Growth
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 9: Tuesday, October 21st: Metabolic Rate & Temperature Regulation (cont.); Thursday, October 23rd: Growth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
_______ is organized addition of new tissue ocurring normally in development from infancy to adulthood
growth
_______ is the process of cells growing in size
hypertrophic
_______ is the process of cells growing in number (tumors)
hyperplastic
_______ tissue is found in the skin and organ lining; covers and protects
epithelial
_______ tissue is found in blood, lymph, bone, and cartilage; transports substances
connective
_______ tissue is found in muscles; contracts and relaxes
muscular
_______ tissue is found in axons and the nervous system; sends chemical signals
nerve
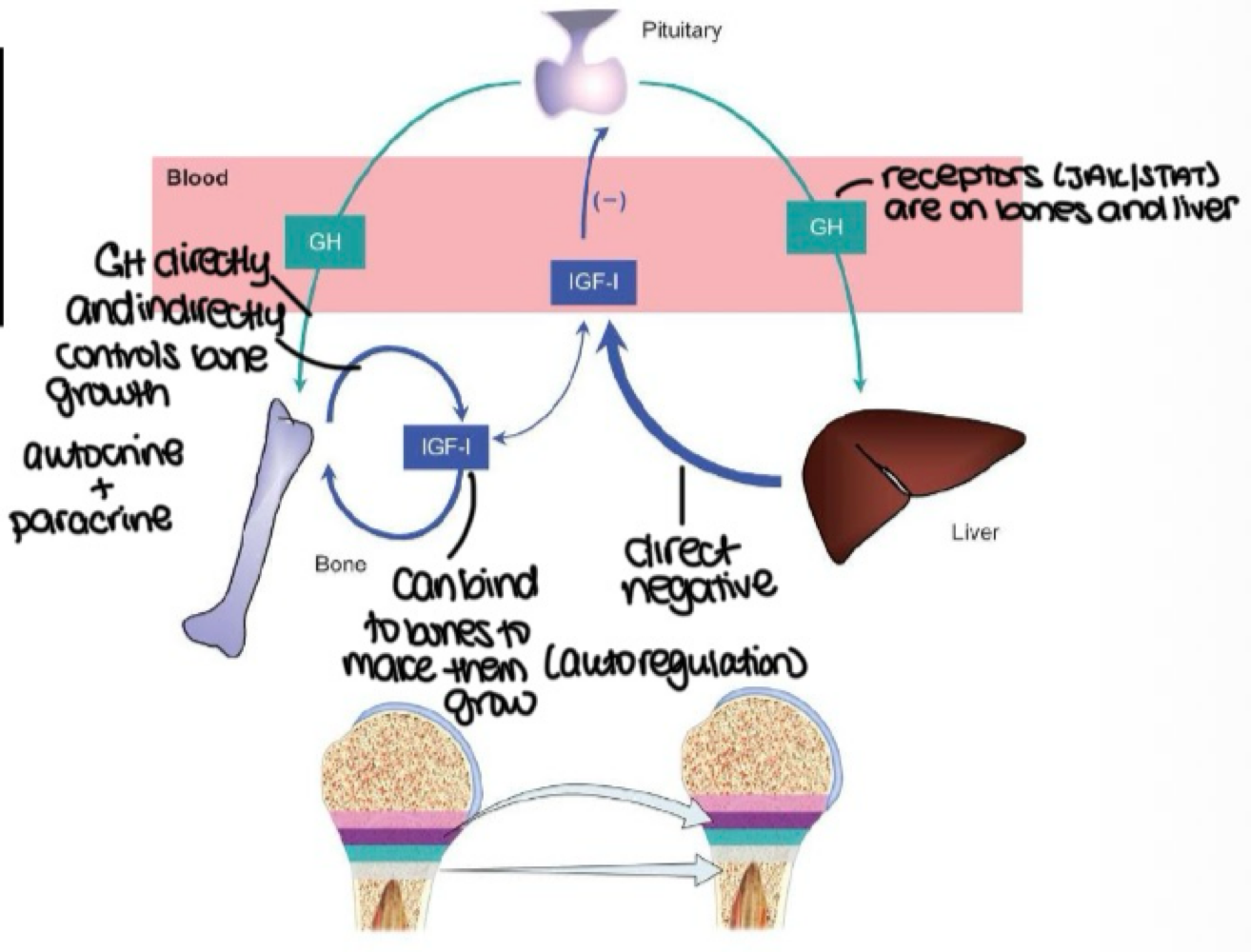
_______ regulation of growth comes from the brain
central
during central regulation, GHRH tells the pituitary to _______ GH, but somatostatin tells it to _______ GH (release or inhibit)
release, inhibit
_______ regulation of growth comes from the cells themselves
local
the liver releasing IGF-1 to inhibit the pituitary is an example of what feedback?
