Oral Pathology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Oral pathology
Study of diseases in the oral cavity
Historical data
Includes family, medical, and dental history
Clinical data
Based on appearance
Color, size, shape, and location
Radiographic data
Used for bony lesions that are not visible clinically
Laboratory data
Blood tests, saliva tests, cultures
Surgical vs Therapeutic Diagnosis
Surgical = Exploratory
Therapeutic = Response to treatment
Pulp vitality
Determines whether tooth pulp is vital or non-vital
Biopsy
Removal of tissue for a microscopic exam
Gold standard definitive diagnosis
Two types: brush and surgical
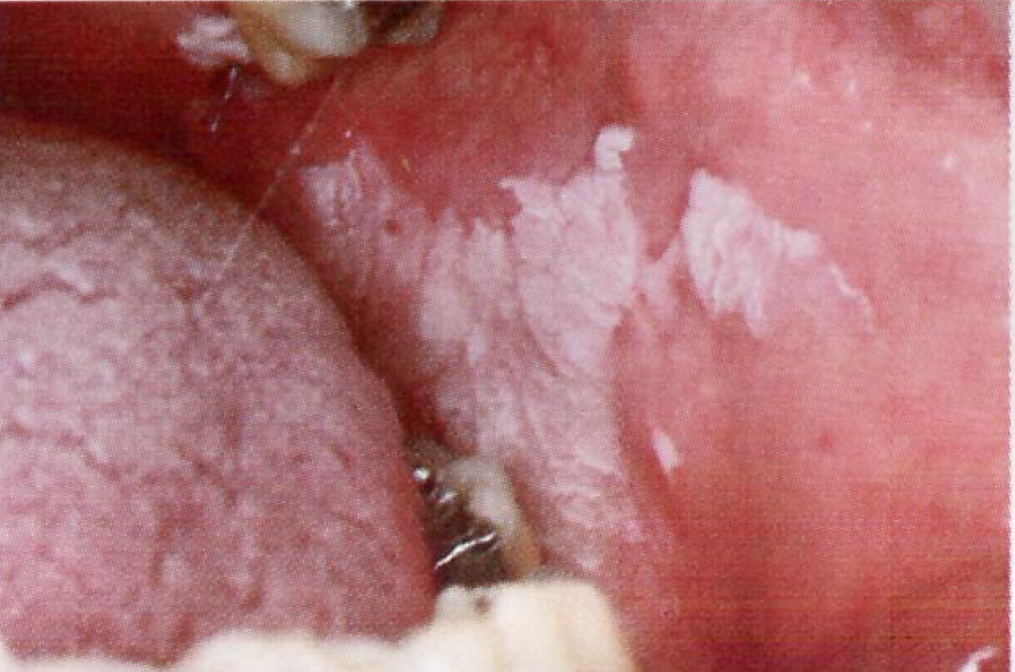
Leukoplakia
White lesion caused by irritation or cancer (requires biopsy)
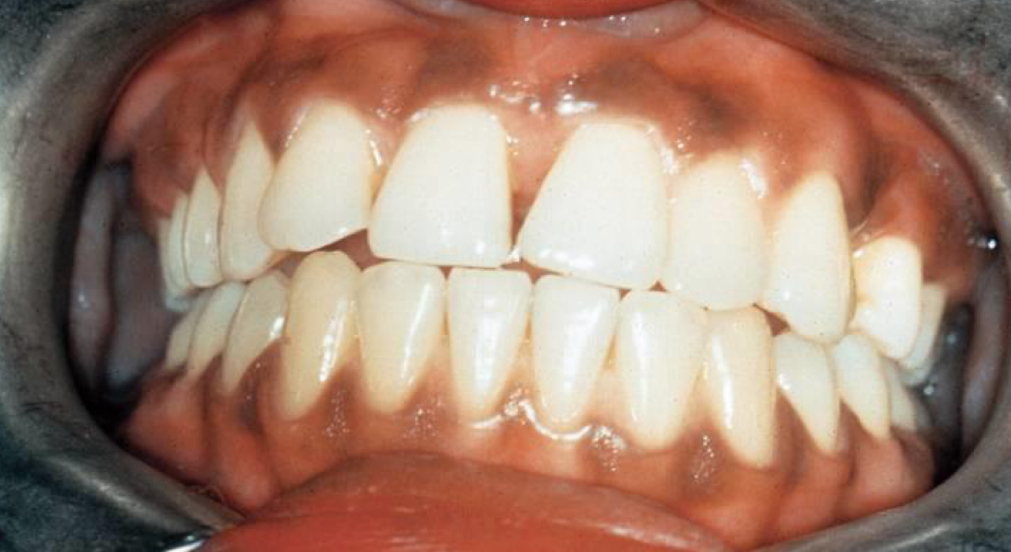
Melanin Pigmentation
Darker pigment caused by excess melanin
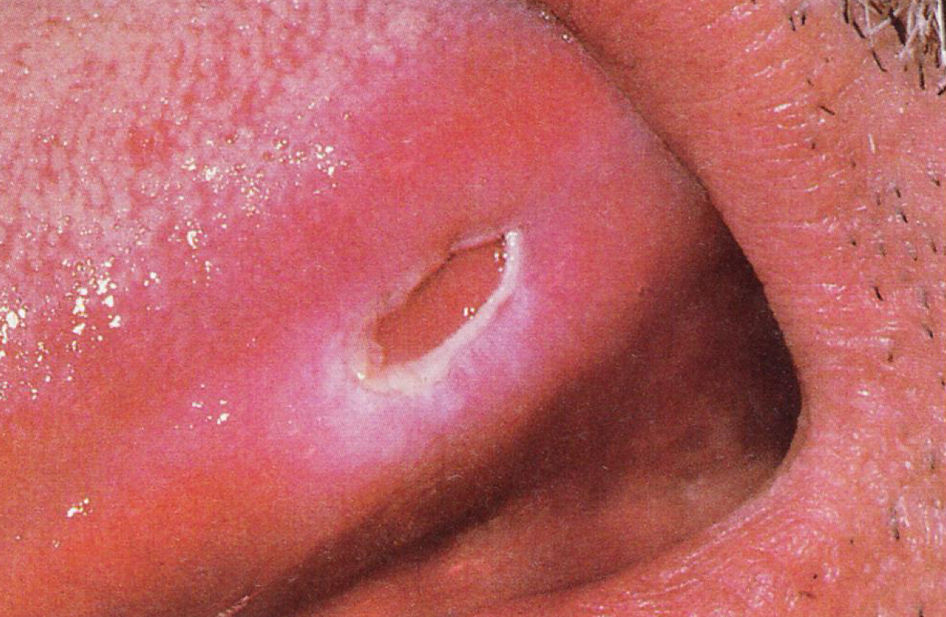
Ulcer
open sore
