Skin/Integumentary System
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
How much does the skin cover?
1.6 to 1.9 m2 in avg adult
What is the body’s largest organ?
Skin
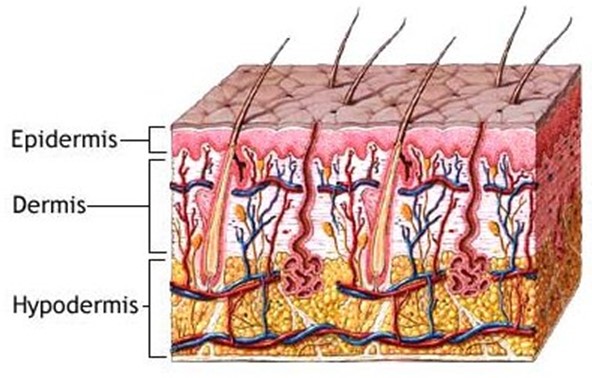
What is the structure of the skin?
Cutaneous
epidermis
dermis
hypodermis
What is considered skin?
appendage
hair
nail
skin glands
Keratinocytes
structural elements of outer skin
90% of cells
Melanocytes
contribute to skin colour + filter UV light
5% of skin
Epidermal Dendritic Cells
role in immune response
branched antigen-presenting cells
are Langerhans cells
Tactile Epithelial Cells / Merkel Cells
forms light touch receptors
attach to sensory nerve endings
Stratum Corneum / Corneocytes (horny layer)
barrier to water loss & many environmental threats
most superficial layer
dead cells filled w/ keratin (barrier)
turnover/ regeneration time
time required for EPIDERMAL cells to form in stratum basale
migrates to skin surface
35 days
Growth factor
regulates epidermal growth & repair
hormones signal tissue repair
shortened turnover time
↑ thickness of stratum coronium
= callus formation
10 to 12 % of all cells in stratum coronium ⇉ mitosis
lamellar corpuscles / pacini corpusle
sense of deep touch, pressure & vibration
Dermo epidermal junction
Partial barrier to the passage of some cells & drugs
basement membrane= fibrous elements + polysaccharides gel
gel (glue) attaches the epidermis to dermis
tactile corpuscle/ meissner corpuscle
detecting light touch
slight pressure
Dermis / corium
middle layer
true skin
thicker than epidermis
gives strength to skin
reservoir= water + electrolytes
sudoriferous (sweat) & sebaceous glands
blood vessels
sensory receptors
rich vascular supply = temperature regulation
Nociceptors
pain, temperature, itch& tickle
Thermo receptors
hot & cold
sensory receptors
meissners corpuscle/ tactile corpuscle
pacinian corpuslce / lamellear corpuscle
nociceptors
