NEUROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
NEUROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
_______ (80%)
_________ (15%)
________(5%)
For confirmation of neurologic diagnosis
History (80%)
Physical & Neurological Examination (15%)
Ancillary Procedure (5%)
DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS
This comprise the most meaningful information of the initial (and often subsequent) steps of clinical diagnostic reasoning, informing the diagnostic workup, and treatment plans
history and physical examination
HISTORY TAKING IN NEUROLOGY
Chief Complaint
Present Illness
Past History
Prenatal
Perinatal
Neonatal
Medical History
Immunizations
After COVID vaccination, pt had stroke, myasthenia gravis, parkinson’s worsened, memory problems (worsened), etc
Illnesses
Operations
Injuries
Family History
Social History
Review of Systems
to determine if there are correlations with the present condition
Growth and Development
Psychomotor
Habits
Educational
Nutrition
Behavioral History
Habits
3 QS TO ASK
Is there a neurological problem?
may be one or all three questions are (+)
Focal neurologic deficits
Are there s/sx?
Check based on history, subjective & objective data gathered
Increased intracranial pressure
Positive? Do we see any evidence?
Signs of meningeal irritation
Where is the neurological problem?
Levelize
Lateralize
Localize
What is the neurological problem?
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF NEUROLOGICAL LESIONS
Alteration in the level of consciousness
Aphasia, Apraxia, Agnosia
_______: language difficulty
_______: difficulty performing tasks
_______: loss of ability to recognize objects
Changes in memory, syncope, seizures
_______: transient loss of consciousness
______: abnormal electrical change in the brain
Alteration in the level of consciousness
Aphasia, Apraxia, Agnosia
Aphasia: language difficulty
Apraxia: difficulty performing tasks
Agnosia: loss of ability to recognize objects
Changes in memory, syncope, seizures
Syncope: transient loss of consciousness
Seizures: abnormal electrical change in the brain
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF NEUROLOGICAL LESIONS
Sensory changes
Dizziness
Hearing loss
May be a problem with the temporal lobe (Heschl's gyrus) or tympanic membrane
Impaired vision
Headaches
Involuntary movements
Muscle weakness
Gait disorders
IS THERE A NEUROLOGICAL PROBLEM?
Meningeal irritation
The classic triad of meningitis is _____________
______ intracranial pressure
Focal neurologic deficits
fever, headache, and meningismus
Increased
I. MENINGEAL IRRITATION
Headache/vomiting with:
______ : stiff neck, meningismus
_______: (+) when passive flexion of the neck results in spontaneous flexion of the hips and knees
________: (+) Passive extension of the leg elicits pain
Thigh and knee flexed → (+) Passive extension of the leg elicits pain
Nuchal rigidity
Brudzinski sign
Kernig Sign
I. MENINGEAL IRRITATION
Patients with bacterial meningitis have either a fulminant illness that develops over a matter of hours or a subacute illness that progresses over 24 to 72 hours
The patient’s level of consciousness may become progressively worse over a short period of time
As the disease progresses, and the complications of seizures, increased intracranial pressure, and cerebral ischemia and intracerebral hemorrhage occur, the patient’s level of consciousness evolves from lethargy to stupor to obtundation
II. INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
3 signs→ ___________ (HPV)
Crushing Triad is? ( IB DPR)
Headache ,Vomiting , Papilledema
INC BP, DEC PULSE,DEC RESPIRATION
II. INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Headache/vomiting with
___________
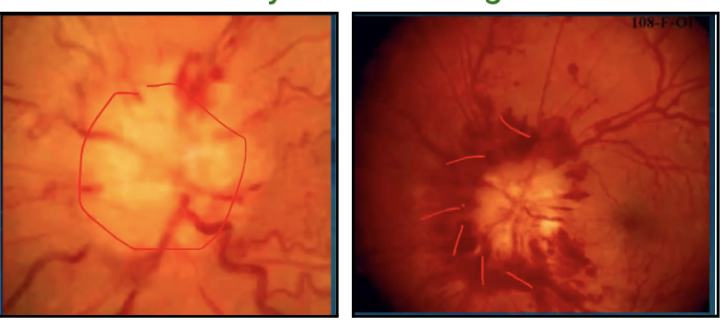
optic nerve is not well defined and optic disc is not delineated
typically bilateral, due to elevated intracranial pressure (ICP)
Can be a diagnostic clue to underlying secondary cause of high ICP such as brain tumor or venous sinus thrombosis
Can develop in the absence of subjective or objective vision loss and in the absence of other signs of high ICP such as headache.