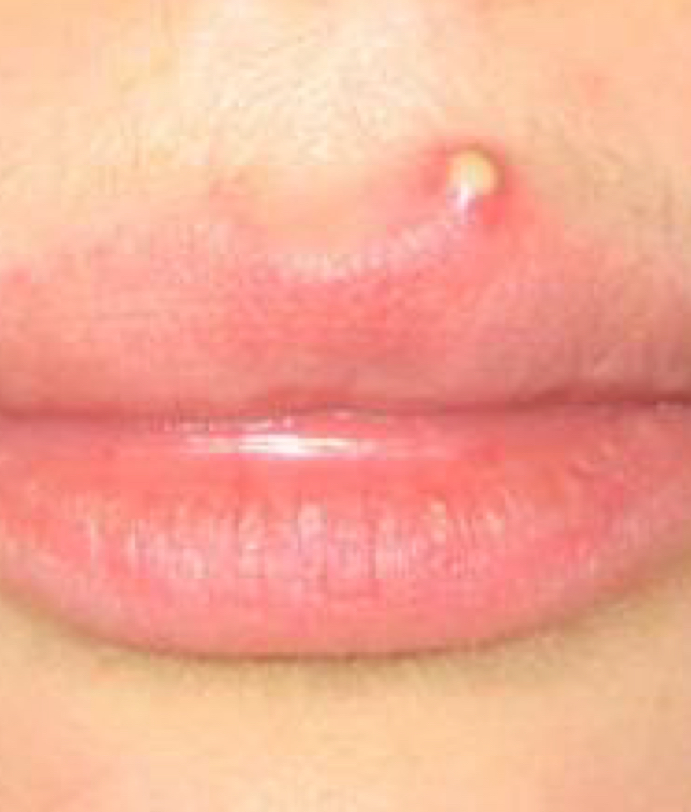
Pustule
Small blister or pimple on the skin containing pulse

Hematoma
Collection of blood outside blood vessels
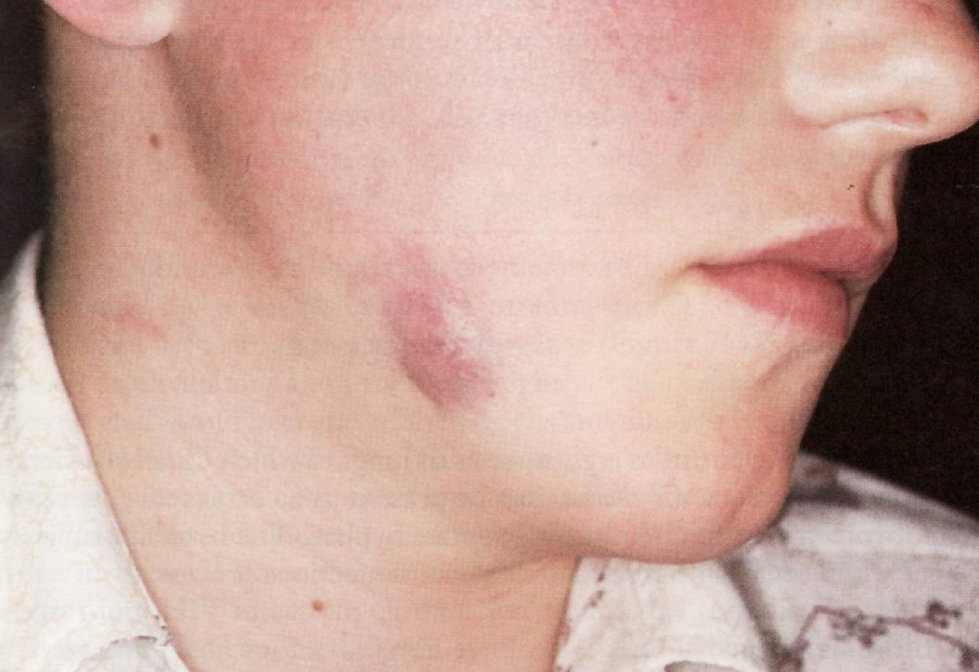
Abscess
Localized collection of pus
Usually from infection
Periapical Abcess
Bacterial infection at the apex of the tooth
Caused by an infected nerve usually from decay
Vestibular Abcess
Spread into surrounding tissues
May involve face

Cellulitis
