[A&P 1] Unit 2 Review Questions
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
A
Which of the following relationships between a tissue and its general function is not correct?
a) Epithelial : digestion
b) Connective : support
c) Muscle : movement
d) Nervous : control
A
An area in the body exposed to the external environment would be composed of which of the following tissue types?
a) Epithelial tissue
b) Connective tissue
c) Muscle tissue
d) Nervous tissue
B
With which portion of an epithelial cell in the stomach would food be in contact?
a) Basal surface
b) Apical surface
c) Basal lamina
d) Reticular lamina
A
Which of the following tissue types would you expect to find on a surface of the body that is subjected to friction?
a) Epithelial tissue
b) Connective tissue
c) Muscle tissue
d) Nervous tissue
D
Which characteristic of epithelial tissues would you expect to find in a duct that is subject to a high degree of pressure (such as the male urethra)?
a) Cuboidal shape
b) Simple layering
c) Pseudostratified layering
d) Stratified layering
C
Which of the following types of epithelial tissues is best suited for areas of the body where diffusion or filtration occurs?
a) Stratified columnar
b) Simple cuboidal
c) Simple squamous
d) Stratified squamous
B
Which of the following specialized terms reflects the epithelial tissue found lining the inside of blood and lymph vessels?
a) Epithelium
b) Endothelium
c) Mesothelium
d) Squathelium
C
Which of the following specialized terms reflects the epithelial tissue found lining the inside of the serous membrane?
a) Epithelium
b) Endothelium
c) Mesothelium
d) Squathelium
D
The presence of which type of epithelial tissue is lining the glands?
a) Simple squamous
b) Stratified squamous
c) Transitional epithelium
d) Simple cuboidal
A
The mucus-secreting cells prevalent in simple columnar epithelium are known as __________.
a) goblet cells
b) cup cells
c) chalice cells
d) mucocells
A
Which classification best suits the sweat glands?
a) Exocrine
b) Endocrine
c) Exocrine and endocrine
d) Holocrine
D
Which of the following glands are holocrine glands?
a) Pancreas
b) Sweat glands
c) Salivary glands
d) Sebaceous glands
A
The major distinction between endocrine glands and exocrine glands is that endocrine glands secrete their product into _________.
a) the blood
b) a duct
c) the stomach
d) the bladder
B
Which of the following tissues is the most abundant and widely distributed?
a) Epithelial
b) Connective
c) Muscle
d) Nervous
A
You would expect to find ____________ fibers in areas that undergo a lot of stretch and rebound.
a) elastic
b) collagen
c) reticular
d) white
C
Of the following cell types, which can migrate through the matrix of connective tissue and devour foreign materials?
a) Fibroblasts
b) Osteocytes
c) Macrophages
d) Chrondroblasts
D
Of the four main classes of connective tissue, which has the fluid ground substance?
a) Connective tissue proper
b) Cartilage
c) Bone tissue
d) Blood
B
Of the following connective tissues, which generally takes the most time to recover from injury?
a) Bone
b) Cartilage
c) Areolar connective tissue
d) Adipose tissue
A
Which type of connective tissue stores fat and synthesizes blood cells?
a) Osseous tissue(bone)
b) Areolar tissue
c) Adipose tissue
d) Cartilage
D
Why is blood classified as a connective tissue?
a) Blood connects two areas of the body.
b) Blood provides mechanical support of organs.
c) Blood stores large quantities of lipids.
d) Blood develops from mesenchyme.
C
Which of the following types of cartilage is compressible and resists tension well?
a) Hyaline cartilage
b) Elastic cartilage
c) Fibrocartilage
d) Articular cartilage
A
The primary functional cell found in nervous tissue is the ___________.
a) neuron
b) fiber
c) fibroblast
d) squamous
B
Which of the following pairs is not correct?
a) Skeletal muscle : striated
b) Cardiac muscle : voluntary
c) Cardiac muscle : striated
d) Smooth muscle : involuntary
D
Which muscle cells are spindle-shaped?
a) Skeletal muscle
b) Dense muscle
c) Cardiac muscle
d) Smooth muscle
B
Of the three primary germ layers, which is responsible for developing into nervous tissue?
a) Endoderm
b) Ectoderm
c) Mesoderm
d) All three primary germ layers develop into some type ofnervous tissue.
