Compound Microscope
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
it supports the tube and connects it to the base
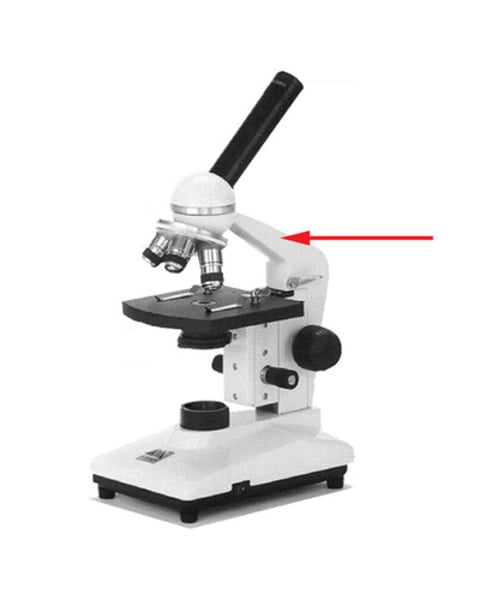
arm

the bottom of the microscope, used for support
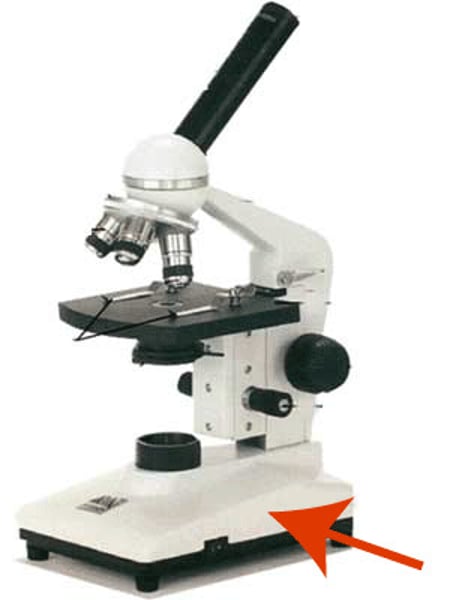
base

the lens at the top that you look through, usually 10x or 15x power
eyepiece lens
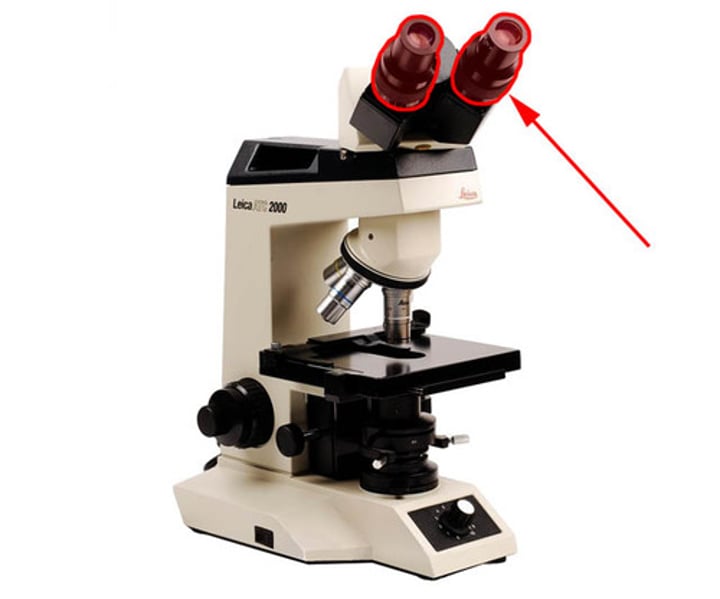
connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses
tube
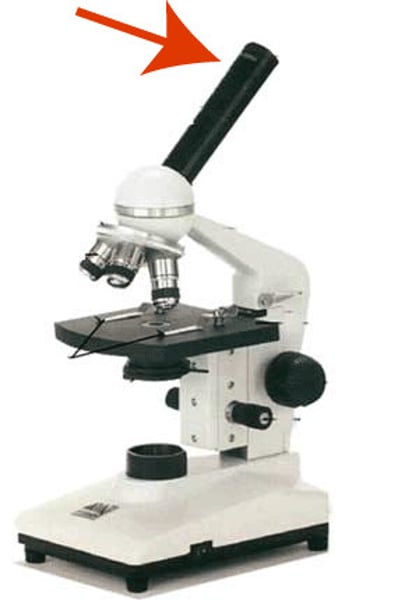
serves as the light source for a microscope during slide specimen visualization
illuminator or light source
