Kidneys
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Homeostasis
maintaining a stable internal environment within set limits
Negative feedback
Restores system to their original level by reversing any change
Functions of kidneys (4)
Excretion of nitrogenous waste
Osmoregulation
Ultrafiltration
Selective reabsorption
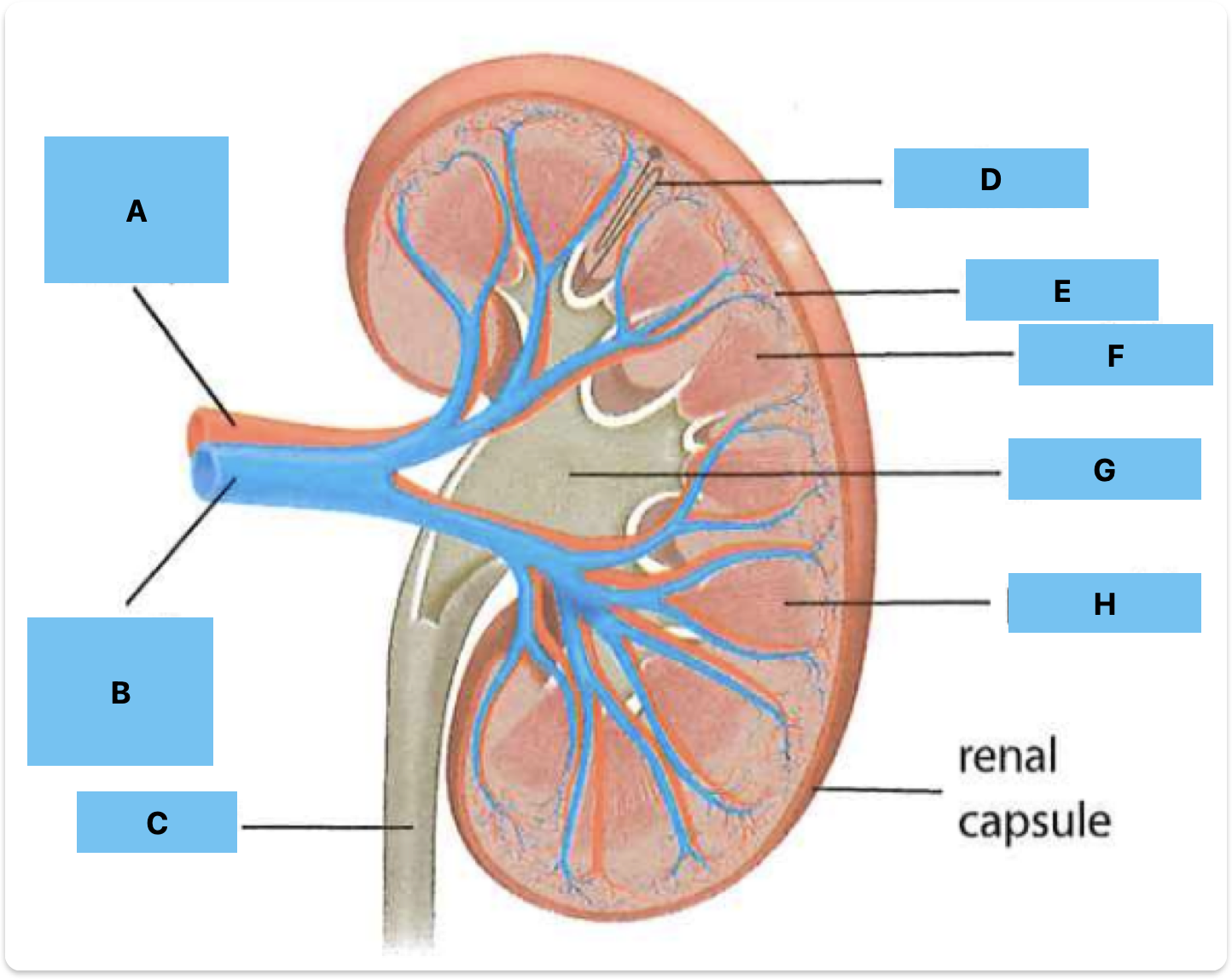
Label A-H
Renal artery
Renal vein
Ureter
nephron
cortex
medulla
pelvis
Pryamid??
