PLTW Human Body Systems EOC Review
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Fibrous Joints
Immoveable joints that are held together by fibers.
Cartilaginous Joints
Partially moveable joints held together by cartilage.
Synovial Joints
Freely moveable joints that have a cavity where the bones meet that allow movement.
Flexion
A type of movement that decreases the angle of a joint.
Extension
A type of movement that increases the angle of a joint.
Abduction
A type of movement that moves a limb away from the body (midline).
Adduction
A type of movement that moves a limb closer to the body (midline).
Plantar Flexion
A movement that bends at the ankle, pointing toes down and taking the heal off the floor.
Dorsiflexion
A type of ankle movement that points the toes up and puts the heel on the floor.
Comminuted
What type of fracture is this?
Spiral
What type of fracture is this?
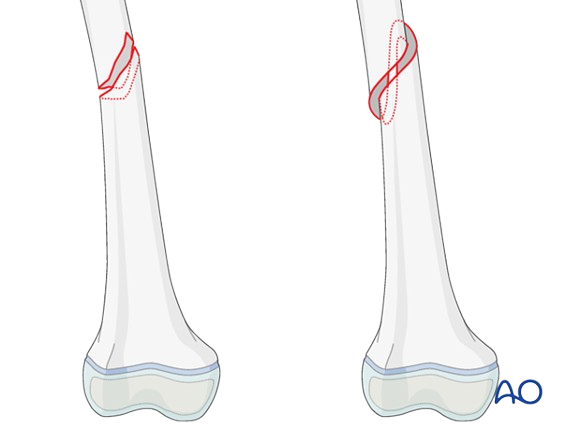
Oblique
What type of fracture is this?
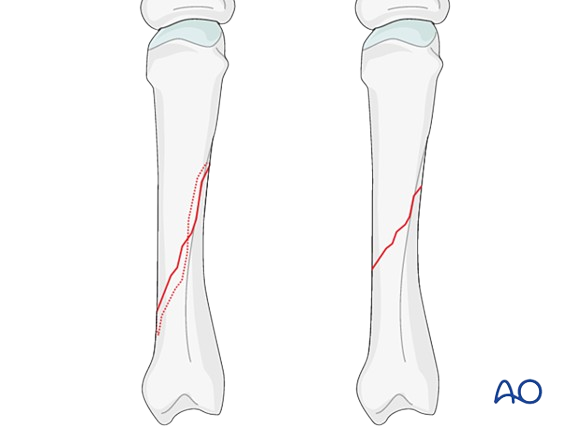
Transverse
What type of fracture is this? (there are closed and complex varients [if they’re inside the body still])
![<p>What type of fracture is this? (there are closed and complex varients [if they’re inside the body still])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ef04941e-7fc8-48fc-9537-5967e0743354.png)
Hematoma
The first step in bone remodeling, where inflammation occurs and a blood clot forms?
Fibrocartilaginous Callus
The second step in bone remodeling where fibrous tissue forms and a layer of collagen forms where the bone will later remodel onto?
Bony Callus
The third step in bone remodeling, cartilage converts to bone as it’s calcified
Bone Remodeling
The last step in bone remodeling, clasts keep breaking down bone so blasts can build new bone.
Cervical, Coccyx, Lumbar, Sacral, Thoracic
The order of the vertebra
Left Atrium/Ventricle
Where deoxygenated blood passes through the heart to the lungs
Right Atrium/Ventricle
Where oxygenated blood passes through the heart from the lungs to the rest of the body
Tidal Volume
The volume (L) of air one is intaking subconsciously
Residual Volume
The volume of air in one’s lungs that cannot be exhaled
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
The maximum amount of air one can breath in (beyond normal breathing)
Expiratory Reserve Volume
The minimum amount of air one can breath out (beyond normal breathing)
Vital Capacity
The total lung capacity excluding residual volume
Total Lung Capacity
The total lung capacity including residual volume
Epidermis
The top layer of skin
Dermis
The larger, middle layer of skin. Include pores and hair follicles.
Subcutaneous Tissue
The last layer of skin, composed of fat/adipose
Cornea
Transparent tissue at the front of the eye, refracts light, protects the eye, and helps the eye focus
Iris
The circular, pigmented layer of the eye anterior to the cornea, controls the amount of light entering through the pupil.
