anatomy lec9 Joints
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Which joint allows for flexion and extension only?
A. Pivot joint
B. Hinge joint
C. Saddle joint
D. Ball-and-socket joint
B
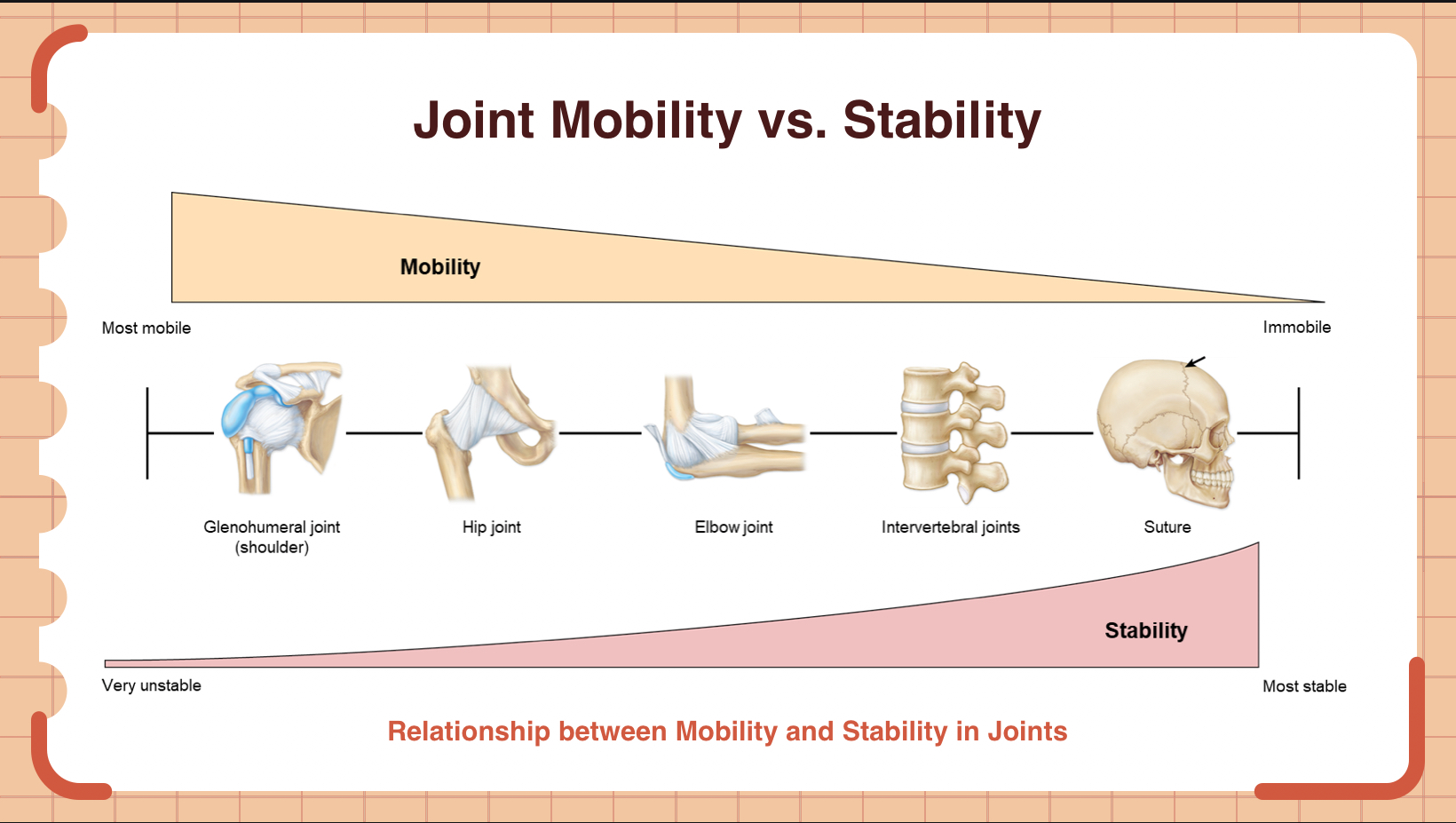
True or False: Joints with more mobility generally have greater stability.
A) True
B) False
B
attach slide 3
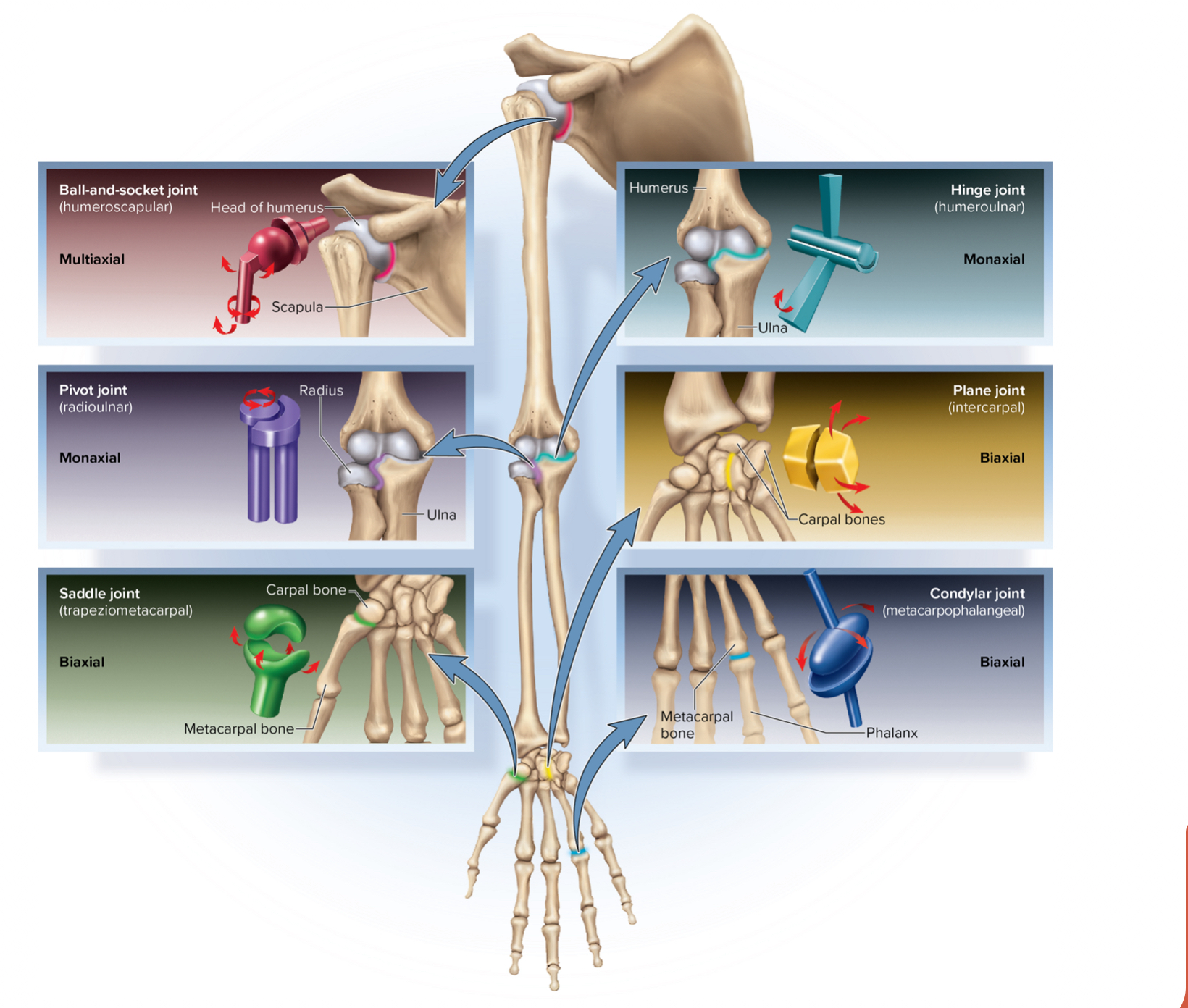
What type of joint is classified as a triaxial joint?
