COMMUNICABLE DISEASE
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Normal Flora (Resident Microbes )
Microorganisms (usually bacteria) that normally exist in the body and are Harmless
Transient Microbes
Microorganisms that we acquire when we interact with other humans or our environment
Under some conditions, the interaction with endogenous microbes can be harmful for the host, and opportunistic infections may occur.
Body Defenses
First Line of Defense (External Defense System)
Second Line of Defense (Immune Response)
First Line of Defense (External Defense System)
SKIN
Chemical Barriers (secretions such as tears, saliva, sweat and mucus)
Second Line of Defense (Immune Response)
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) seek out and destroy disease-causing organisms or substances through the lymphatic system
types of (Immune Response)
• Neutrophils • T helper cells • Cytotoxic T cells • Macrophages • Dendrite cells • B cells • Suppressor T cells
How Reproduction of Microorganisms Injure the Patient?
• Competes with the host metabolism
• Cellular damage produced by microbes
• Intracellular multiplication
The Infectious Process
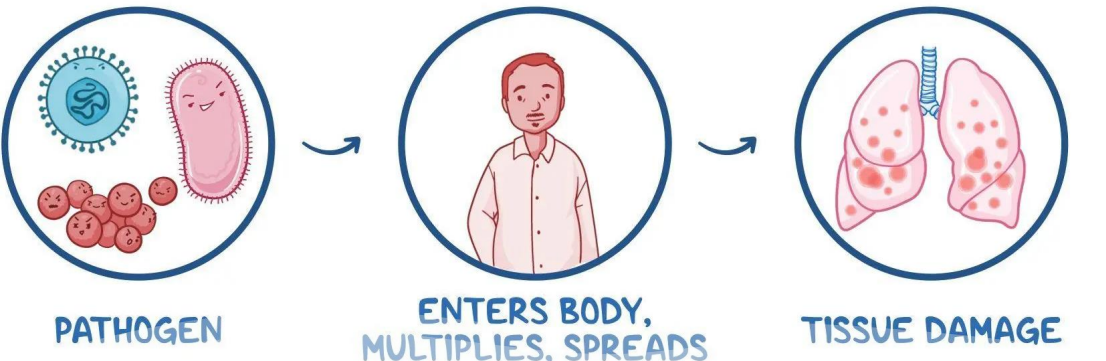
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases
• Entry of the pathogen into the body
• Attachment of pathogen to some tissues within the body
• Multiplication of the pathogen
• Invasion/spread of the pathogen
• Evasion of host defenses
Infection
Entry and multiplication of an infectious agent in or on the tissue of a host causing CLINICAL SIGNS and SYMPTOMS.
Colonization
Infectious agent fails to cause injury to the host. (WITHOUT SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS)
Infectious Disease
State in which the infected host displays a decline in wellness due to the infection
Virulence
How harmful the pathogen is.
Colonization x Infection x Infectious Disease
Microbiology Laboratory Reports (Primary source of information about most bacterial infections)
3 components:
• Smear and stain
• Culture- organism identification
• Sensitivity- antimicrobial susceptibility
Why Does Infection Occur?
• Antibiotic and Antiviral Drug Resistance
• Multiple strains (viruses/influenza) that a single vaccine cannot protect against them.
• New infectious agents occasionally arise (HIV and Coronavirus).
• Opportunistic organism can cause infection in immunocompromised patients.
• Microbes localize in the body making the treatment difficult (bones and CNS)
• No immunization.
• Increase in air travel can spread virulent organisms to a heavily populated area within hours and over great distances.
• Biologic warfare and bioterrorism (anthrax and plague).
• Use of immunosuppressive drugs and invasive procedures increases the risk of infection.
4 Stages of Infection
INCUBATION PERIOD
PRODROMAL STAGE
ILLNESS STAGE
CONVALESCENT STAGE
INCUBATION PERIOD
agent’s entry in the host and the onset of symptoms
• Silent stage (no symptoms)
• Transmission and replication
PRODROMAL STAGE
onset of nonspecific symptoms until specific symptoms begin to manifest
• Vague complaint (mild and generalized symptoms)
• E.g. low-grade fever, body weakness, fatigue
ILLNESS STAGE
manifesting specific symptoms of an infectious process.
• Clinical stage
CONVALESCENT STAGE
acute symptoms begin to disappear until the client returns to previous state of health
• Healing stage
Kinds of Infection
1. Subclinical or Asymptomatic
2. Latent infection
3. Exogenous Infection (Cross infection)
4. Endogenous Infection
5. Health care-associated Infections (HAIs) (nosocomial infection)
1. Subclinical or Asymptomatic
• Laboratory-verified infection that presents no signs and symptoms.