direct negative feedback

the pituitary releasing GH to act on theparaventricular nucleas in the hypothalamus is an example of what feedback?
indirect negative feedback

what element is needed in cells to release GH from the cell?
calcium

what growth stage does solely IGFs and insulin control?
prenatal
what growth stage doesIGFs, insulin , GH, and T3 control?
childhood
what growth stage does IGFs, insulin, GH, T3, and sex steroids control?
adolescence
what growth stage does all growth hormones control at different levels?
adulthood
true or false: sex differences show growth curves
true
_______ is a condiiton characterized by a decrease in growth and the inability ot develop cancer
dwarfism
_______ is a condiiton characterized by excessive growth after adulthood
acromegaly
abnormal development of anterior pituitary, synthesis and secretion of GH, and GH receptors will cause _______
GH hyposecretion
abnormal anterior pituitary/hypothalamuc tumors, secretion of pituitary cells, and GH secreting tumor sells will cause _______
GH hypersecretion
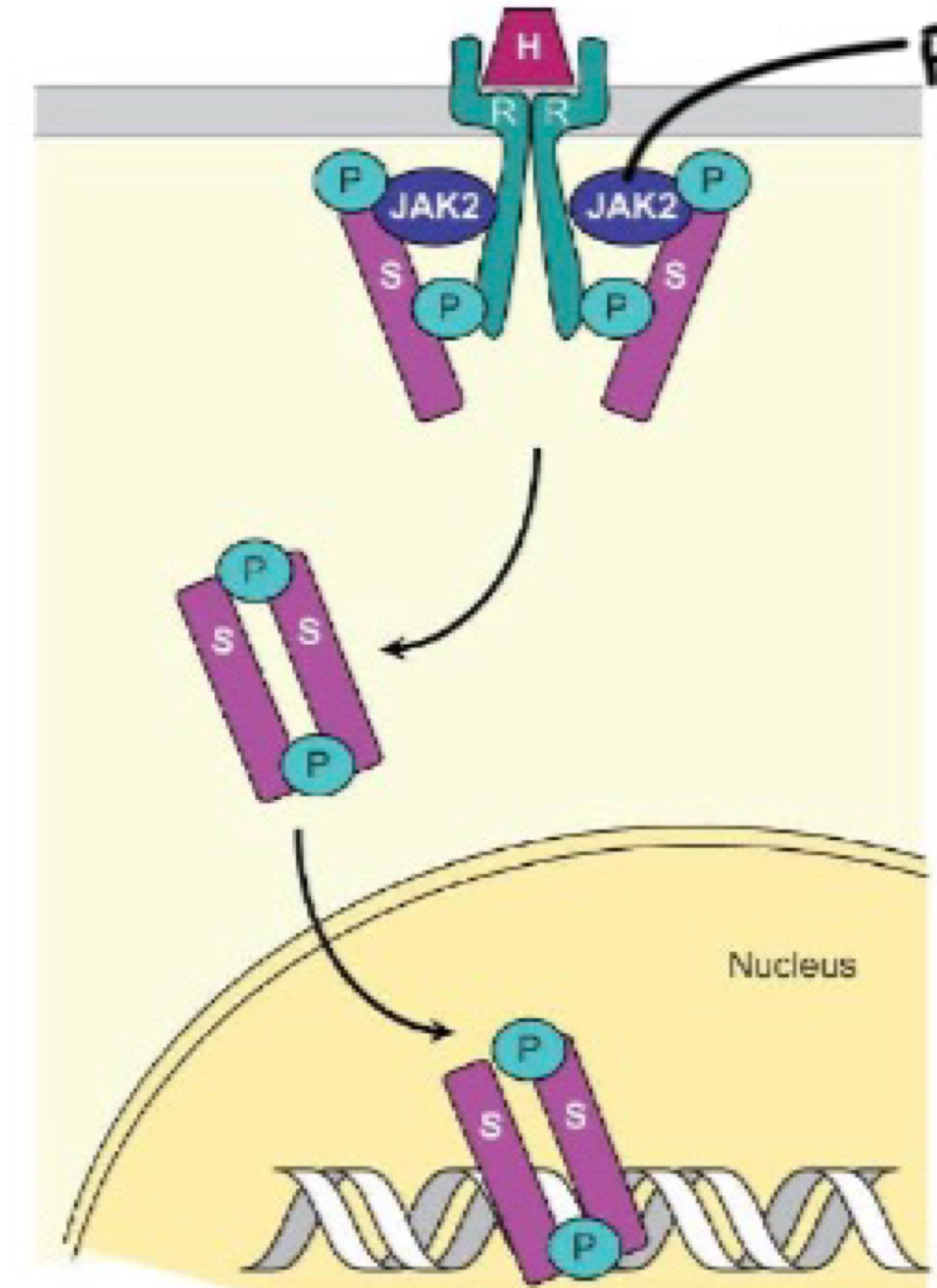
GH is produced by _______ cells in the anterior pituitary in light adn heavy forms due to alternative splicing
somatotrope