A) Condylar joint
B) Pivot joint
C) Hinge joint
D) Ball-and-socket joint
D
Which type of connective tissue binds bone to bone in ligaments?
A) Elastic connective tissue
B) Dense irregular connective tissue
C) Hyaline cartilage
D) Dense regular connective tissue
D (This tissue is characterized by its collagen fibers arranged in parallel, providing tensile strength and resistance to stretching in one direction)
check ex on slide 36
Describe the structural differences between fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints.
Fibrous: Dense tissue, no cavity (space btw articulating bones), most are immobile (synarthrosis)
Cartilaginous: Articulating bones joined by cartilage, no cavity (space btw articulating bones), little to no movement (AKA ampi/synarthrosis)
Synovial: Fluid-filled cavity, capsule, cartilage, ligaments…. functionally classified as diarthrosis, makes up most joints
A(n) _________ joint is an immobile joint
A) synarthrosis
B) amphiarthrosis
C) diarthrosis
D) synovial
A
Which of the following injuries involves the stretching or tearing of ligaments?
A) Strain
B) Sprain
C) Fracture
D) Dislocation
B
Which type of joint is held together by dense regular connective tissue?
A) Synovial
B) Cartilaginous
C) Fibrous
D) Bony
C
Explain the inverse relationship between mobility and stability in joints. Provide an example.
Joints that are more mobile tend to be less stable, and vice versa. This is because the structure of the joint often trades off stability for increased range of motion. For example, the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is highly mobile but is more unstable, making it more at risk of dislocations. In contrast, sutures in the skull are very stable (immobile) and provide strong protection for the brain.
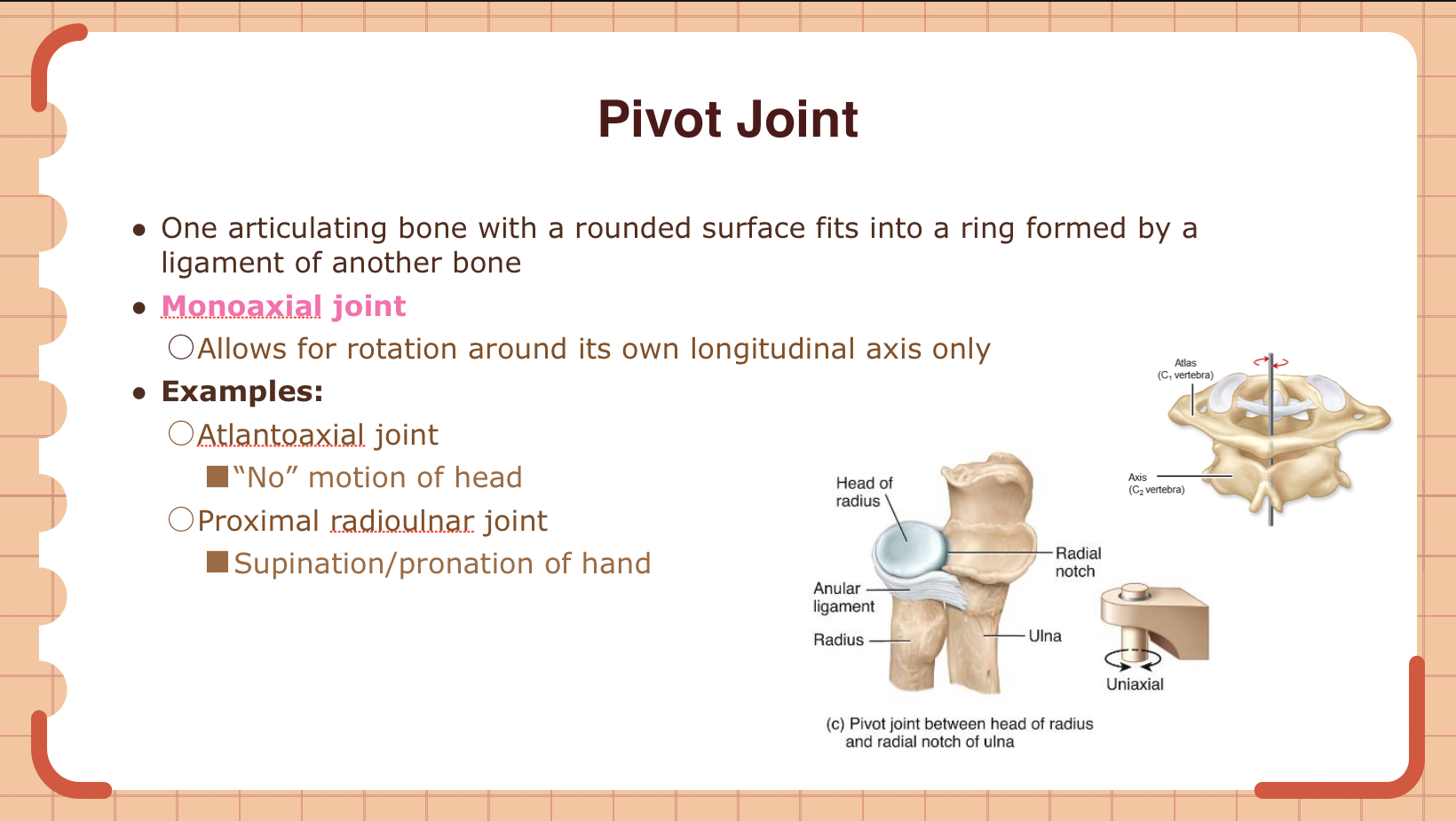
The atlantoaxial joint allows for what movement of the head?
A) Nodding "yes"
B) Shaking "no"
C) Tilting side to side
D) Circumduction
B
Which movement is allowed by a pivot joint?
A) Flexion and extension
B) Abduction and adduction in a plane
C) Rotation around its longitudinal axis
D) Gliding
C
attach slide 29
True or False: Sutures are functionally classified as amphiarthroses.
A) True
B) False
B (sutures are classified are synarthrosis bcuz they are immobile fibrous joint)
Which type of fibrous joint is characterized by articulating bones joined by long strands of dense regular connective tissue, such as the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna?