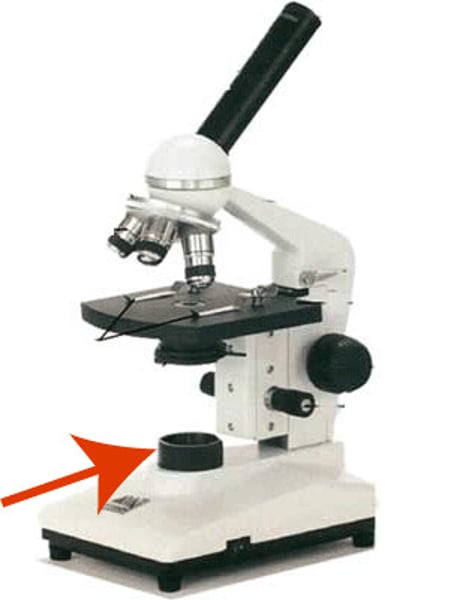

a flat platform where you place your slide
stage
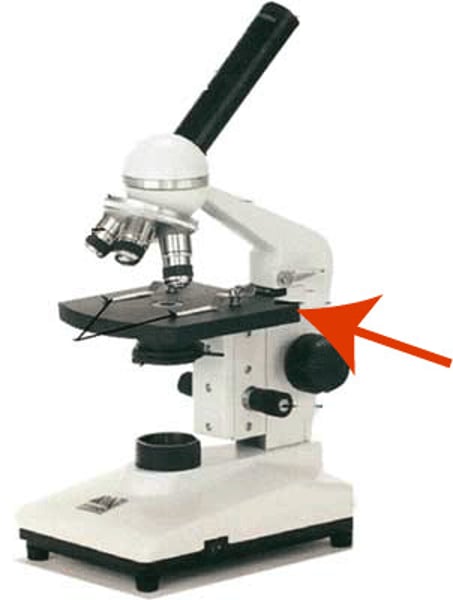
holds the slides in place for viewing
stage clips
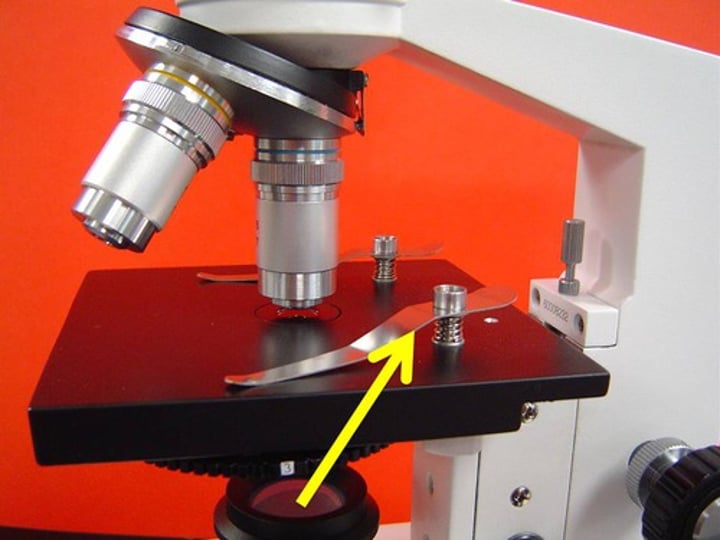

part of the microscope that holds two or multiple objective lenses and helps to rotate objectives lenses and also helps to easily change power
revolving nosepiece
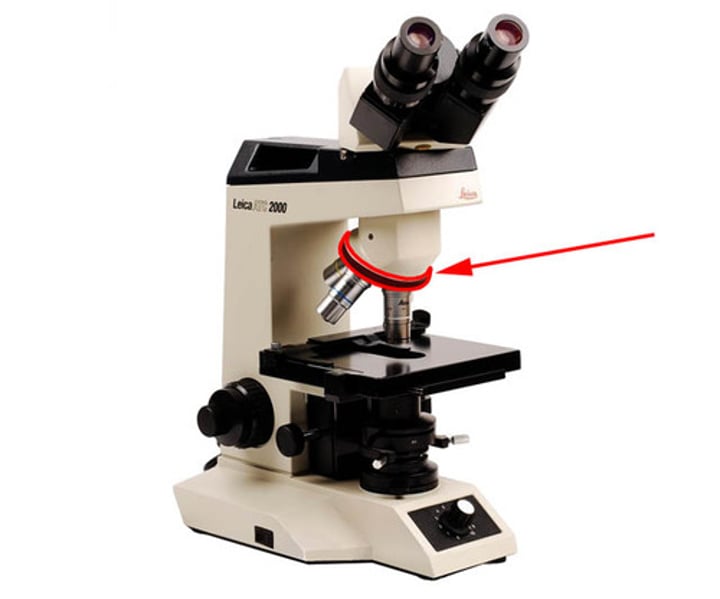
these are found on the nosepiece and range from 4x, 10x, 40x, and sometimes 100x powers
objective lenses
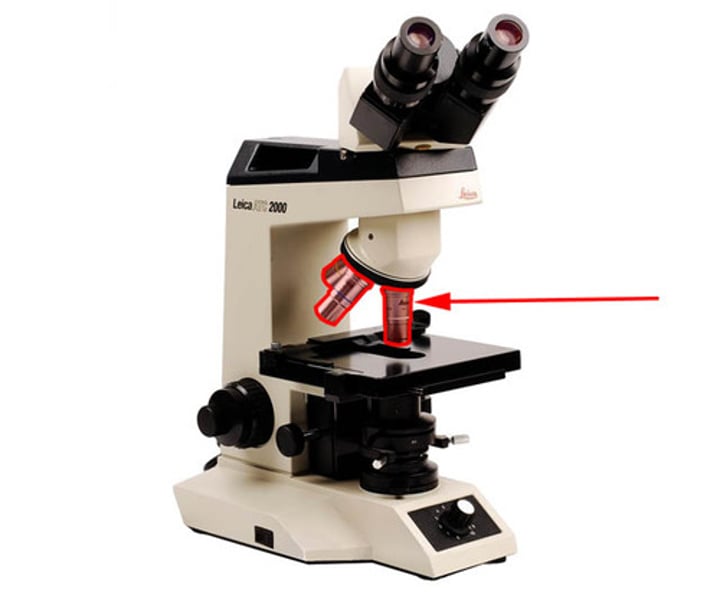
