BIO 201 Skeletal System Exam With complete verified solutions + Rationales
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What are the 3 components of the skeletal system?
bones, ligaments, cartilage
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, movement, hemopoiesis, electrolyte balance, and energy storage
What does hemopoiesis mean?
blood cell formation in red marrow
What are the 2 main components of electrolyte balance?
Ca+ and phosphate ions, na, K (collagen and phosphate)
What does Orthopedics mean?
study of the skeletal system
Osteo-
Chondro-
Arthro-
-bone
-cartilage
-joint
What are the four tissue types?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What three things do tissue mostly contain of?
cells, fibers, and ground substance
What are the functions of the connective tissue?
-connects organs to each other
-gives support & protection (physical & immune)
What are the types of connective tissue?
-fibrous connective tissue (dense)
-supportive connective tissue (cartilage, bone)
-fluid connective tissue
Where is dense regular connective tissue found?
tendons and ligaments (it attaches muscles to bones and holds bones together)
What type of connective tissue is cartilage and bone?
supportive connective tissue
What are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
What are the two types of bone?
spongy and compact
What does a chondroblast become?
a chondrocyte
What is cartilage?
Supportive connective tissue with rubbery matrix produced by chondroblasts that heals slowly and has no blood vessels
What does chondroblasts produce?
matrix
When are chondroblasts called chondrocytes?
when they are surrounded in lacunae
What defines the cartilage?
the ground substance
What is the perichondrium?
the connective tissue that envelops cartilage where it is not at a joint.
What are the two layers of the perichondrium?
fibrous layer (inner part) and chondrogenic layer (outer part)
Which layer of the perichondrium contains many chondroblasts?
the chondrogenic layer
Which part of hyaline cartilage does not have perichondrium?
the articular cartilage
Which cartilage is the most common?
hyaline cartilage
What does hyaline cartilage look like?
bluish white, glassy in appearance
What does hyaline cartilage do?
firm/slightly pliable support, eases joint movements
What are examples of hyaline cartilage?
costal cartilage, tip of the nose, epiphyseal plate, trachea, fetal skeleton
What does elastic cartilage contain a lot of?
elastic fibers
What does elastic cartilage look like?
hyaline cartilage with weblike mesh of elastic fibers amongst the lacunae
Does elastic cartilage have a perichondrium?
yes, always
What is the function of elastic cartilage?
provides flexible, elastic support
What are some example of elastic cartilage?
external ear (pinna), epiglottis, eustachian canal
What does fibrocartilage contain?
parallel collagen fibers (lots of fibers)
Which cartilage is the strongest?
fibrocartilage
Which cartilage is really good with shock absorption?
fibrocartilage
Does fibrocartilage have a perichondrium?
no, never
What are example of fibrocartilage?
pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs
What is osseous tissue?
bone tissue
What is bone made up of?
cells, fibers, and ground substance (just like any other tissue)
How is the matrix of bone tissue?
hard
How has bone matrix been hardened?
by deposition of minerals
What can bone refer to?
osseous tissue or organ
What are the cells of osseous tissue?
osteogenic cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
What are osteogenic cells and what do they do?
stem cells and they form new osteoblasts
Where are osteogenic cells found?
in endosteum or periosteum
What is bone matrix?
combination of organic and inorganic matter
What is the organic matter of bone matrix?
collagen plus other proteins and it is 1/3 of bone weight
What is the inorganic matter of bone matrix?
mostly hydroxyapatite and 10% calcium carbonate and 2/3 of bone weight
What are the two components of hydroxyapatite?
calcium phosphate salt
What two things do bones need for their composite?
minerals and proteins
What do minerals in bone do?
resist compression which help with strength
What does protein do in bone?
resist tension/twists which helps with flexibility
What does spongy bone look like?
porous, looks like a sponge with small spaces, found at the end of bones
Which, spongy or compact bone, is deep or superficial?
spongy - deep
compact - superficial
What does compact bone look like?
hard, dense part of bone, but not solid, contains blood vessels and nerves, forms the surface of ALL bone
What are two bone shapes? And what do they look like?