A) Syndesmoses
B) Suture
C) Gomphoses
D) Synostosis
A
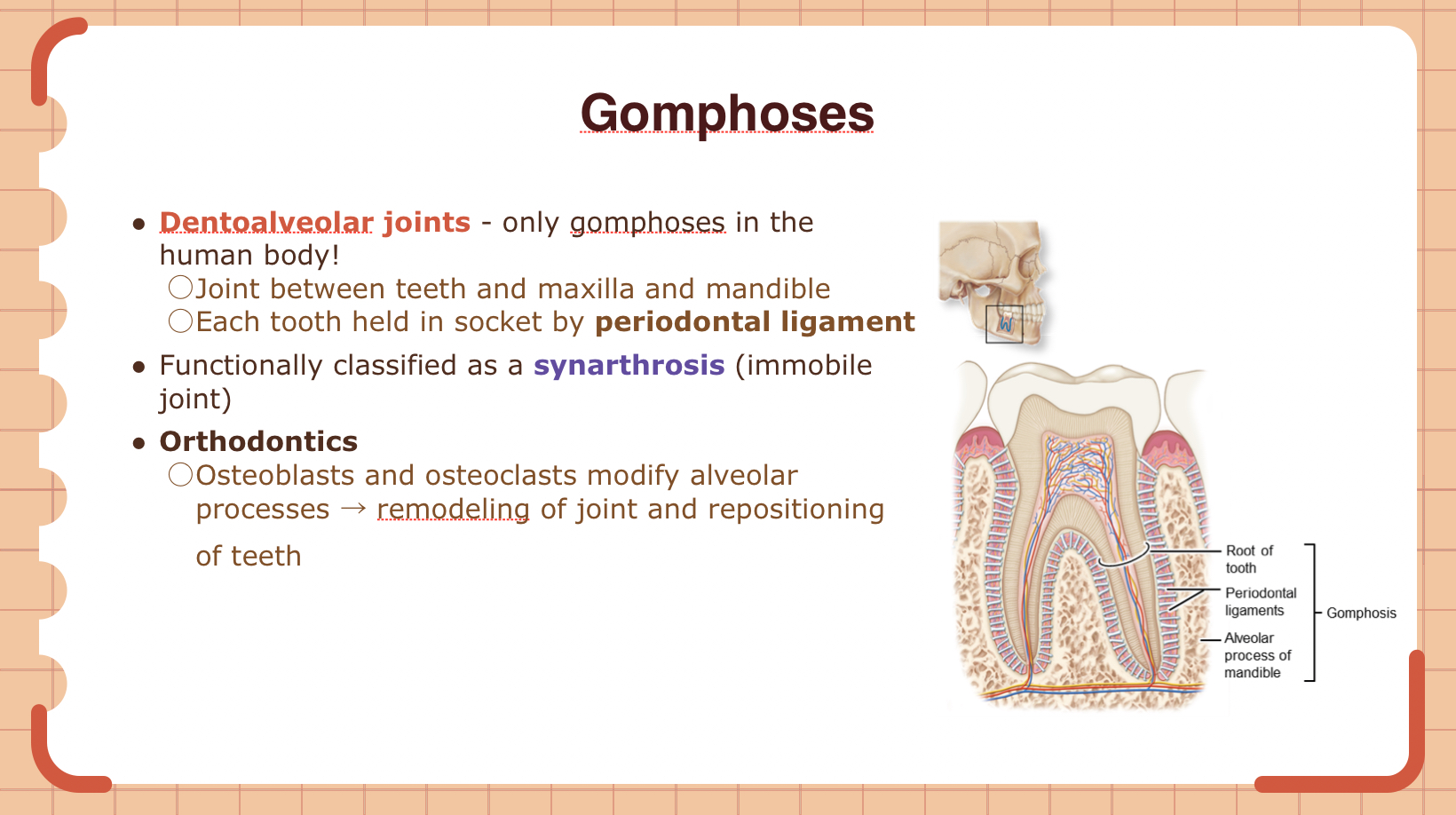
Explain the process and significance of remodeling in dentoalveolar joints.
Remodeling in dentoalveolar joints repositions teeth via osteoblast/osteoclast activity, modifying alveolar bone. This process is crucial in orthodontics.
attach slide 8
Which of the following structures is a fluid-filled saclike extension of the joint capsule that reduces friction between moving structures?
A) Tendon sheath
B) Ligament
C) Meniscus
D) Bursa
D
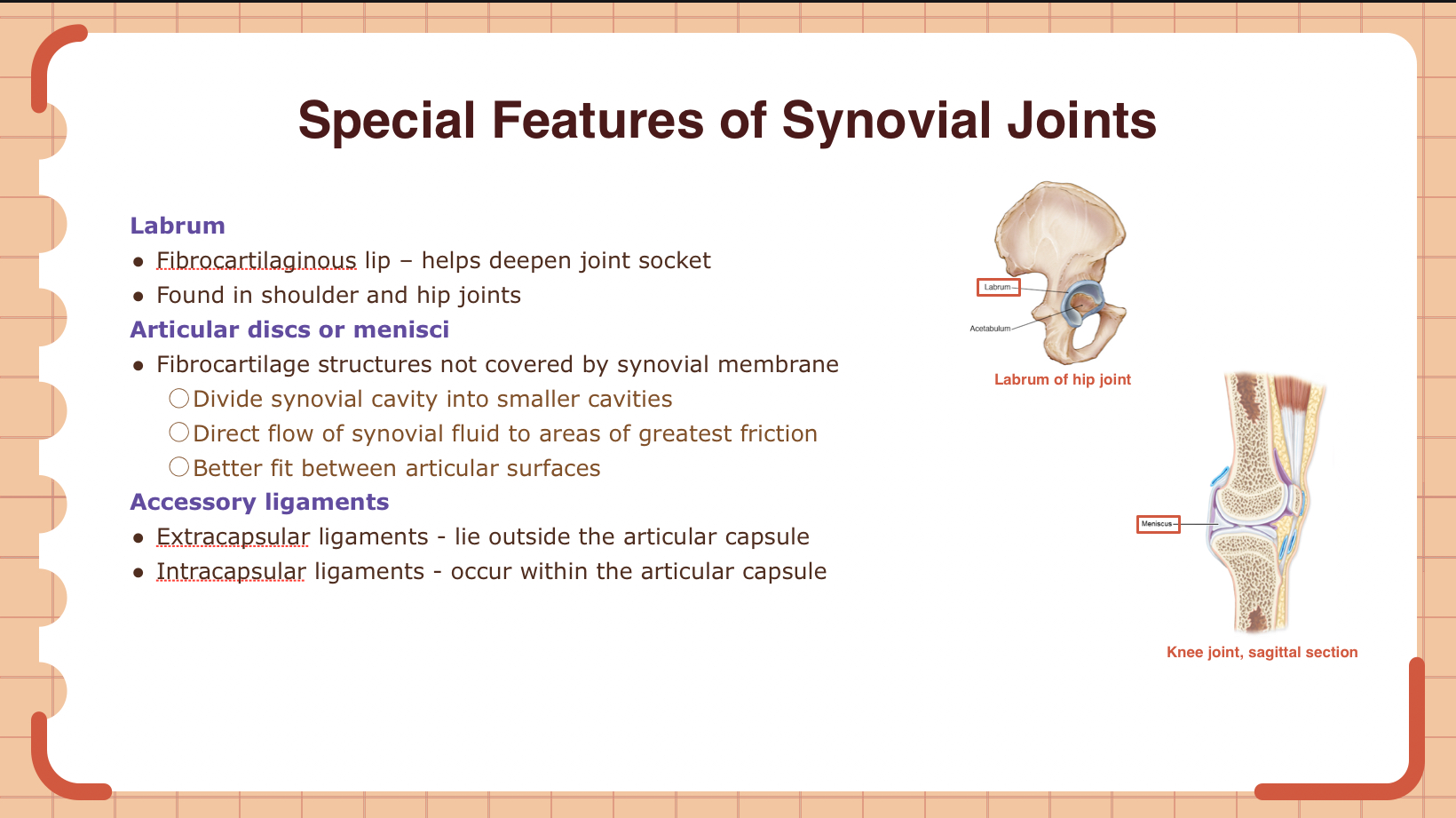
What is the function of the labrum found in some synovial joints like the shoulder and hip?