D
Which is incorrect regarding increasing age?
a) Muscular tissue begins to atrophy
b) Epithelia thins
c) Tissue repair is less efficient
d) Decreased risk of cancer
D
The skin plays a role in the manufacture of vitamin __________________.
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
C
Which of the following types of skin cancer is the most dangerous?
a) Basal cell
b) Squamous cell
c) Melanoma
d) All are equally dangerous.
D
The principal role of melanin is to __________.
a) give one that "healthy tan look"
b) keep the body cool
c) provide a waterproof layer
d) shield the nucleus from damage by ultraviolet radiation
B
The touch sensors of the epidermis are the _________.
a) keratinocytes
b) tactile cells
c) epidermal dendritic cells
d) melanocytes
C
One critical function of sebum, in addition to roles in waterproofing and skin softening, is that it provides protection against ____________.
a) overexposure to the sun
b) overheating
c) harmful bacteria
d) abrasions or cuts to the skin
D
Which of the following is not a type of cartilage?
a) Hyaline
b) Elastic
c) Fibrocartilage
d) Dense regular
B
Fibrocartilage would be found at which location?
a) Elbow
b) Knee
c) Larynx
d) External ear
C
The terms "long," "short," "flat," and "irregular" are used to classify bones based on their ________.
a) tissue content
b) function
c) shape
d) weight
A
The most important characteristic for designating a bone as a long bone is _________.
a) its elongated shape
b) its total length
c) its length relative to other bones
d) its location in the body
D
Which of the following is NOT a function of bones?
a) Protection
b) Support
c) Mineral storage
d) Transportation
D
Which of the following is not a type of bone cell?
a) Osteoblast
b) Osteoclast
c) Osteocyte
d) Osteoclasp
C
An adult male is donating red bone marrow to determine if he is a match to a leukemia patient. Most likely, the doctor will collect the bone marrow from his ____________.
a) femoral diaphysis
b) humeral diaphysis
c) sternum
d) skull
B
A group of concentric rings of bone matrix, comprising the functional unit of long bones, is called a(n) __________.
a) lamella
b) osteon
c) pillar system
d) Sharpey's system
D
Adjacent osteocytes communicate via gap junctions found within ________.
a) lacunae
b) Volkmann's canals
c) Haversian canals
d) canaliculi
A
The principal component of bone that contributes to its hardness is __________.
a) hydroxyapatite
b) collagen
c) osteoid
d) organic
B
Which characteristic of cartilage enhances its job as the precursor to endochondral bone?
a) Cartilage can decay easily.
b) Cartilage can accommodate mitosis.
c) Cartilage is a weak tissue.
d) Cartilage is retained as part of the skeletal system.
C
Most bones formed via intramembranous ossification are ________ bones.
a) long
b) short
c) flat
d) irregular
B
What would long bone growth look like in an individual whose cartilage in both epiphyseal discs stopped dividing?
a) The long bones would grow excessively.
b) The long bones would cease growth in length.
c) The long bones would cease growth in width.
d) The long bones would appear normal.
A
Which of the following bone cell types is primarily responsible for initiating ossification of bone?
a) Osteoblasts
b) Osteoclasts
c) Osteocytes
d) Chondroblasts
B
Adding new bony matrix to injury sites is known as _________.
a) bone sizing
b) bone deposition
c) bone resorption
d) bone addition
A
In a patient whose parathyroid glands have been removed, you would expect that person's blood calcium levels to _______.
a) decrease
b) increase
c) stay the same
d) increase twofold
B
Calcium's primary homeostatic importance to the body is primarily _____________.
a) to strengthen bone
b) to function in numerous metabolic activities (muscle contraction, blood coagulation)
c) to whiten our teeth
d) both a and c
C
A disease caused by vitamin D deficiency in children is termed:
a) Paget's disease
b) Osteoporosis
c) Rickets
d) Osteomalacia
C
At what age are nearly all bones completely ossified and skeletal growth ended?
a) 35
b) 15
c) 18-25
d) 28
B
I am a layer of the epidermis. I am composed of a thin layer of dying or dead keratinocytes. My cells contain keratohyalin and lamellar granules. What is my name?
A. Stratum corneum
B. Stratum granulosum
C. Stratum spinosum
D. Stratum basale
B
Which layer of the epidermis is only present in thick skin?
A. Stratum spinosum
B. Stratum lucidum
C. Stratum granulosum
D. Stratum corneum
D
Which of the following is not one of the basic tissue types?