thermoreceptors
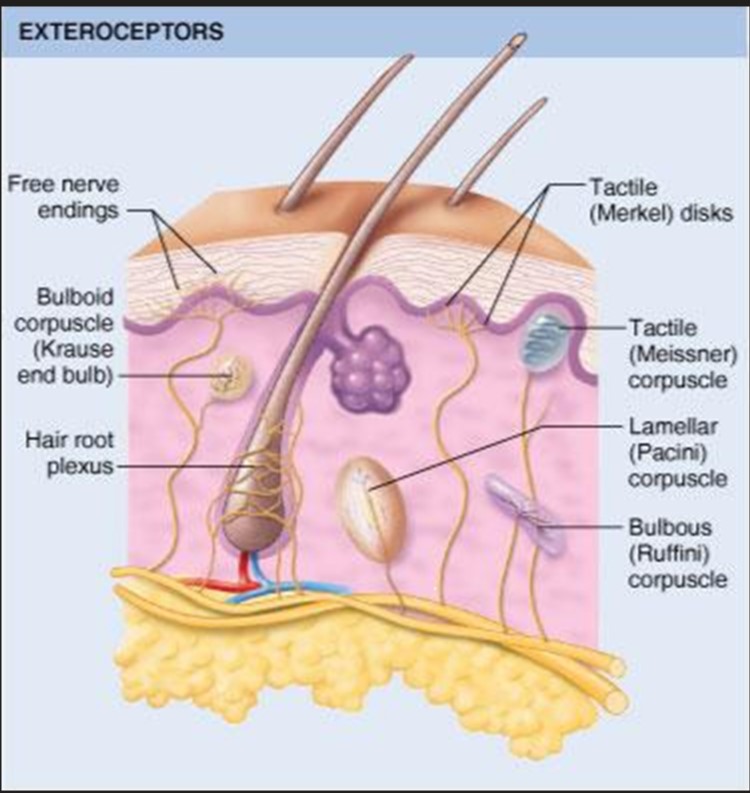
exteroceptors
body surface
merkle disk
meissner
ruffini
krause end bulb
free nerve endings / nociceptors
hair root plexus
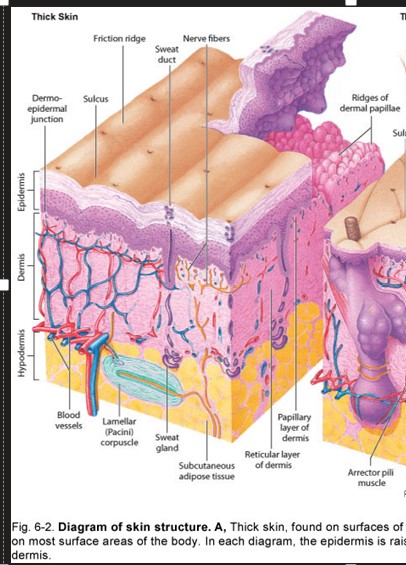
Where is thick skin found?
surfaces of the palms & soles of feet

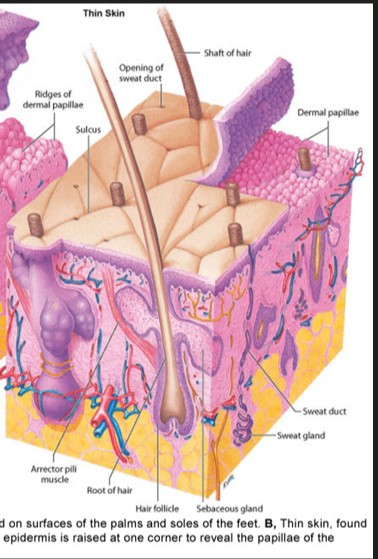
Where is thin skin found?
most surface areas of body
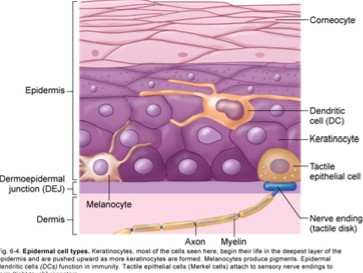
Epidermis contains
Keratinocytes
melanocytes
epidermal dendritic cells
tactile epithelial cells / merkel cells
stratum corneum/ horny later
lamellar corpuscles
dermo epidermal junction
merkle disk
gentle touch
meissner
touch & low frequency vibration
Ruffini
crude & persistent touch
krause end bulb
touch & low freq vibration, textural sensation
free nerve endings (nociceptor)
pain
hair root plexus
detects movement of hair
Pain receptors
free nerve endings = nociceptors
located on surface of body (exteroceptors)
In deep visceral organs: viseroceptors
Brain does not have
Acute/ Fast (A) Pain
superficial injury of trauma
nerve fibers are [ in skin] + mucous membrane + superficial
ex., slamming your finger in car door
Chronic/ slow (B)
dull or aching pain in VISCERAL structures
can be severe = kidney or gallstones
diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage)
uncontrolled diabetes causing a loss of ability of sense pain on certain areas of body surface
skin of feet
patients w/ diabetes should be closely monitored for adequacy of cutaneous sensations
referred pain
location far removed from site of injury or disease
due to mixing/ convergence of sensory nerve impulses from disease organ & skin area
ex. Heart attack pain , can occur at left shoulder or left arm
Hypodermis
subcutaneous layer / superficial fascia
forms connections btwn skin + other structures
adipose + connective tissue
subcutaneous injections
layer of fat btwn skin & muscle
insulin, morphine, heparin