• A person may be a carrier and can transmit infection to others
2. Latent infection
Occurs when microorganism remains inactive and dormant in the host and may last for years
3. Exogenous Infection (Cross infection)
Due to microorganism entering the host’s body from the environment.
4. Endogenous Infection
Normal flora is transmitted to sites outside their natural habitat
5. Health care-associated Infections (HAIs) (nosocomial infection)
• Develops while the patient is in a health care facility.
• Mostly transmitted through direct contact
Disease
• Any condition that impairs or damages the normal structure or function of an organ or the body
Geographical Distribution of Diseases
Endemic
Epidemic
Pandemic
Sporadic
Endemic
• Disease found in a certain geographical area/region or in a specific group of people within a country.
• Ex. Schistosomiasis is rampant in Samar and Leyte provinces
Epidemic
• Disease that occur in greater than expected numbers in a specific area over a particular time. • A sudden rise in the number of cases more than what is expected.
• Ex. Increase of diarrheal disease in an evacuation area.
Pandemic
An epidemic that affects several countries or continents. Ex. HIV/AIDs
Sporadic
• Diseases that occur occasionally and irregularly with no specific pattern. Usually involve few people during a particular time. • Ex. Tetanus, gas gangrene
Primary prevention
• Promote health • Prevent exposure • Prevent disease
Secondary prevention
Stop or slow the progression of disease to prevent or limit permanent damage, through the early detection and treatment of disease
Tertiary prevention
• Limit the impact of that damage
Disease is the result of all agent forces within the dynamic system consisting of the following:
• Agent
• Host
• Environment
Infectious Agent
Microorganisms or pathogens that cause infection
Factors influencing the cause of disease:
Pathogenicity
Infectivity
Virulence
Infective dose
Pathogenicity
ability of organism to cause disease.
Infectivity
ability of the organism to infect the host.
Virulence
ability of the organism to produce disease.
Infective dose
number of organisms and the amount of toxin released by the organism needed to induce the disease.
Host
1. Patient (case)
2. Carrier
3. Suspect
4. Contact
1. Patient (case)
infected and manifests the sign and symptoms of the disease.
• Someone who needs medical care and treatment.
2. Carrier
appears healthy but harbors the organism.
• Capable of transmitting the disease but does not manifest its signs and symptoms.
3. Suspect
Person whose medical history, signs and symptoms suggest that such a person is suffering from that particular disease
4. Contact
Person who has been in close association with an infected person, animal, object.
Environment Components
Physical- inanimate surroundings (geophysical condition and climate)
Biological- living things around the affected individual (plants and animal life)
Socio-economic- level of economic development (crowding, sanitation availability of health services)
Chains of Infection
Infectious Agent
Reservoir
Portal of Exit
Mode of Transmission
Portal of Entry
Susceptible Host
Infectious Agent
An Organism that causes disease.
Reservoir
The place where an infectious agent lives and multiply
Portal of Exit
Route in which the organism leaves the reservoir
Mode of Transmission
How the infectious agent travels from the infected person to another person
Portal of Entry
Any body opening that allows the infectious agent to enter
Susceptible Host
A non-infected person who could get infected.
General IPC measures:
UNIVERSAL PRECAUTION - Set of guidelines focused on preventing blood-borne pathogens.
Isolation Precautions
• Standard precaution
• Transmission-based precaution
Standard Precaution
• Principle: “All blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions (except sweat), non-intact skin, and mucous membranes may contain transmissible infectious agents.”
Patient Placement
Empiric Precautions
Cohort Isolation
Designated ward-specific Precautions
Empiric Precautions
single room
Cohort Isolation
Patients with same infectious condition= same room, if single room is not feasible.
Designated ward-specific Precautions
In hospitals with a consistent large number of patients with the same infectious condition= allocated specific ward
Social Hand Hygiene
at least 20 seconds
When hands are visibly dirty or contaminated with biological materials:
Hand wash with soap and water.
When hands are not visibly soiled:
Use alcohol-based, waterless antiseptic agents for routine decontamination
In areas with known virulent or resistant organisms are likely to be present:
Use antimicrobial agents (e.g., Chlorhexidine gluconate)
Exposure to sporeforming pathogens (C. difficile outbreaks)
Use Gloves and perform hand washing with antimicrobial soap and water
Surgical masks Placed on healthcare personnel
to protect them from contact with infectious material from patient
-Respirators reduce airborne pathogens
Surgical masks Placed on coughing patient
to limit potential dissemination of infectious respiratory secretions.