GH receptor is a _______ in the cytokine receptor family, which is enzyme linked
glycoprotein
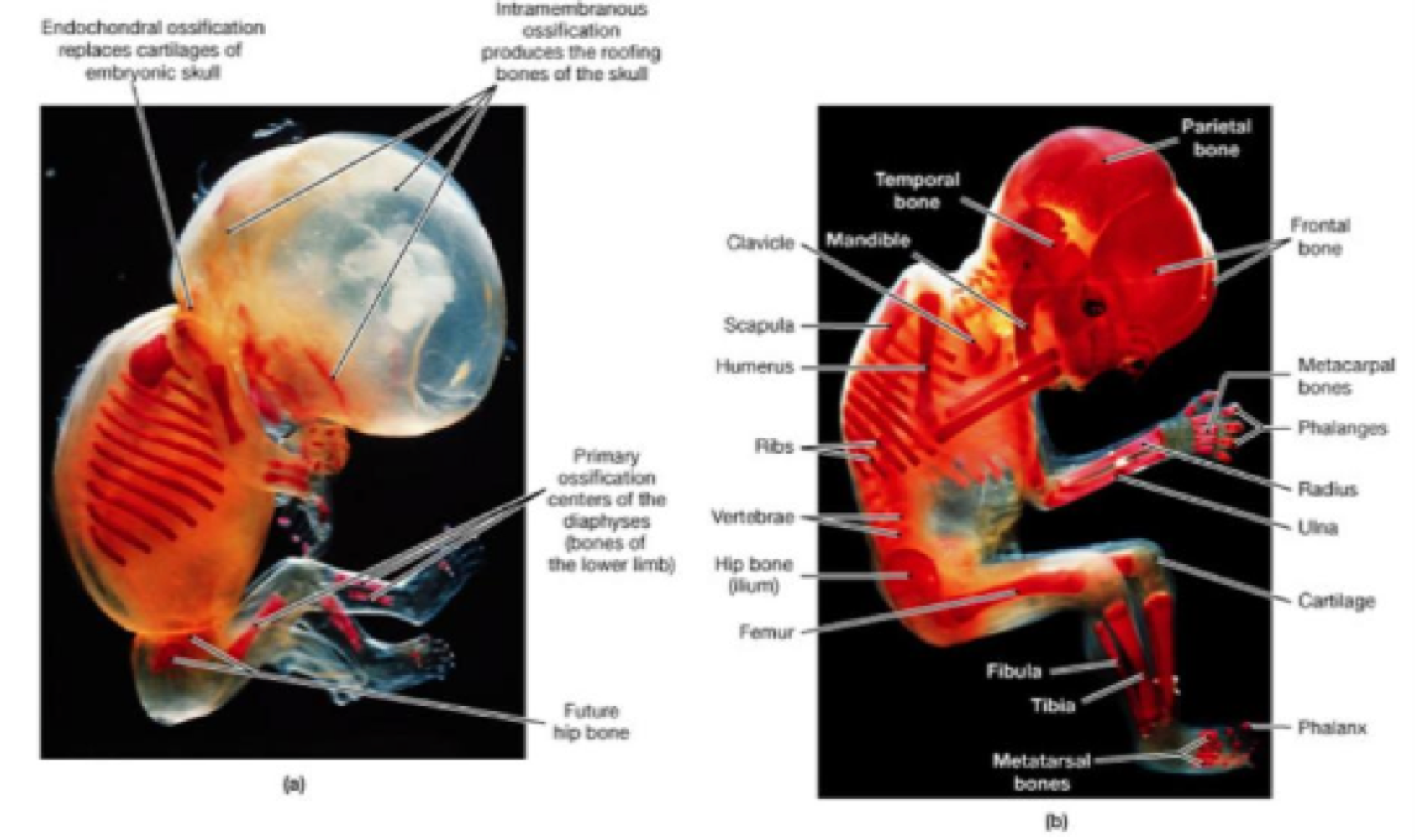
_______ is when bone form from mesenchymal tissue
intramembrane ossification
_______ is when catilage is the model, then bones replace it
endochondra ossification
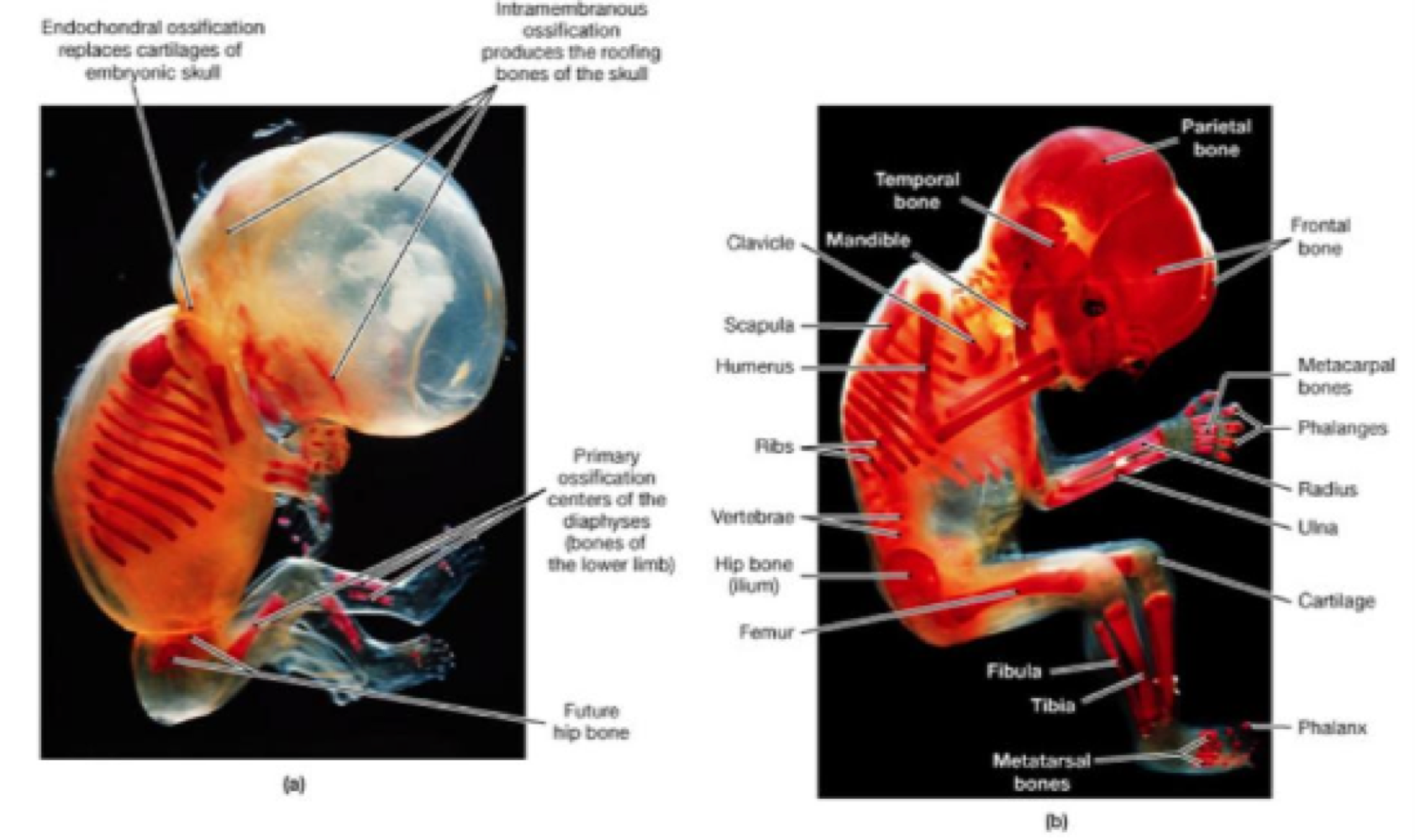
IGF, insulin, and placental lactogen regulate _______
