informational Social Influence
Conforming because you believe the group knows more.
Conditions That Increase Conformity
Include group size, unanimity, respect for group, and insecurity.
Obedience
Following commands from an authority figure.
Conditions That Increase Obedience
Presence of an authority figure, prestige, no role models for defiance.
Social Facilitation
Improved performance on easy tasks when others are watching.
Social Loafing
Doing less when working in a group.
Deindividuation
Loss of self-awareness in a group-can lead to impulsive acts.
Group Polarization
Group discussions strengthen a shared opinion, causing your viewpoint to become more extreme.
Groupthink
Desire for harmony leads to poor decision-making.
Social Trap
Pursuing self-interest harms the group in the long run.
Self-Serving Bias
The tendency to attribute successes to self and failures to outside factors.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Belief that leads to its own fulfillment (if you think something bad is about to happen and then something bad happens).
Mere Exposure Effect
Repeated exposure increases liking.
Altruism
Helping others with no expectation of reward.
Bystander Effect
The idea that someone is less likely to help in a situation when other people are present.
Social Exchange Theory
Helping is based on a cost-benefit analysis. (Helping someone thinking you’ll gain something from it.)
Ingroup Bias
Favoring your own group (people you identify with).
Outgroup Bias
Disliking those not in your group (people you don’t identify with).
Just-World Phenomenon
Belief that people get what they deserve.
Door in the Face
Start with a big request, then ask for something smaller (what you really wanted).
Confederate
An actor in a study pretending to be a participant.
Dispositional Attributions
Explaining behavior based on personality.
Situational Attributions
Explaining behavior based on circumstances.
Optimistic vs Pessimistic Explanatory Style
Optimistic = Bad events are temporary; Pessimistic = Bad events are permanent.
Actor/Observer Bias
We blame our behavior on situations, but others behavior on their personality.
Upward vs. Downward Social Comparison
Comparing yourself to those better (upward) or worse (downward). (Upward social comparison is comparing yourself to someone richer than you and downward is comparing yourself to someone poorer).
Relative Deprivation
Feeling worse off compared to others.
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Explains two ways of persuasion: central (logic) and peripheral (emotional).
Central Route to Persuasion
Using logic and evidence to convince.
Peripheral Route to Persuasion
Using emotion, appearance, or status to convince.
Halo Effect
One good trait makes us think everything about that person is good.
Superordinate Goals
Shared goals that override differences.
Burnout
Emotional exhaustion from prolonged stress.
Social Debt
Feeling the need to repay someone for a favor.
Social Reciprocity Norm
We help those who help us.
Social Responsibility Norm
We help those who depend on us.
Secure Attachment
Comfortable with closeness, upset when gone but recovers. (Baby is distressed when the caregiver leaves, but quickly calms and reconnects when they return.)
Insecure Avoidant
Avoid closeness, shows little emotion. (Baby shows little distress when the caregiver leaves and avoids them upon return.)
Insecure-Anxious/Ambivalent
Clingy and insecure, unsure if love will be returned. (Baby is extremely upset when the caregiver leaves and is not easily comforted when they return.)
Insecure-Disorganized
Fearful, confused-often due to trauma. (Baby displays confused, contradictory behaviors—may freeze, approach then avoid, or act fearfully.)