A) To reduce friction between bones
B) To deepen the joint socket
C) To produce synovial fluid
D) To attach muscles to bones
B
Attach slide 19
What type of cartilage covers the articulating surfaces of synovial joints, reducing friction and acting as a shock absorber?
A) Elastic cartilage
B) Hyaline cartilage
C) Fibrocartilage
D) Reticular cartilage
B (also called articular cartilage)
attach image on slide 18
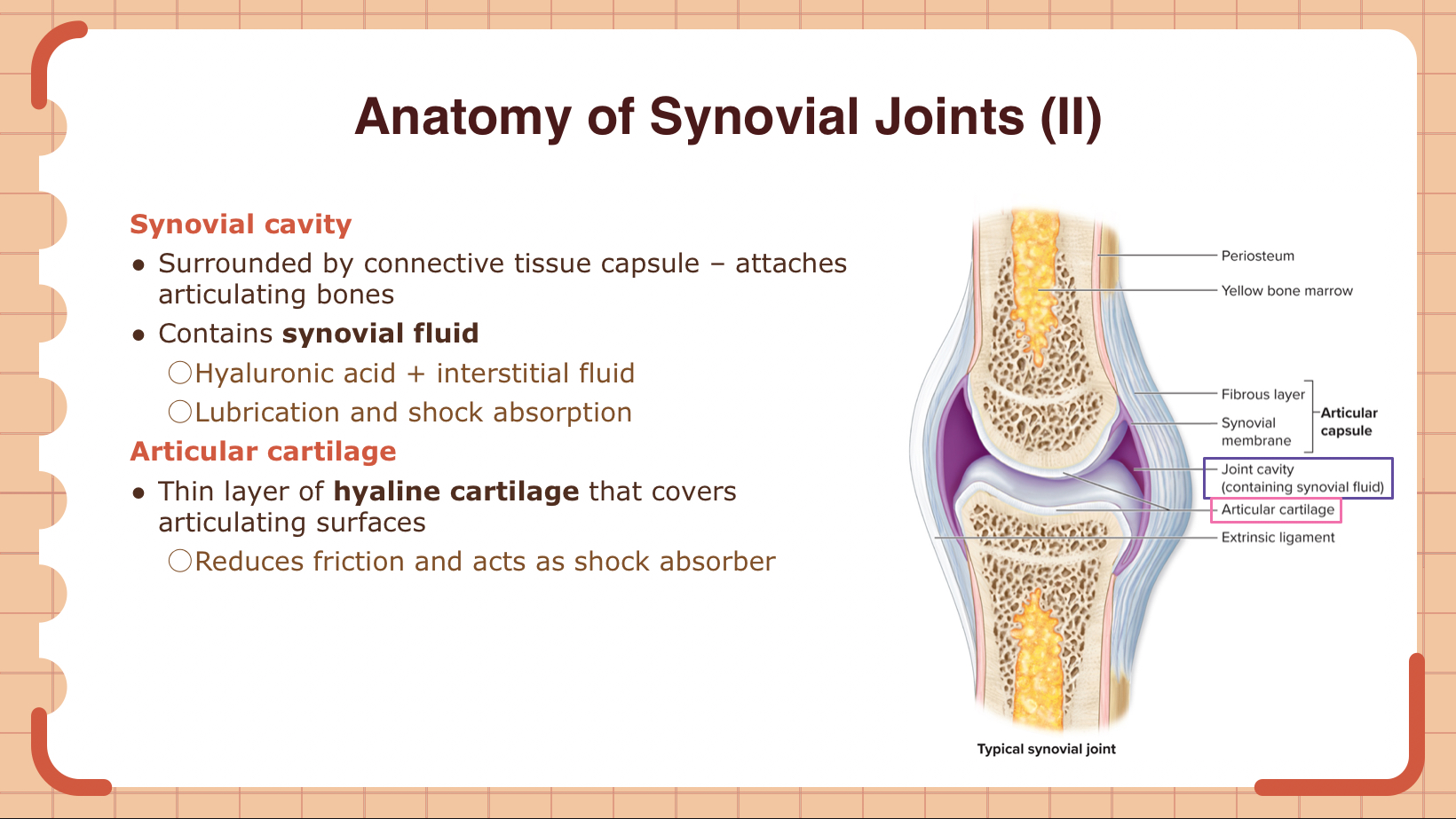
Synovial fluid contains ________ and _________
Hyaluronic acid and interstitial fluid
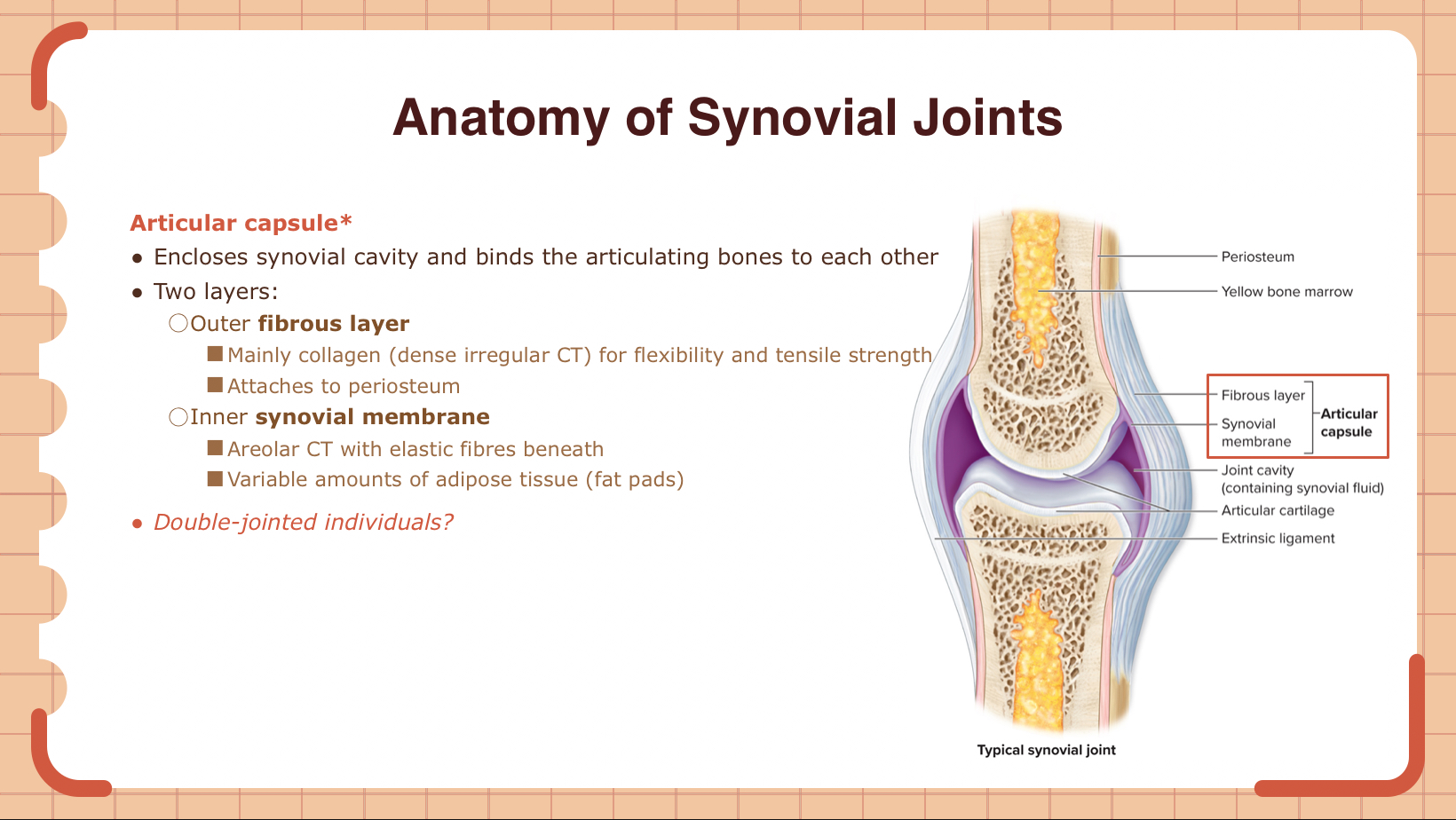
The outer fibrous layer of the articular capsule is composed of:
A) Hyaline cartilage
B) Dense regular connective tissue
C) Dense irregular connective tissue
D) Adipose tissue
C
attach slide 17
Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing feature of synovial joints?
