Simple machines, Motion + structures, Materials + Plastics , Intros
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Effort
A machine's input force that drives the movement
Load
A machine's output force that results from the movement
Fulcrum
The pivot point against which a lever is placed to get a purchase, or on which it turns or is supported.
Levers
A rigid bar that rotates around a fulcrum.
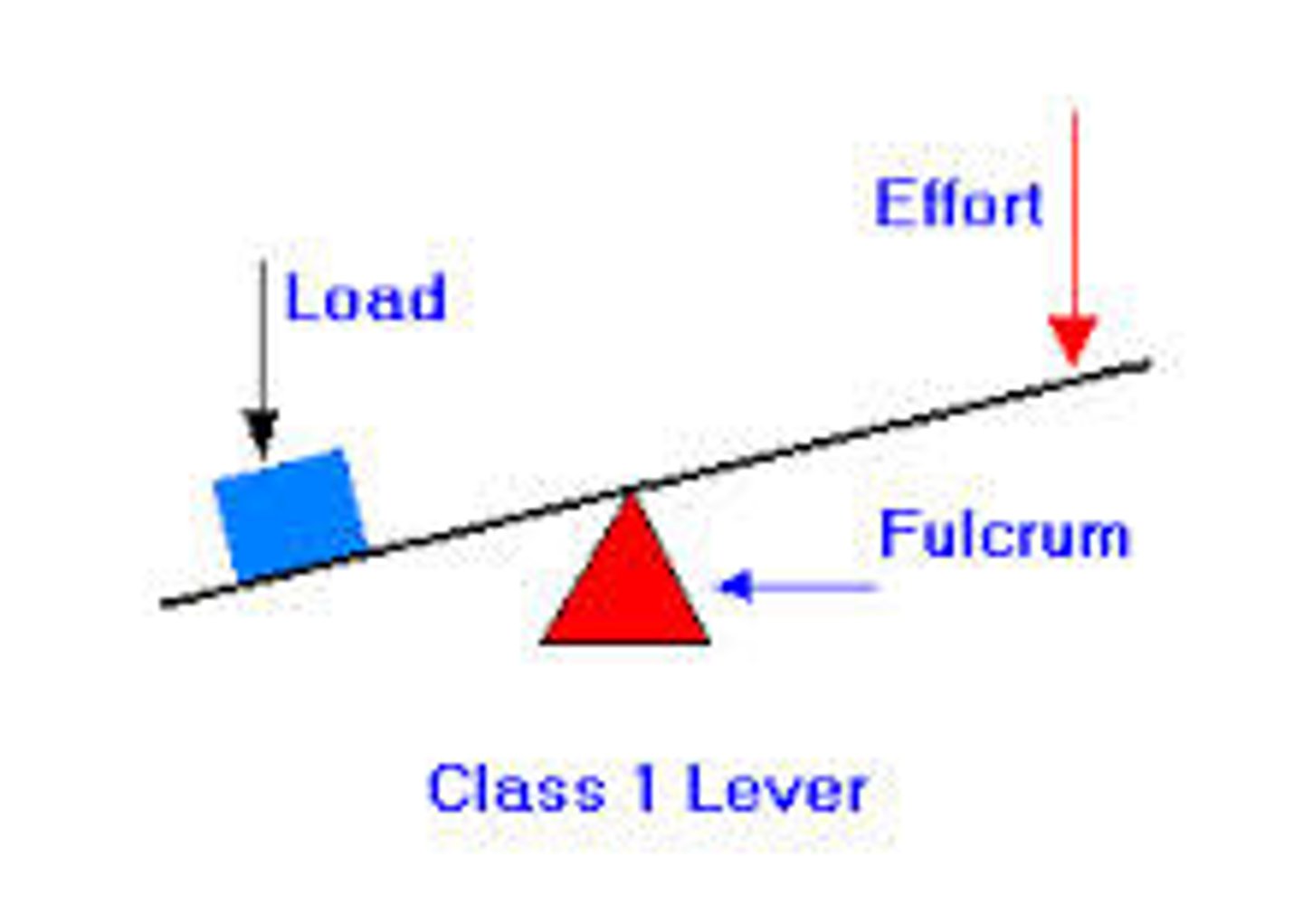
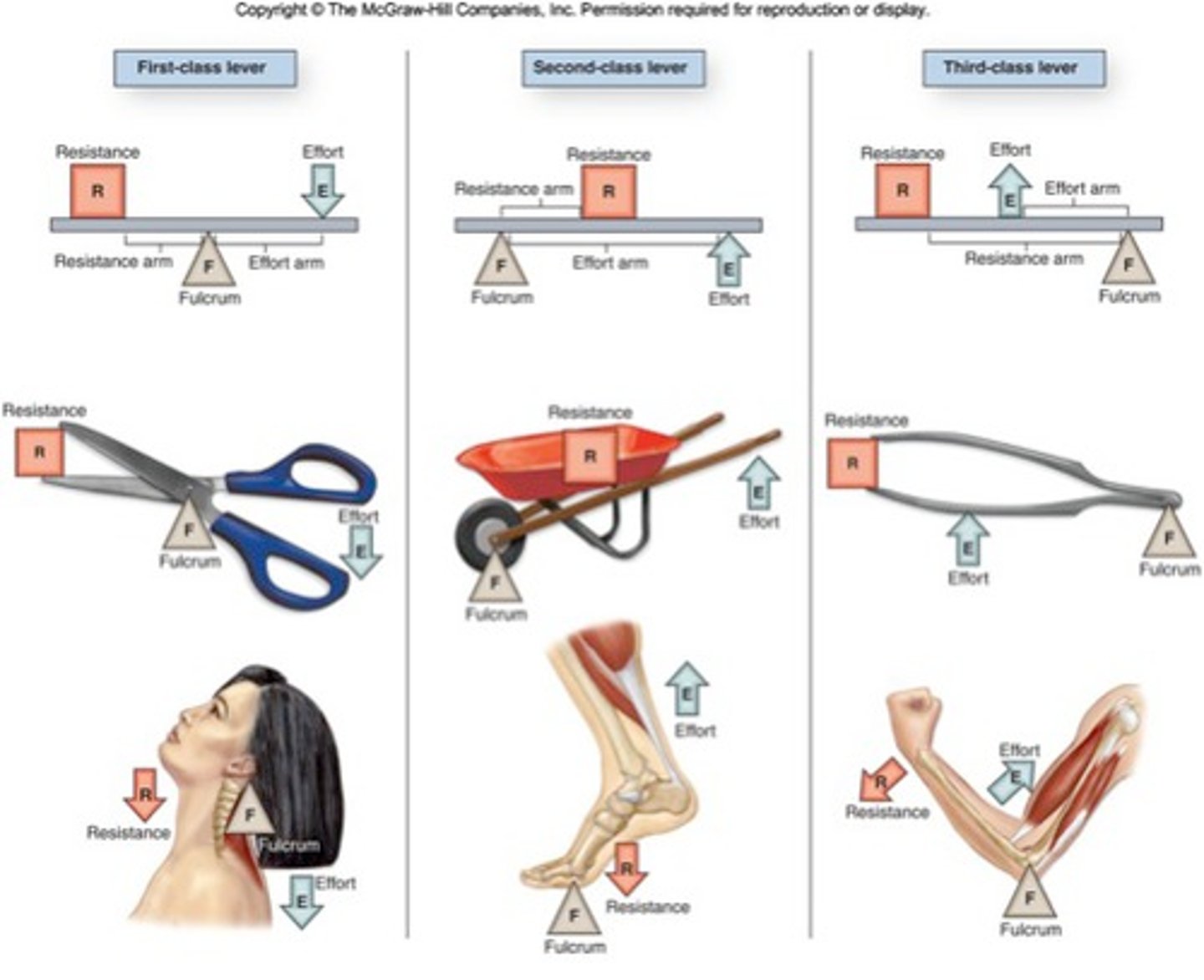
1st class lever
The fulcrum is between the effort and the load. (seesaw, scissor)
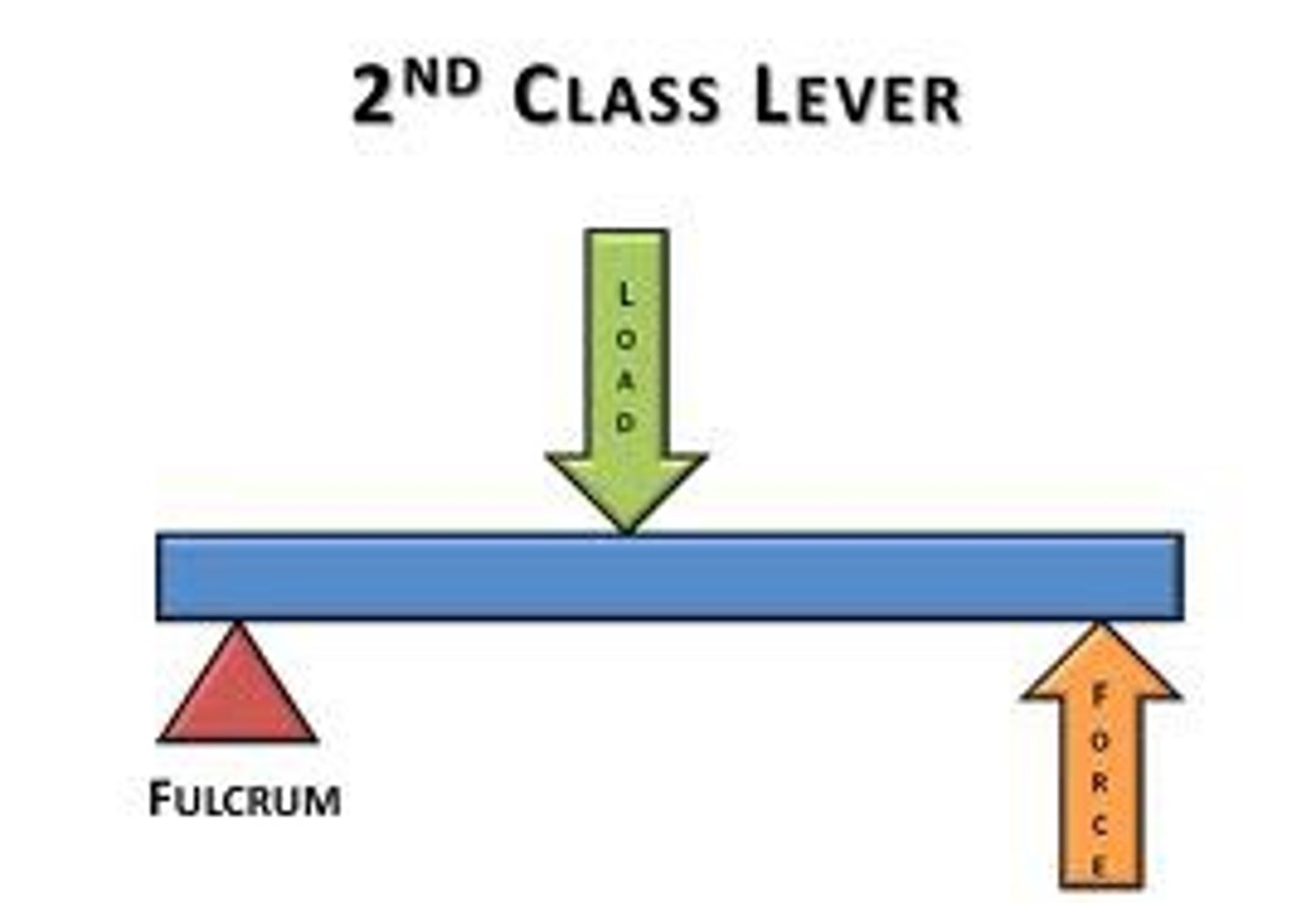
2nd class lever
The load is between the effort and fulcrum. (wheelbarrow, door)
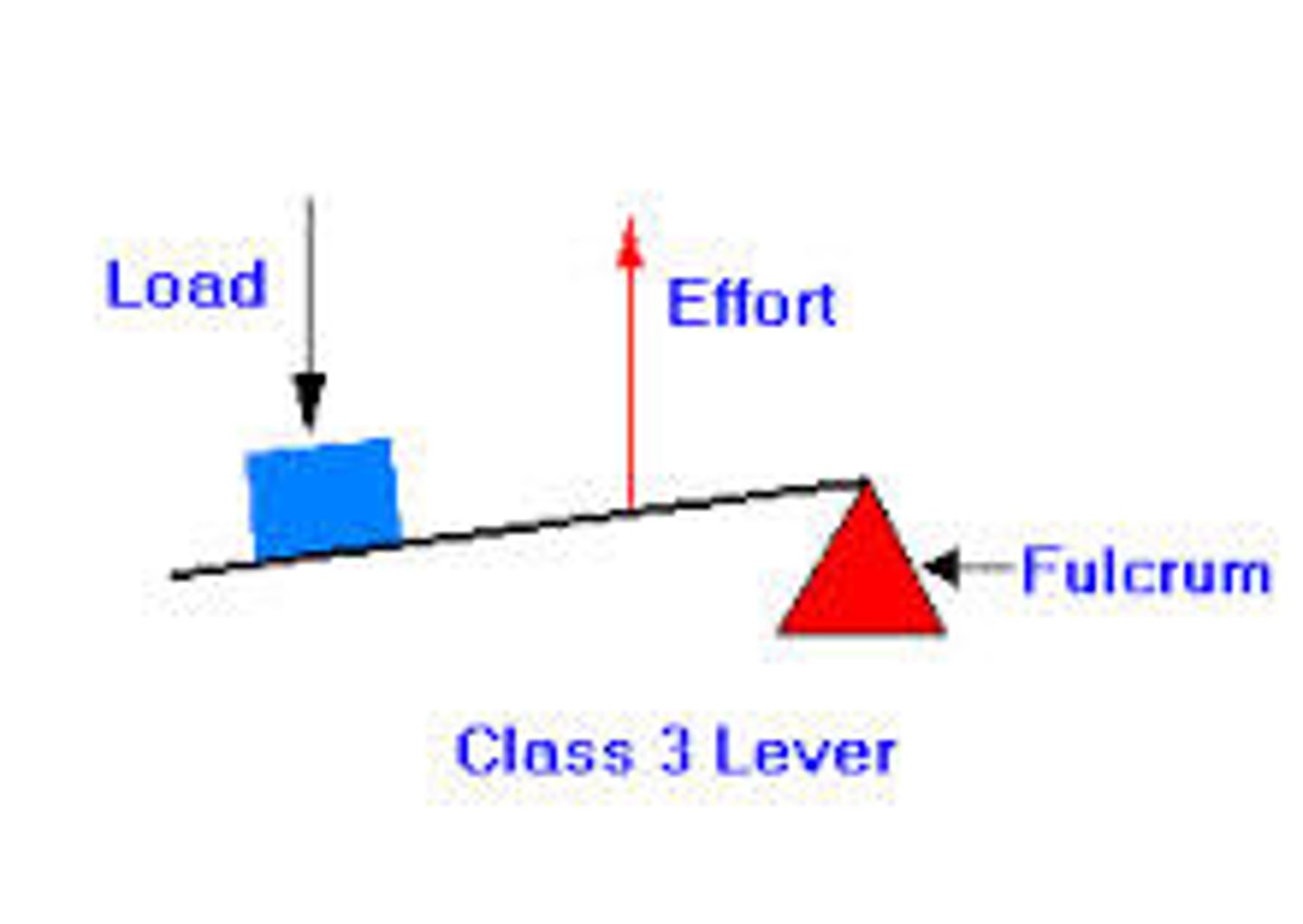
3rd class lever
The effort is between the load and fulcrum.