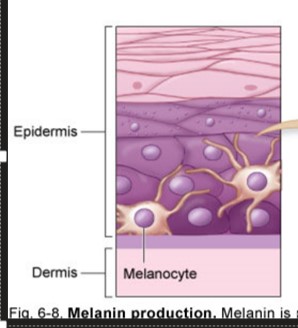
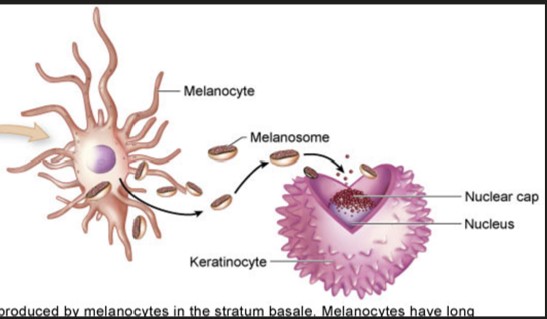
melanin
dark pigments in skin, hair & iris of eye
produced by melanocytes
forms a cap over the nucleus of Keratinocytes protecting it from UV radiations
Beta- carotene
orange pigments from food can change skin color
hemoglobin
changes in blood flow
redder: blood flow to skin = ↑ inflammation
cyanosis: bluish = inadequate oxygenation of blood
Jaundice
yellowish Discolouration of skin & other tissues
ex., white (sclera) of the eye
accumulation of bile pigments due to improper liver functioning ex., hepatitsis
neonatal jaundice
metabolic + physiological adjustments after birth
until day 8 in normal birth
day 14th for premature
treatment = phototherapy (light)
Functions of Skin
Protection
Surface Film
Sensation
flexibility
hormone production (vitamin D)
execration
immunity
What does the function protection do?
physical barrier to microorganisms
barrier to chemical hazards
↓ potential for mechanical trauma
prevents dehydration
protects from excess UV rays exposure (melanin fx)
what does the function Surface Flim do?
residue + secretion of sweat + sebaceous glands + dead epithelial cells
antibacterial + antifungal activity
lubrication
hydration of skin surface
buffer of caustic irritants
blockage of toxic agents
Desquamation
shedding of epithelial elements
what does the function : Sensation do?
acts as a sophisticated sense organ
detects stimuli of
pressure
touch
temperature
pain
other general senses
what does the function flexibility do?
permits change in body contours w/o injury
supple & elastic
what does the function hormone production do?
produces vitamin D
skin + UV = cholecalciferol (precursor)
blood transports precursor → liver & kidneys = vitamin D
vita D = hormone
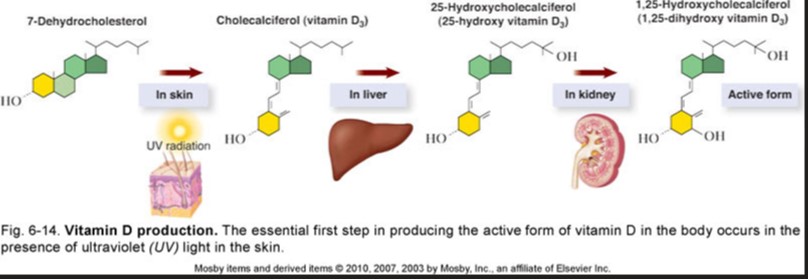
what does the function excretion do?
filters wastes
water
urea/ ammonia / uric acid
what does the function Immunity do?
