BIBC 100 Midterm 3
1/366
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
367 Terms
What are the three main types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides.
What is a monosaccharide?
A single polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone unit
Give examples of monosaccharides.
Ribose, D-glucose, fructose, galactose.
What are oligosaccharides?
Carbohydrates with 2-20 monomers
Give examples of disaccharides.
Sucrose, lactose, maltose
What are polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates with 20+ monomers
Give examples of polysaccharides and their functions
Starch (plant energy storage), glycogen (animal energy storage), cellulose (plant structure)
What are the characteristics of monosaccharides?
Colorless, water-soluble, crystalline, containing a carbonyl group and two or more hydroxyl groups.
What is an aldose?
A monosaccharide with an aldehyde group (carbonyl at the end)
What is a ketose?
Monosaccharide with a ketone group (carbonyl at any position other than the end)
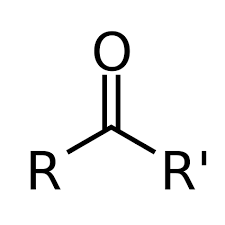
What is this?
Ketone
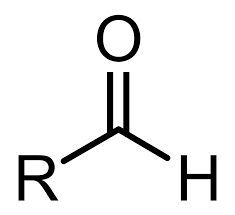
What is this?
Aldehyde
How are 4-carbon and 5-carbon ketoses named
By inserting “ul” into the name of the corresponding aldose
How would you name a ketone ribose?
ribulose
What is a chiral carbon?
A carbon atom attached to four different groups.
How do you determine the number of possible stereoisomers for a monosaccharide?
2^n, n = # chiral carbons
L vs D isomers?
L-isomers have OH on the left, D-isomers have OH on the right
What is a Fischer projection?
A 2D, vertical representation of a 3D carbohydrate
What is an anomeric carbon?
The carbon derived from the carbonyl group during cyclization of a sugar
How do you distinguish between alpha and beta anomers?
In alpha anomers, the OH group is opposite to the CH2OH group; in beta anomers, they are on the same side.
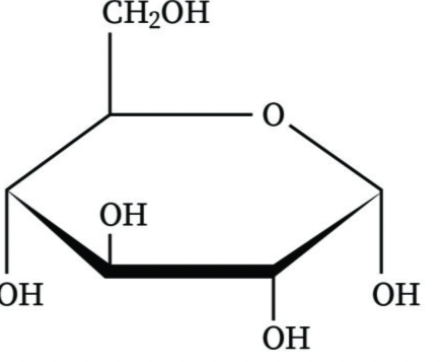
Is this an alpha or beta anomer
alpha
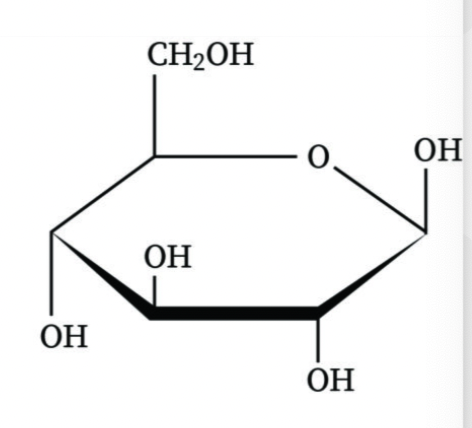
Is this an alpha or beta anomer?
Beta
What is a glycosidic linkage?
A bond formed between an anomeric carbon and a hydroxyl carbon of another monosaccharide
What are homopolysaccharides?
Polysaccharides made of repeating monosaccharide units
Give an example of homopolysaccharides and their functions
Starch/glycogen (energy storage), cellulose (Structural support)
What are heteropolysaccharides?