(broom, fishing rod, tweezer)
How does fulcrums position impact effort?
The fulcrums position from the load determines the amount of effort needed. If fulcrum is closer to the load, less effort is needed to move the load. If fulcrum is closer to effort, the load will move a greater distance.
Velocity Ratio (VR)
VR = d1/d2
d1 - Distance of fulcrum(m) to effort d2 = distance of fulcrum to load (m)
Efficiency
The effectiveness of the machine, done by comparing MA and the VR.
How will an absence of friction or wear and tear, impact a machine?
The machine would have 100% efficiency (MA = VR)
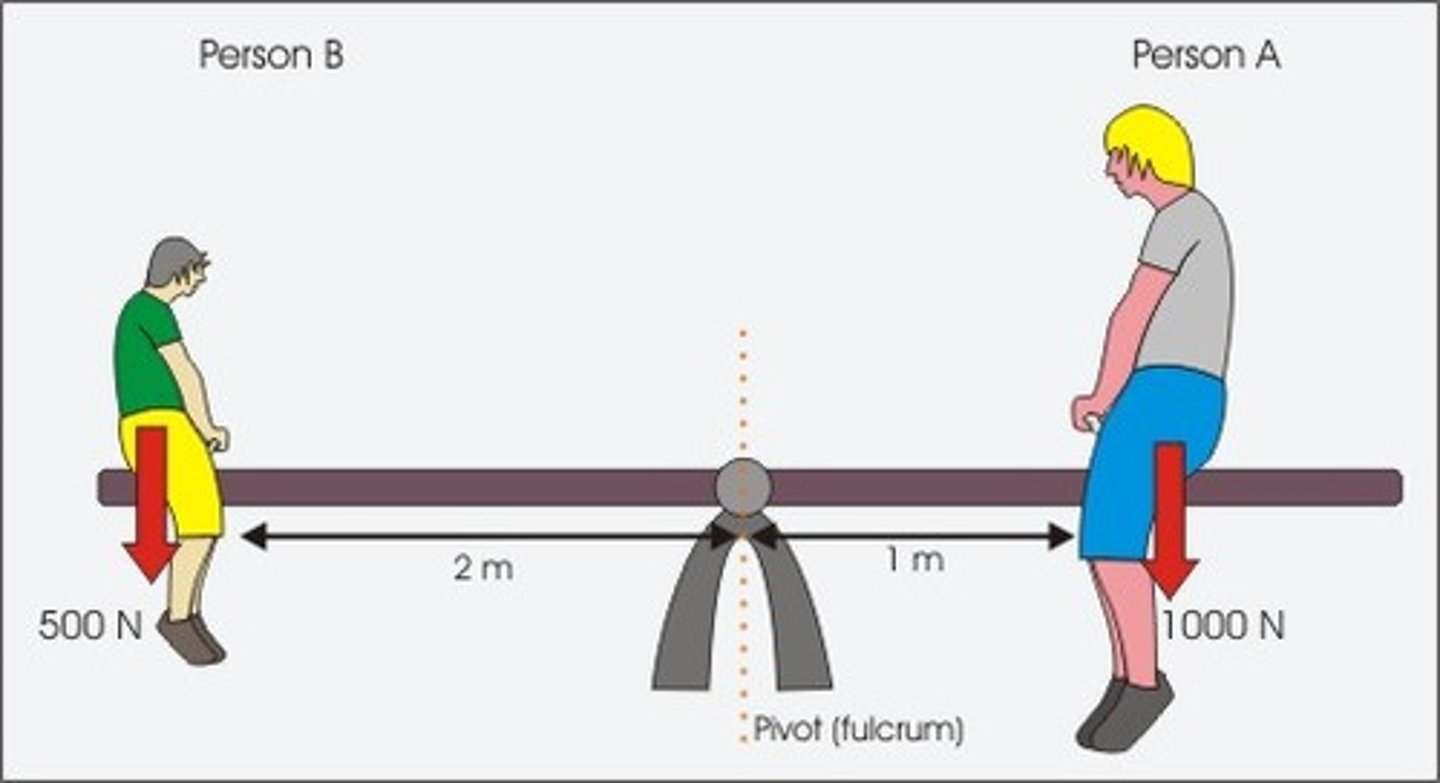
Moments
A moment refers to the turning effect of a force around a fulcrum
Moments if a body is balanced (lever in equilibrium)
The total clockwise moment = the total anticlockwise moment (of the same point)
The sum of moments about the fulcrum is equal to 0.
Inclined plane
involves a plane surface inclined at a small
angle to the horizontal. It is used to lift a heavy mass up the plane by applying an effort along the plane
Pulleys
A pulley is a wheel with a grooved rim, or a combination of such wheels mounted in a block, for a cord or chain to run over for changing the direction or magnitude of a force, making it easier to lift a load.
What are the 3 types of pulleys?
Fixed, Moveable and compound
Fixed pulley
-Only one pulley/wheel fixed in place
-only redirect force (therefore no MA)
-make it easier to lift an object because you can pull down using weight to lift the object
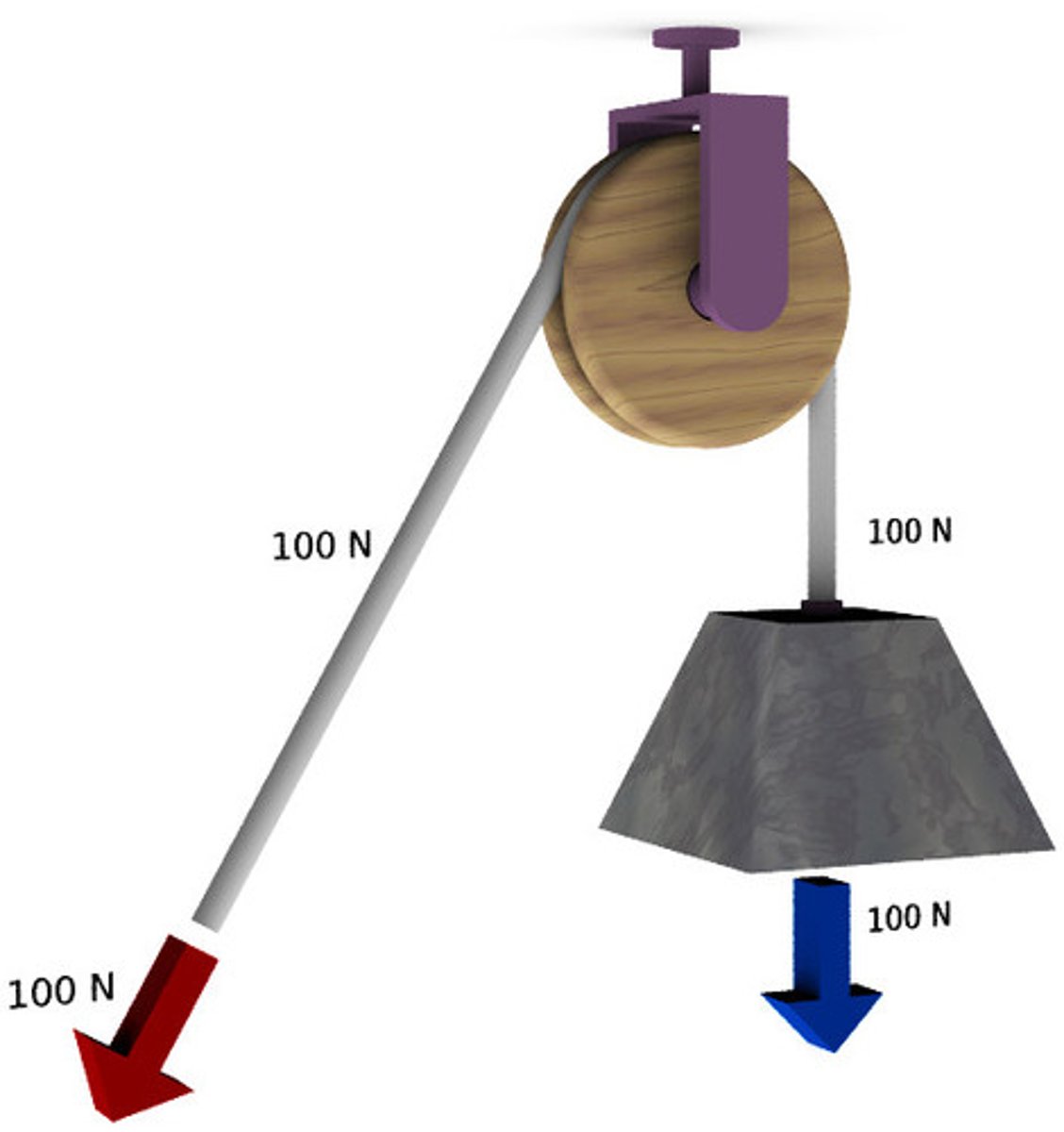
What is the Ideal Mechanical Advantage of a fixed pulley?