epidermal dendritic cells trigger helpful immune reactions
phagocytic cells destroy bacteria
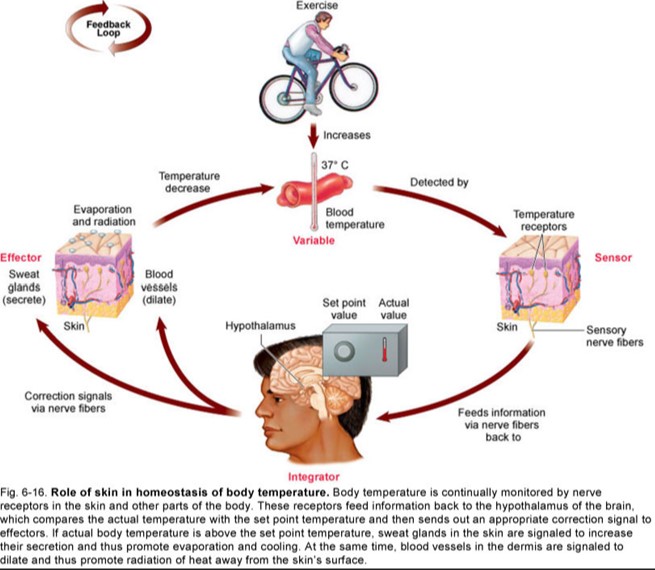
Homeostasis of body temperature
body temperature
heat production
muscles & liver metabolism
direct relationships btwn amount of muscles activity & heat production
must equal heat lost
80% occurs through skin
20% through mucosa of:
respiratory
digestive
urinary tracts
evaporation
heat energy is expended
important @ high temp when it is only method
heat can be lost from skin
radiation
transfer of heat from one object to another w/o contact
important for cool environmental temps
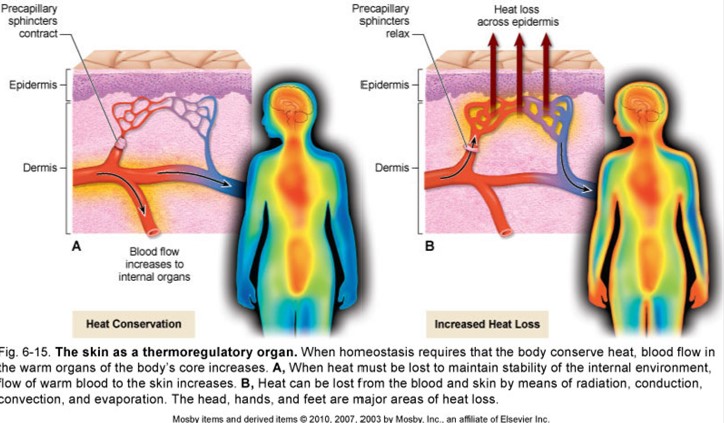
vasoconstriction
↓ heat loss due to ↓ blood flow across peripheral tissue
vasodilation
↑ heat loss due to ↑ blood flow across peripheral tissue
heat loss
controlled by -tive feedback loop
hypothalamus monitors body's internal temp
vasodilation = if temp ↑ hypothalamus ⇉ sweat glands + blood vessels of skin
hypothalamus continues until normal body temp
hirsutism
excessive hair growth from drugs
minoxidil ( Rogaine )
cyclosporine
Androgenic alopecia
male pattern baldness
genetic tendency + male sex hormones
nails - Epidermal cells
hard keratin
nail body
visible part of each nail
root
cuticle
nail in groove hidden by fold of skin
Lunula
moon-shaped white area nearest root
nail bed
layer of epithelium under nail body
abundant blood vessels
can be pink under translucent nails
cyanotic nail
bluish colour
inadequate oxygenation
due to cardiovascular and/ or respiratory disorders
nail growth
by mitosis in STRATUM BASALE under lunula
avg. 0.5 mm / week
1 inch / yr
onycholysis
separation of nail from the nail bed
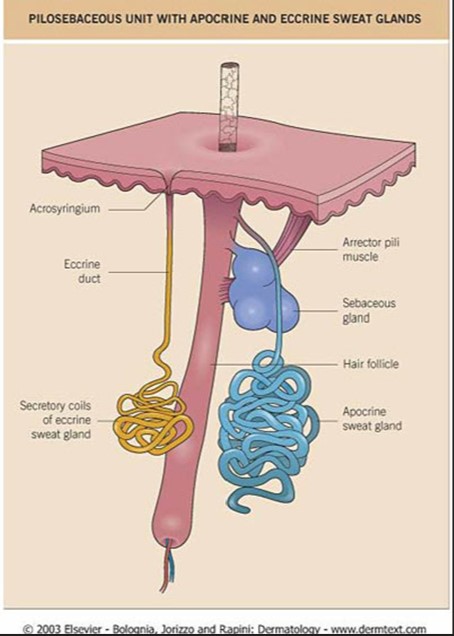
eccrine glands
small numerous sweat glands
over total BSA w/ exception of few small areas
secretes: perspiration or sweat
eliminates wastes: urea , ammonia , uric acid
maintains constant core temp
apocrine glands
body odor
limited distribution
located: axillar & around anogenital areas
NOT involved in regulation of body temp