A) Articular capsule
B) Nerve and blood vessels
C) Synovial fluid
D) Tendons
D (tendons are associated with muscles and help stabilize joints, they are not structural features of synovial joints themselves. They attach muscle to bone)
The pubic symphysis is an example of a(n) __________, which is functionally classified as an amphiarthrosis.
A) synchondrosis
B) symphyses
C) suture
D) syndesmosis
B (its amphiarthrosis bcuz it becomes more mobile during pregnancy)
Epiphyseal plates are examples of which type of joint?
A) Symphysis
B) Syndesmosis
C) Synchondrosis
D) Gomphosis
C
Describe the structure and function of the articular capsule in a synovial joint.
The articular capsule encloses the synovial cavity and binds the articulating bones to each other. It has two layers: an outer fibrous layer made of dense irregular connective tissue for flexibility and tensile strength, and an inner synovial membrane made of areolar connective tissue with elastic fibers, responsible for producing synovial fluid.
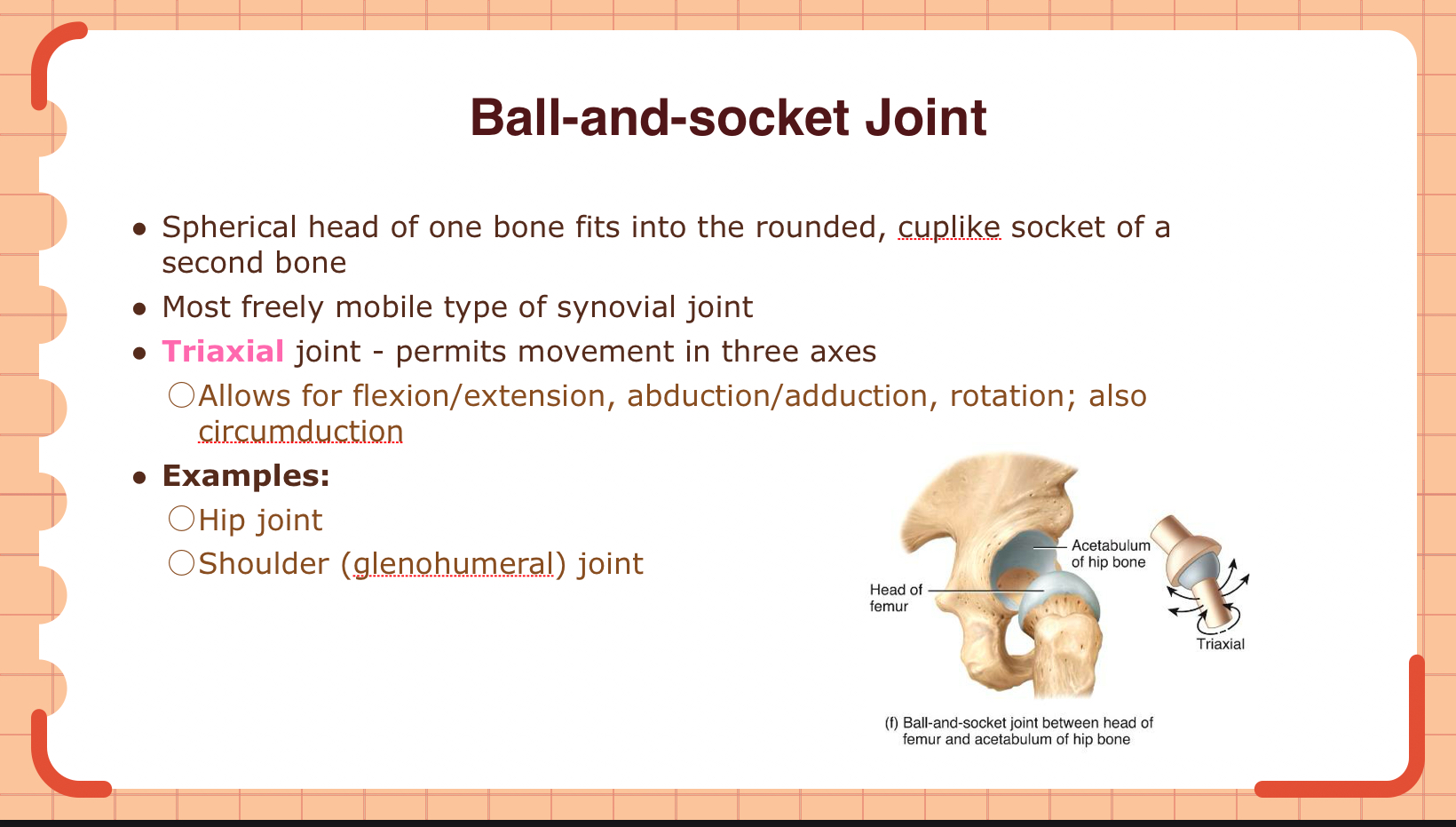
Describe the characteristics of a ball-and-socket joint.