A. Muscle
B. Connective
C. Epithelial
D. Blood
C
Which tissue type lines our body cavities and glands?
A. Connective
B. Adipose
C. Epithelial
D. Nervous
D
Which tissue type is always avascular?
A. Connective
B. Muscle
C. Bone
D. Epithelial
A
What kind of epithelia line the urinary bladder?
A. Transitional
B. Simple cuboidal
C. Simple squamous
D. Stratified squamous
B
The primary functions of the tubules of the kidneys are secretion and absorption of substances. Which tissue type forms these tubules?
A. Stratified cuboidal epithelium
B. Simple cuboidal epithelium
C. Simple squamous epithelium
D. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
B
What kind of gland is depicted in this image? (tube and sac-like gland with multiple ducts)
A. Simple branched tubular
B. Simple branched acinar
C. Compound tubuloacinar
D. Endocrine
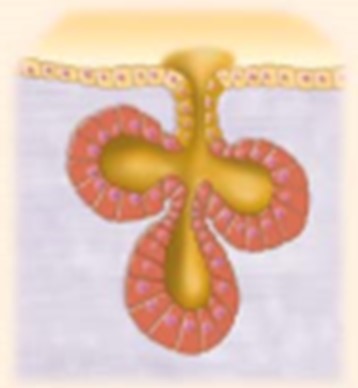
D
All of the following are general characteristics of connective tissue, except which one?
A. Multiple cell types
B. Extracellular matrix
C. Extracellular fibers
D. Avascular
B
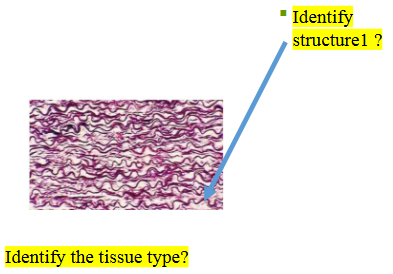
What kind of fibers are these? (multiple wavy lines running parallel to each other)
A. Collagen
B. Elastic
C. Reticular
D. Polyester
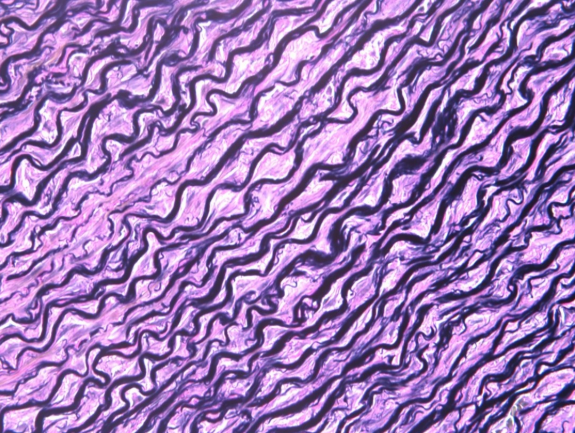
C
Which one of the following is not an example of loose connective tissue proper?
A. Areolar
B. Reticular
C. Hyaline
D. Adipose
C
What type of connective tissue forms our ligaments and tendons?
A. Adipose
B. Dense irregular
C. Dense regular
D. Areolar
A
What kind of connective tissue is found in the walls of large arteries?
A. Elastic
B. Areolar
C. Adipose
D. Reticular
D
What tissue type forms the embryonic skeleton and our nose?
A. Bone
B. Elastic cartilage
C. Fibrocartilage
D. Hyaline cartilage
C
What tissue is depicted in this image (there are striations and multiple nuclei present)
A. Cardiac muscle
B. Smooth muscle
C. Skeletal muscle
D. Salmon fillet
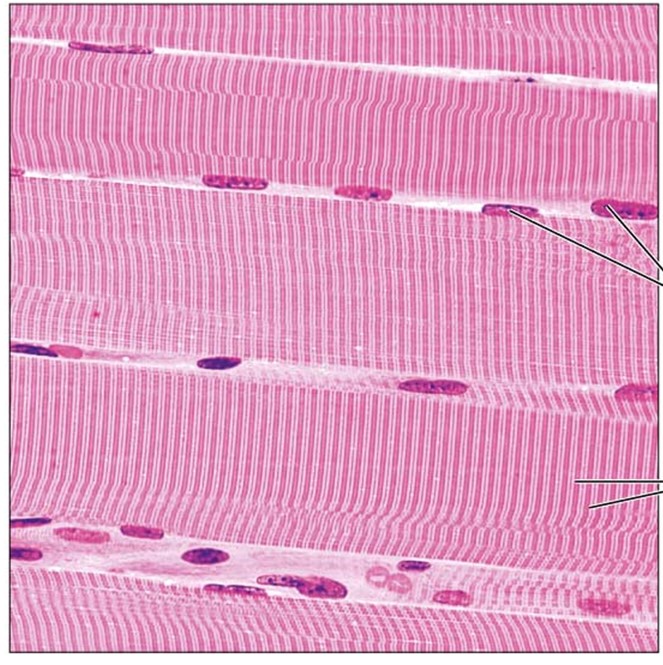
D
What type of membrane lines the body cavities that open to the exterior?