Long bones
- longer than wide (femur, humerus)
Flat bones
- usually enclose organs (scapula, os coax, many skull bones)
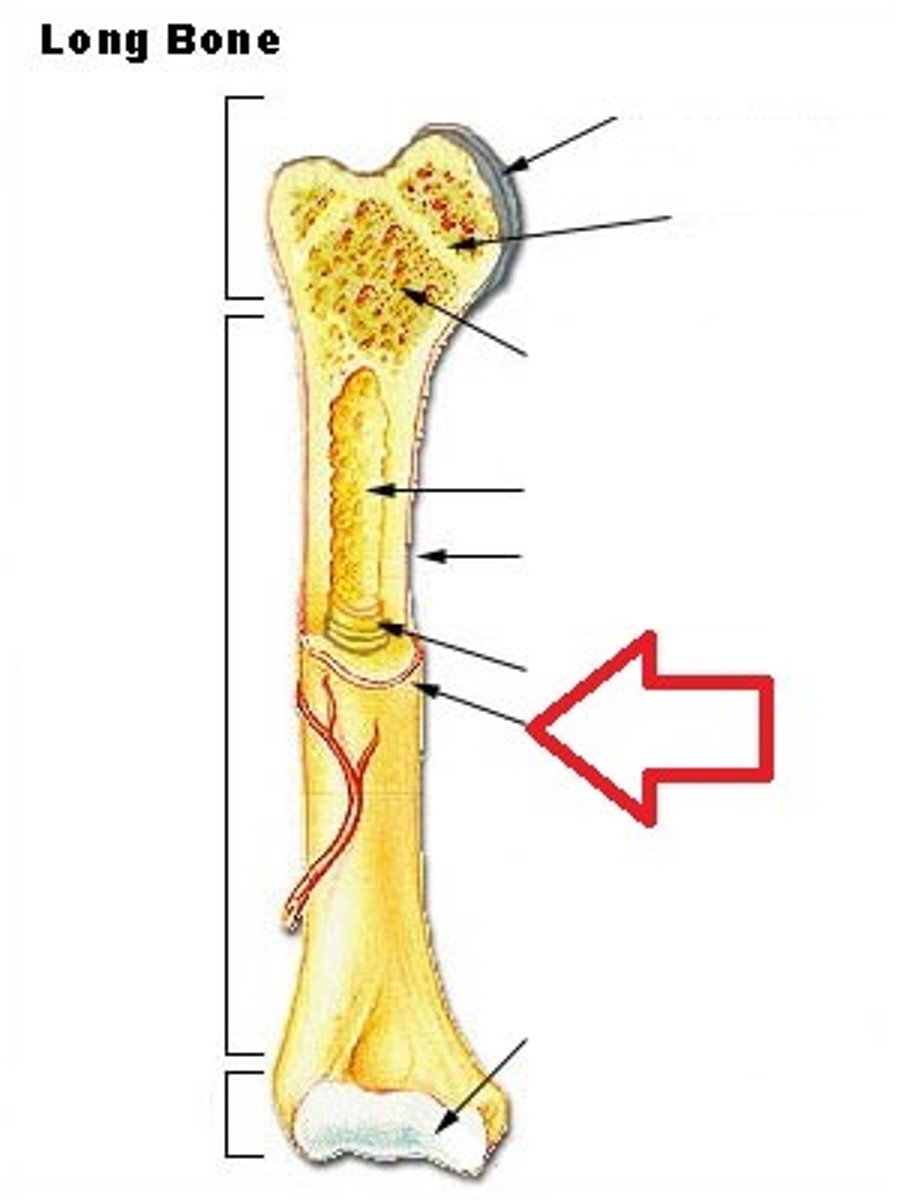
What are the parts of a long bone?
diaphysis - shaft (middle)
epiphysis - head at each end of bone (attaches tendons and ligaments)
medullary (or marrow) cavity - center of diaphysis
What important thing does compact bone contain?
osteon
What is an osteon?
- concentric layers (lamellae) surrounding the Haversion canal aka Haversian system
- cylinder of matrix surrounding central canal (long cylinders)
What do osteocytes do?
maintain bone matrix
What are lacunae? What are canaliculi?
lacunae - spaces containing osteocytes
canaliculi - extensions of lacunae that have extensions of osteocytes running through them
What is the interstitial lamellae of compact bone?
incomplete lamellae found between osteons
What are Volkmann's canals?
canals containing blood vessels passages where blood vessels and nerves run, they connect one central canal to another
What is spongy bone?
lattice of trabeculae spaces filled with red bone marrow, not randomly arranged
What is bone marrow?
soft tissue in medullary cavity of long bones, amid trblecula, and wishing larger central canals
What are the three types of bone marrow?
red marrow, yellow marrow, and gelatinous marrow
What is Red bone marrow?What type of tissue does it have?
reticular connective tissue + stem cells + adipose tissue. It is hemopoietic tissue which produces blood cells through a process called hemopoiesis. It is also more common in children than adults.