= to sexual scent glands of other animals
sebaceous glands
secretes sebum: oily substance that keeps hair & skin soft & pliable
prevents excessive water loss
anti-fungal activity
in DERMIS
except in palms & sole
secretions ↑ in adolescence
formation of pimples & blackheads
meds such as accutane
acne
over active sebaceous gland + blockage + inflammation of their ducts
Pilosebaceous unit w/ apocrine & eccrine sweat glands
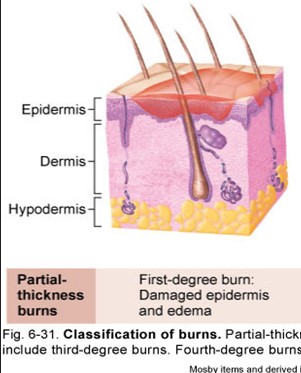
1st degree burn
damaged epidermis & edema
partial thickness burns
edema ( fluid trapped = swelling)
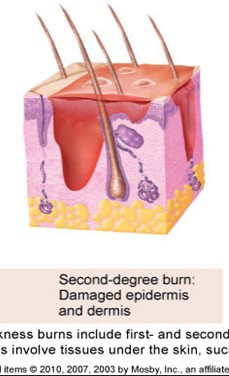
2nd burns
damaged epidermis & dermis
partial thickness burn
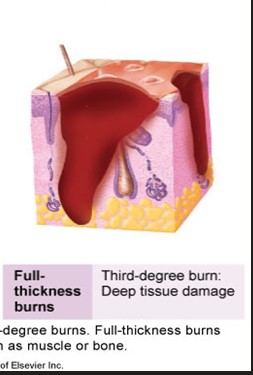
3rd degree burn
deep tissue damage
to the subcutaneous
Children cycle life
smooth + unwrinkled + elasticity + flexibility
few sweat glands
rapid healing
adults cycle of life
development & activation of sebaceous + sweat glands
Increase
sweat production
body odor
sebum production (acne)
old age cycle of life
wrinkling
decrease in
sebaceous & sweat gland activity
less sebum productions
body’s ability to cool itself
skin cancer
95% of skin cancer = basal cell & squamous cells carcinomas
very responsive to treatment & seldom metastasize ( spread)
malignant melanoma
metastazie
tumor produced by melanocytes
occur on the skin but spread to gastrointestinal tract & brain
35, 000 cases reported per year
7000 = deaths
kaposi sarcoma
immune deficiencies
ex., AIDS
producing purple papules → lymph nodes + internal organs
ringworm
tinea = fungal infection of the skin
mycoses
fungal infection of skins ; skin or nails
also cause infections in mouth, throats lungs, urinary tract
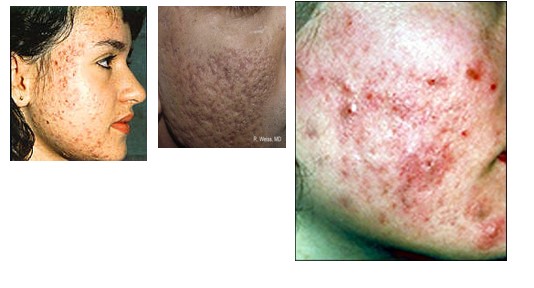
Acne Vulgaris
self limited disorder
primarily in teenagers & young adults
areas of the body that have the greatest # of sebaceous glands
face, neck, chest, upper back & upper arm
external factors
oil, greases, dye in hair products
detergents, soap , astringents
occlusive clothing : turtleneck & bra straps
psychological stress