Round head fits in cup-like socket
Freely mobile
Triaxial
Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, rotation, circumduction
Hip, shoulder joints
attach slide 32
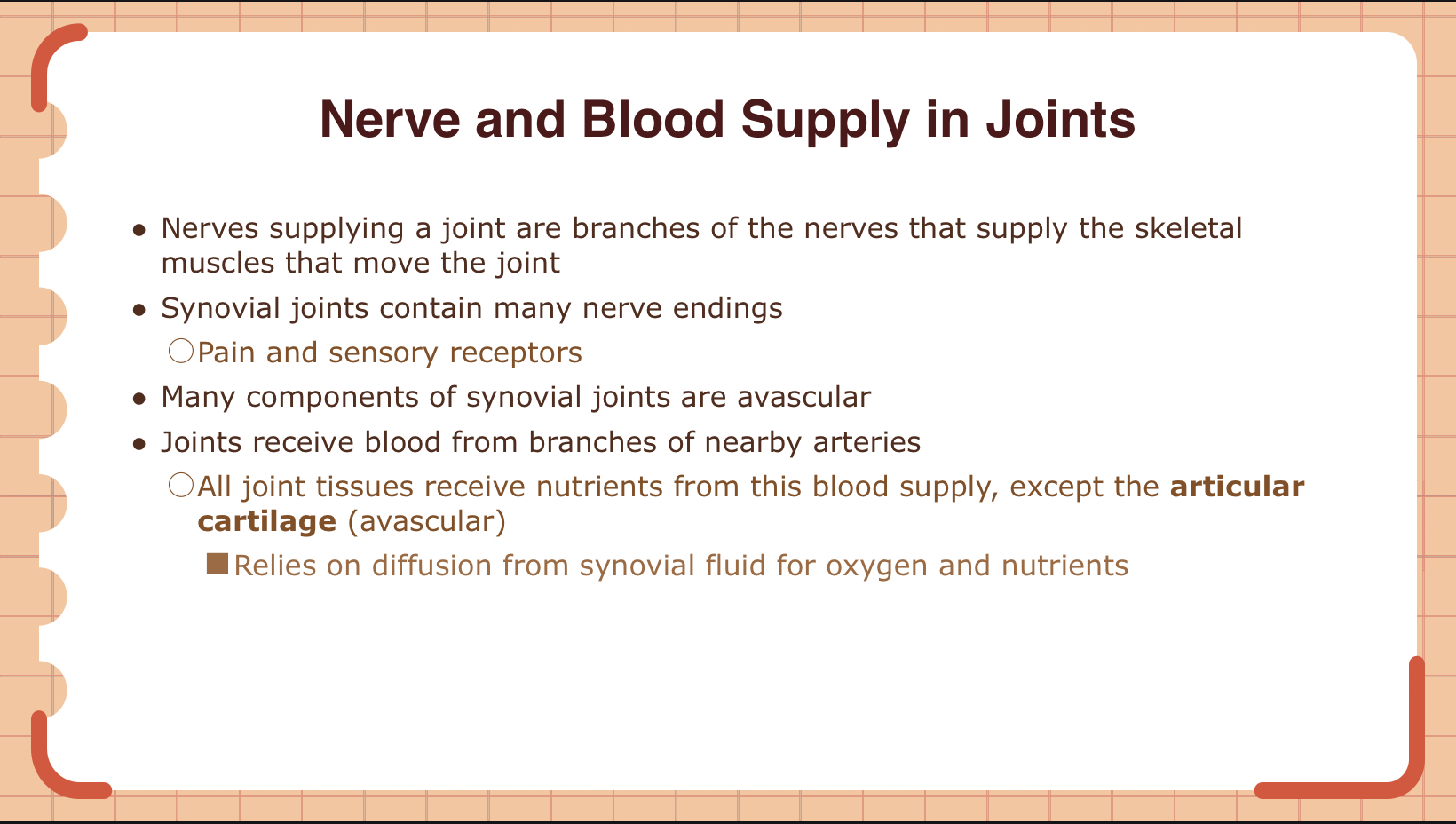
True or False: Articular cartilage in synovial joints relies on blood vessels for oxygen and nutrients.
A) True
B) False
B (all joint tissues receive nutrients from this blood supply except AC bcuz they’re avascular)
attach slide 21
Which type of motion does NOT occur at synovial joints?
A) Gliding
B) Angular motion
C) Rotation
D) None
D
A monoaxial joint moves in how many planes or axes?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
A
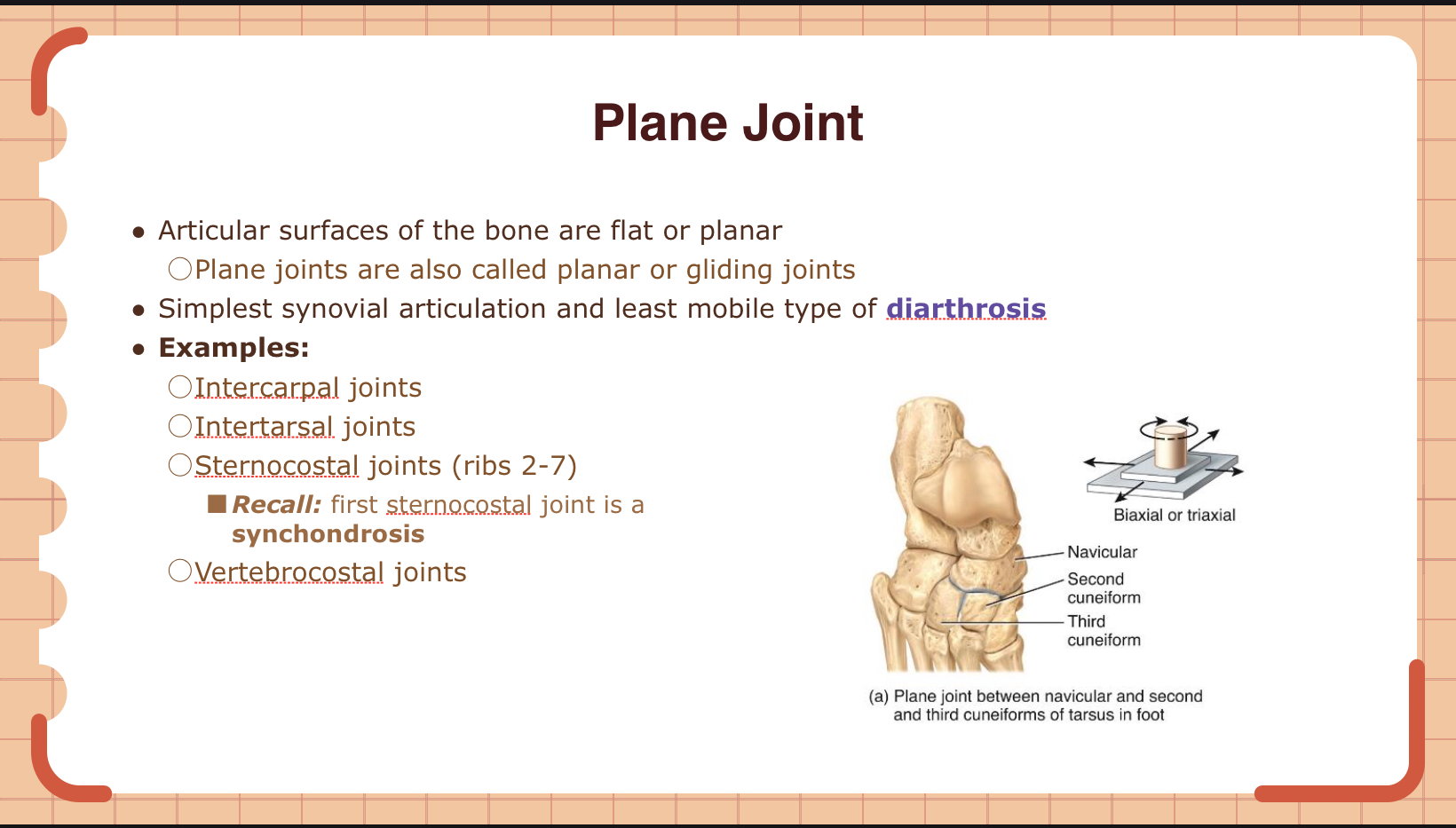
Which type of synovial joint is also known as a gliding joint?