IMA = 1
Moveable pulley (lifting pulleys)
-set of wheels and a rope
-lower pulley moves up when the rope is pulled =, creating a MA by reducing effort load
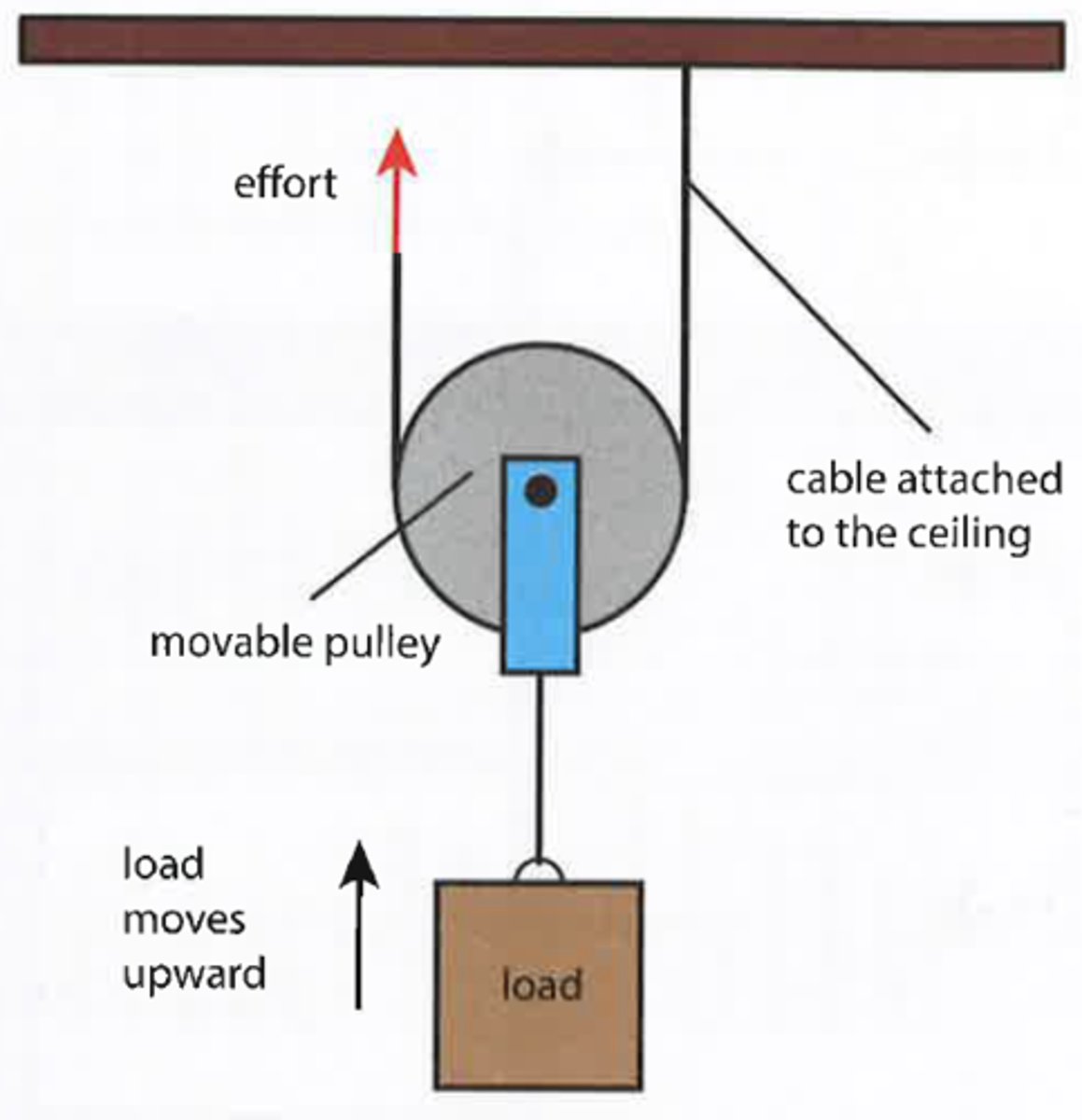
What is the Ideal Mechanical Advantage of a moveable pulley?
IMA = 2
Compound Pulley
Combines a fixed (not moving) pulley with a movable pulley (attached to the load)
When there is more than one pulley or wheel, lower pulleys move up when the rope is pulled and are called moving pulleys.
These combinations are called compound pulleys
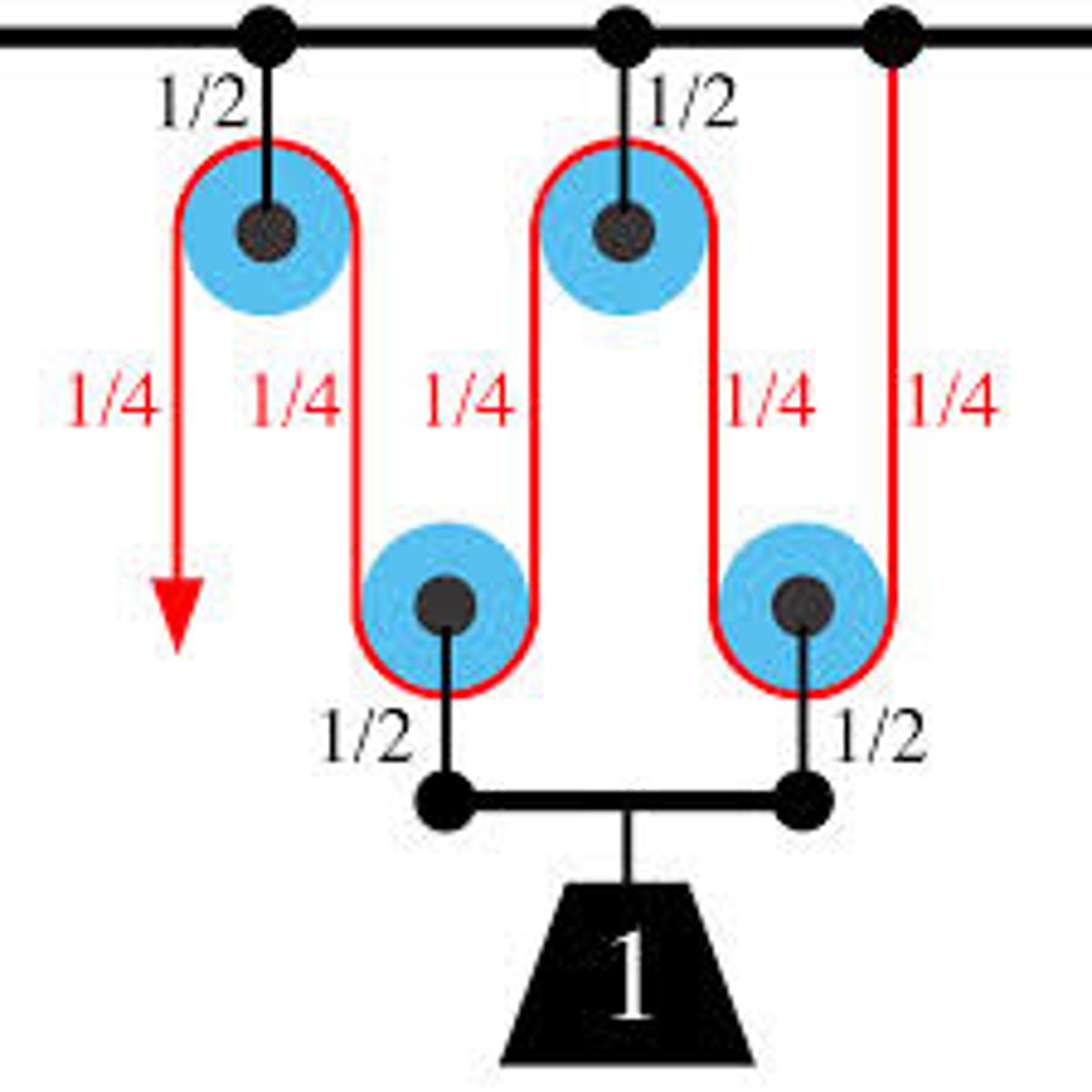
What is the MA of Compound Pulleys?
