Stabilising & Directional & Disruptive selection
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
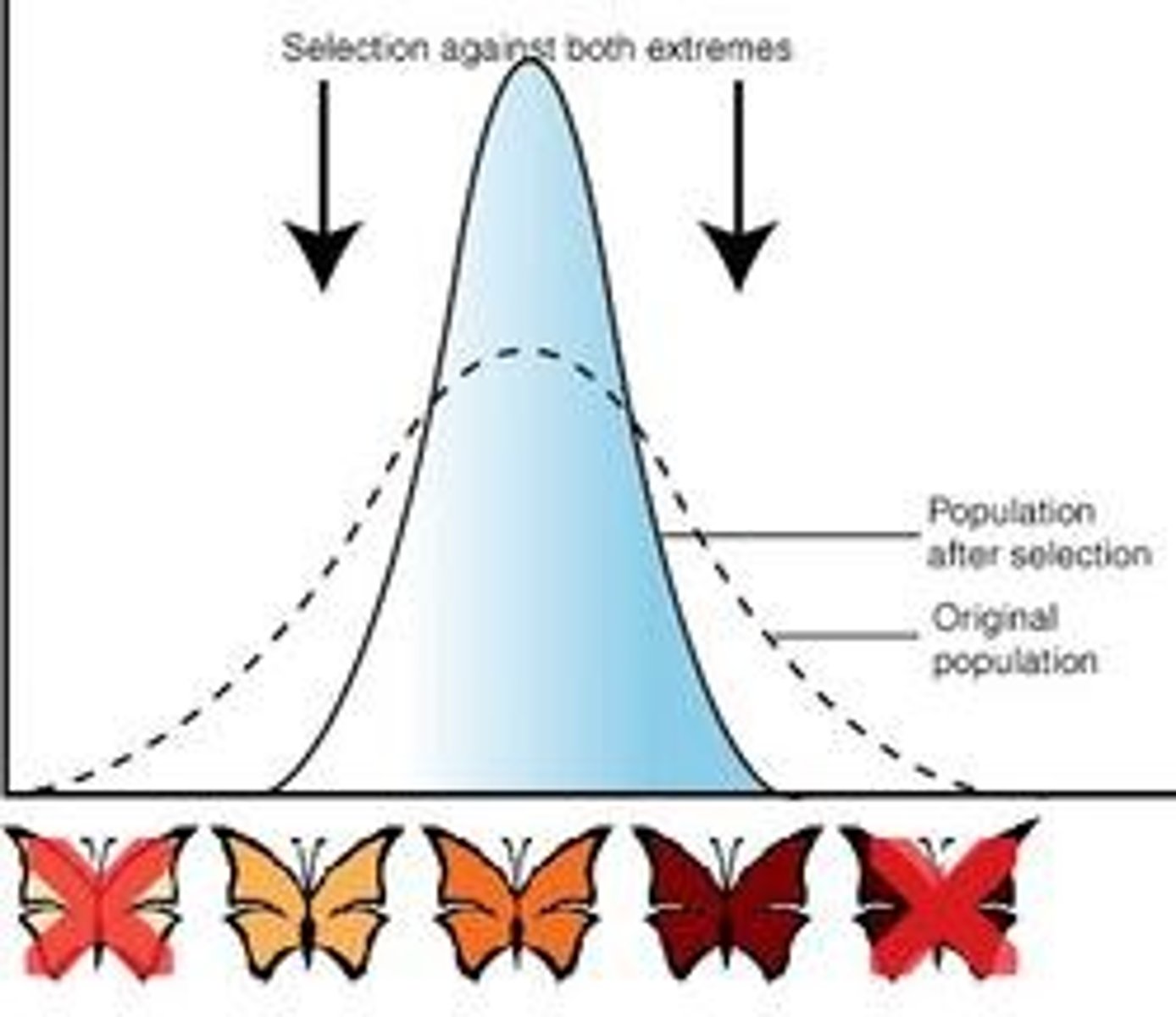
What is stabilising selection?
A type of natural selection where the mean phenotype is selected for, and extreme phenotypes are selected against.
Stabilising selection graph
When does stabilising selection in a population occur?
It occurs in all populations where environment is stable
What is the result of stabilising selection?