A) Hinge joint
B) Pivot joint
C) Plane joint
D) Condylar joint
C
attach slide 27
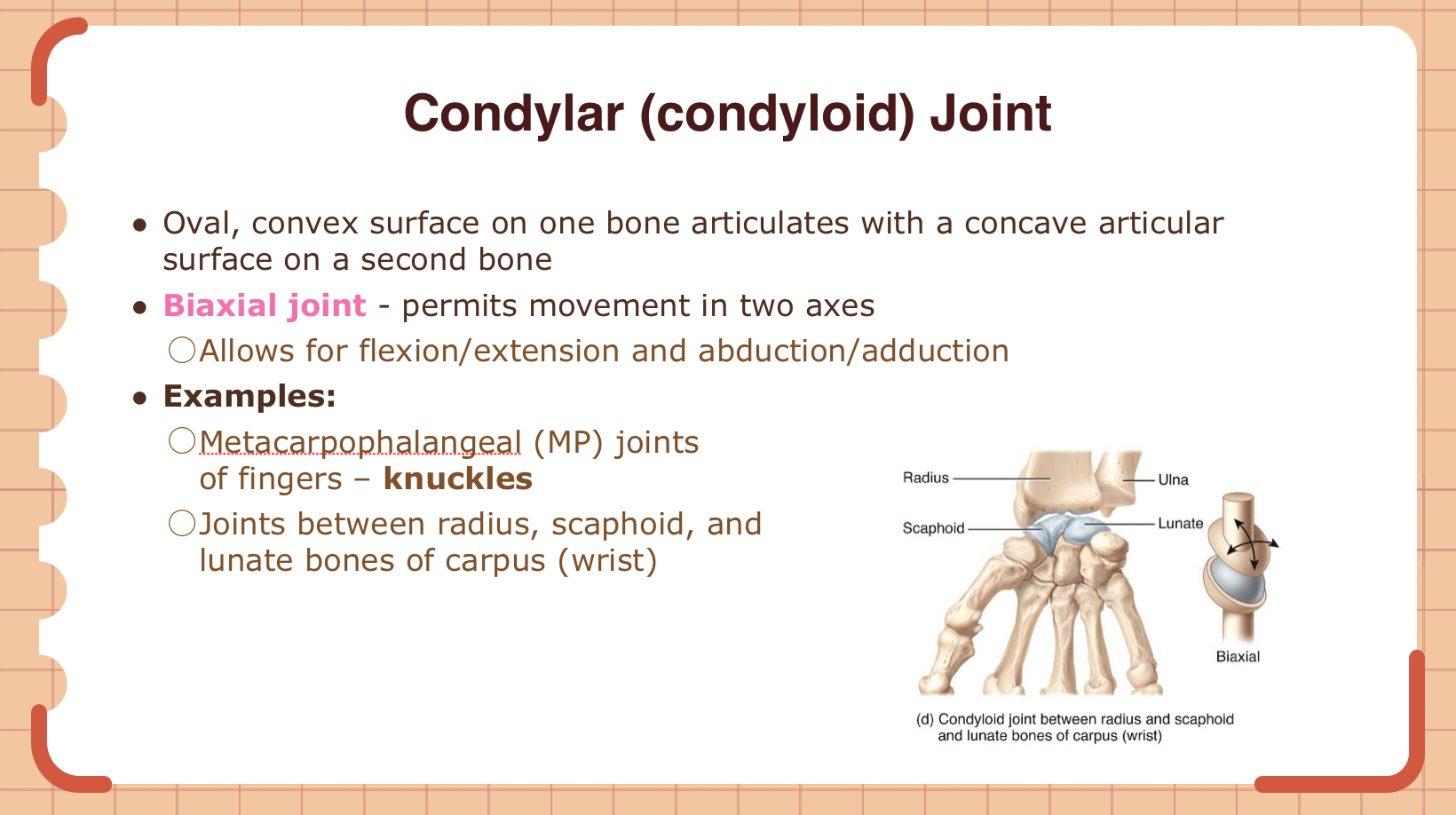
Metacarpophalangeal joints (knuckles) are examples of which type of synovial joint?
A) Saddle joint
B) Condylar joint
C) Ball-and-socket joint
D) Hinge joint
B (biaxial joint)
attach slide 30
What happens to joints as we age
A. Thickening of articular cartilage
B. Lengthening of ligaments
C. Increased synovial fluid production
D. Thinning of articular cartilage
D
slide 45
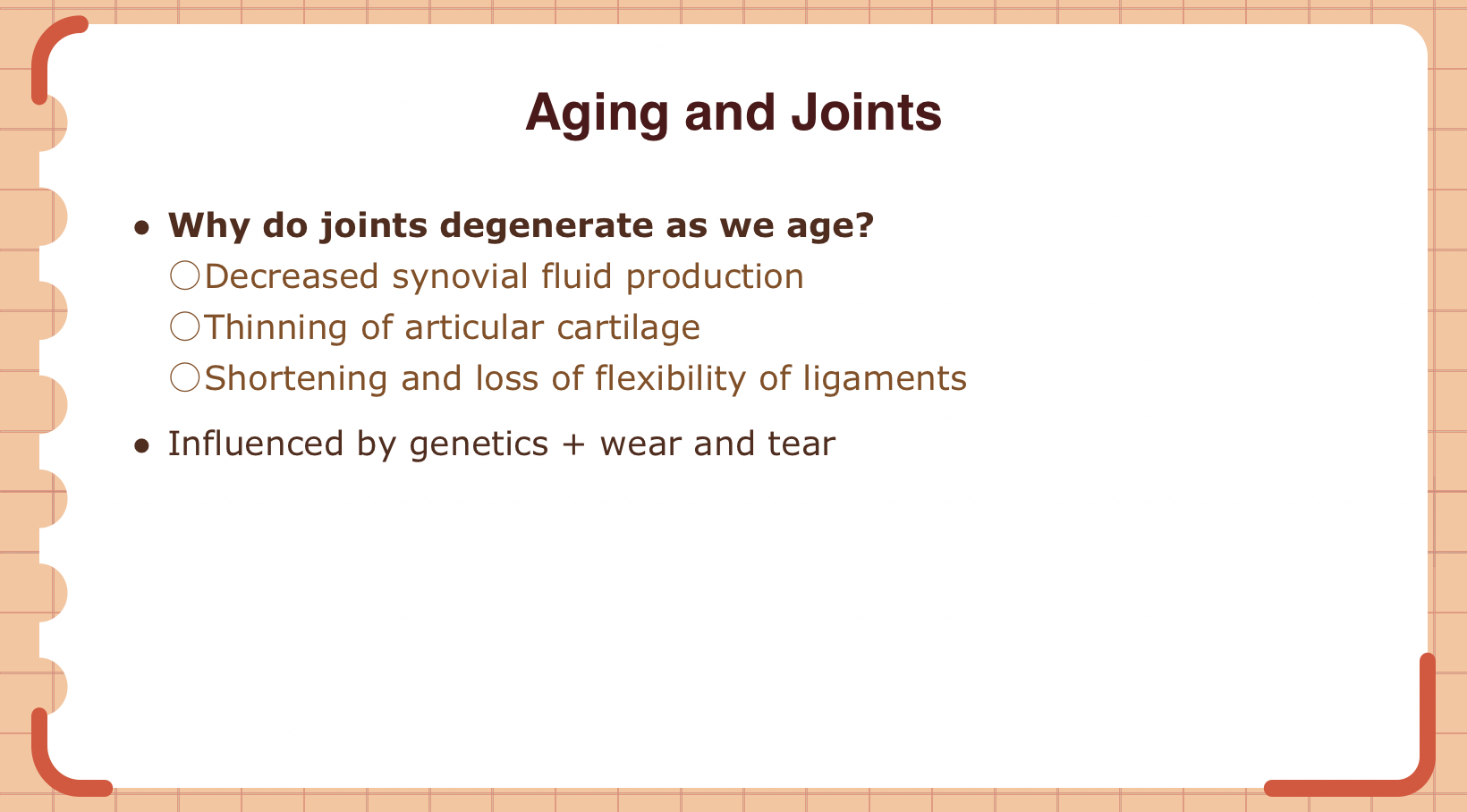
Which type of synovial joint permits thumb opposition?
