Externalities
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
define negative production externality
A negative externality is a negative cost on a third caused by the actions of a producer
Draw a negative production externality
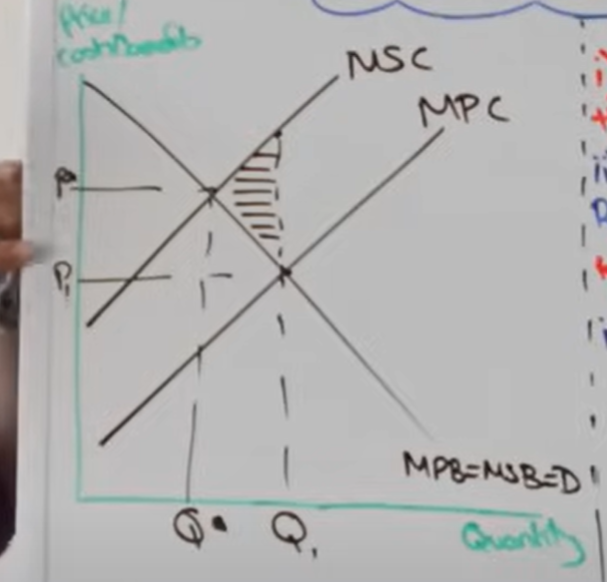
Analyse a negative production externality
Firms act in their own self interest and produce at Q1 instead of Q star
This is an over production of this good or service
At Q1 the price is also too low and does not take into account external costs only private costs - this increases the over production and consumption of this good
All this amounts to a misallocation of resources and allocative inefficiency
Define a negative consumption externality
Costs to 3rd parties caused by the actions of consumers
Draw a negative consumption diagram
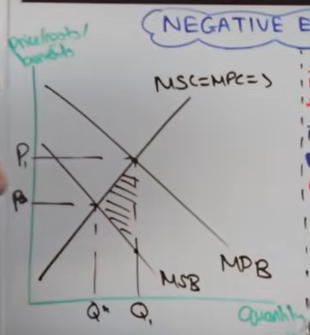
Analyse a negative consumption externality
Consumers act in their own self interest and don’t take into account the 3rd party costs
This leads to over-consumption of this good/ service
And finally at q1 there is a misallocation of resources and allocative inefficiency
Examples of negative consumption externality
Unhealthy eating and excessive alcohol consumption leads to a heavier burden on health services (Third party)
Define a positive consumption externality
A positive consumption externality is a benefit to a third party caused by the actions of a consumer
Give an example of a positive consumption externality
Getting vaccinated stops you from getting an illness and spreading it to vulnerable individuals
Eating healthy means less hospital trips leading to a lighter burden
Draw a positive consumption externality
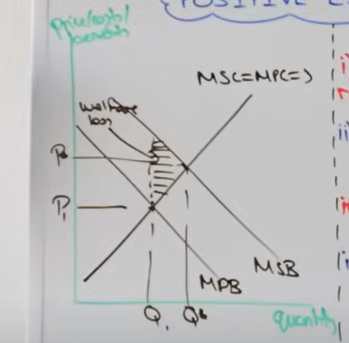
Why is there a welfare loss in a positive consumption externality
In the difference between private and social optimum external benefits is greater than external cost and so society misses out on external benefit
Analyse a positive consumption externality diagram
Consumers are self-interested and prioritise their private benefit over social benefit
This leads to an under consumption of this externality
So at Q1 there is an misallocation of resources and there is allocative inefficiency
Define a positive production externality
A benefit to third parties caused by the actions of a producer
What is an example of a positive production externality
Firms offering training schemes this improves a workers skills and then these workers can be poached by other firms benefitting them without setting up training schemes of their own
Or firms copying new innovations after R and D investment from other firms
Draw a positive production externality
Why is there a welfare loss
Because firms are only producing at Q1 instead of Q star society we miss out on q star - q1 and at these quantities social benefit is bigger than social cost so we miss out on social gain
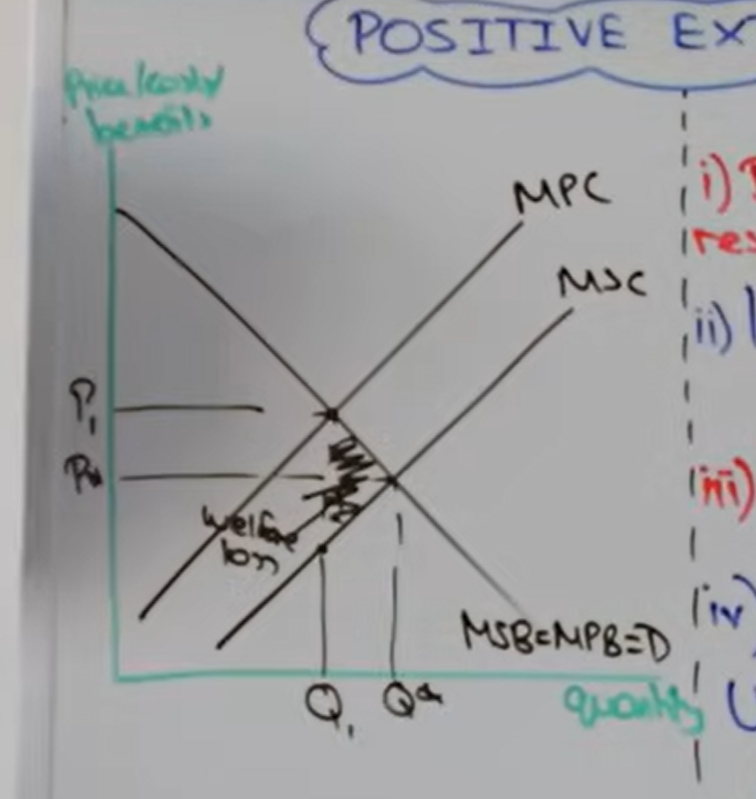
Analyse a positive externality diagram
Firms act in their own self interest and ignore the social benefits and prioritise private benefit
This leads to the under-production of the good or service as firms produce at private equilibrium
This is a misallocation of resources and is allocative inefficient