bone development
bone growth continues via _______ for length, and _______ for diameter
endochondral ossification, appositional growth
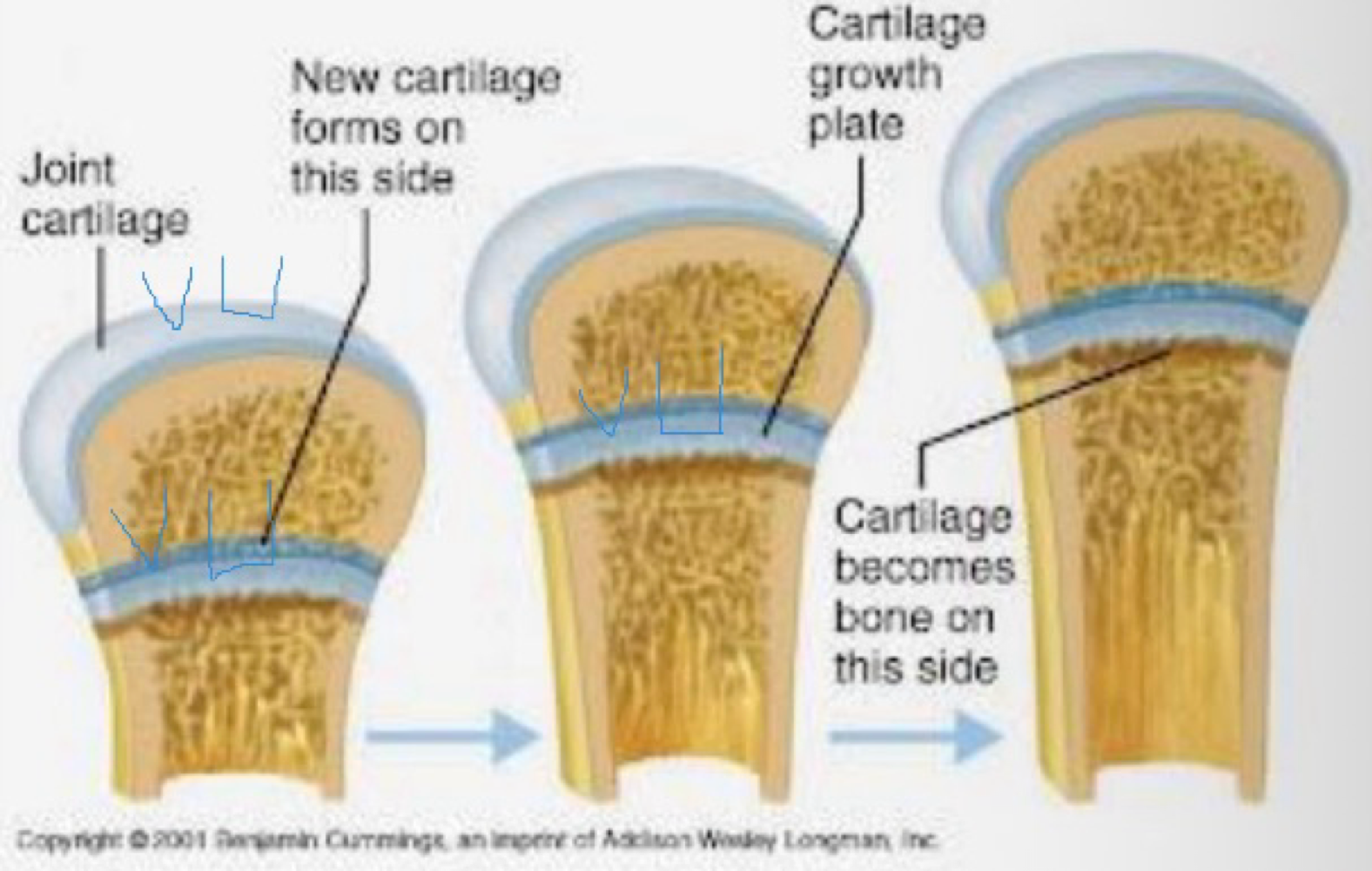
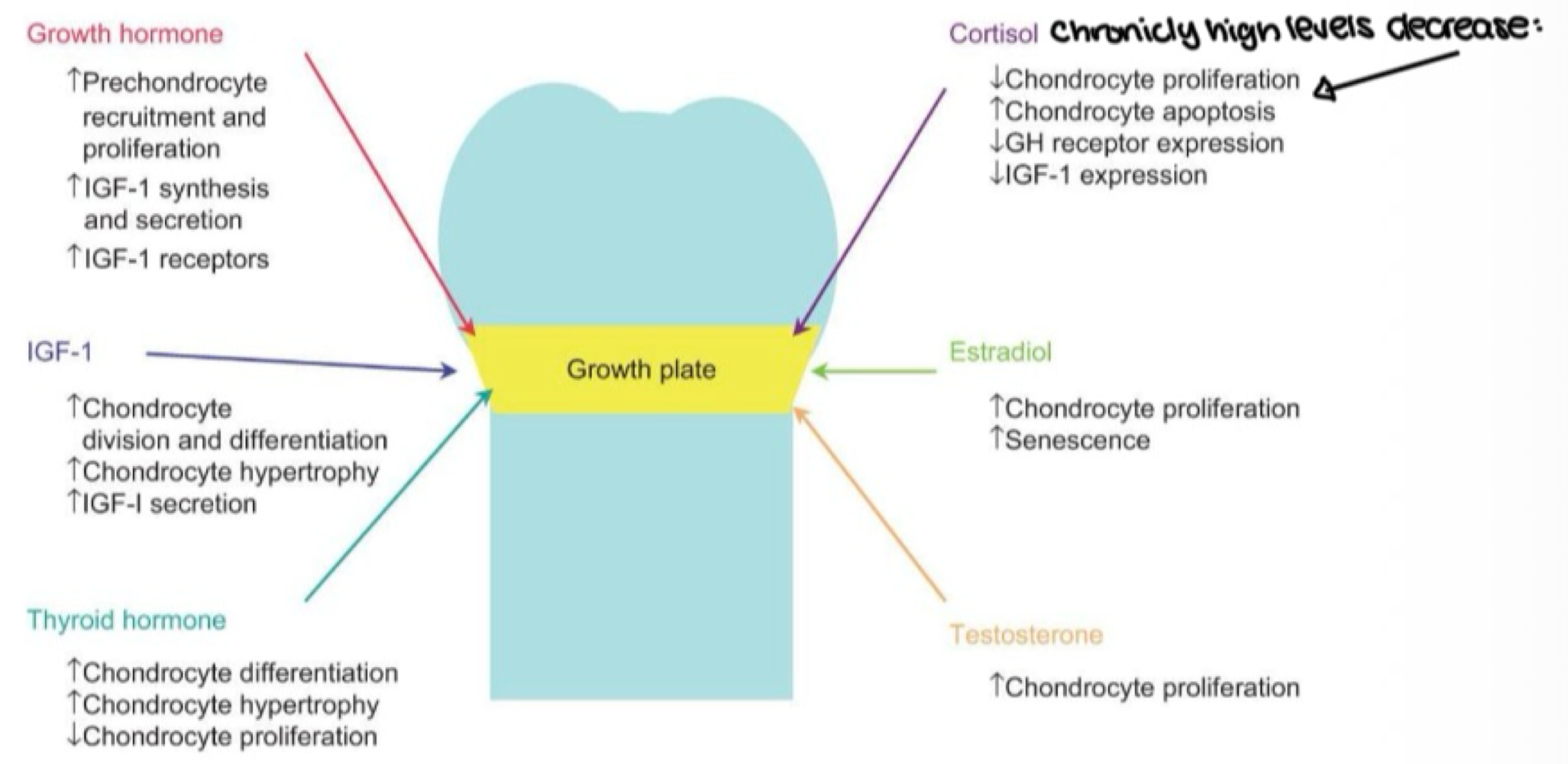
growth plate activity depends on what two hormones signaling each other?
GH and IGF-1
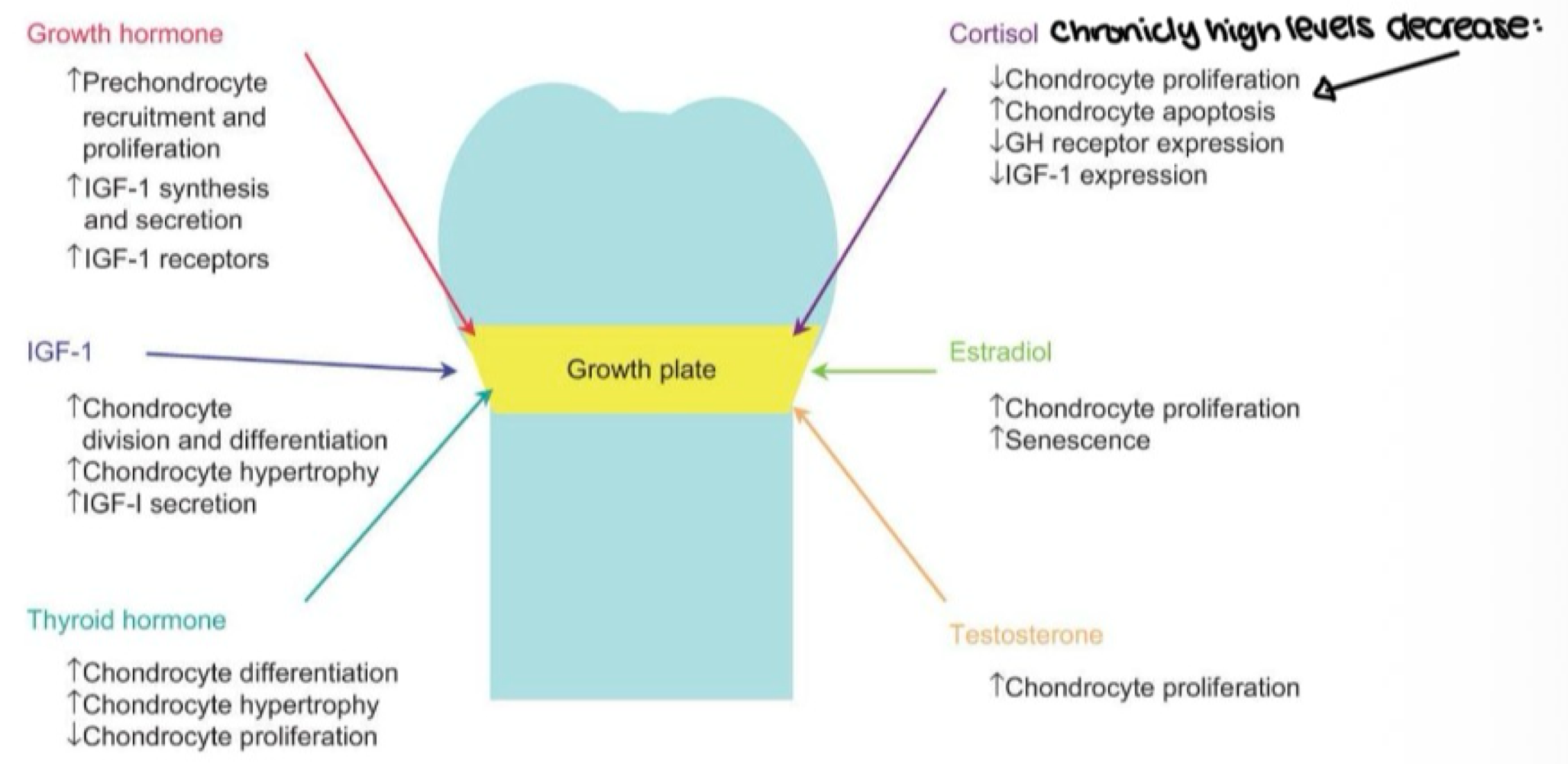
waht two hormones accelerate the closure of growth plates at puberty?