Infection spreading in soft tissues
Severe inflammation, redness, fever
Dangerous because it may spread to eye/ brain
Antibiotics
Treat bacterial infections like Abcess or cellulitis
Penicillin, Clindmycin
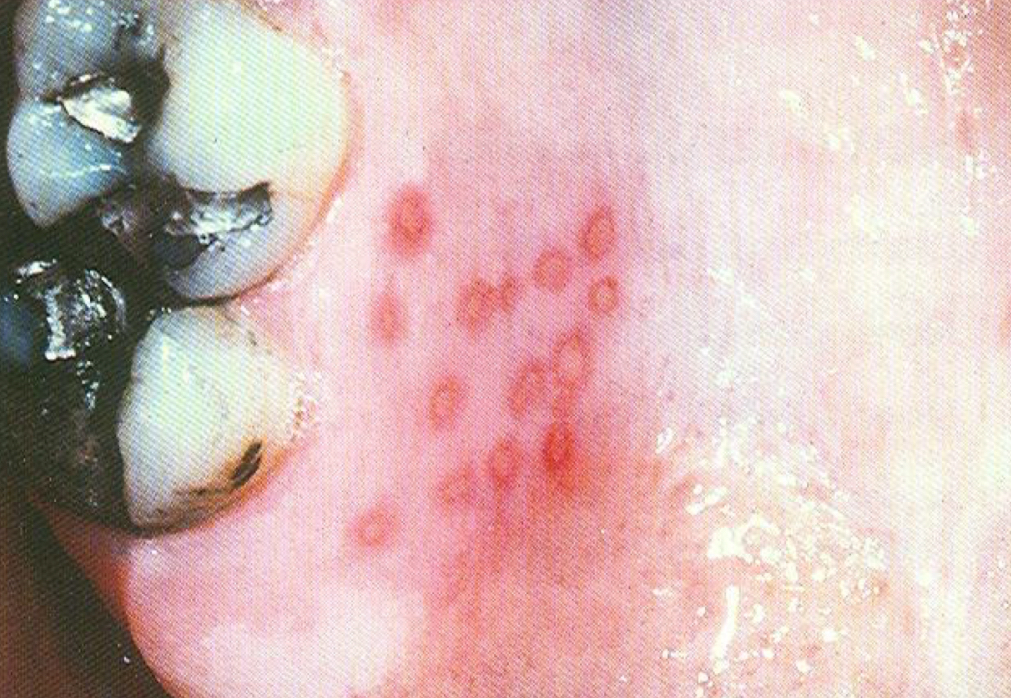
Herpes simplex
Multiple painful ulcers on palate or attached gingiva
Triggered by sunlight, stress, menstruation
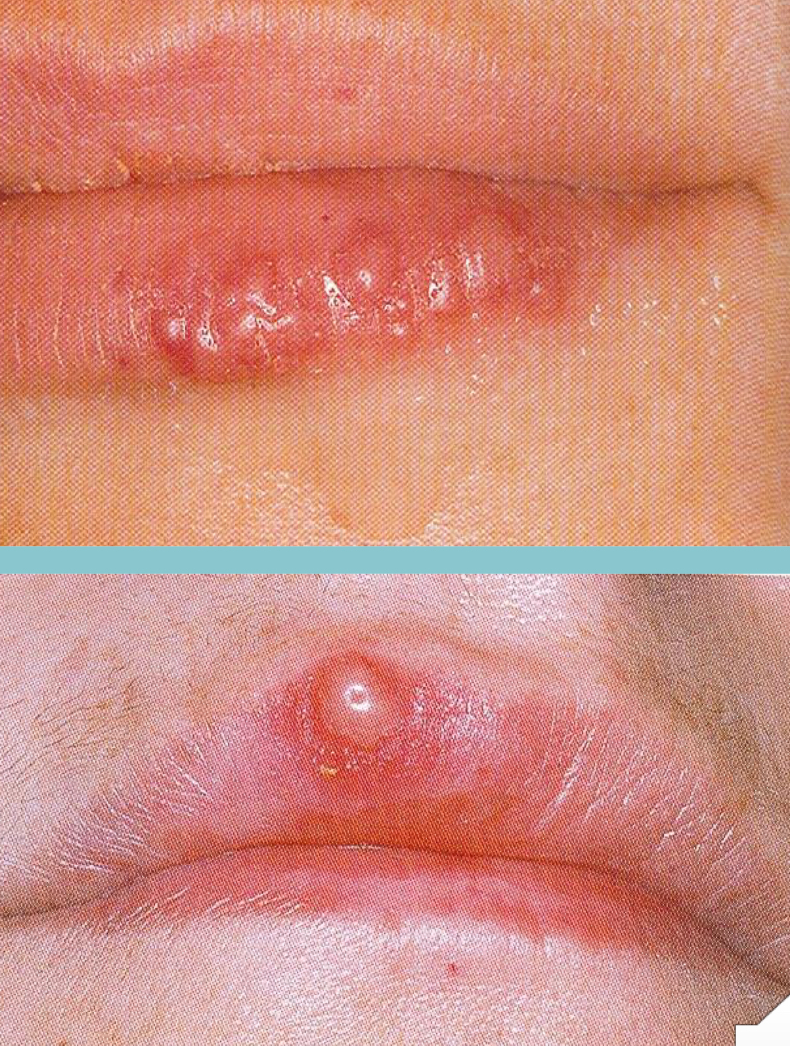
Herpes labialis
“Cold Sore/Fever Blister” On lips
Varicella vs Zoster