A. Plasma membranes
B. Serous membranes
C. Cutaneous membranes
D. Mucous membranes
A
What is the correct order of epidermal strata, from deepest to most superficial?
A. Basale, spinosum, granulosum, corneum
B. Corneum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
C. Basale, granulosum, lucidum, spinosum
D. Lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, corneum
D
The area of hair where cell division (growth) occurs is known as what?
A. Fibrous sheath
B. External root sheath
C. Internal root sheath
D. Matrix
D
What layers of the skin are damaged in a second-degree burn?
A. Epidermis, dermis and hypodermis
B. Epidermis only
C. Dermis only
D. Epidermis and dermis
C
Which type of exocrine gland secretion involves a breakdown of the entire secretory cell?
A. Apocrine
B. Merocrine
C. Holocrine
D. Endocrine
A
What tissue type forms the embryonic skeleton?
A. Hyaline cartilage
B. Fibrocartilage
C. Elastic cartilage
D. Bone
B
What tissue is this? (tissue with striation and gap junctions)
A. Skeletal muscle
B. Cardiac muscle
C. Smooth muscle
C
Which of the following is false regarding the skeletal system?
A. It provides protection for other organs.
B. It provides the site for hematopoiesis.
C. it maintains the blood PH
B
All the following are true of spongy bone, except which one?
A. It lines medullary cavity, just under the endosteum
B. It's more dense than compact bone
C. It contains marrow
D. It is composed of trabeculae
B
The proximal radioulnar joint is what kind of synovial joint?
A. Hinge
B. Pivot
C. Condylar
D. Saddle
C
Which of the following is false regarding endochondral ossification?
A. Results in the formation of long bones
B. Bone replaces a hyaline cartilage model
C. Process continues until death
D. Forms the medullary cavity
D
In which epiphyseal plate zone do osteoclasts erode cartilage & osteoblasts form new bone?
A. Proliferation zone
B. Hypertrophic zone
C. Calcification zone
D. Ossification zone
B
Which of the following is false regarding synovial joints?
A. A synovial cavity joins bones together.
B. Synovial joints are synarthroses.
C. Synovial fluid provides joint lubrication.
D
The site where two or more bones meet is called a(n) __________.
a) cartilage connection site
b) alignment site
c) auriculation site
d) articulation site
C
Which of the following correctly lists the three structural types of joints?
a) Bony, cartilaginous, immovable
b) Synarthrotic, diarthrotic, amphiarthrotic
c) Fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
d) Sutures, syndesmoses, gomphoses
B
An amphiarthrotic joint exhibits which level of movement?
a) Immovable
b) Slightly movable
c) Freely movable
d) Slightly immovable
A
Of the following types of joints, which type occurs only in the skull?
a) Suture
b) Ball and socket
c) Hinge
d) Symphysis
A
The __________ the ligament fibers of a syndesmosis, the __________ the degree of movement.
a) longer; greater
b) longer; smaller
c) shorter; greater
d) wider; smaller
D
Which of the following joints is a site of long bone growth?
a) Symphysis
b) Ball and socket
c) Gomphosis
d) Synchondrosis
C
When someone has "slipped a disc" of their vertebral column, which type of joint have they disrupted?
a) Synchondrosis
b) Suture
c) Symphysis
d) The connections between the vertebrae are notexamples of joints.
