2.1.4 Flashcards
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
based on 2.1 Fiona's notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Phlebotomist
Draw blood from patients
Median Cubital Vein is a large and easy accessible vein blood is usually drawn from
General Blood Draw Steps
Greet and Identify the Patient
Prepare Equipment and Patient
Perform Hand Hygiene
Select the site for blood draw
Apply temporary tourniquet and don gloves
Disinfect the area
Take the blood, filling all needed blood sample tubes
Safely discard contaminated materials
Complete Blood Count
A relative count of each type of cell
Leukocytes
White Blood Cells (WBC)
Normal Range 3.4-9.6 billion cells/L
High WBC can be infection or disease
Low WBC can be a condition such as low vitamin deficiency
Erythrocytes
Red Blood Cells (RBC)
Normal Range for Males: 4.34-5.65 trillion cells/L
Normal Range for Females: 3.92-5.13 trillion cells/L
High RBC can indicate heart disease, lung disease, or dehydration
Low RBC can indicate vitamin B deficiency, internal bleeding, malnutrition or kidney disease
Hemoglobin
HB/Hgb
Normal Range for Males: 13.2-16.6 grams/dL
Normal Range for Females: 11.6-15 grams/dL
High HB means High iron protein amount
Low HB leads to fatigue and breathing issues
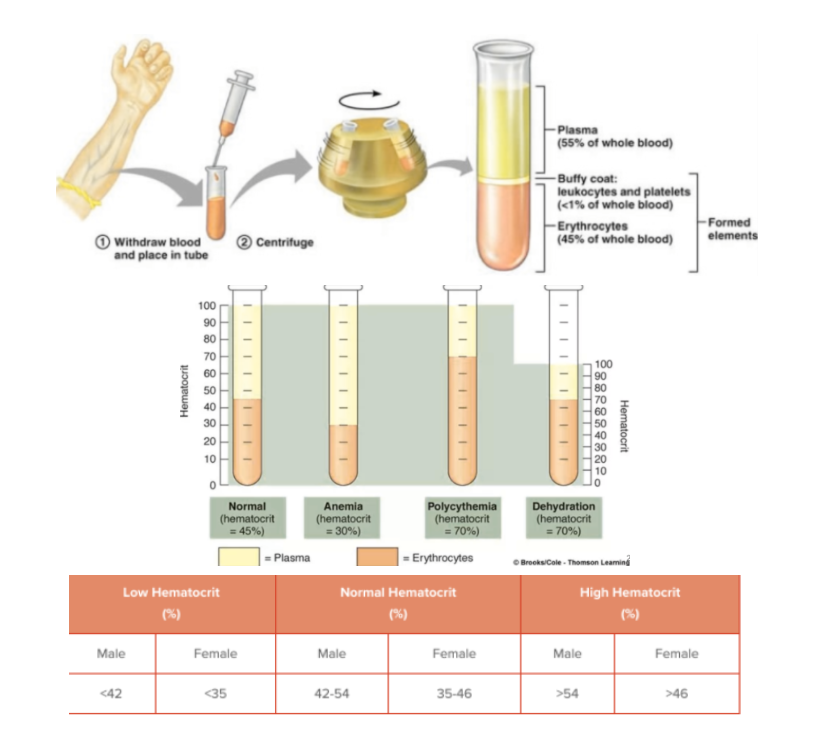
Hematocrits
HCT
Normal Range for Males: 38.3-48.6 %
Normal Range for Females: 35.5-44.9 %
High HCT indicate heart disease, lung scar and thickening, dehydration
Low HCT indicates infection, long term illness, WBC disorder
Thrombocytes
Platelets (PLT)
Normal Range for Males: 135-317 billion/L
Normal Range for Females: 157-371 billion/L
High PLT can indicate infection or clotting
Low PLT can indicate excessive bleeding, blood cancers, autoimmune diseases, pregnancy, heavy alcohol consumption, or can be a medication side effect.
Career Connection - Hematologist
Specializes in diagnosing and treating blood disorders
Could work in blood banks, pathology labs, and private clinics
Hematocrit Test is a test that measures the percentage of red blood cells compared to the total blood volume
hematocrit levels
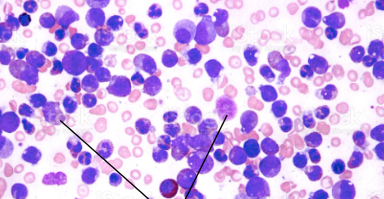
Leukemia
Cancer when the white blood cells are high and red blood cells and platelets are low
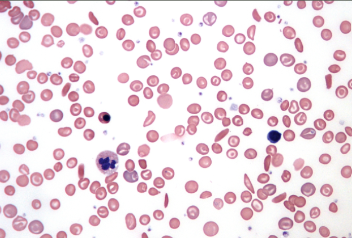
Sickle Cell Disease
Irregularly shaped blood cells that are deoxygenated and tend to stick together and are unable to move through the blood. They can block vessels and prevent movement of oxygenated cells.