Varicella = chickenpox in children
vesicles, fever, contagious
Zoster = shingles in adults
Unilateral painful vesicles
Antiviral drugs
Not very effective
Palliative drugs relive symptoms
Corticosteroid drugs suppress inflammation
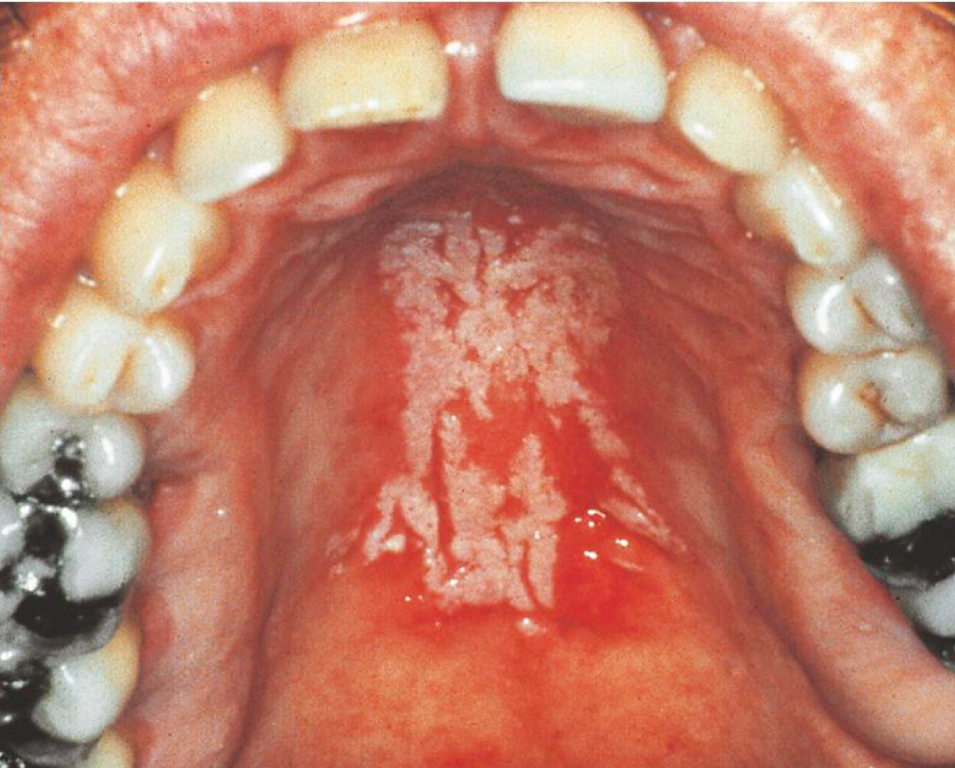
Candidiasis (thrush)
White curd-like material that wipe off
Red underneath
Candida albicans
Opportunistic infection
Occurs when antibiotics kill off specific bacteria → fungal overgrowth