- Selective pressure at both ends of distribution
- Favours the mean (selection for the mean, selection against the extremes)
- Increase in allele frequency at means
- Decrease in allele frequency at extremes
- Tends to eliminate extremes, and the mean is unchanged
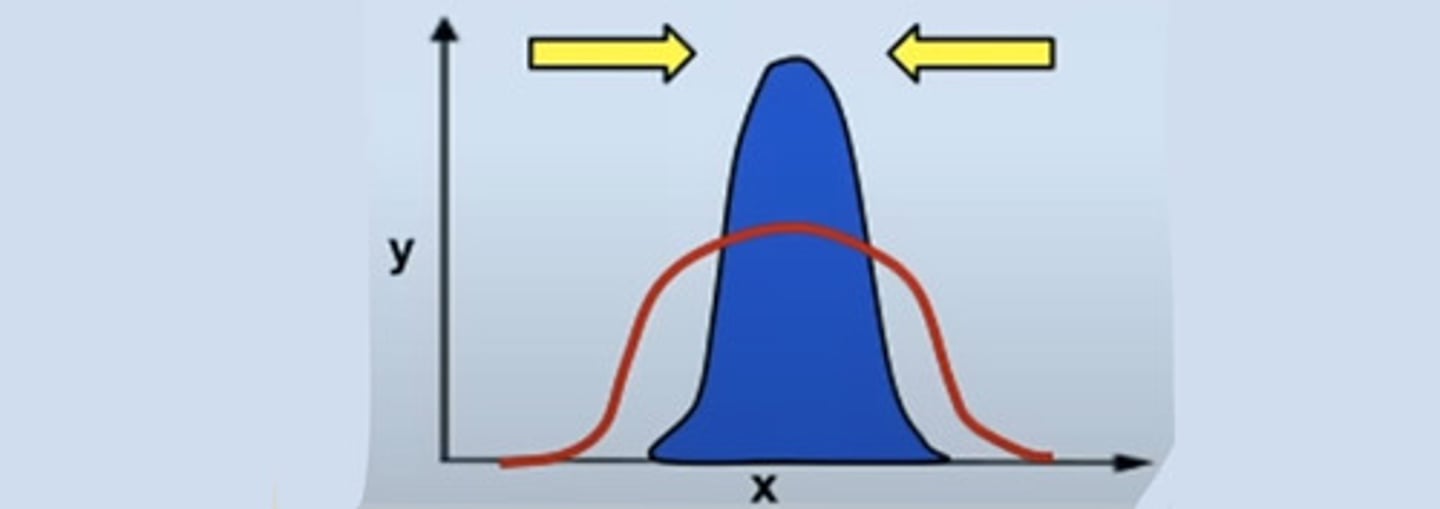
