Thermochemistry Review
Calorimetry
Measuring the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
q = m ⋅ c ⋅ ΔT
- q = heat (J)
- m = mass of water (g)
- c = specific heat capacity (J/(g ⋅ °C))
- ΔT = change in temperature (°C; Final - Initial)
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg or 1g of the substance by 1°C.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.186 J/(g ⋅ °C)
Heat flow (Enthalpy)
Increases the thermal energy of one body and decreases the thermal energy of the other.
Enthalpy (ΔH) is the amount of heat transferred during a reaction.
Both open and closed systems have heat transfer.
ΔH = q / moles
- ΔH = enthalpy change (J / mol)
- q = heat energy (J)
- moles = number of moles reacted (mol)
Standard conditions
Thermochemical standard state conditions
- T = 298.15 K or 25°C
- P = 1.00 atm
- 1M concentration in an aq solution
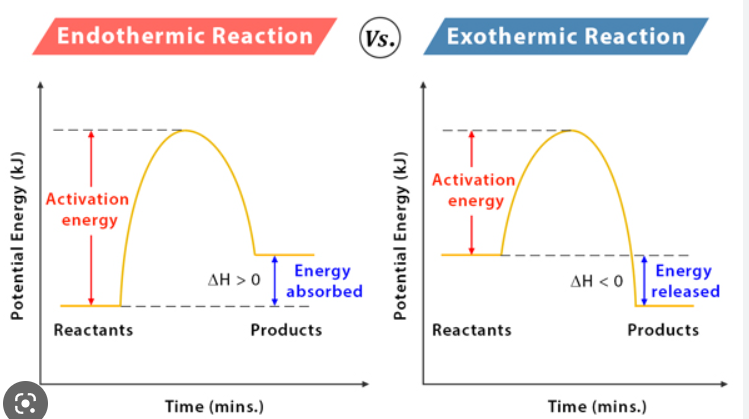
Endothermic & Exothermic
| Endothermic | Exothermic |
|---|---|
| Absorbs heat / energy. Feels cold. +ΔH. ↓ΔT. Hp > Hr.S → L → G | Releases heat / energy. Feels hot. -ΔH. ↑ΔT. Hp < Hr.G → L → S |
All Ways To Calculate Enthalpy Change
Graphs
- The difference between the starting and ending energy. Found at the beginning and end of a graph.
- Activation energy (Ea) is the difference between the highest point of the graph and the starting energy.
Hess’s law
Give multiple reactions and their corresponding enthalpy you must get certain molecules to cancel out by either multiplying the whole equation or flipping them.
- Flipping = flip sign of ΔH.
- Multiplying = multiply sign of ΔH.
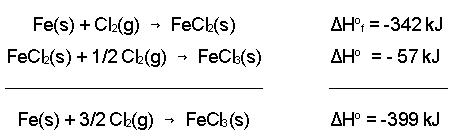
ΔH0 = ΣHf0p - ΣHf0R = q / moles
For all of the following use:
ΔH0 = ΣHf0p - ΣHf0R
- ΔH0 = standard enthalpy change (kJ/mol^-1)
- ΣHf0p = sum of standard heat of formation for the products
- ΣHf0R = sum of standard heat of formation for the reactants
- You will be given Hf values for each of the reactants and products.
Heat of formation
- From its elemental form.
- 2C(s) + 3/2H2(g) + 1/2Cl2(g) → C2H3Cl(g)
Heat of combustion
- CxHy + O2 → H2O + CO2
Heat of fusion / vaporization
Solid to a liquid to a gas
H2O(s) → H2O(l)
- ΔH = 1.43 Kcal (1 Kcal = 4.184 kJ)
Maxwell Boltzmann
Describes the distribution of speeds among the particles in a sample of gas at a given temperature.