a rotating disk under the stage. this part controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. (located below microscope stage and above the condenser lenses)
diaphragm or iris
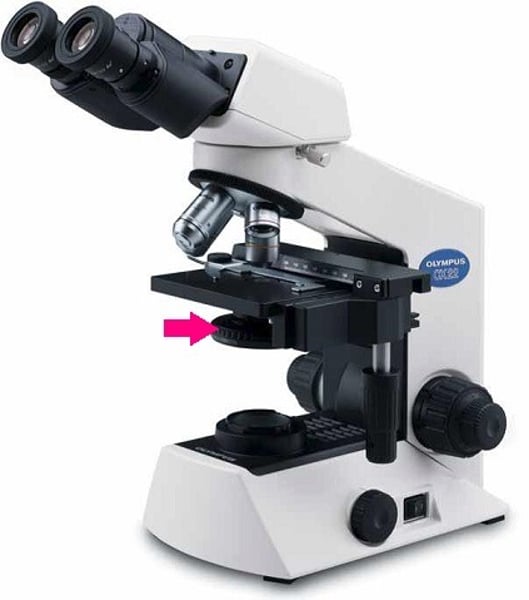

part used to collect and focus light from the illuminator on to the species. (located under diaphragm)
condenser
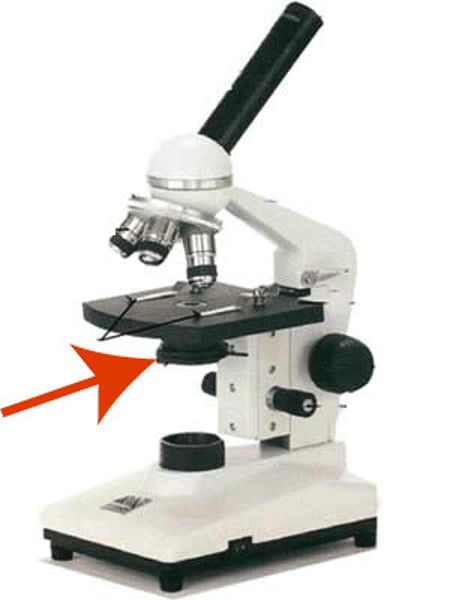
large knob used for focusing the image under low power
coarse adjustment knob
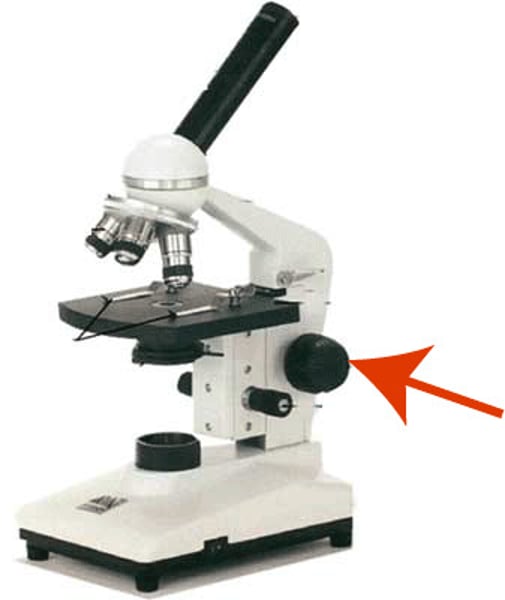

these allow you to move your slides
stage control
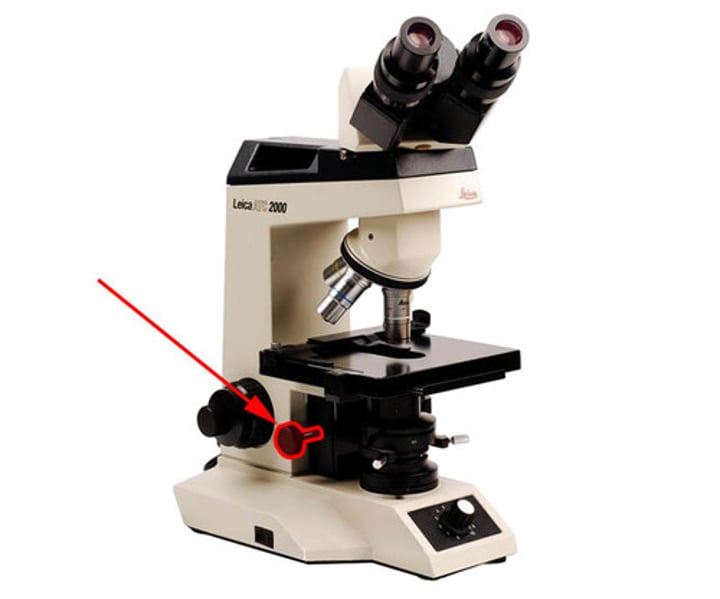
it is used to vary the light that passes through the stage opening and helps to adjust both the contrast and resolution of a specimen