estrogen and testosterone
GH acts on liver → stimulates IGF-1 and IGF-2 release → enters blood; promotes bone growth is an _______ mechanism of GH action
indirect
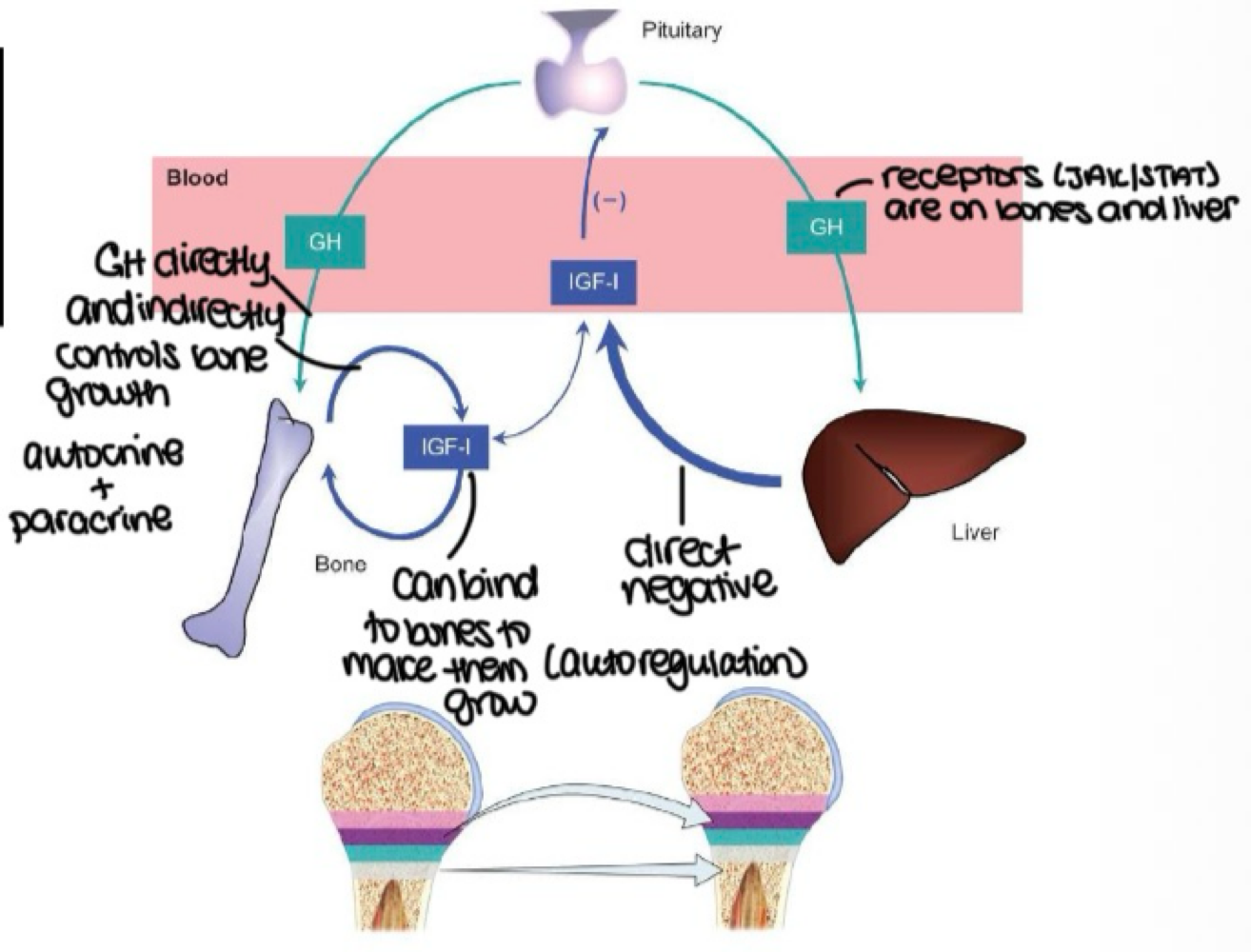
GH acts on tissues to induce IGF-1 production is an _______ mechanism of GH action
direct
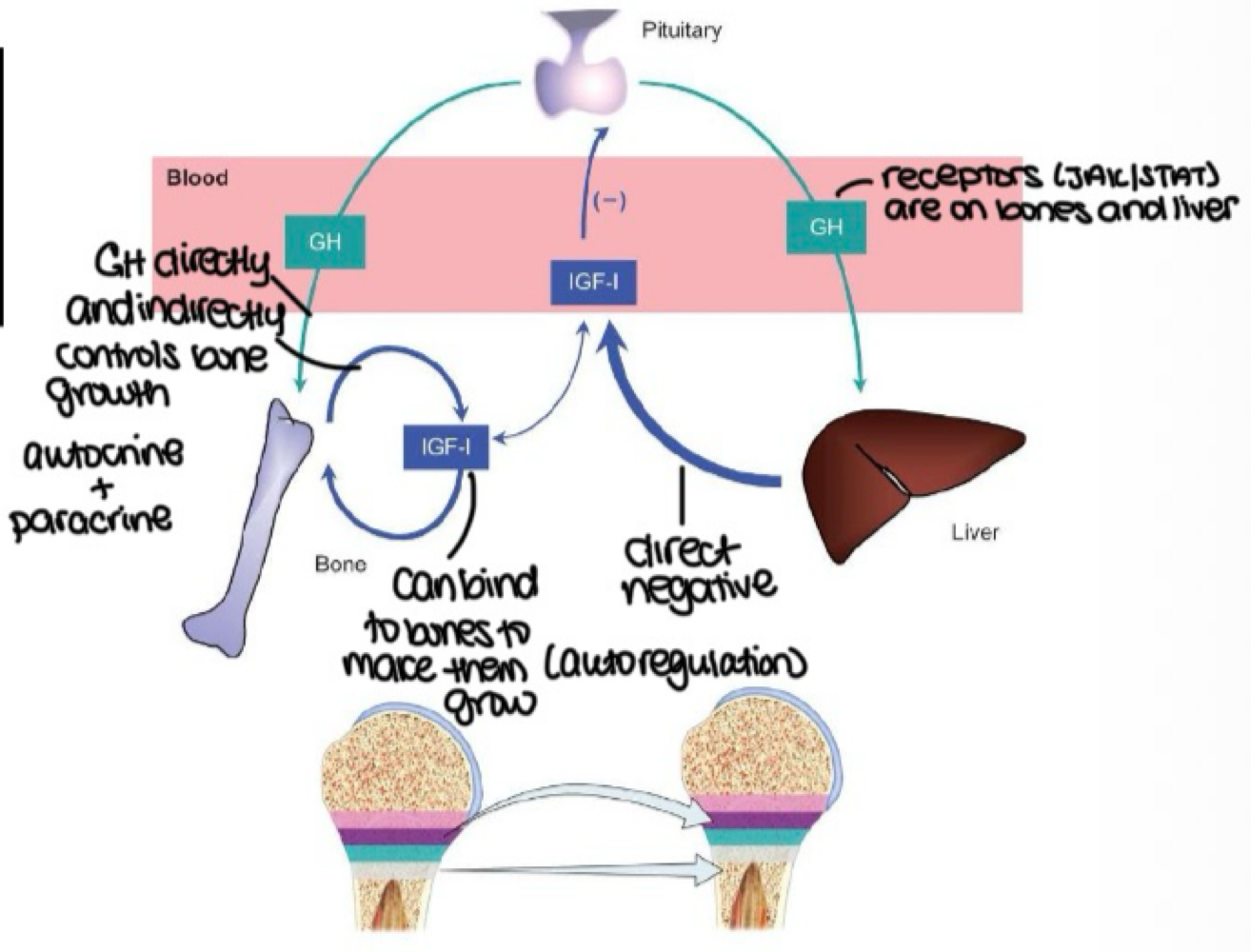
IGF-1 inhibitng GH release is a _______ mechanism of GH action
negative feedback
_______ affects growth and glucose regulation, where as _______ affects substance clearance ein lysosomes (IGFs)
IGF-1, IGF-2
_______ are hormones that have the following characteristics:
stimulate endocondroal and interstitial bone growth
control fetal and placental growth
decrease fat deposition
increase fat metabolism for energy and protein synthesis
promote organ/tissue growth (except thyroid and reproductive)
insulin-like growth factors
_______ are hormones that are permissive for GH and IGF action
thyroid hormones
_______ are hormones that promotes fetal growth, supports postnatal GH effects, regulates glucose and fat, and binds IGF-1 receptors to enhance anabolic effects
insulin
_______ are hormones that antagonize insulin if its too high
GH
_______ are hormones that are needed for GH synthesis, and increases somatostatin if its levels are too high
glucocorticoids
_______ hormones support leukocyte maturation
thymic
_______ hormones support smooth muscle and fibroglast growth
PDGF
_______ inhibit local mitosis, causing “growth” breaks
chalones