diet
type 1 acne
comedones w/ small inflamed papule or pustule
no scarring present
treatment for type 1 acne
topical therapies, BC pills
type 4 acne
numerous large cysts
on face , neck & upper trunk
severe scarring
treatment for type 4 acne
Accutane tabs
can cause severe birth defects
treatment for noninflammatory (Comedones) acne
topical retinoids (tretinoin, adapalene)
salicylic acid
azelaic acid
benzoyl peroxide
glycolic acid
treatment for inflammatory acne
papular
topical retinoids
benzoyl peroxide
azelaic acid
topical antibiotics
sodium sulfacetamide
pustular
oral antibiotics
nodulocystic
isotretinoin
oral corticosteroids
what is the treatment for hormonally- induced acne
oral contraceptives
spironolactone
corticosteroids
flutamide
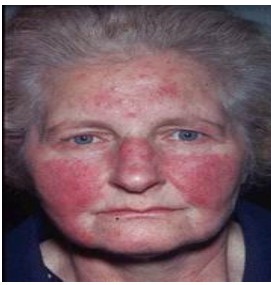
acne rosacea
in middle-aged & older adults
vascular dilation of the central face
nose ,cheeks, eyelids & forehead
unknown cause
is chronic
treatments for acne rosacea
topical antibiotics: METRONIDAZOLE gel
benzoyl peroxide
treatment for acne rosacea w/ papular or pustular lesions
TRETINOIN creams
when it’s unresponsive to other treatment
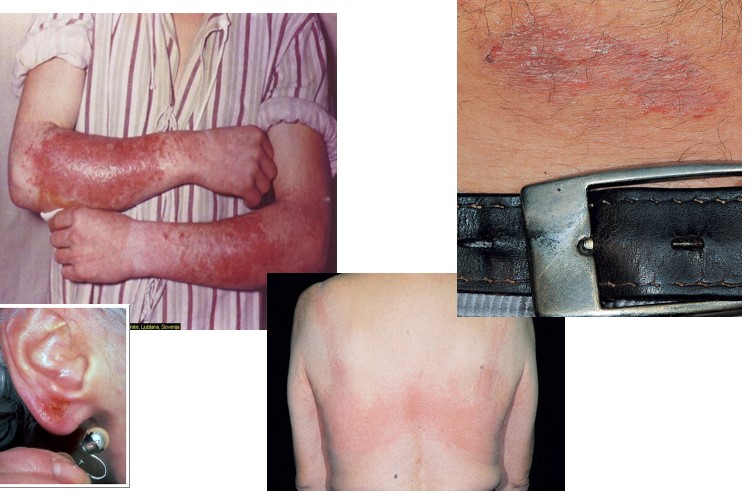
Allergic contact dermatitis
any dermatitis arising from DIRECT skin exposure to a substance
allergic = immune response
irritant- induced = directly damages skin
common sensation in North America is plant oleoresin
poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac
treatment for allergic contact dermatitis
corticosteroids: topical or oral in acute phase
hydrocortisone
BETNOVATE cream
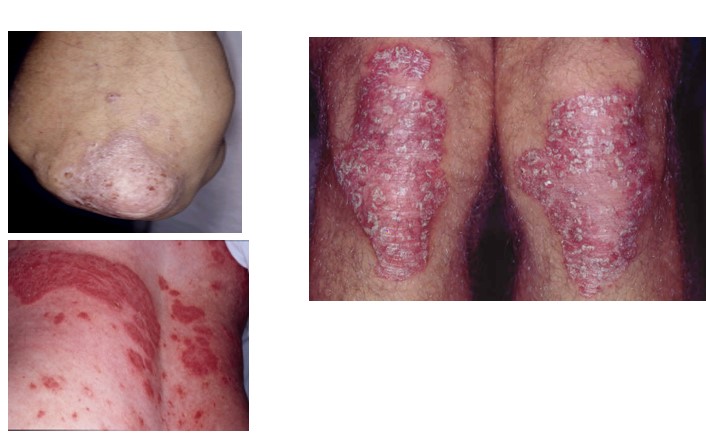
Psoriasis
red plaques w/ sliver scales
developed as a 2ndary response = triggered by WBC
Plaque psoriasis
symmetrically distributed plaques
scalp, extensor elbows , knees & back
pustular psoriasis
most severe form
erythema ( redness) , scaling & sheets of superficial pustules w/ erosions
nail psoriasis
typical abnormality
pitting w/ colour changes & crumbling of nail
treatments for psoriasis
topical emollients, topical steroids (BETNOVATE) ,TAR