MA = Number of Rope segments
IMA of Compound Pulleys(no friction) ?
MA = Load / Effort = W/F
Screws
A cylinder with a spiral groove around its outer surface, called the thread, use for conveying motion or bringing pressure to bear. The pitch is the distance between the threads.
Gears
A wheel with teeth that interlock or slot into others to create motion.
What are the advantages Gears can give?
Gears can give torque (force) or speed advantage
Torque
The term used instead of force when describing wheels and gears that rotate
Driving gear
Also called the driver, it is The gear that supplies energy. Sometimes a handle can be used to turn the driving gear.
Driven Gear
Also called the follower, it is the gear to which the force is directed.
Speed advantage in gears
When a large gear turns a smaller gear, turning the smaller wheel more times for the effort involved
Torque Advantage in gears
When a smaller gear turns a larger gear requiring less force to create a motion.
Idle gear
A gear added between the driver and driven gears to make them both go the same way (2 gears meshed together causes them to go opposite directions). The idler gear has no impact on the MA.
Gear Ratio > 1
Torque Advantage
Motion
The change of position of an object with respect to time
What are the 4 types of motion?
Linear, Rotary, Oscillating, Reciprocal
Linear motion
An object moving in a straight line
Rotary motion
An object moving in a circle or part of a circle (an arc)
Oscillating motion
Backward and forward motion in an arc
Reciprocal motion
Backward and forward motion in a straight line
How does a crank and piston change motion?
Rotating the crank makes the piston go back and forth in a reciprocating motion
How does a winch change motion?
Rotating the handle of a boat winch pulls the boat out of the water in a linear motion
What is the strongest shape for structures?
Triangles

How can triangles enhance a rectangle
A rectangle alone is unstable because lateral forces cause shear and joint rotation. Triangle braces transfer loads into axial compression, making the structure rigid.
How are domes strong?
Domes can resist compression however aren't usually used in modern construction due to its difficulty to construct and furnish

How are cylinders strong?
Cylinders have a curved shape that distributes force evenly around the surface, making it strong against compression

Bridges
Bridges must withstand many forces, and are often very high to allow ships to pass under (adding more stress to vertical supports).
What are the two types of bridges?
Cable-stayed and Truss bridges
Cable-stayed bridges
The main force acting on a cable-stayed bridge is gravity pushing down on the bridge and vehicles. Each stay (cable) is under tension, transferring the force to the towers, which are under compression force being pulled down from the stays above but supported by the ground, efficiently distributing the load and reducing bending in the deck.
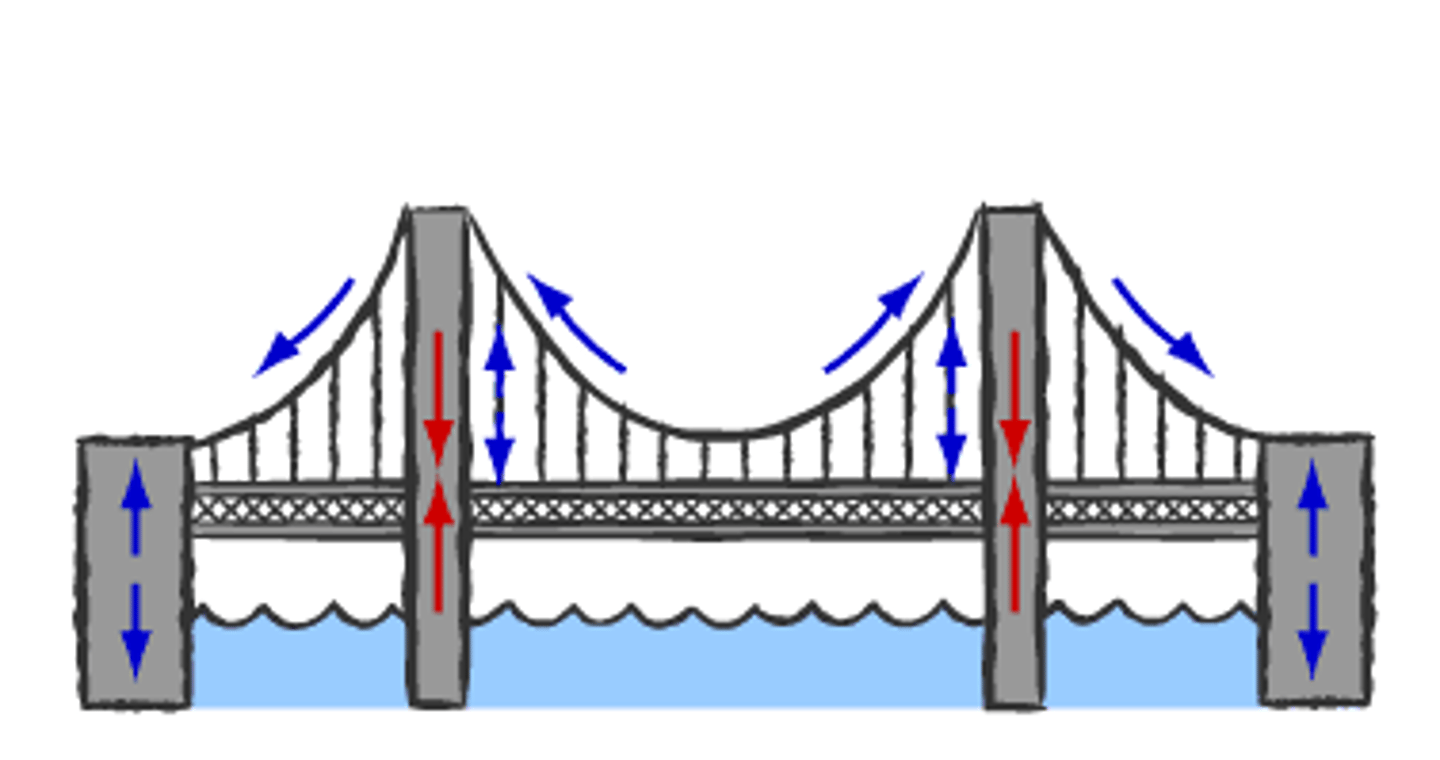
Truss Bridges
A truss bridge uses triangles to distribute force on a bridge, with each part of the triangle under either compression or tension force.