Polysaccharides made of different monosaccharide units
Give examples of heteropolysaccharides
agarose, peptidoglycan, hyaluronan, heparin
Describe starch
Plant storach polysaccharide containing unbranched amylose and branched amylopectin
is amylose branched or unbranched
unbranched
is amylopectin branched or unbranched
branched
describe glycogen
animal storange polysaccharide, stored in liver and muscle
describe cellulose
linear, unbranched homopolysaccharide with D-glucose residues
what kind of glycosidic linkages does cellulose have?
beta 1-4
what are the primary functions of carbohydtrates?
energy source, stuctural support, protection
why store carbs as polymers and not monomers?
to avoid high osmotic pressure that would cause cells to be lysed
what is a puranose
six membered ring
does a puranose always have 6 carbons?
no
furanose
five membered ring
does a furanose always have 5 carbons?
no
How do you identify the anomeric carbon?
it’s usually carbon #1 and drawn on the far right corner in hexagon/pentagon shapes
what is sucrose made of
glucose and fructose
what is lactose made of
glucose and galactose
what is maltose made of
glucose and glucose
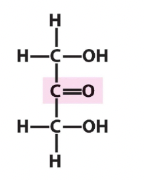
ketose or aldose
ketose
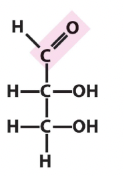
ketose or aldose
aldose
what’s the name for a 6 carbon aldose?
aldohexose
what’s the name for a 4 carbon ketose?
ketotetrose
what’s the name for a 5 carbon monosaccharide? (unspecified aldose/ketose)
pentose
what monosaccharide is not a chiral compound?
dihydroxyacetone
why does stereochemistry matter?
interactions between biomolecules are stereospecific
are most biologically relevant monosaccharides L or D?
D
what kind of glycosidic linkage is common in sucrose?
alpha 1-2
what kind of glycosidic linkage is common in trehalose?
alpha 1-1 linkage
how often do branches occur in amylopectin?
24-30 residues
how often do branches occur in glycogen?
8-12 residues
why is having more branching more efficient?
more branches —> more ends —> faster hydrolysis —> sugars released faster
what kind of linkage is found in amylose
alpha 1-4
what kind of linkage is found in amylopectin
alpha 1-6
what kind of linkage is found in glycogen
alpha 1-4 and alpha 1-6
where are storage carbohydrates usually located?
amyloplasts, liver, skeletal muscle
why can’t vertebrate animals digest cellulose?
we can’t break the beta 1-4 linkages
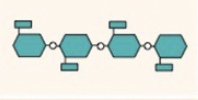
what is this
cellulose-diagram

what is this
amylose-diagram
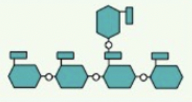
what is this
amylopectin-diagram
what is this
cellulose-shape
what is this
glycogen-diagram
what is this
amylopectin-shape
what is this
amylose-shape
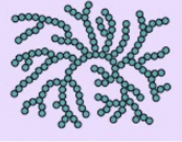
what is this
glycogen-shape
which carbohydrates are plants?
cellulose, amylose, amylopectin
which carbohydrates are animal?
glycogen
why is h bonding important for polysaccharide folding?
they have lots of hydroxyl groups
what do polysaccharide folding conformations favor?
h-bonding
what kinds of bonds dictate polymer subunits?
covalent
what kind of bonds stabilize 3d polymer structures?
weak interactions: h bonds, hydrophobic, van der waals, electrostatic
what do amylose chains form
helices
why can we stain starch blue?
amylose helix can hold iodine
what does cellulose form?
rigid chain
how does cellulose form it’s conformation?
hydrogen bonds between cellulose strands
what are exoskeletons made of?
chitin, second most abundant polysaccharide in nature
what is agarose composed of?
repeating dimers of D-galactose
what kind of linkages are in agarose?
beta 1-4 linkage to 3-6 anhydrogalactose
what do agarose polymers form?
double helix crosslinked together
what is peptidoglycan made of?
repeating disaccharides (NAG and NAM)
what kind of shape does peptidoglycan form?
strong sheet structure with chains cross linked together
describe the general structure of a lipid
hydrophilic polar head, hydrophobic nonpolar tail
Fatty Acid Nomenclature Names
chain length:# double bonds (double bond location)
saturated fatty acid
no double bonds, straight and packed closely together
what stabilizes saturated fatty acid structure?
hydrophobic and van der waals forces
do saturated fatty acids have high or low melting points
high
what does desaturation do for a fatty acid?
a kink in hydrocarbon chain that prevents close packing
more double bonds = __ bends = __ interactions = __ melting point
more, weaker, lower
longer chain = __ interactions = __ melting point
more, higher
what are the five classes of structural fatty acids?