Papilledema
II. INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Headache/vomiting with
_______
Eye is medially deviated
Double vision (CN 4 & 6)
Diplopia d/t inc. ICP – CN 6 palsy
Lateral rectus palsy secondary to Abducens nerve lesion
Initial stage: _____ affected
Later stage: _____ affected
Diplopia with internal squint
initial → one eye affected
later → both eyes affected
II. INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Headache/vomiting with
Deterioration in __________
Leads to comatose state of patient
Arousal system is compromised
Wakefulness and awareness of self and environment
CONSCIOUS COMA
Deterioration in the level of consciousness
II. INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Headache/vomiting with
Bulging fontanel (tense), separation of sutures, rapid enlarging head size ( Pediatric)
______ fontanelle – hungry
_____ fontanelle – INC. ICP
Depressed fontanelle
Bulging fontanelle
III. FOCAL NEUROLOGIC DEFICITS
Weakness
Sensory deficits
Cranial nerve deficits
Disturbance in higher intellectual functions eg: Memory impairment, Emotional & behavioral changes (organic), Language disturbance, & Seizure
Sensory impairment in trunk & extremities
CONT →
III. FOCAL NEUROLOGIC DEFICITS
Cranial nerve deficits eg: diplopia, dysphagia, dysarthria, facial numbness, & sensory impairment
_______ – Swallowing problems
_____ – Speech articulation
Weakness or paralysis of extremities
Weakness – _______ tract affected
1st neuron: _____
2nd neuron: Short interneuron w/ anterior horn cell
3rd neuron: anterior horn cell, peripheral nerve, myoneural junction
Cranial nerve deficits eg: diplopia, dysphagia, dysarthria, facial numbness, & sensory impairment
Dysphagia – Swallowing problems
Dysarthria – Speech articulation
Weakness or paralysis of extremities
Weakness – corticospinal tract affected
1st neuron: UMN
2nd neuron: Short interneuron w/ anterior horn cell
3rd neuron: anterior horn cell, peripheral nerve, myoneural junction
III. FOCAL NEUROLOGIC DEFICITS
Incoordination, poor equilibrium
Cerebellar symptoms
2 hemispheres: ___ control
Problem with coordination
Tests: _______
Vermis
Controls ___
Truncal ataxia
Gait ataxia
Wide BOS
Leaning to the lesion
Intention tremor
Reflex asymmetry, pathological reflexes (+ Babinski)
Always sensory and motor component
limb control
finger to nose test
trunk control
Neurologic Examination
Mental Status
Cranial nerves
Motor
Cerebellar
Reflexes
Sensory
Where is the lesion?
levelize
lateralize
Muscle Disease
_____ & ____ weakness
what part usually?
atrophy of involved muscles
absent sensory sign except for? (PT)
proximal & symmetrical weakness
limb girdle usually
absent sensory signs except for pain & tenderness
READ & ANALYZE
NMJ Lesion Site
Purely ____
cranially and spinally innervated muscles
____ pattern
____ reflexes
(+) response to ______
Myastenia Gravis
____ muscles are affected
normal when rested but weakness progress as day ends
motor
diurnal
intact reflexes
anticholinesterase
eye muscles
NMJ Lesion Site
____ or ____ muscle weakness without sensory symptoms
_______ and facilitation of strength with repeated activity suggest a neuromuscular junction disorder
______ suggests myopathic disorders but also can be reported in motor neuron and basal ganglia disease
limb or cranial muscle weakness
fatigability
cramping
Peripheral Nerve Lesion
Distal ______ symptoms
weakness is likely to be more severe _____
symmetrical unless compression injury
atrophy with time
Caused by _____( 3)
distal sensory & motor
distally
symmetrical
DM, Chronic alcohol intake, Guillain–Barré syndrome
Spinal Cord Lesion
______ often _____ deficit
Normal above lesion; below the level of lesion + symptoms
Prominent __________
Catheterization & manual evacuation of feces
_______ level
Extinction of sensory determination a few levels below the lesion in spinal cord traumas
Bilateral often symmetrical
Incontinence
Sensory
Spinal Cord Lesion
If there is neck or back pain → _______ suspected
no pain →______ is likely
The level of a spinal compressive lesion is indicated by cutaneous ____ loss than by ____ signs
Lesion that causes spastic paraparesis is anywhere above the lumbar segments
compressive lesion
multiple sclerosis