What is directional selection?
A type of natural selection where one of the extremes of the alleles is favoured for, and the other extreme is favoured against.
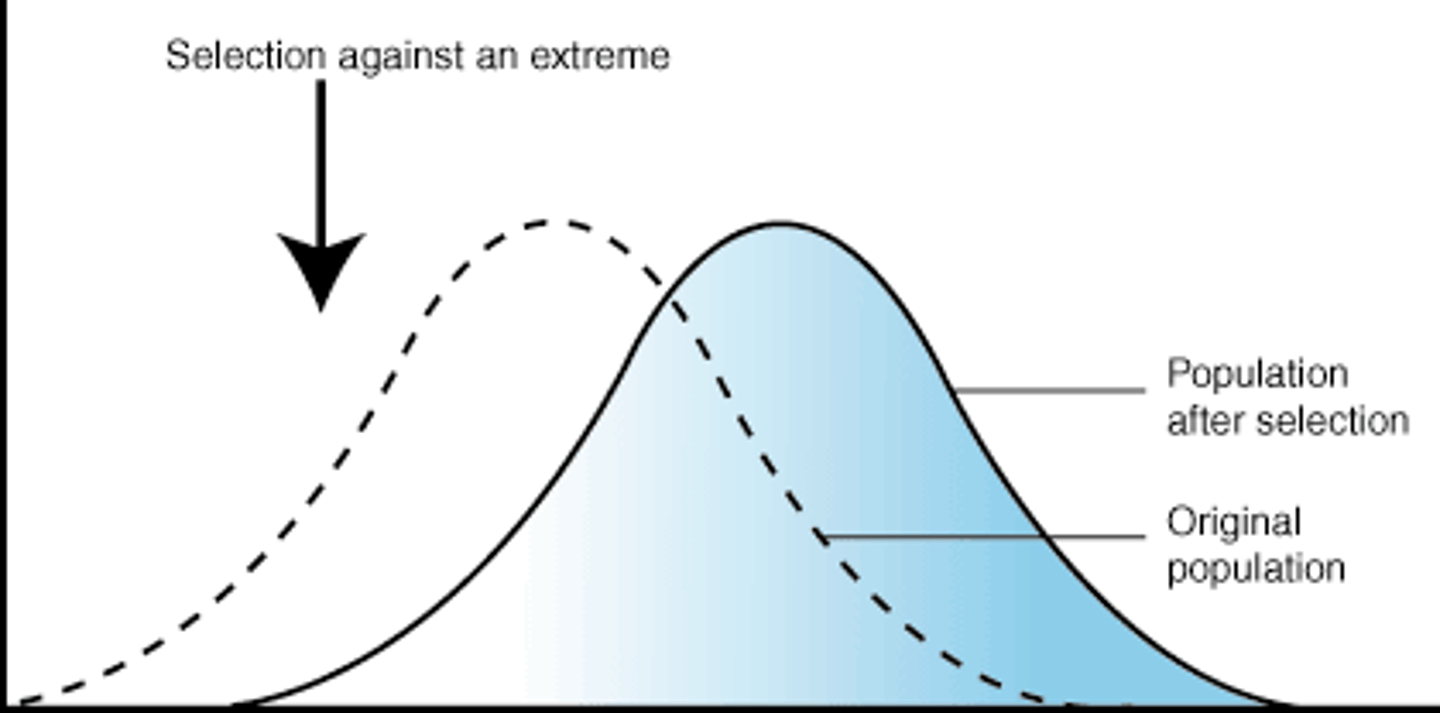
Directional selection graph
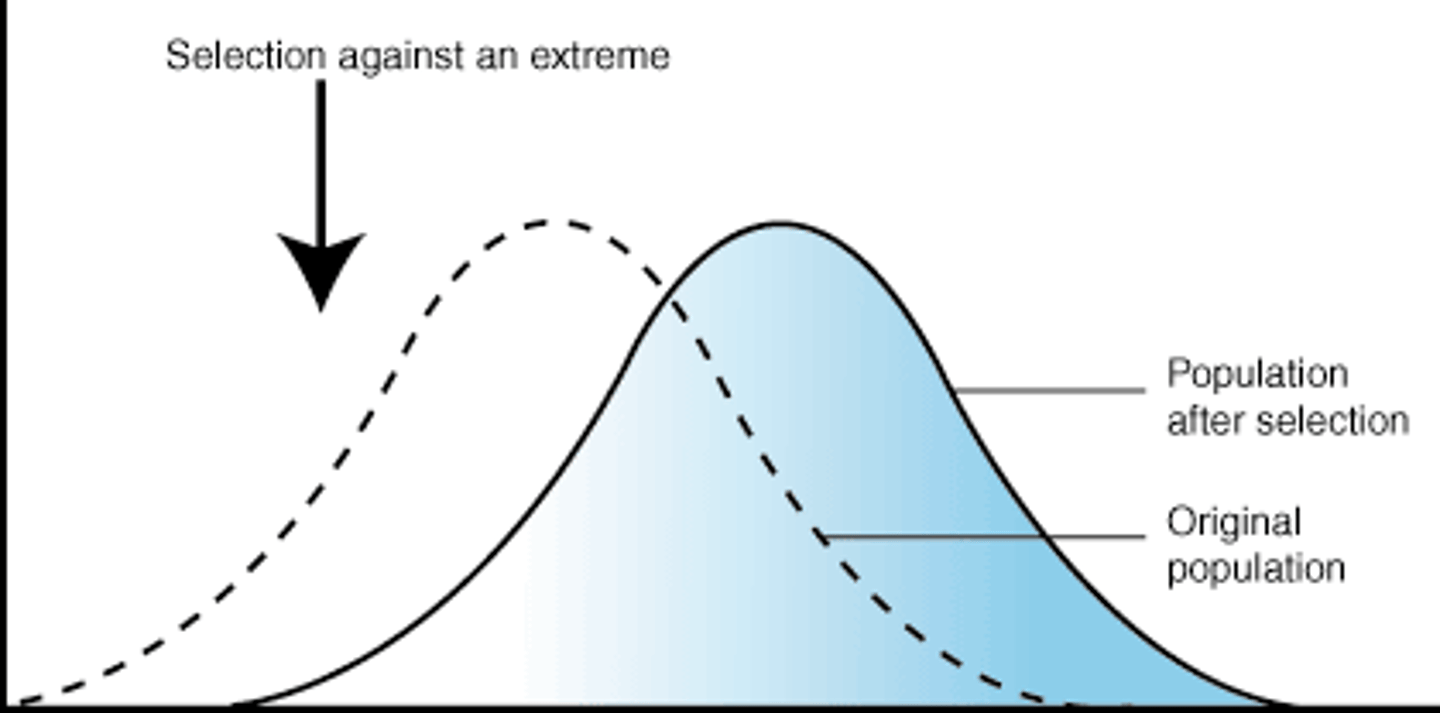
1) Why does directional selection occur?