glycerophospholipids, galactolipids/sulfolipids, archaea tetraether lipids, sphingolipids, cholesterols
describe the general structure of a glycerophospholipid
glycerol backbone with two fatty acids ester linkaged together
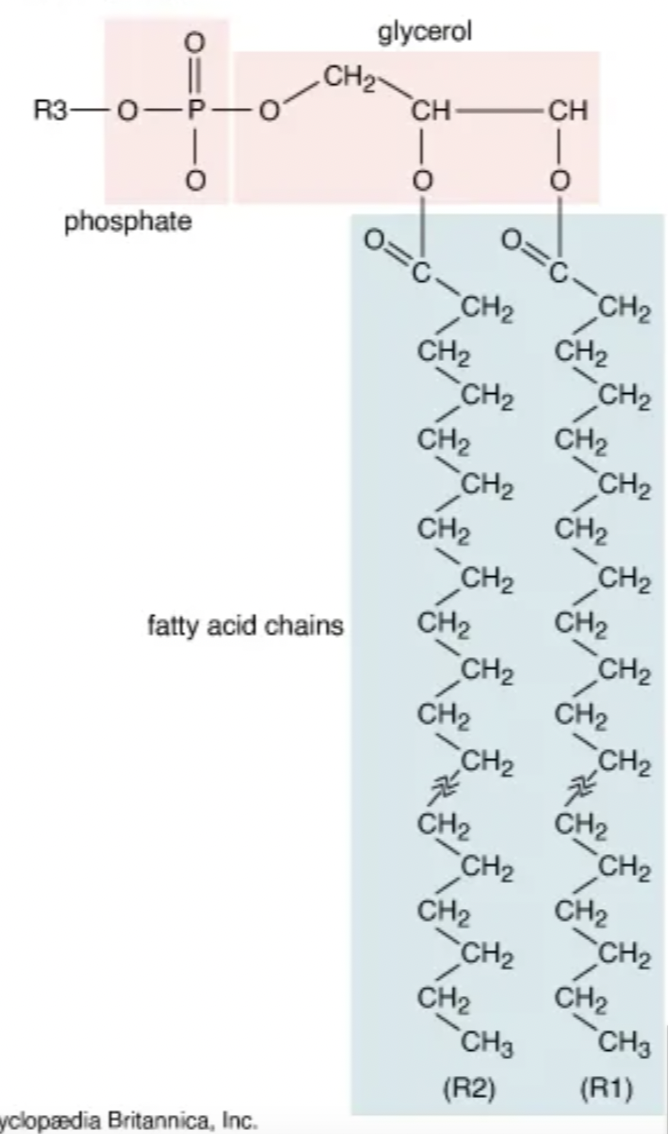
what is this
glycerophospholipid
describe the general structure of a galactolipid
galactose residues forming a sugar headgroup glycosidicly linked to C3 of the glycerol backbone with no phosphate
what differentiates a sulfolipid from a normal galactolipid?
sulfolipids have a sulfated sugar as their head group, allowing them to carry a negative charge
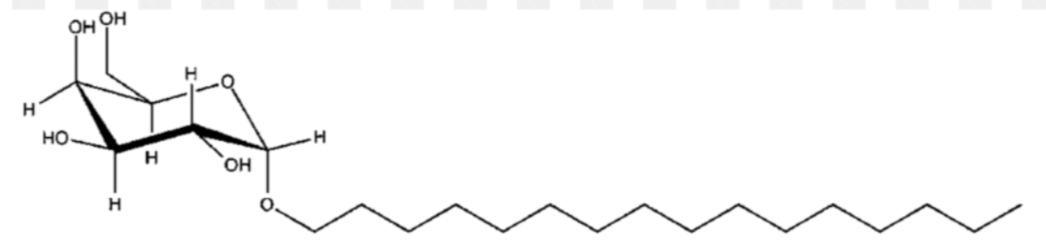
what is this
galactolipid
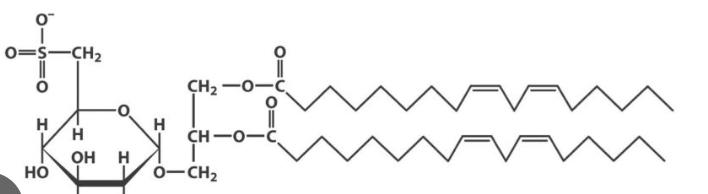
what is this
sulfolipid