3 main types of truss bridges
Warren, Pratt, Howe
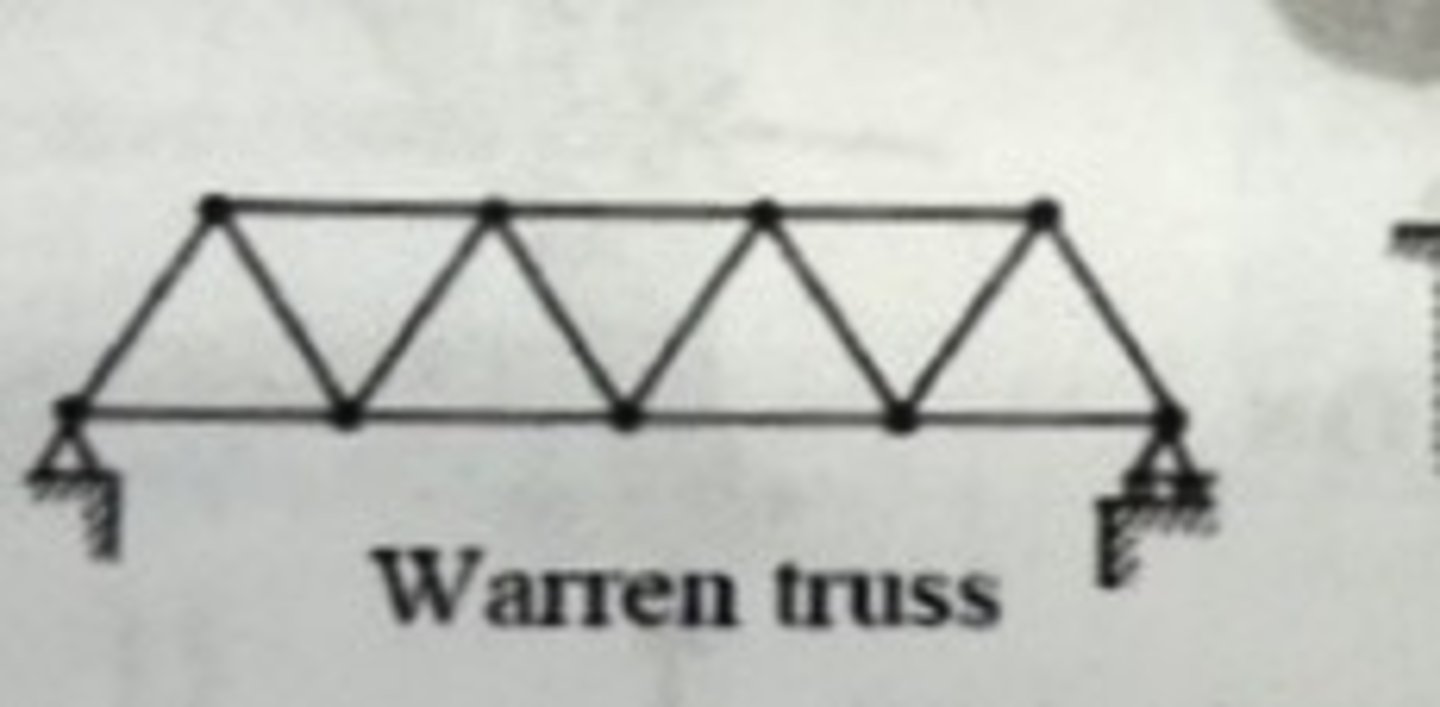
Warren truss bridges
A Warren truss bridge uses a series of equilateral triangles, with members alternating between tension and compression, making it efficient for evenly distributed loads.
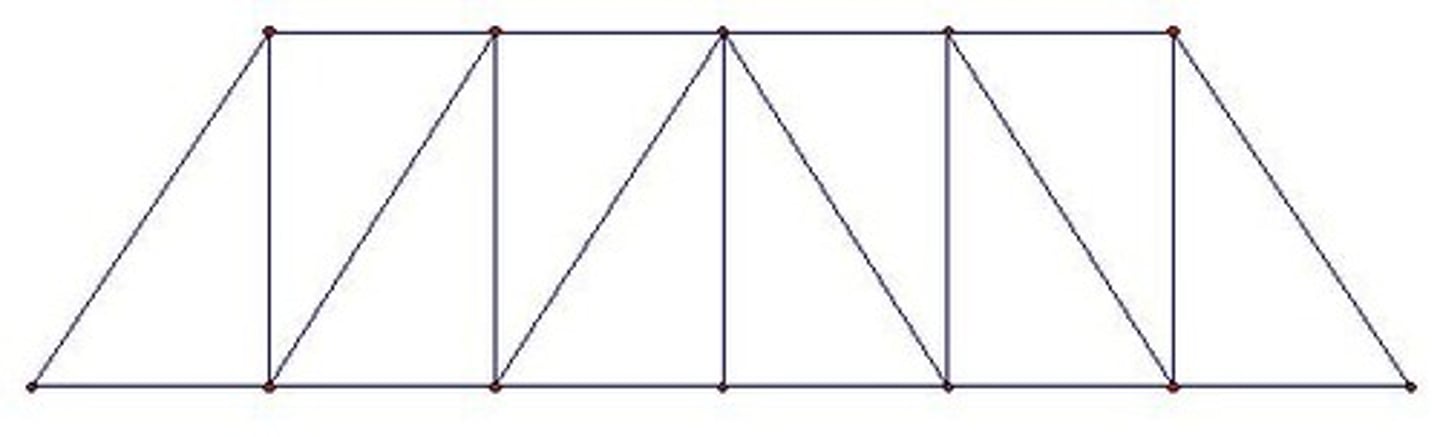
Pratt truss bridge
A Pratt truss bridge has diagonals that slope toward the center, carrying tension, while the verticals carry compression, making it efficient for heavy central loads.

Howe truss bridge
A Howe truss bridge has diagonals that slope away from the center, carrying compression, while the verticals carry tension, making it well suited for timber construction
Moments
Moment are the rotational or turning forces acting on an object.
Other names for moments
Torque or the moment of a force
What does a moment force produce?
A moment force produces a turning action that's clockwise (+ve) or anticlockwise (-ve). They are measured in Newton metres (Nm)
Moments in a balanced body
If a body is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a point equals the total anticlockwise moment about the same point.
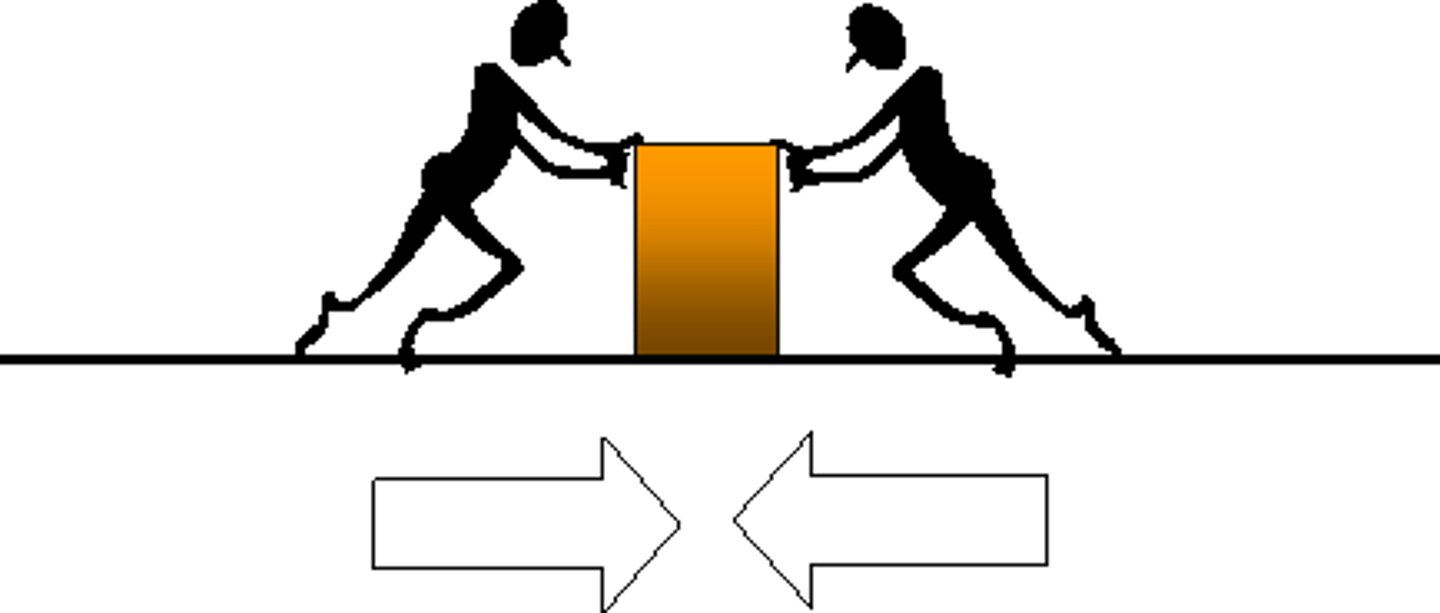
Force in equilibrium
When 2 or more forces acting on an object and it remains at rest. (all forces acting on object are balanced)
Why is equilibrium important in engineering?