sensory loss »»»»»» motor signs
Brainstem/Cerebellum Lesion
_______ cranial nerve deficits
Ataxia
Altered ____
Usually ______ pyramidal tract signs
pathological reflexes on both side
ipsilateral
sensorium
bilateral
Brainstem Lesion
_______ cranial nerve deficits
Lesions in the right midbrain/pons/medulla will have same side deficits
______ hemiparesis with Babinski
_____ limb ataxia
__________ - lesion at the median longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) syndrome
MLF connects cranial nerves 3,4,6,8
Problems in the movement of eye (one and a half syndrome)
Ipsilateral cranial nerve deficits
Contralateral
Ipsilateral limb ataxia
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia MLF
Cerebellum Lesion
Incoordination, poor equilibrium
Vermis → Truncal or gait ataxia, no limb ataxia
Hemispheres → ipsilateral limb ataxia
Intention tremor
_____ → finger to nose test, heel-knee-skin test
________ → alternate pronation supination test
Hemisphere & vermis lesion can co-exist together
(+) Titubation
Extremity problems
vermis
ipsilateral
Dysmetria
Dysdiadochokinesia
Cerebrum Lesion
Disturbance in higher intellectual functions
_____ impairment
_____ and ____ changes (organic)
Discrete deficits
____ disturbance
_____ impairment
Seizure, delirium and dementia
hemiplegia, aphasia or hemianopia
memory
emotional & behavior
language
intellectual
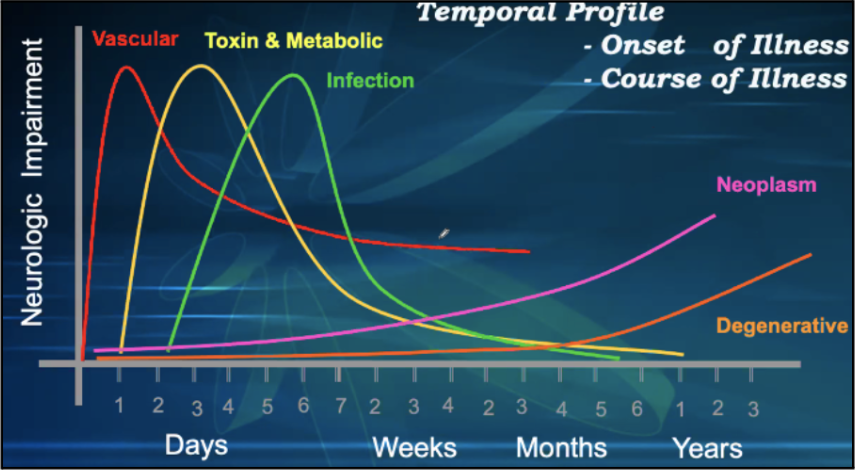
Neurologic Illness according to Onset
________
vascular, acute demyelinating ,trauma
________
mass lesions
Degenerative disease
__________
Infection, metabolic, intoxication, nutritional
Minutes to a day
Insidious ( weeks or months)
One day to several days
CATEGORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES
Congenital/Hereditary/Developmental
Craniostenosis, Spina bifida, Aneurysm (some are congenital but they also develop over time), AVM
_________ = premature closure of sutures of the skull
Craniostenosis
CATEGORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES
Traumatic
Epidural & Subdural hematoma
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Cerebral contusion,concussion
Infection
Meningitis, Encephalitis, Brain abscess
CATEGORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES
Degenerative
Alzhimer, Parkinson’s disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Demyelinating
Post infectious/ post vaccinal: Encephalomyelitis,
Multiple Sclerosis
Landry Guillan Barre syndrome
Metabolic/Endocrine
Hypoglycemia, Hypoxia (chronic lung disease), Hyponatremia (low sodium), Hypercalcemia (high calcium)
Drug overdose
Hyponatremia
DM
CATEGORIES OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES
Nutritional deficiency
Vit B1, B6, B12 deficiency
Tumor
Immunologic
Polymyositis, Dermatomyositis, Guillain-barre, Myasthenia Gravis, Autoimmune encephalitis
Post infectious and postvaccinal encephalomyelitis
________: destruction of matured myelin sheath
_________: destruction of myelin sheath while it is being formed
Demyelinating
Dysmyelinating
Diagnostic Tests
________ → Mass lesions, strokes, head trauma, demyelinating disease, brain abscess
_______→ seizures
Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Diagnostic Tests
_________ → Mass lesions, strokes, demyelinating disease, brain abscess
_________ → Myopathies (check for the level of muscle enzymes)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Muscle Biopsy
Diagnostic Tests
________ → Neuropathies, Myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barre syndrome
________ → CNS infections (Meningitis, encephalitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage)
Nerve stimulation studies (NSS)
Lumbar Puncture
Diagnostic Tests
______ → Hypokalemic paralysis
______ → Muscle disease, polymyositis, dermatomyositis
Total CPK level = very high
Serum Potassium
Total CPK (creatine phosphokinase)
Diagnostic Tests
______ → Aneurysm, aterio-venous malformation
______ → Stroke and hydrocephalus
Angiogram
Transcranial US
Diagnostic Tests
_____ → fx
______ → Pott s Disease
Skull X-ray
Spine X-ray
Diagnostic Tests
_________ → Pt w/ CNS manifestation of HIV/AIDS, TB, viral encephalitis
Serologic test
Read Chapter of Meritts →
“Great minds think alike, but lovers think as one” ❤🔥