Angular cheilitis
Fungal infection at commisure
Diagnosed via therapeutic evaluation
Antifungal drugs
Nyastatin
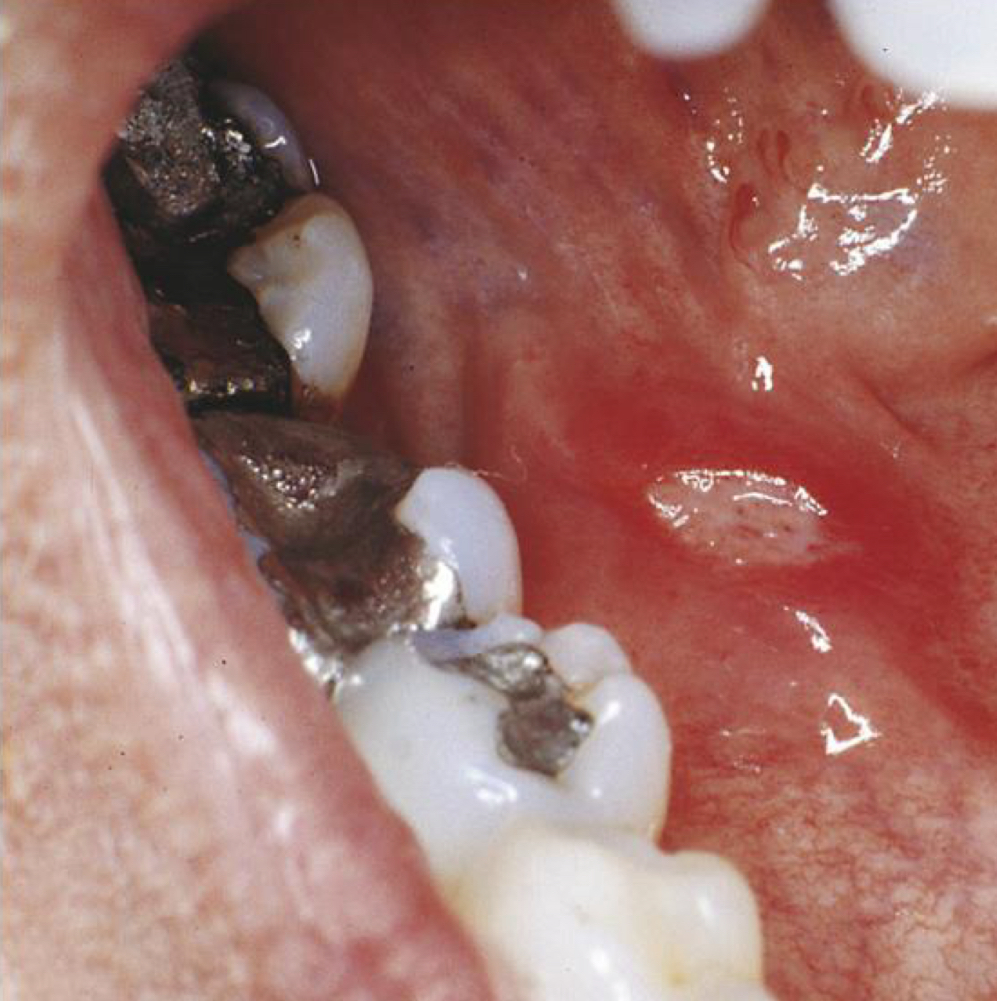
Aphthous ulcers
“ Canker Sore”
Shallow, yellow centers that are painful
Moveable mucosa
Minor vs Major Aphthous Ulcers
Minor = shallow
Less than 6 episodes
Heal within 7-10 days
Major = deep
Larger, deeper ulcers >1cm
Painful, inability to eat
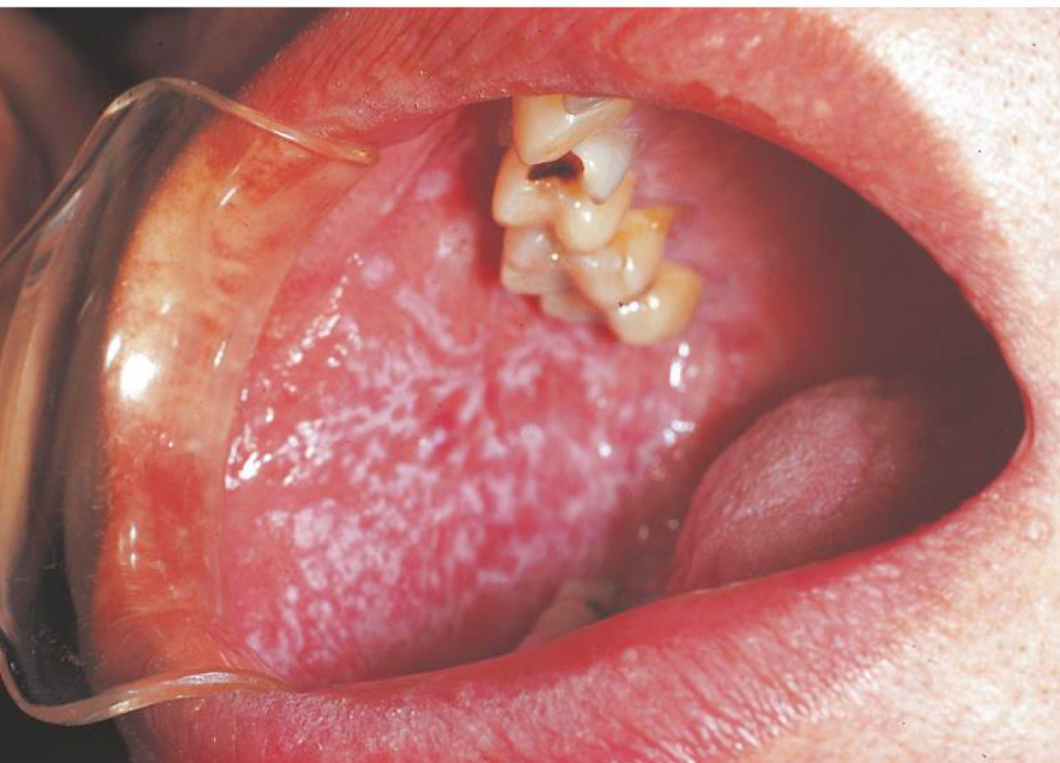
Lichen planus