A
All synovial joints are __________.
a) diarthrotic
b) amphiarthrotic
c) synarthrotic
d) none of the above
D
Which of the following synovial joint components is responsible for secreting synovial fluid?
a) Articular cartilage
b) Synovial cavity
c) Articular capsule
d) Synovial membrane
C
What is a flattened sac that reduces friction between andjacent structures during joint activity called?
a) Tendon sheaths
b) Menisci
c) Bursae
d) Synovial membranes
D
The greatest degree of motion that synovial joints display is described as __________.
a) nonaxial movement
b) uniaxial movement
c) biaxial movement
d) multiaxial movement
C
Which of the following is not a factor that stabilizes joints?
a) Articular surfaces
b) Muscle tone
c) Bursae
d) Ligaments
A
Pointing your toes downward is described as which type of movement?
a) Plantar flexion
b) Dorsiflexion
c) Pronation
d) Supination
B
The knee joint is most susceptible to injury when __________ blows are applied to the knee.
a) vertical
b) lateral
c) posterior
d) inferior
A
An injury common to baseball players is a torn rotator cuff. This collection of muscles and tendons is associated with the __________ joint.
a) shoulder
b) elbow
c) hip
d) knee
A
The most common form of chronic arthritis is__________.
a) osteoarthritis
b) rheumatoid arthritis
c) gouty arthritis
d) subluxation
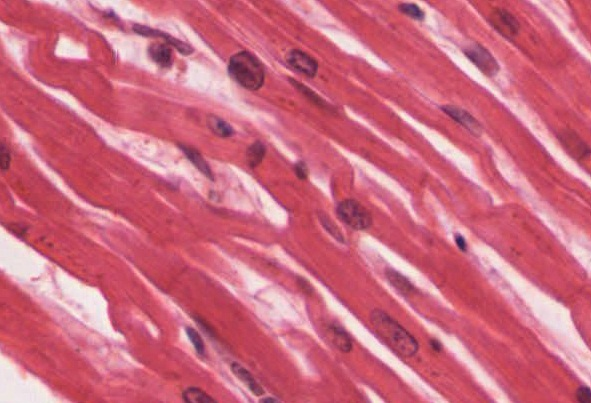
cardiac tissue
What type of tissue is this?
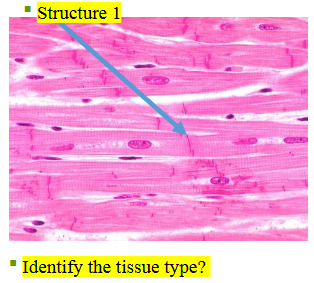
intercalated discs
What does structure 1 display?
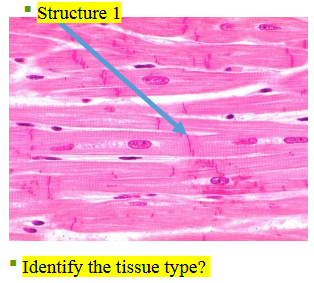
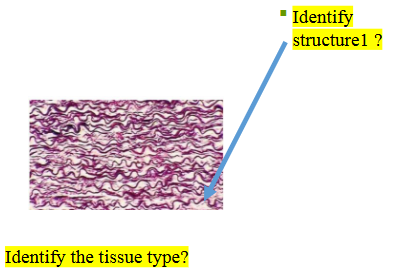
elastic tissue
What type of tissue is this?
elastic fibers
What does structure 1 display?
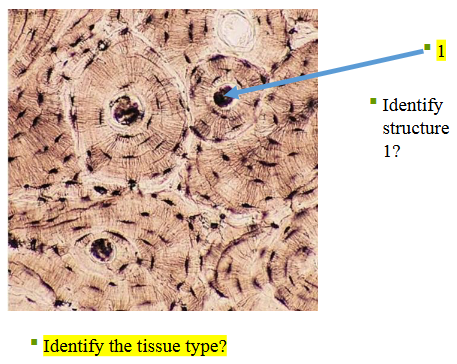
osseous tissue
What type of tissue is this?
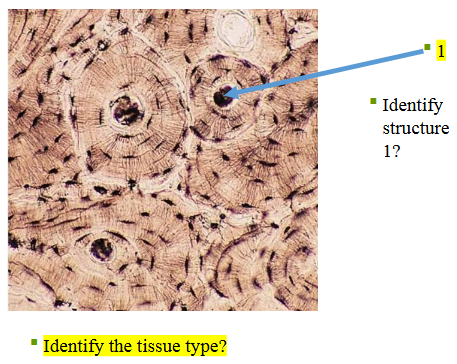
osteon
What does structure 1 display?