The population is subject to new selection pressure that favours an extreme characteristic (perhaps due to environmental change)
2) Why does directional selection occur?
When conditions change, particular adaptations give a survival advantage
3) Why does directional selection occur?
Over time, the mean will shift as the allele frequency increases for subsequent generations, decreasing the allele frequency at the other extreme
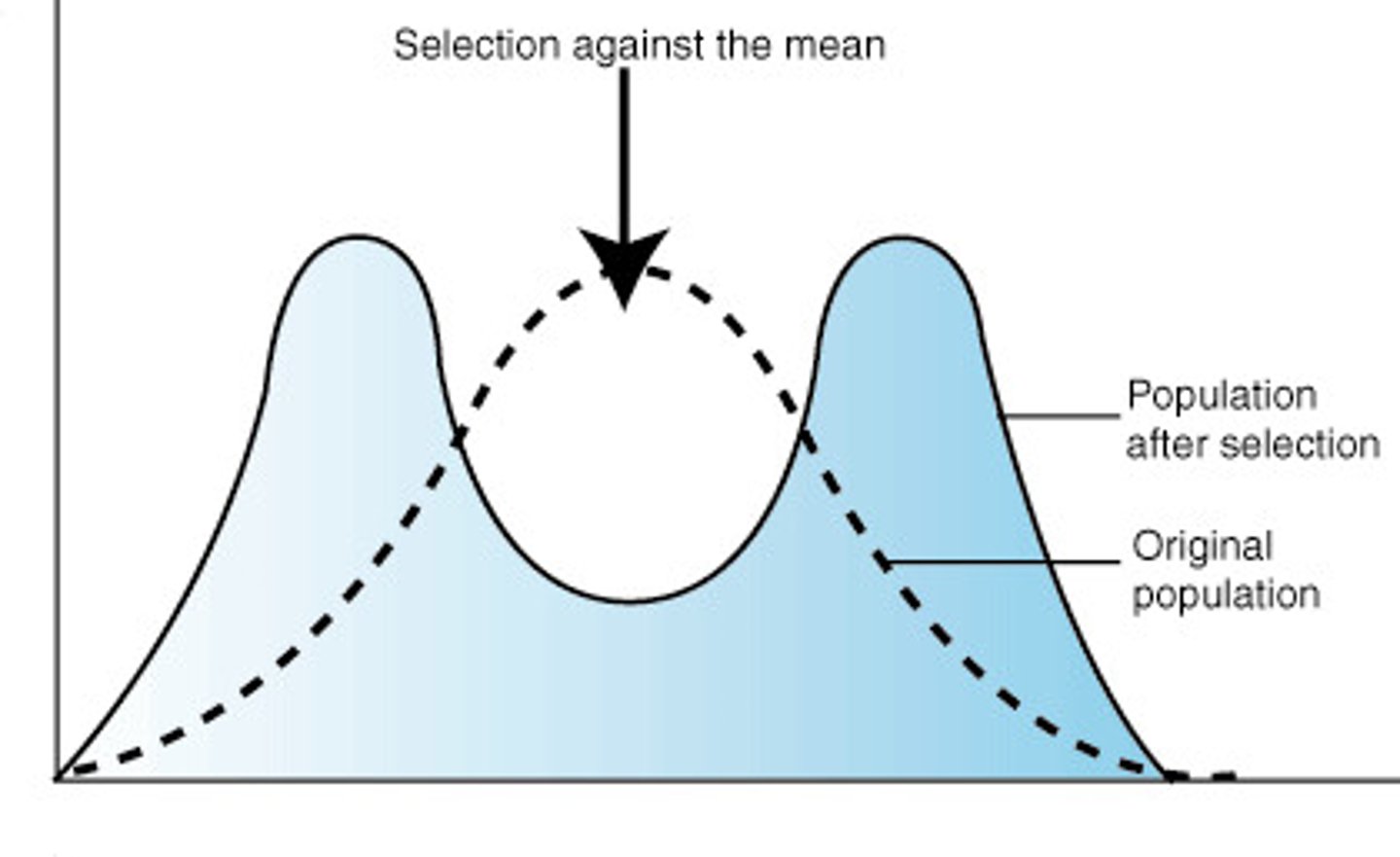
What is disruptive selection?
A type of natural selection that favours both extremes in a range of phenotypes, but selects against the mean phenotype.
The organisms with intermediate phenotypes are selected against and more than one distinct phenotype is selected for, leading to more than 1 modal class.