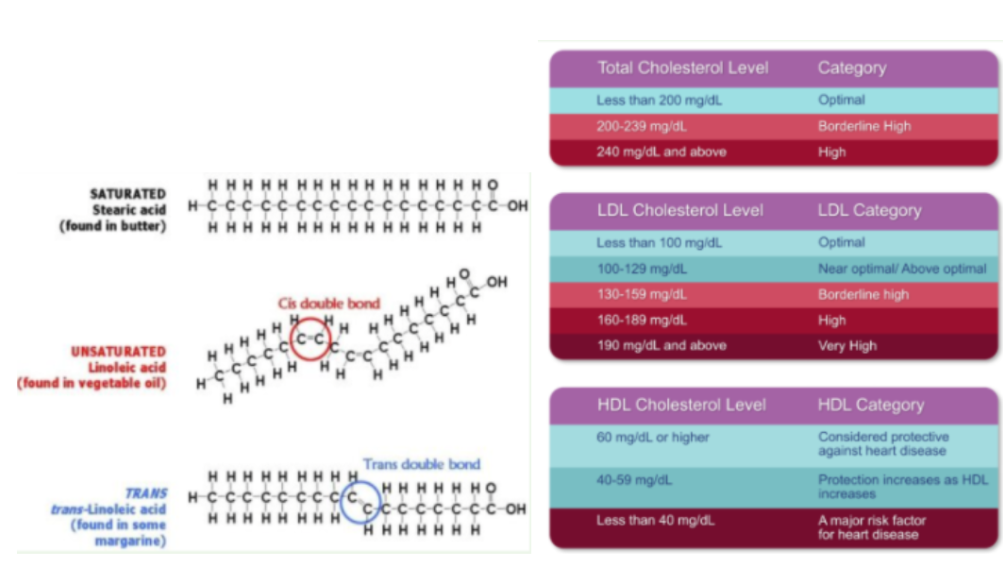
Cholesterol (Lipid Panel)
Cholesterol - Fat (lipid) molecule needed by the cell to function
Used to produce steroid hormones
Produced in liver and absorbed from food
High cholesterol can damage artery walls and contribute to plaque buildup
Normal Range: <100mg/dL
High: 160mg/dL
LDL - Low Density Lipoprotein (Lipid Panel)
Responsible for transporting cholesterol cells
Known as “bad cholesterol”
Can build up in the arteries and form plaque
HDL - High Density Lipoprotein (Lipid Panel)
Responsible for removing excess cholesterol from bloodstream and transport to the liver
“Good cholesterol”
Saturated Fat (Lipid Panel)
Solid at room temp
Increase LDL
Found in beef, pork chicken, turkey, fried foods, dairy
Too much can cause plaque buildup in arteries
Unsaturated Fat (Lipid Panel)
Liquid at room temp
Decrease LDL and increases HDL
Found in cooking oil, avocados, nuts and seeds, fishHelps get rid of the LDL that causes blockages
Have double bonds
High Cholesterol Medications (Lipid Panel)
Statins (reduce fats)
Niacin (reduce LDL and triglycerides, increase HDL)
Bile Acid Binding Drugs
Fibrates
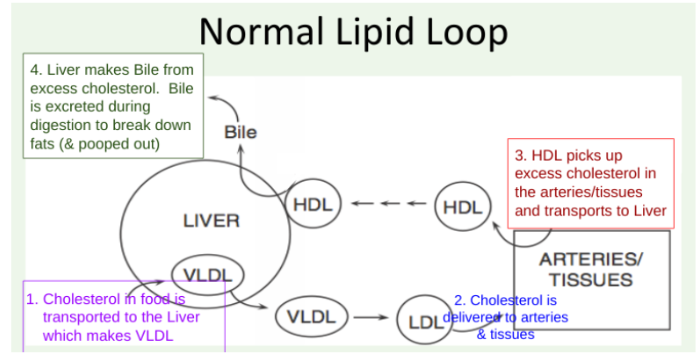
Normal Lipid Loop (Lipid Panel)
Total, LDL, HDL Cholesterol Levels (Lipid Panel)
Metabolism (Metallic Panel)
refers to all the chemical reactions and operations that go on inside the body
Abnormal results can indicate diabetes, kidney problems, hormone issues
Hormones (Metallic Panel)
chemical signals that help communicate info inside the body
Glucose (Metallic Panel)
Simple sugar used by body for energy
High levels may indicate diabetes
Electrolytes (Metallic Panel)
Help keep water balances
Makes sure nerves, brain, muscles, and heart function properly
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and Creatinine (Metallic Panel)
Waste filtered out of blood by kidney
Give indications of kidney functioning