Cell Biology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
the late 1500’s
Light Microscope was invented in
1665
Robert Hooke identified cells
1839
Cell Theory - Cells are theorized as the building blocks of all life
Who invented cell theory?
Botanist Matthias Schleiden and Zoologist Theodore Schwann
in a polar covalent bond, what happens to the partial positive charge?
oxidized
in a polar covalent bond, what happens to the partial negative charge?
reduced
96% of living matter
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen
Ionic
oppositely charged ions - metal to non metal - atoms transfer electrons
Covalent
oppositely charged atoms - nonmetal to nonmetal - atoms share electrons
Electronegativity
attraction of an atom for electrons
Nonpolar
Similar - Equal electronegativity
Polar
Electronegativity difference
Hydrogen
Hydrogen connected to an electronegative atom that’s connected to another electronegative atom
van der wals interactions
attractions of positive/negative regions of molecules
temporary, very weak



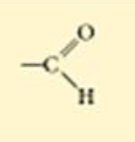

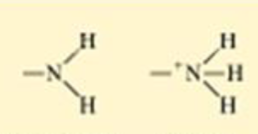

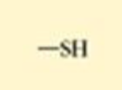

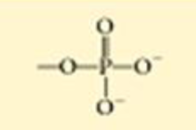
How much of a cell is made of water
70-95%
Sugars →
Polysaccharides and Oligosaccharides
Fatty Acids
Fats and Lipids
Amino Acids
Proteins
Nucleotides
Nucleic Acids
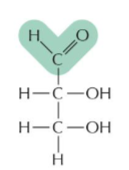
aldose
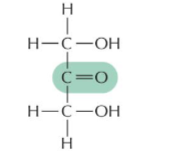
ketose
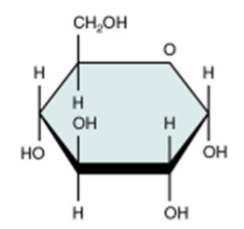
glucose
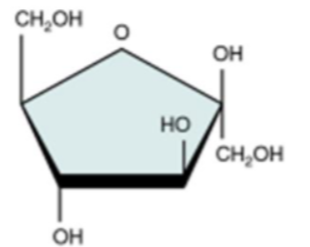
fructose
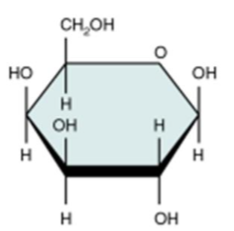
Galactose
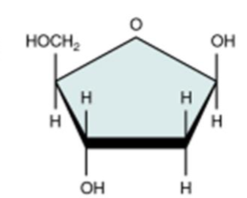
deoxyribose
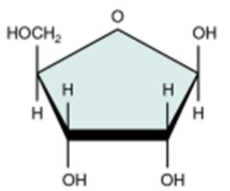
Ribose
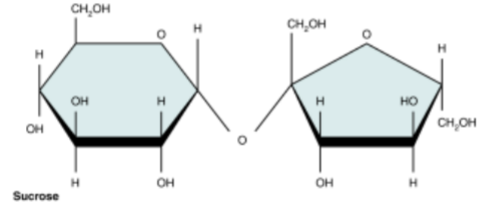
Sucrose
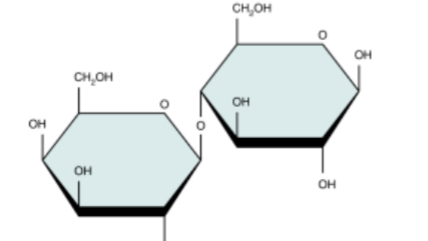
lactose
condensation
water expelled - energetically unfavorable
hydrolysis
water consumed - energetically favorable
lipid head
hydrophilic, carboxylic acid
lipid body
hydrophobic, carbon tail
saturated fat
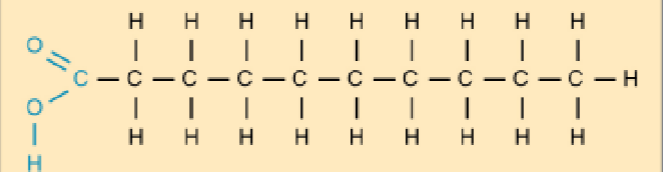
unsaturated fat
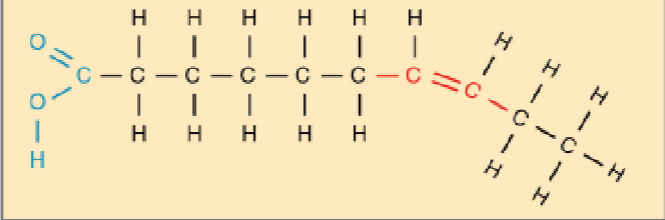
how do saturated fats act at room temperature?
solid
how do unsaturated fats act at room temperature
cannot solidify
Alpha-linolenic acid
18 carbons, 3 double bonds
Eicosapentanoeic acid
20 carbons, 5 double bonds
Docasahexonic acid
22 carbons, 6 double carbons
Steroids are
lipids
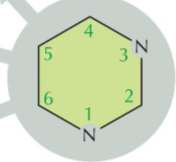
Pyramidine
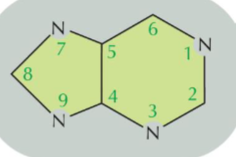
Purine
pentose
a five carbon sugar
Functions of nucleotides
carry chemical energy
combine w other groups to form coenzymes
small intracellular signaling
enzymatic proteins
act as enzymes
Structural Protiens
Support
Transport Protiens
transport other substances
hormonal protiens
coordination of an organisms activities
receptor protiens
respond to cell to chemical stimuli
motor proteins
movement
defensive proteins
protection against disease
protein make up
amino group, carboxyl group, r group
polymers of amino acids
polypeptides