Chronic autoimmune condition
Wickham’s Striae ( white lacy pattern)
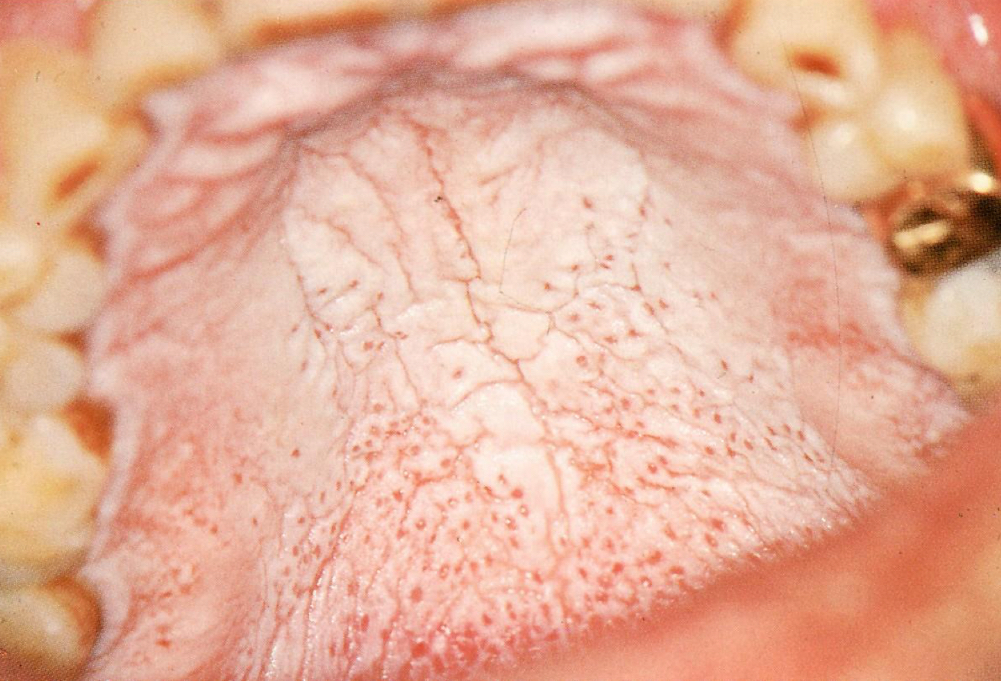
Nicotine stomatitis
Keratinized hard palate with red duct openings
not cancerous
Glossitis
Inflammation of the tongue
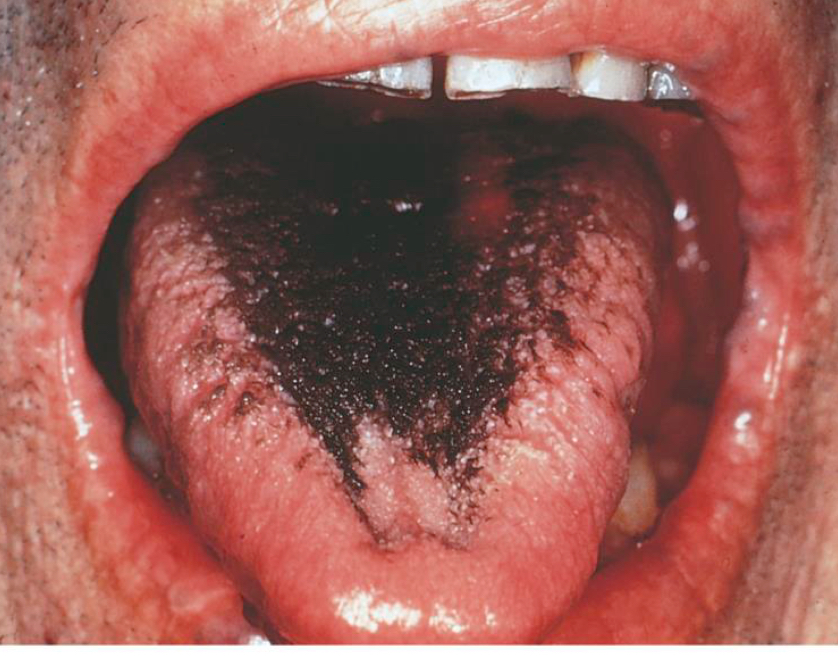
Hairy tongue
Elongated filiform papillae
Stained by food/tobacco
Often from antibiotics
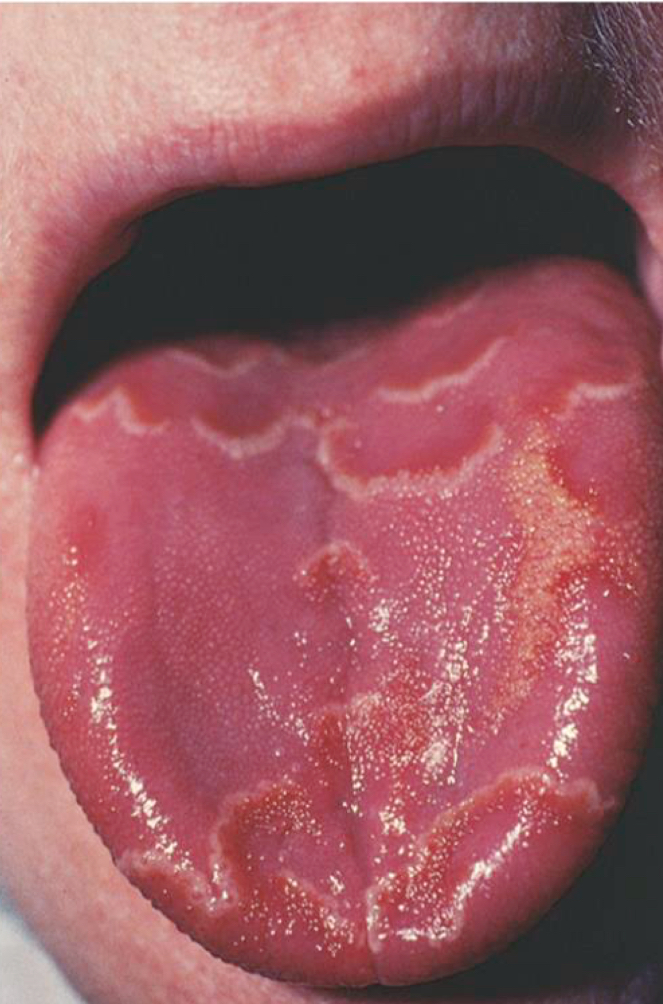
Geographic tongue
Migratory desquamation of filiform papillae