What is yellow bone marrow?
adipose tissue, it does not produce blood but it can revert to red bone marrow during anemia
What is gelatinous bone marrow?
Seen in the elderly where yellow marrow is replaced with a reddish-like jelly material.
What is the periosteum?
connective tissue sheath around bone exterior, it provides attachment point between bone and muscle
What are the two layers of periosteum?
Fibrous layer (outer layer)
- can be continuous (toughing) with tendons and ligaments, contains collagen
Osteogenic later (inner layer)
- "bone forming layer" which contains many osteoblasts and osteogenic cells
What are sharpey fibers?
collagen fibers that penetrate into bone matrix which help anchor periosteum to bone
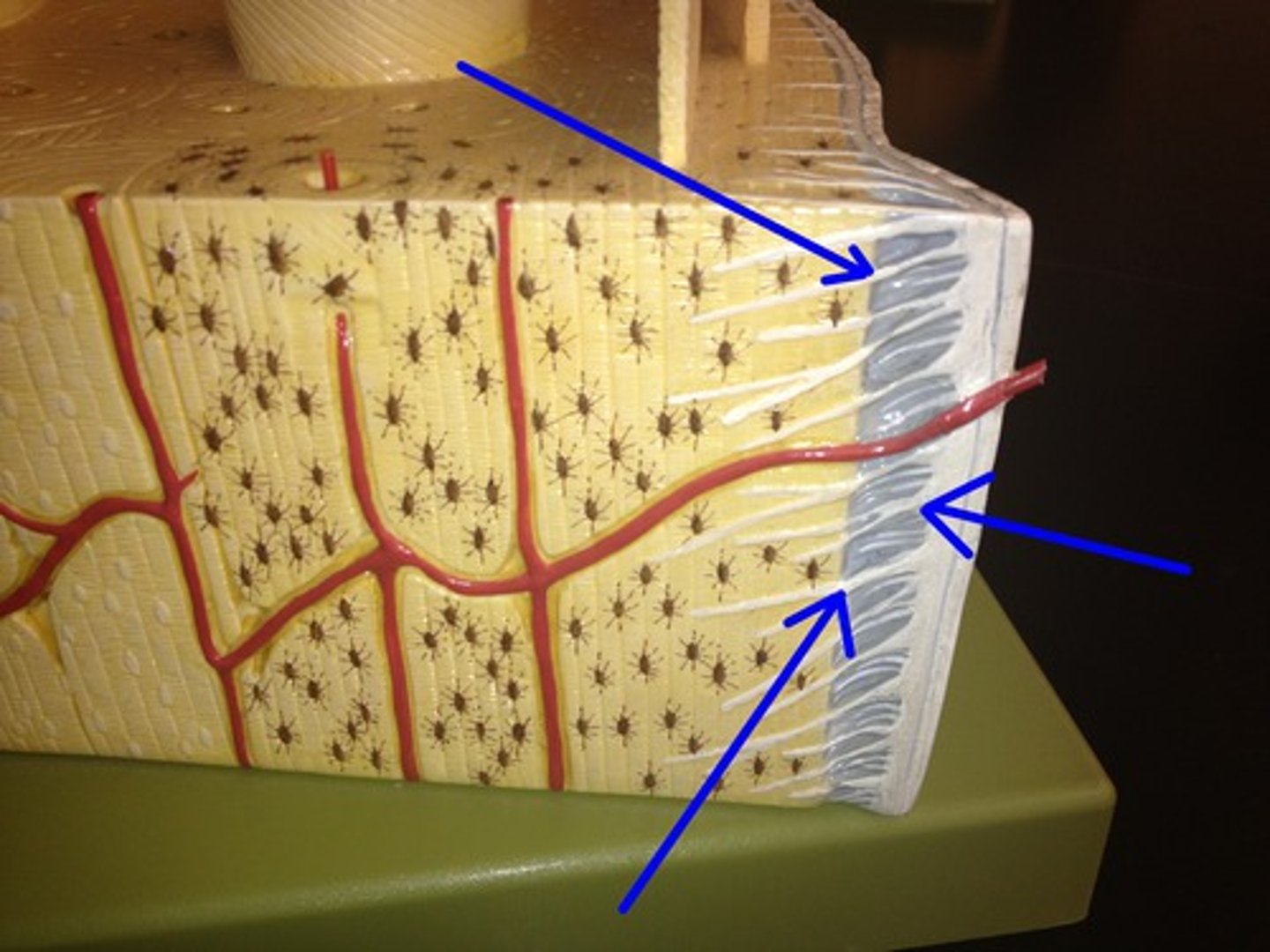
What is the endosteum? What type of CT is it?
lines the medullary cavity of bone and also central canals and surrounds trabeculae, it is reticular connective tissue
What is the epiphyseal plate?
hyaline cartilage that separates diaphysis and epiphysis, it is only in children and adolescents and it is the site of elongating youth.