Lens
Focuses light onto the retina, and allows clear vision.
Pupil
Dark, circular opening in the center of the iris, regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
Retina
Tissue layer in the back of the eye, receives light and converts it into electrical signals. (____→optic nerve→brain)
Optician
Fits and dispenses glasses, contacts, and other visionary aids
Optometrist
Diagnoses and treats vision problems and eye diseases
Ophthalmologist
Performs medical and surgical treats of vision and eye issues
Dendrite
Receives a nerve signal and sends it to the soma
Axon
The “tail” end of a nerve
Nodes of Ranvier
Areas on the axon not covered by the myelin sheath; where ions move in and out.
Axon Terminal
Branching end of an axon; faces next cell/synapse
Soma
The cell body of a neuron; has the nucleus and makes proteins
Schwann Cells
Cells imbedded in the myelin sheath which make it.
Myelin Sheath
Coated on an axon
Terminal Button/Bud
“Buds” at the end of the axon terminal
Central Nervous System
The brain and spinal chord are a part of the ____________
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves except for the brain and spinal chord are a part of the ______________
Cerebrum
Conducts higher order thinking /conscious thought and action. Obtains information from surroundings. (Lobe of brain, encapsulates other sub-lobes)
Frontal Lobe
Lobe of the brain that allows for critical thinking and problem solving, personality, motor, speech, and emotion (cerebrum)
Parietal Lobe
Lobe of the brain that receives sensory information from the body
Occipital Lobe
Lobe of the brain that allows for vision
Temporal Lobe
Lobe of the brain that allows for memory, speech, and emotion.
Cerebellum
Part of the brain that allows for balance and motor coordination, muscle memory, and gait
Brain Stem
Part of the brain that allows for basic life functions (homeostasis, heart rate, etc.)
Depolarization
The point in nerve activity when the threshold is reached and sodium channels open, allowing sodium into the cell.
Repolarization
The point in nerve activity when potassium channels open (after the closing of sodium channels) and allow for potassium to leave the nerve cell.
Hormones
Chemical messengers in blood that are released by the endocrine system.
Nervous System, Endocrine System
The ________ allows for quick, short-term responses, while the ________ allows for long-term responses.
Kidneys
Filter blood and remove waste from the body (organ)
Ureters
Carry urine to bladder from the kidneys
Bladder
Holds urine, expands and contracts easily with its type of cells.
Urethra
Tube for urine to exit the body
P-Wave
First “bump” of EKG, tracks the electrical signal that allows for contraction of the heart .
QRS Complex
The spike of an EKG graph, represents the contraction of the ventricles.
Rods
Cells in eyes, responsible for night vision (no color) and peripheral vision.
Cones
Cells in eyes, responsible for daytime vision (color) and front vision.
Anterior
Towards the front of the body
Posterior
Towards the back of the body
Superior
Towards the top of the body
Inferior
Towards the bottom of the body
Medial
Towards the middle of the body
Lateral
Away from the middle of the body
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
Distal
Away from the point of attachment
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Ventral
Towards the front of the body (stomach)
Dorsal
Towards the back of the body (back)
Transverse Plane
Plane that cuts the body in half, superior and inferior
Coronal Plane
Plane that cuts the body in half, dorsal and ventral
Sagittal Plane
Plane that cuts the body in half, medial and lateral
Tarsal
Relating to the ankle
Femoral
Relating to the thigh
Popliteal
Relating to the back of the knee
Axillary
Relating to the armpit area
Under 20
When to start dialysis?
Under 15
When to be eligible for a kidney transplant?
Inguinal
Groin area
Lumbar
Relating to the lower back
Antecubital
Relating to the front of the elbow
Coxal
Relating to the hip
Cervical
Relating to the neck
Sternal
Relating to the chest (sternum)
Gluteal
Relating to the buttocks
Thoracic
Relating to the chest
Patellar
Relating to the kneecaps
Buccal
Relating to the cheek
Olecranal
Relating to the (back of the) elbow
Calcaneal
Relating to the heel
Orbital
Relating to the eyes