Decontamination of the Environment
environment should be cleaned with a neutral detergent and water except in circumstances that require additional disinfection (e.g., blood and body fluid spillages) or contamination of specific organism that require patient to be isolated.
Blood spillage management
Cover spillage with disinfectant
Body fluid management
Do not use chlorinebased disinfectants directly on acidic solution
Disinfection of Equipment
Non-critical equipment (Low-Risk)
Semi-critical /critical (Intermediate/High risk)
Non-critical equipment (Low-Risk)
Use neutral detergent and water
Semi-critical /critical (Intermediate/High risk)
decontamination and sterilization.
Healthcare waste management:
Black - Dry noninfectious waste.
Green -Wet noninfectious waste.
Yellow - Infectious waste.
Puncture proof containers - Sharps
Needlestick Prevention
• Do not recap used needles.
Instead, place it directly into punctureresistant containers at the point of use.
Use one-handed scoop technique or deploy safety device attached to the needle.
Sharps containers must be locked when two-thirds full prevent overfilling. Do not push the needles into a container that is full.
Airborne Precaution
• Isolation room with negative pressure (minimum 6 air exchanges), rapid turnover of air and air either highly filtered or exhausted directly outside.
• Healthcare workers must always wear N95 respirators.
• Room doors should remain close at all times.
• Nurse should validate negative air pressure of the room
Droplet Precaution
close respiratory or mucous membrane contact with respiratory droplet
• Wear surgical face mask
• Stand 3-6 feet away form the patient.
• Room doors may be opened.
• May cohort patient.
Contact Precaution
• Used for organisms that are spread by skin-to-skin contact (direct contact) or contact with environment (indirect contact).
• Hand hygiene
• Gloves and gown are a must.
• Preferably private room.
• Masks are not needed.
• Doors do not need to be closed.
Protective Environment (Reverse Isolation)
Expanded isolation technique used for immunocompromised condition.
• Stem cell transplantation
• Conditions that severely suppress immune system (HIV/AIDs; Cancer)
Interventions
• Special airflow and filtration rooms (+ air pressure, smooth surfaces).
• Staff must be free from signs and symptoms of illness.
• Sterile PPE when caring for patient.
• Limit visitors (<12 y.o. are not allowed).
Health CareAssociated Infections
Specific criteria: Length of time in the facility before the onset or appearance of the infection.
• If new symptoms appear within 48 hours of admission, 3 days after discharge, or 30 days after an operation
Nursing interventions to prevent HAI
Primary way to break the chain of infection: HAND WASHING.
Preventive measures: IMMUNIZATION
Disposal of infectious materials to moistureresistant biohazard containers.
Reducing catheter related infections:
Specific Organism with HAI Potential
Clostridium Difficile
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
Clostridium Difficile
Handwashing with soap and water is recommended
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Vancomycin and Linezolid are the treatment of choice
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
penicillin formulations (ampicillin), aminoglycosides (gentamycin), and linezolid
Aspects of Care of Patients with Communicable Diseases
Preventive Aspect: Health Education, Immunization, Immunity
Curative Aspect: Medical Management (physicians), Nursing Management
Rehabilitative Aspect: Activity, Nutrition
• Measles and Polio are highly heat sensitive=
store in freezer
Only BCG is discarded 4 hours after reconstitution
(immunization is scheduled in the morning)
Types of Antigen:
Inactivated (killed organism)
Live attenuated (weakened)
Inactivated (killed organism)
• Multiple doses are needed. • A booster dose is needed.
Live attenuated (weakened)
• Only single dose is needed • Confers to long lasting immunity
What Damages Vaccine?
• Heat and light (especially live vaccines)
• Freezing damages the killed vaccine and toxoid
• Antiseptics, disinfectants, detergents and alcohol lessens potency of vaccine. (Use WATER when cleaning the ref/freezer
Contraindications to Vaccines
All vaccines may be given at the same visit,
If vaccines must be given of separate visits interval should at least 4 weeks.
If patient develops encephalitis, anaphylaxis or a moderate to severe sequelae of a previous vaccine, DO NOT GIVE THE NEXT DOSE!
Some live vaccines (varicella &MMR) must not be given to immunocompromised people and pregnant.
Reducing Risk To The Patient
• Catheter-related sepsis should be suspected in a patient who has unexplained fever, redness, swelling, and drainage around a vascular catheter insertion site.
• Patient teaching must emphasize that home needs must be “clean” not sterile.
• For immunocompromised patient, restrict visitors who are sick, and family members should be reminded to follow recommendations for hygiene, storage, and safe cooking times and temperatures