What is an epiphyseal line?
found in adults and it it where the epiphyseal plate used to be.
What is articular cartilage?
hyaline cartilage covering the joint surfaces and it has no perichondrium
What are osteoblasts?
bone forming cells, they synthesize organic components of bone matrix and they help mineralize bone. They are found in endosteum and the inner layer of periosteum and also in metaphysis.
What are osteocytes?
mature osteoblasts trapped in lacunae, lacunae are connected through canaliculi. Osteocytes are connected by gap junctions which transfer signals and they maintain bone matrix.
What are osteoclasts?
bone dissolving cells, they are created by fusion of mono blasts and they are large. They live in resorption bays (small pits etched into bone surface).
What kind of border do osteoclasts have? What is released?
they have a ruffled border, inholdings of cells on the side facing bone. H+ is released into ECF at ruffled border, acid phosphatase is also released.
What is the process of bone formation?
called ossification or osteogenesis and it starts early in development and continues til age 25.
What are the methods of bone formation?
Endochondral ossification (long bones)
Intramembranous ossification (flat bones)
-both processes are initiated by blood vessel invasion and they use the same cells/enzymes to build bone of same components
What is intramembranous ossification?
The transformation of mesenchyme tissue into bone.
1. you have a flat tissue called mesenchyme
2. converted to osteoid tissue
3. osteoblasts add in collagen
4. once collagen is laid down, you can now deposit the membrane
What is endochondral ossification?
the formation of bone from pre-existing hyaline cartilage models
What is the epiphyseal plate?
flat plate of hyaline cartilage seen in young, growing bone
Metaphysis
transitional zone between the cartilaginous head and shaft, it works to transform cartilage to bone.
What are the five zones of metaphysis?
-reserve cartilage
-cell proliferation
-cell hypertrophy
-calcification
-bone deposition
What is the zone of reserve cartilage?
reserve cartilage (aka resting zone), it has no sign of transforming into bone and it is furthest away from the marrow space
What is the zone of cell proliferation?
chondrocytes multiplying and lining up in rows of small flattened lacunae
What is the zone of cell hypertrophy?
chondroblasts enlarge and no longer divide, the cartilage walls thin, combined with proliferation expands bone length
What is zone of calcification?
minerals deposited in matrix when chondroblasts rupture, this helps cement epiphysis to diaphysis and it is temporary
What is zone of bone deposition?
walls of lacunae break down and chondrocytes die and leave longitude channels, osteoclasts dissolve calcified cartilage, and osteoblasts line channel walls and deposit bone and form concentric lamellae
What are the 2 mechanisms of bone growth?
Interstitial growth
- adds matrix internally which adds length to the bone and it is a type of growth seen in epiphyseal plate, it is only in infants and children
Appositional growth
-adds matrix to the external surface which widens the bone and it is in both children and adults
What is bone remodeling?
bone is living tissue and it changes with use and disuse, bone density decrease with age and the remodeling allows body access to Ca+
What is bone physiology?
-requirement for bone growth
-mineralization
-mineral restoration
-calcium and phosphate homeostasis
What are the three requirements from bone growth?
Salt - calcium and phosphorous
Vitamins - vitamin A, K, B12, C, D
Hormones - parathyroid, sex, growth, calcitriol, thyroid, glucocorticoids, insulin
What is mineralization?
the crystallization of calcium and phosphate ions which is mineral deposition, ions are taken from blood plasma and deposited on bone tissue
Explain ectopic ossification.
the formation of osseous tissue in tissue beside bones (ex: arteriosclerosis - calcification of arterial walls)
What is mineral resorption?
the process of dissolving bone and releasing minerals into the blood which is carried out by osteoclasts.
What is the role of phosphate in the body?
it helps regulate body pH balance and it is in DNA, RNA, phospholipids, and ATP