MIC 206: Lab 12, 16, 13 - Simple, Endospore, Gram Stainings
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the 3 types of cell morphology (simple staining)
Bacillus (rod-shaped), cocci (golfball shaped), and spirillum/curved (corkscrew)
What do stains contain (simple staining)
Coloring bearing ions called chromophores
What does adding the colored compounds do (simple staining)
Add contrast for visiility
What charge are bacterial cells (simple staining)
Bacterial cells are negatively charged
What is the charge of basic stains and examples (simple staining)
Positive charged → Cations
ex: methylene blue, safranin, and crystal violet
What is the charge of acidic stains and examples (simple staining)
Negative charge → Anions
ex: nigrosin
What are the steps of a smear prep (simple staining)
Draw a circle about the size of a quarter on the bottom of the slide
(if using) Broth: take 1 or 2 loops of bacteria
(if using) Plate: use a loop of water, then small amount from slide of a colonyMake sure to smear it around the slide
Allow it to air dry
Heat fix (hold slide in front of bacticinerator for about 5 seconds)
What are the steps of a simple stain (simple staining)
Smear prep
Heat fix
Flood slide with stain
Wash slide with water
Use bibulous paper and blot dry gently
Record images under 100x magnification using oil objective lens
What does heat fixing do (simple staining)
Adheres bacterial cells to the slide and prevents loss of sample during staining procedure
What should you do when you switch to the high power (40x) on a microscope (simple staining)
Do not move the course adjustment, only the fine focus adjustment
Condensor
What should you do when you switch to the oil power (100x) on a microscope (simple staining)
Do not move the course adjustment, only the fine adjustment
Light setting
What are some examples of endospore diseases (endospore staining)
Tetanus, Anthrax, Botulism, Gas Gangrene, Pseudomembranous colitis
What is endospore formation (endospore staining)
Some bacteria form spores when an environment is harsh. Endospores are dormant life forms that are located in different locations within the cell
Are bacterial endospores = to mold spores (endospore staining)
No bacterial endospores are NOT mold spores
What do endospores have (endospore staining)
Spores have tough protein coats highly resistant to normal staining procedures.
The impermeability of the spore coat (exosporium) is responsible for the endospore’s resistance to unfavorable environmental conditions
What is exosporium (endospore staining)
Thin, impermeable spore coat
What is the primary stain in an endospore staining for Schaeffer-Fulton method (endospore staining)
Malachite green
What helps the primary stain penetrate the endospore in an endospore staining for Schaeffer-Fulton method (endospore staining)
Heat/stream is applied to help the primary stain penetrate the endospore
What are characteristics of malachite green that helps it rinse easily from the vegetative cells (endospore staining)
Malachite green is water-soluble and does not adhere well to the cell, and since the vegetative cells have been disrupted by heat, the malachite green rinses easily from the vegetative cells
What do vegetative cells readily take up in an endospore staining for Schaeffer-Fulton method (endospore staining)
The counter stain → Safranin (which is the counterstain of malachite green)
How should cells appear for endospores and vegetative cells in an endospore staining for Schaeffer-Fulton method (endospore staining)
Endospores will appear green/teal
Vegetative cells will appear pink
What is the staining procedure for an endospore staining for Schaeffer-Fulton method (endospore staining)
Prepare and heat-fix a slide with bacteria
Apply malachite green stain continuously over steam for 10 minutes
Rinse with water
Counterstain with Safranin for 1 minute
Rinse with water
Gently blot dry with bibulous paper
View under oil immersion (100x) objective lens
What is peptidoglycan (gram stain)
Cell wall component unique to bacteria largely responsible for the strength of the cell wall
What are gram positive bacteria (gram stain)
Have a thick, mesh-like layer of peptidoglycan
Contains up to 100 sheets of peptidoglycan stacked upon one another
Have more peptidoglycan because they are trying to withstand higher internal pressure
What are gram negative bacteria (gram stain)
Have a thin layer of peptidoglycan in addition to an outer membrane
Peptidoglycan makes up only about 10% of the cell wall, which consist mostly of outer membrane
Minimum 10 sheets of peptidoglycan
What is a primary stain (gram stain)
The first stain added after heat-fixing. Determines the color of Gram-positive cells
What is a mordant (gram stain)
A color fixative, almost always Gram’s iodine. Works by forming a complex molecule with the primary dye so that it is not completely leached out of the thick peptidoglycan
What is a decolorizer (gram stain)
Removes primary stain from Gram-negative cells
What is a counter-stain (gram stain)
The second dye. Added after the decolorizer is washed out. Determines the color of the Gram-negative cells
What is the procedure for a gram stain (gram stain)
Smear prep and heat fix
Flood slide with crystal violet (primary stain) for 60 seconds
Wash with water
Flood with Gram’s iodine (mordant) for 60 seconds
Wash with water
Carefully decolorize with 95% Ethanol (decolorization agent) for 2-3 seconds
Wash with water
Flood with Safranin (counterstain) for 60 seconds
Wash with water
Blot with absorbent paper
(fixation → crystal violet → iodine treatment → decolorization → counterstain/safranin)
What is staining considered
Staining is the art of painting
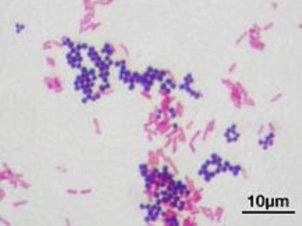
What type of staining is this
Gram stain → mixture of gram + and gram -
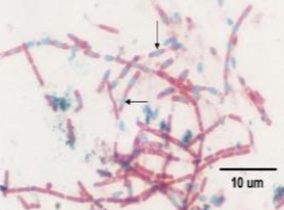
What type of stain is this
Endospore stain