A) Hinge joint
B) Saddle joint
C) Pivot joint
D) Ball-and-socket joint
B (biaxial joint)
attach slide 30
A patient has limited flexion and extension at the elbow. Which type of joint is most likely affected?
A) Plane joint
B) Hinge joint
C) Pivot joint
D) Condylar joint
B
As we age, decreased synovial fluid production and thinning of articular cartilage can lead to what condition?
A) Arthritis
B) Strain
C) Sprain
D) Fracture
A
Which factor does NOT affect the range of motion at synovial joints?
A) Shape of articulating bones
B) Strength of joint ligaments
C) Arrangement of muscles
D) Number of bones in the body
D (odd one out)
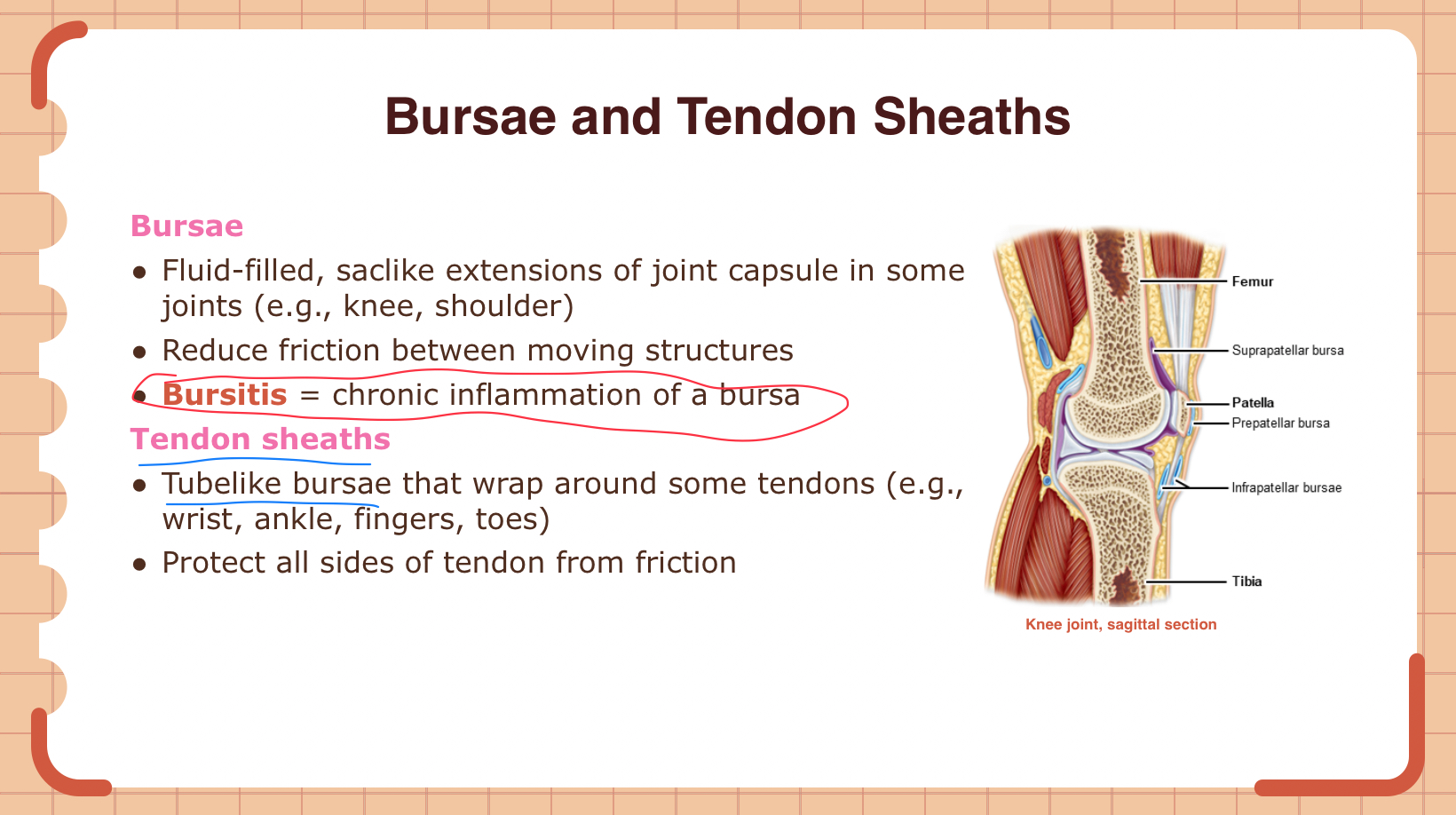
A patient presents with inflammation of the bursa in their knee. What is this condition called?
A) Tendonitis
B) Bursitis
C) Arthritis
D) Sprain
B
attach slide 20
How does articular cartilage receive nutrients, given that it is avascular
The articular cartilage is avascular, meaning it does not have its own blood supply. Instead, it relies on diffusion from the synovial fluid for oxygen and nutrients.
Bonus question
Explain the differences between gomphoses, suture, and syndesmoses joints.
Gomphoses: Tooth to socket, immobile.
Suture: Skull bones connected, immobile.
Syndesmoses: Bones linked by membrane, slightly mobile.
What type of cartilage is located between the bones in a symphysis?
A) Elastic cartilage
B) Reticular cartilage
C) Fibrocartilage
D) Hyaline cartilage
C
The joint movement called eversion involves
A) Turning the sole of the foot laterally
B) Turning the palm of the hand laterally
C) Lateral rotation of the hip joint
D) Medial rotation of the hip joint
A
The interosseous membrane between the radius and the ulna is an example of a:
A) Synchondrosis
B) Suture
C) Synarthrosis
D) Syndesmosis
D
attach slide 7
Clenching the fingers to make a fist, then relaxing and straightening them is an example of _____ and ______
flexion and extension
Look over moment slides form lecture 9