What is the basement membrane
Sieve at base of Bowmans capsule - only allowing small molecules
Describe ultrafiltration
Driven by hydrostatic pressure from the afferent arteriole
Basement membrane acts as a molecular sieve to filter out large molecules
Small molecules such as water, glucose, amino acids, urea and vitamins then move into PCT as glomerular filtrate
How are PCT adapted to selective reabsorption
Microvilli - increase surface area
Plenty mitochondria - provide ATP
Membrane bound transport protein - carry out selective reabsorption
What substances are reabsorbed in PCT
Glucose, amino acids, most water and ions from filtrate back into blood
unnecessary
oops
Deamination
Removal of amine group to leave ammonia and pyruvic acid
What do fish, animals and birds each excrete nitrogen as
Ammonia diffuses into water
Urea in urine
Uric acid
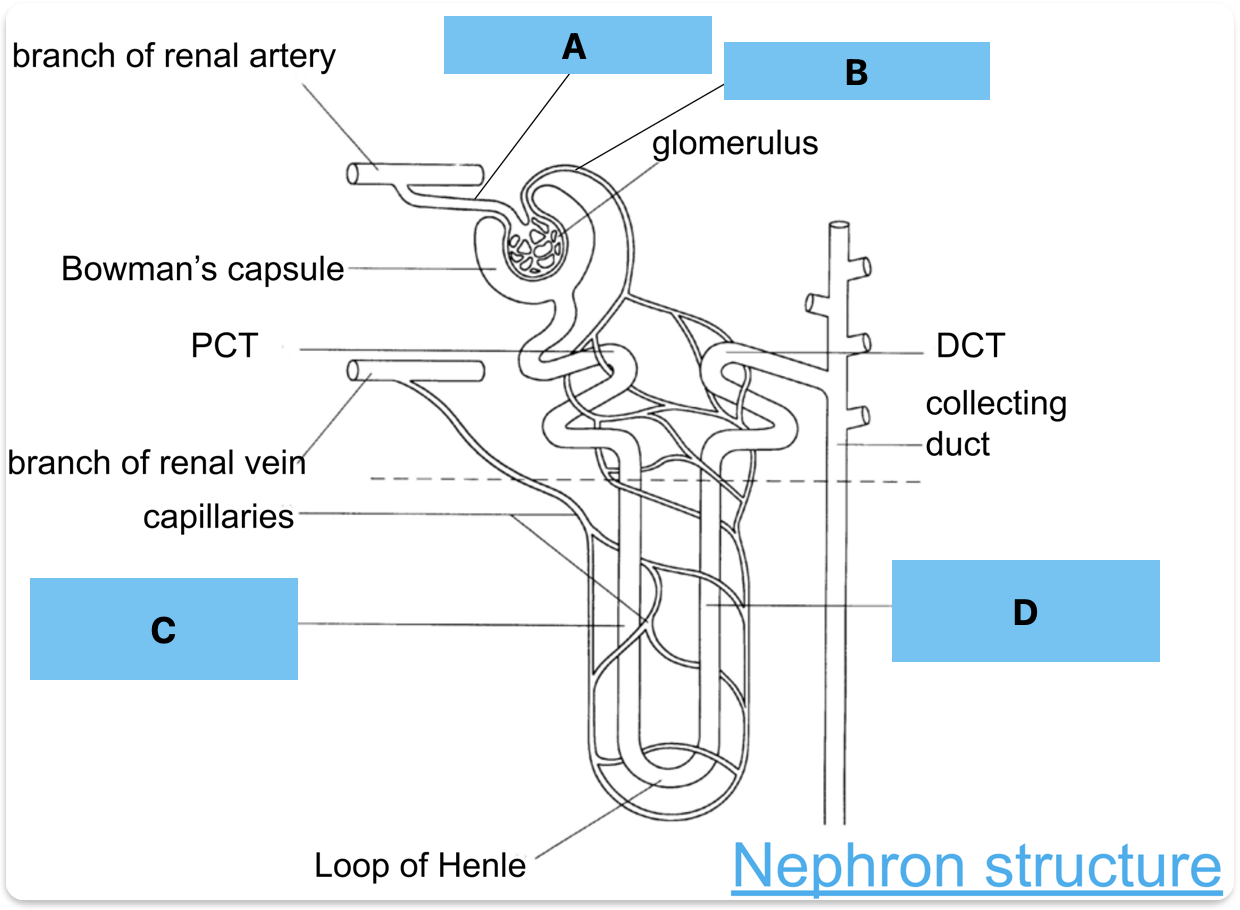
Label A-D
Afferent arteriole
Efferent arteriole
Descending LOH
Ascending LOH
Vasa recta
Surrounding capillary network
Delivers nutrients and oxygen
How is each molecule selectively reabsorbed
Glucose + amino acids - co-transport with Na+
Water - osmosis because solutes leave
Urea - 50% reabsorption by diffusion
How does the loop of henle work
Ions are pumped out actively from ascending limb causing solute potential in medulla to increase
Water moves out descending limb into the blood via osmosis
Descending limb then becomes even more concentrated as it goes down
What is each loop permeable to
Descending loop permeable to water so it can move out
Ascending loop impermeable so ions move out
What happens when there’s a decrease in water potential in the blood plasma
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect decrease in water potential
Posterior pituitary releases ADH
Cells of DCT and collecting duct become more permeable due to aquaporins fusing will cell membrane
More water then reabsorbed from CD into blood
Small volume of concentrated urine then produced
What happens when an increase in water potential is detected
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect
Posterior lobe of pituitary stops release of ADH
DCT and CD become less permeable as aquaporins move out the membrane
Less water reabsorbed into blood
Large volume of dilute urine produced
Treating kidney disease (4)
Low protein diet
Drugs
Dialysis
Kidney transplant
Drugs to reduce blood pressure
Calcium channel blockers
Beta blockers - adrenaline
Describe haemodialysis
Blood is taken from arm and places in countercurrent to dialysis fluid in a machine
Small molecules move through pores but not large molecules
Blood is then returned to the vein
ions and urea diffuse down concentration gradients
Continuos ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
Dialysis fluid passes into abdominal cavity
after 40 mins the fluid is drained form the abdomen into a bag