Map like patches
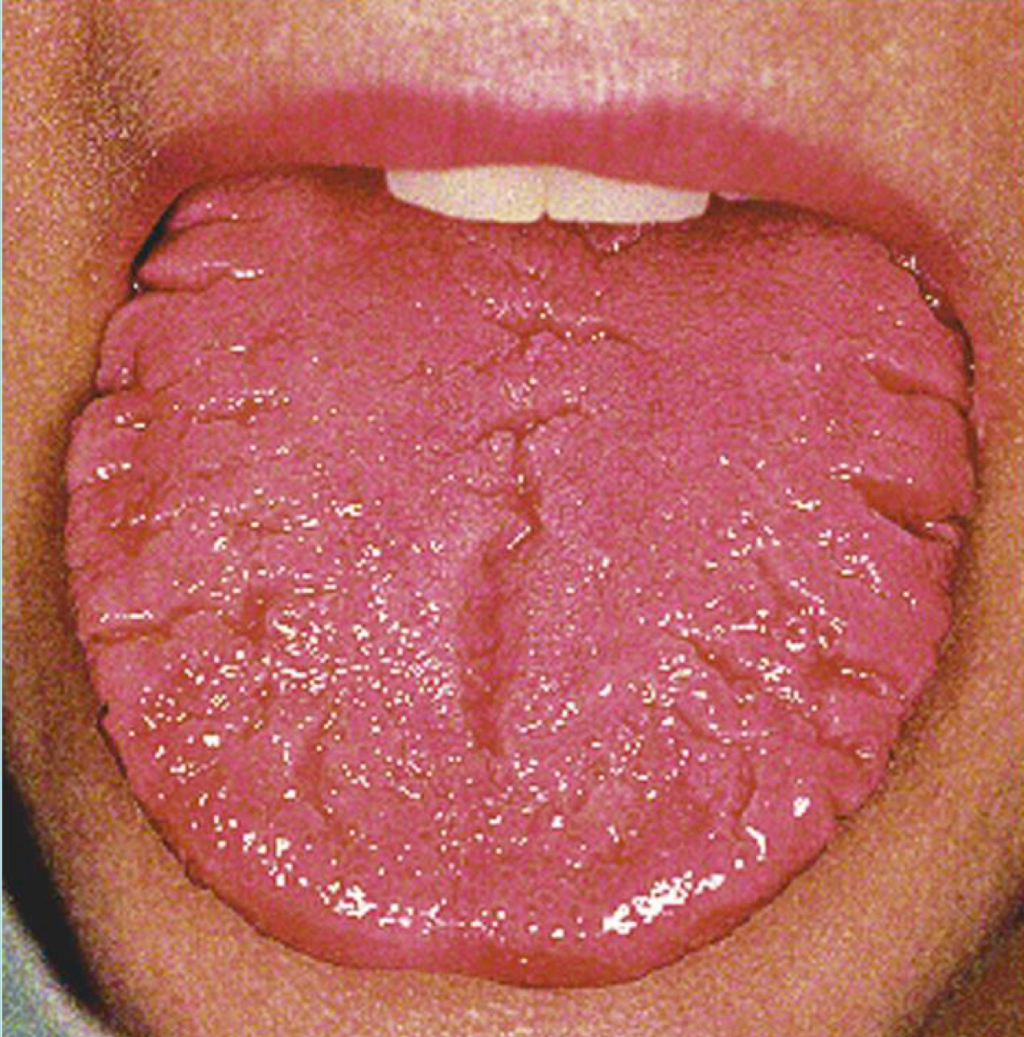
Fissured tongue
Deep grooves with debris irritation
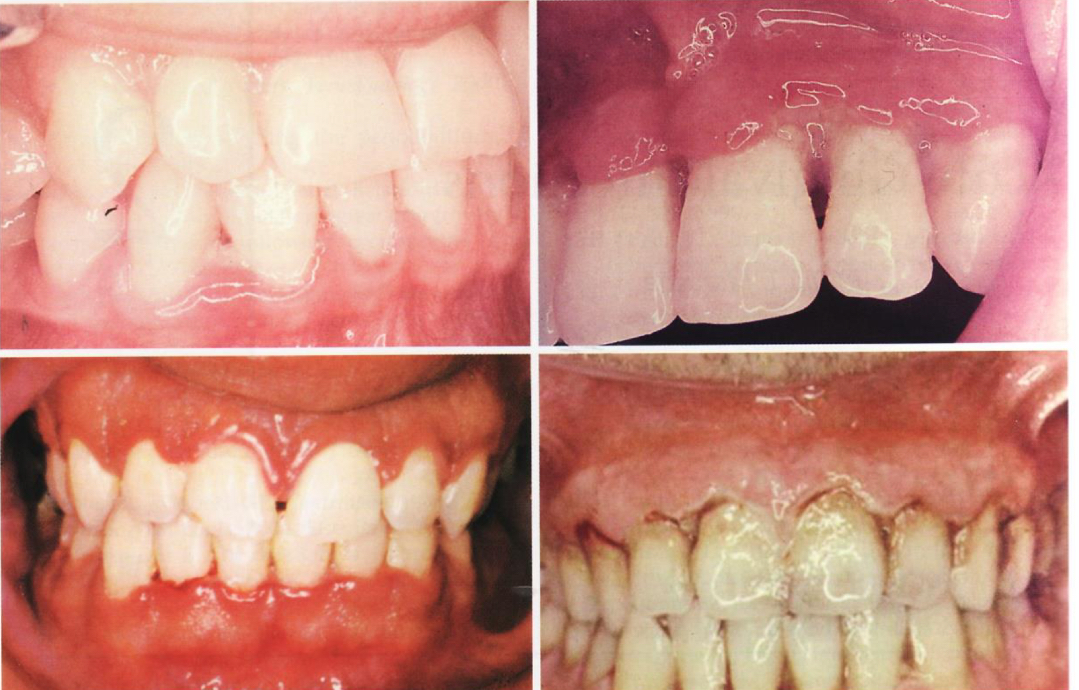
ANUG
Painful, punched-out papilla
Bad taste, odor, fever
Treated with debridement + peroxide
Mandibular vs Palatal tori
Mandibular = dense bone on lingual mandible
Palatal = bone midline palate
Inherited, asymptomatic
What does a Periapical radiolucency indicate?
Bone loss at apex → nonvital tooth
Needs pulp test