It is important because most constructions have to be build to withstand all foreign forces
Requirements for 2 forces in equilibrium
- Be equal in magnitude (size)
- Have lines of action which pass through the same point (i.e. concurrent)
- Act in exactly the opposite direction
Requirements for 3 forces in equilibrium
- they must all be on the same plane ( i.e. coplanar)
- Have lines of action which pass through the same point
(i.e. Concurrent)
-.When the forces are drawn head
to tail, then these lines form a
closed force triangle
Requirements for multiple forces in equilibrium
-ΣFx = 0 (horizontal forces are balanced)
-ΣFy = 0 (vertical forces are balanced)
-ΣM = 0 (moment forces are balanced)
What are the four main types of engineering?
Military, Civil, Chemical, Electrical
What is the problem solving process?
Explore, develop, Generate, evaluate
Simple Machine
A mechanical device that is used to make work easier and assist people by giving them a mechanical advantage.
Mechanical Advantage
A measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system
What does a simple machine do
Create systems for different kinds of movement to occur when force is applied to a load. They are devised to amplify a force
What trade occurs in simple machines?
These devices which trade a small force over a large distance for a large force
over a small distance
Compound Machine
Combinations of two or more simple machines working together
What are the simple engineering machines?
Levers, Wheel and Axel, Inclined plane, Screw, Pulley, Wedge, Gears
What is Mechanical Advantage
Ratio of the effort load (input force) you put in, to the amount of force load (output force) put out
