AP Bio Unit 1
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I'm going to kill myself
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Organic Molecules
Contains hydrogen and carbon
Inorganic Molecules
Does not contain hydrogen and carbon
Wolher’s Experiment
Demonstrated that organic compounds can be synthesized from inorganic precursors, specifically urea from ammonium cyanate. Essentially created the field of biochemistry.
Stanely Miller’s Experiment and the Origin of Life Results
Investigated the origins of life by simulating Earth's early conditions, producing organic compounds from inorganic substances. Presented theories on how life could have started.
Stanely Miller’s Experiment and the Origin of Life Conditions
A closed system of glass tubes and flasks; A boiling flask to simulate Earth’s oceans (water vapor); A chamber with a methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water vapor; Electrodes that produced electrical sparks to simulate lightning; A condenser to cool the gases so they could form droplets.
Eventually, organic compounds formed
Structural Isomers
Same atoms, but differ in their arrangement
Geometric Isomers
Share the same covalent bonds, but differ in arrangement around a double bond or ring (creating trans or cis isomers)
Optical Isomers (Enantiomers)
Molecules are mirror images of each other, but cannot be superimposed on one another
Dehydration Synthesis
Produces water and fuses two monomers together; Produces a water molecule and requires energy
Hydrolysis
Polymers are broken down into monomers. Requires water for each bond broken and releases energy
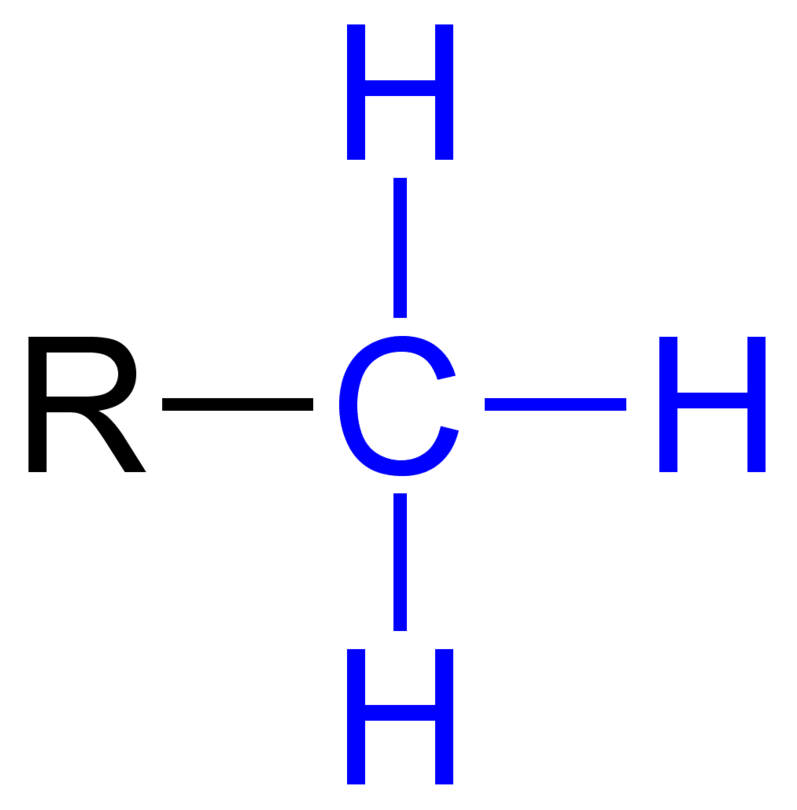
Methyl Group
Insoluble in water (because its non-polar)
Hydroxyl Group
Soluble in water (Polar + Hydrophillic)
Forms hydrogen bonds
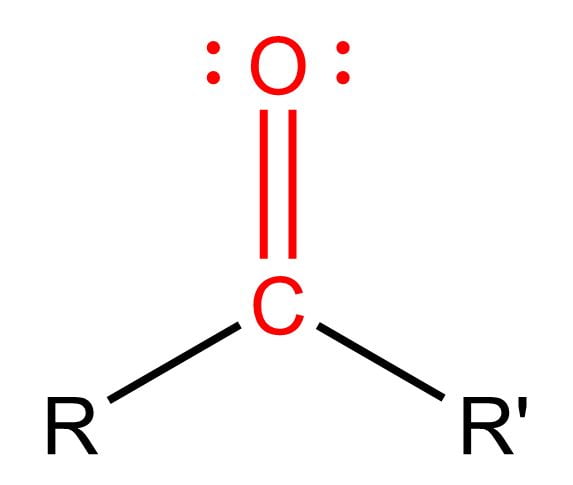
Carbonyl Group
Soluble in water
If on the terminal end = Aldehyde
If internal = Ketone
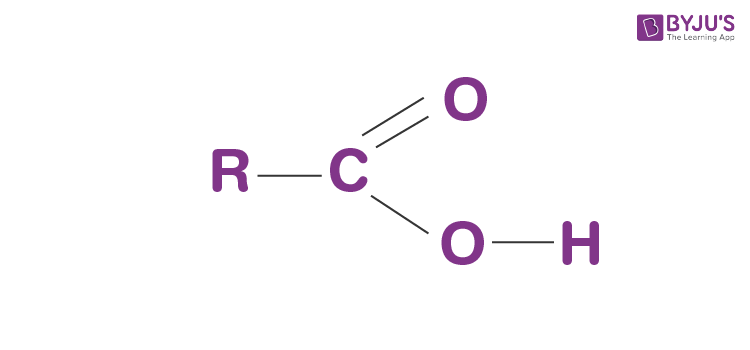
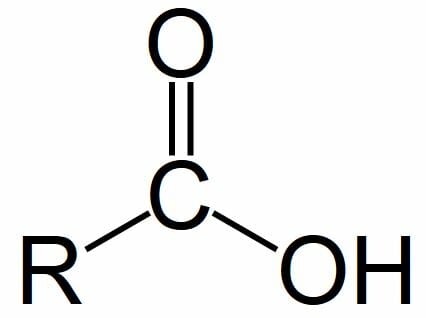
Carboxyl Group
Soluble in water (forms H+ bonds)
Dissociates to release H ions
Organic Acid
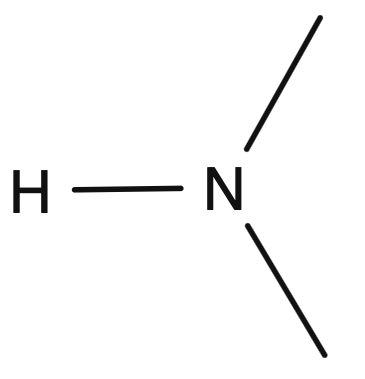
Amino Group
Soluble, forms H bonds
Usually accepts protons to formed charged group
Organic Base

Sufhydryl Group
Soluble (Forms weak H bonds)
Two SH groups are easily oxidized to form Disulfide bond
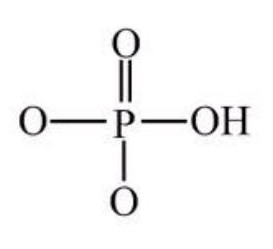
Phosphate Group
Formed when phosphoric acid
Combines with organic compounds
Soluble
Forms H bonds
Usually disociates to release H+ ions