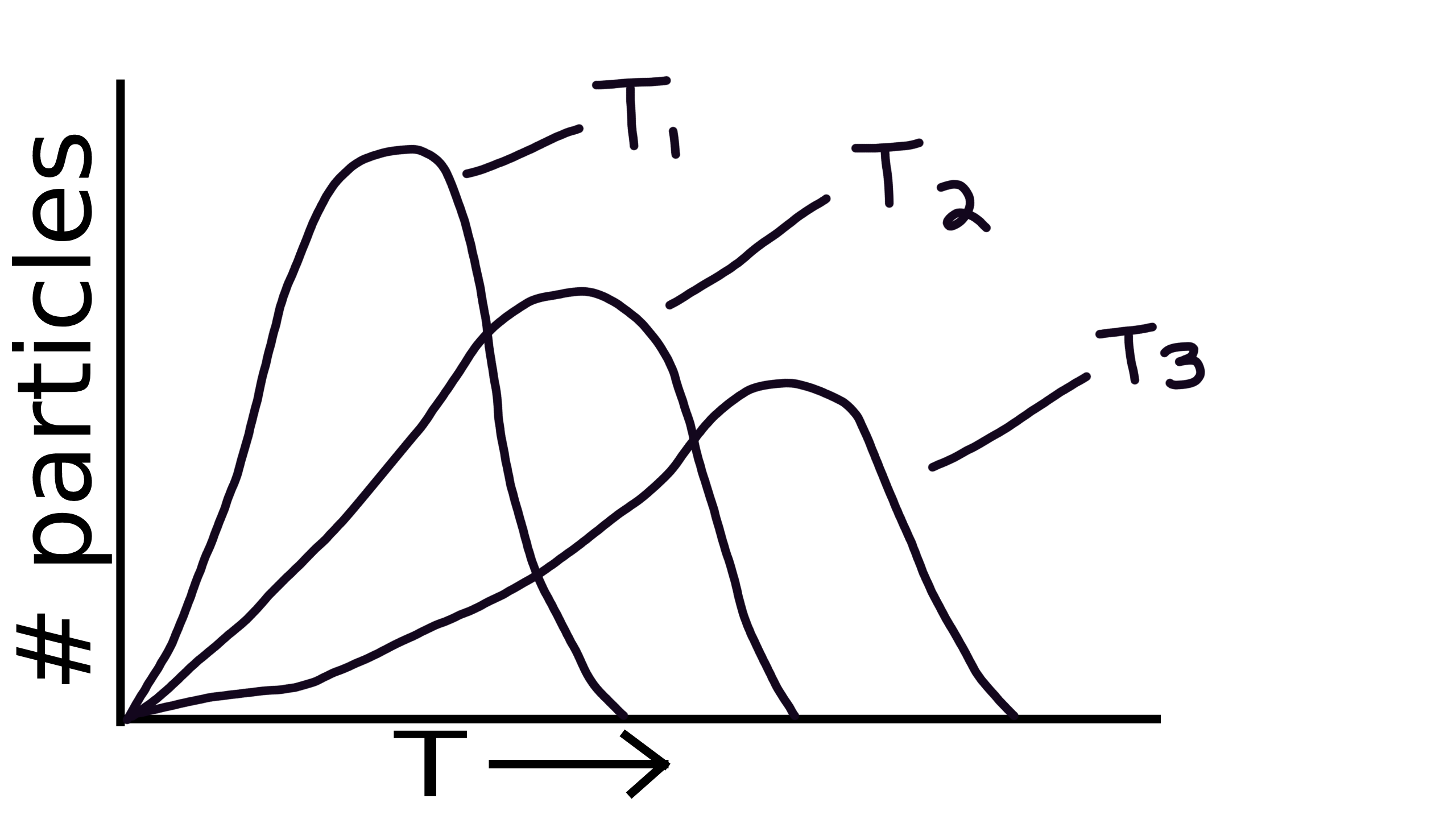
T1 < T2 < T3
Higher temperature means lower peak and moved farther right.
Low temperature will have higher peak and moved father left.