FL
Force Load or output force
FE
Force effort or input force
Force advantage (trade speed for force)
A machine makes it easier to move a heavy object but at a slower speed
Speed advantage (trade force for speed)
A machine makes the load go faster but with a weaker force
MA<1
No force advantage, distance advantage
MA>1
Force advantage
Newton 1st law
A body in motion remains in motion or a body at rest unless acted upon by a force
Newton 2nd law
Force (newtons) equals mass (kg) times acceleration (m/s²)
Newton 3rd law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Weight
Force exerted on a body of matter due to gravity
Weight formula
Weight = Mass x Gravity
Force
The push or pull on an object (anything that causes an object, mass, to start moving)
What are the 5 types of forces that directly affect objects?
Compression, tension, shear, torsion, refraction
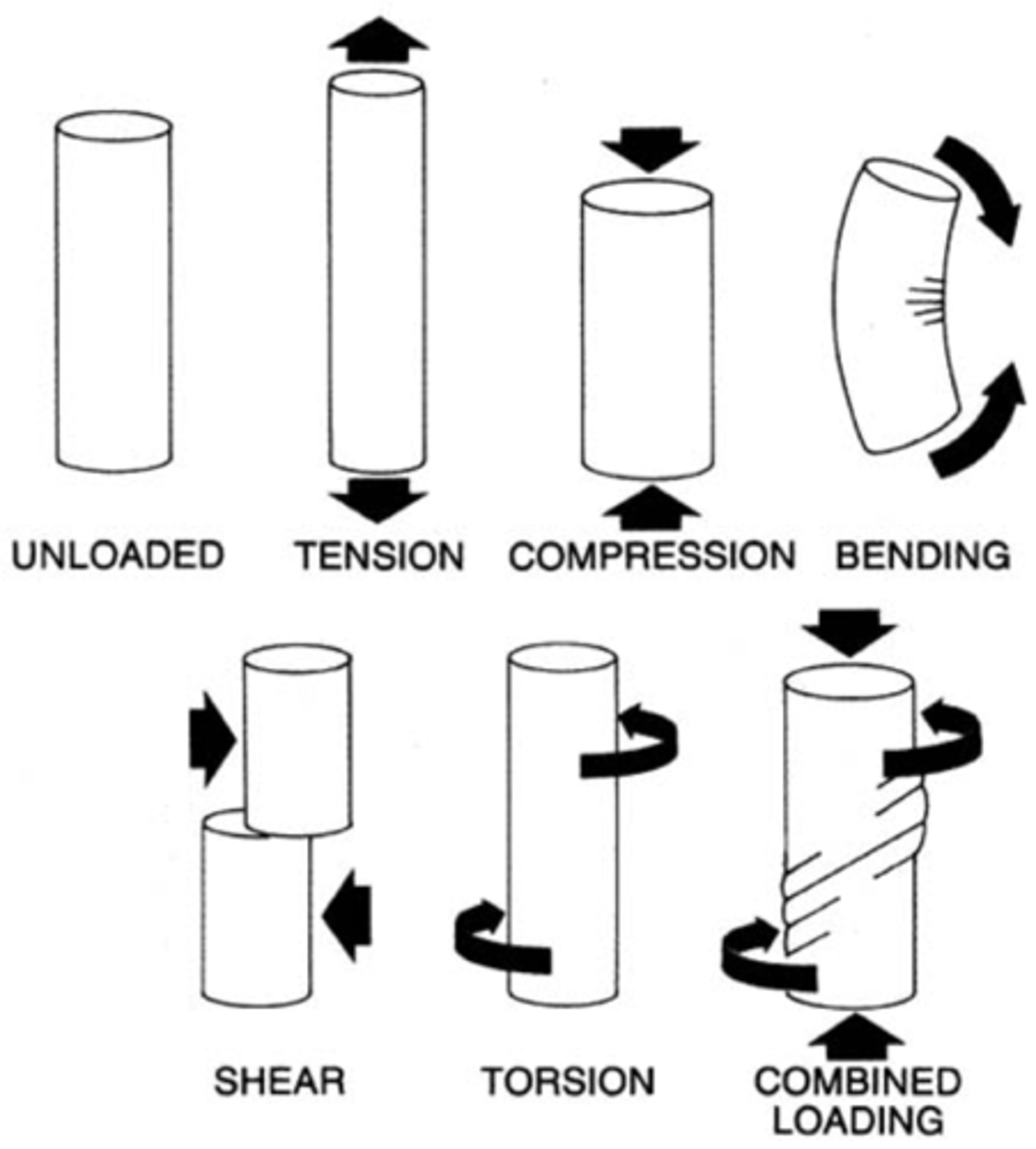
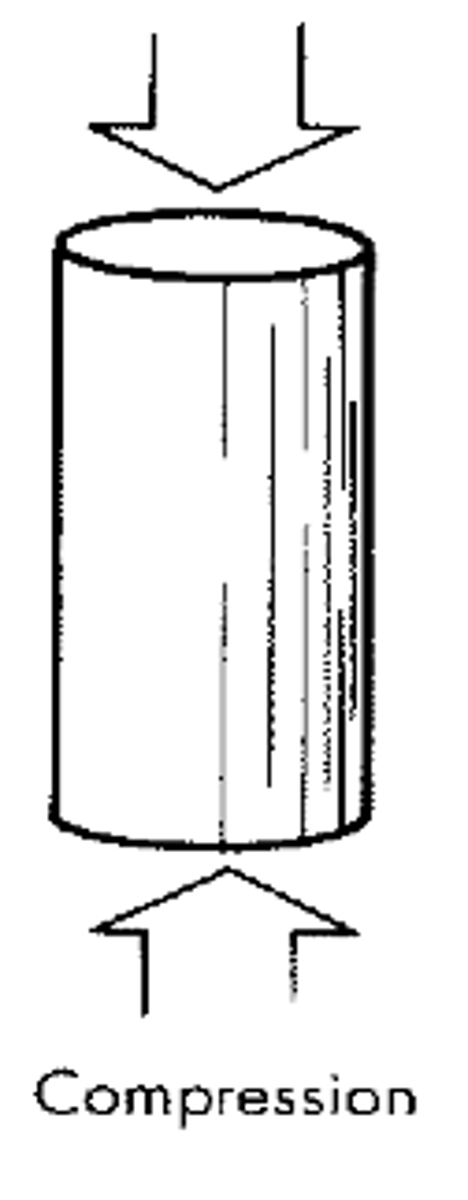
Compression (Axial)
A squashing force
Tension (axial)
A stretching force

Shear (Transverse)
Two forces pushing inwards but past each other
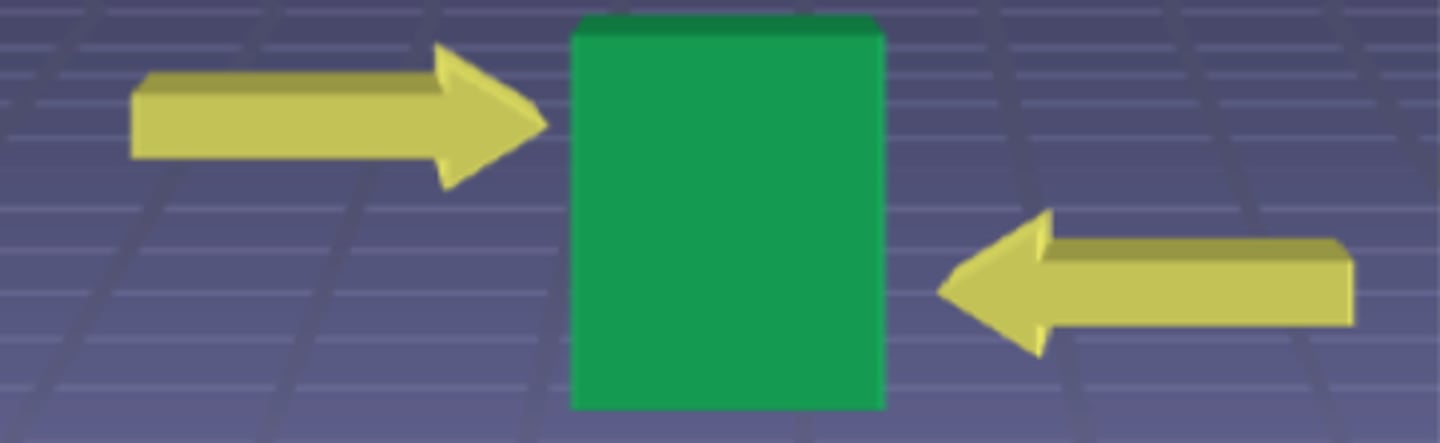

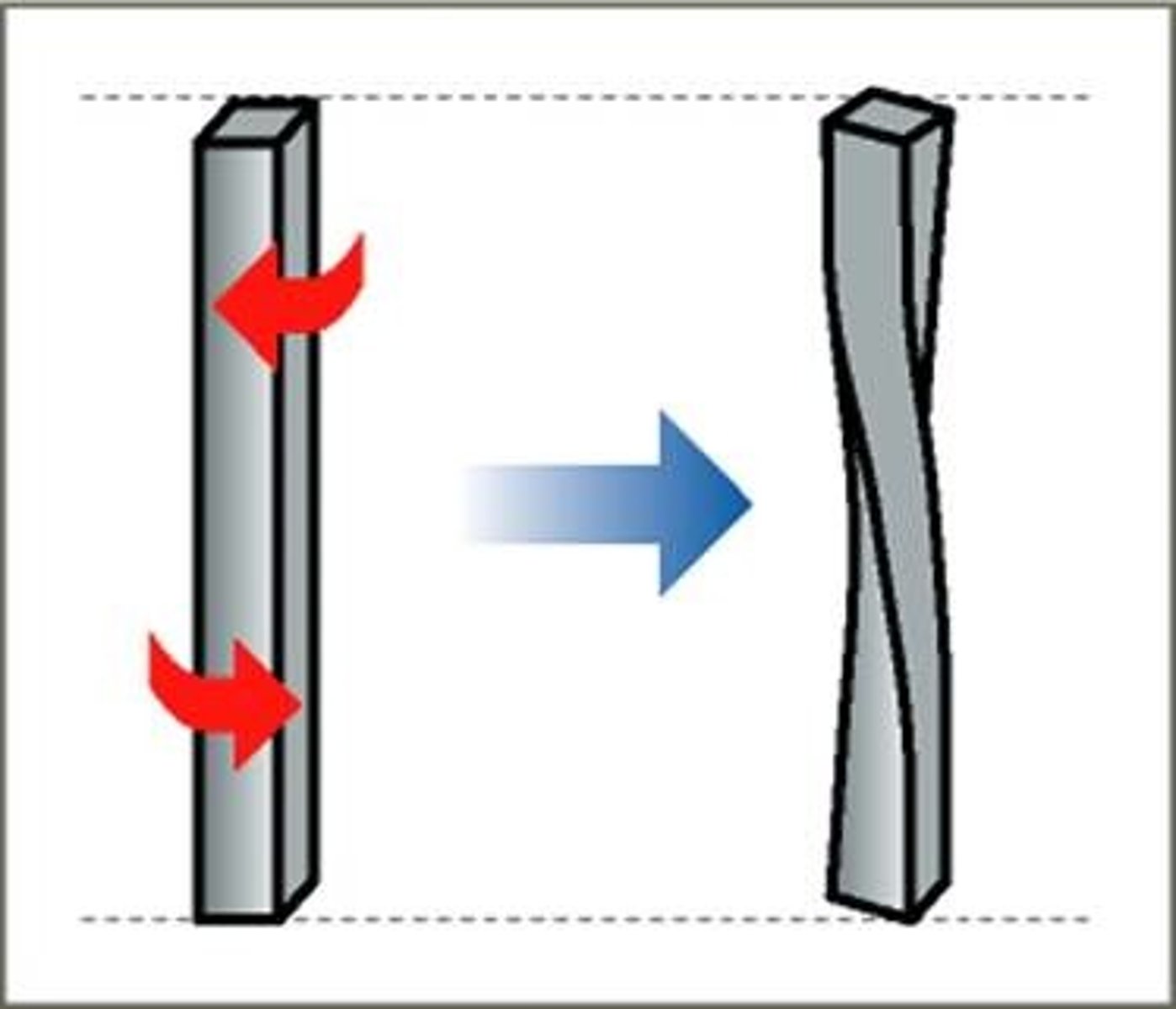
Torsion (Torsional)
A twisting force
Refraction
A bending force
Axial force
Acts along the member's axis
Transverse force
Acts perpendicular to the axis
Torsional Force
Acts around the axis, twisting the member
Engineering
Engineers are creators and problem solvers use science and maths to apply
Come up with ideas and applications to transform new realities in the world.
Work in industries like construction, transport, food, aerospace etc.
Gear Ratio < 1
Speed Advantage