brightness adjustment
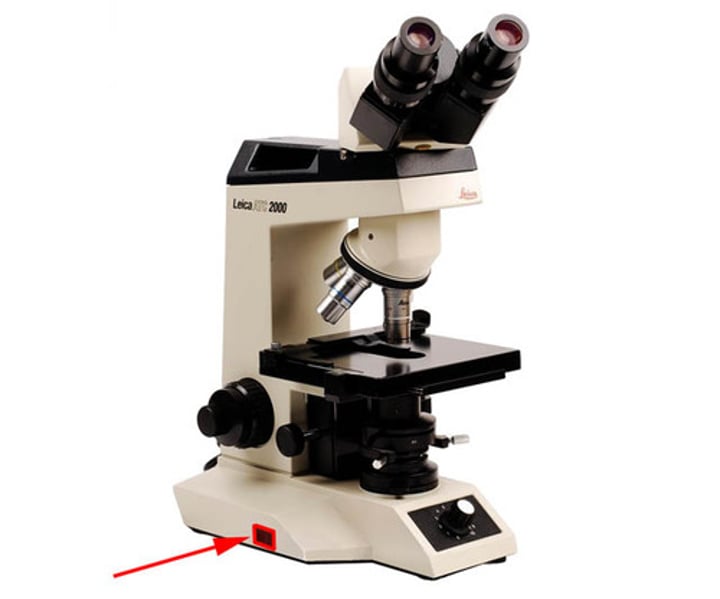
turns the illuminator on and off
light switch
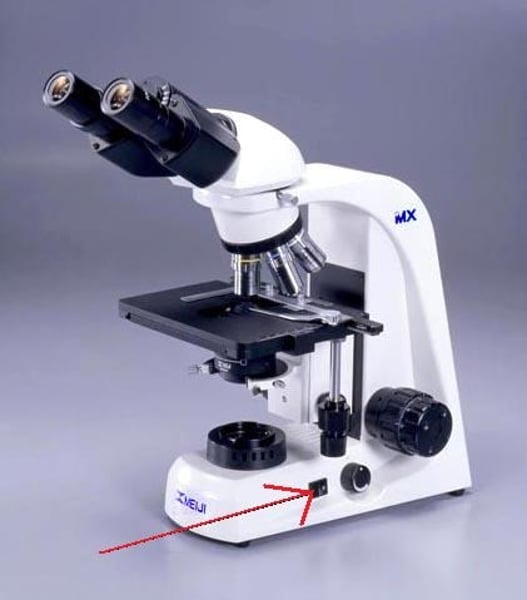
smaller knob used for focusing the image within the medium and high-power objective
fine adjustment knob
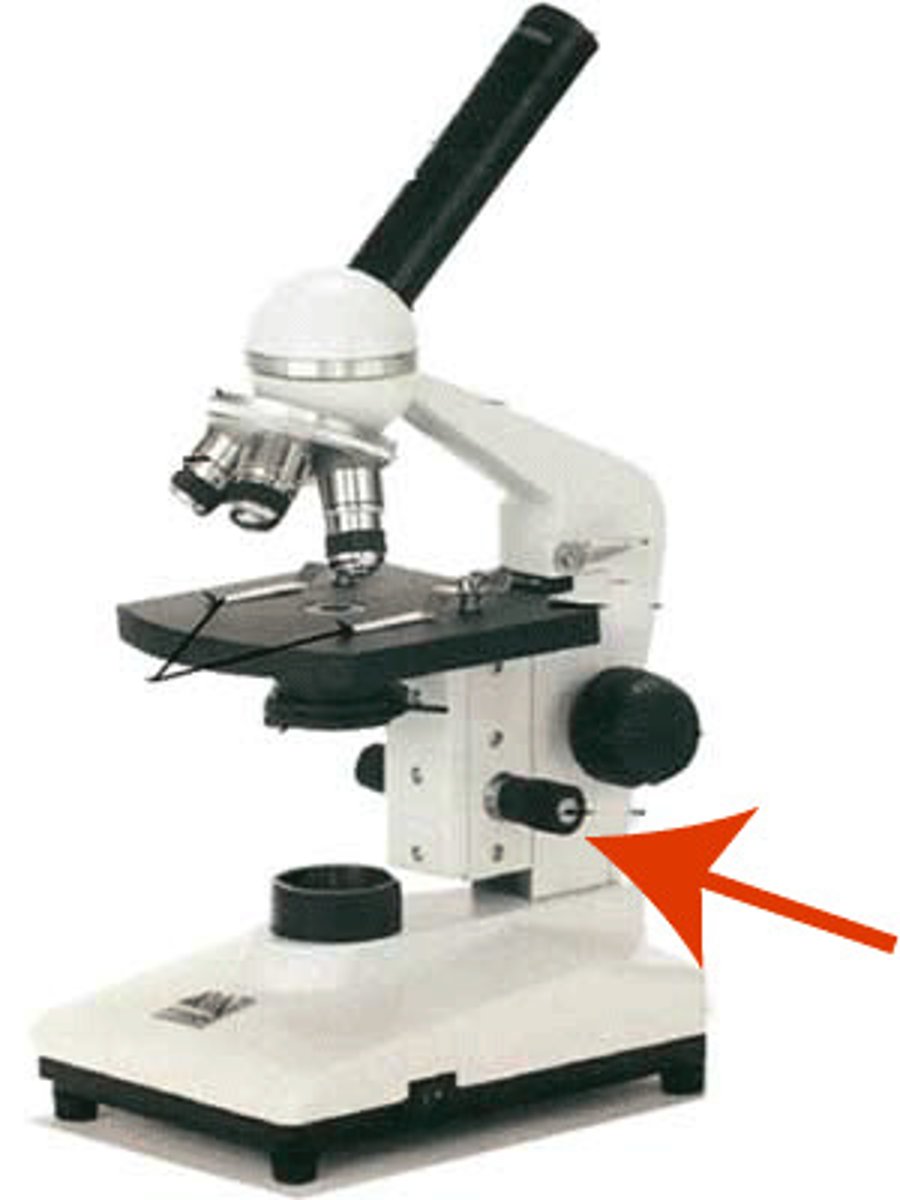
supports the objective lenses and ocular lenses
head

circular area on stage through which light passes
aperture

a knob or lever that adjusts the magnifier on the viewfinder to compensate for differences in vision.
diopter adjustment
why do you start with the longest objective lens before viewing?
having start with the longer lens before viewing makes it so that when you switch from 4x to 10x then 40x you won't hit the slide with the objective lens.
what is the difference between magnification and resolution?
magnification- making an image appear larger. up until the limit of resolution.
resolution- minimum distance apart that two objects can be for them to appear as two separate items.
what is the formula for magnification?
magnification = image size/actual size
do you start with the fine or coarse knob adjustment?
CORSE KNOB. it is used for initial focus by moving either the stage or the objective lenses up and down.
what is the order you should use the objective lenses in?
4x -> 10x -> 40x
do you ensure the slide touches the first objective lens?
NO. be sure there is room for the slide to move into place.
if the slide you placed on stage is not moving around when you turn the stage control what do you think you forgot to do?
adjust the stage clips properly onto the slides
what are the 3 main things you observe when looking at an onion cell?
nucleus, cell wall, cytoplasm
what are the 3 main things you observe when looking at one cheek cell
cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
how much iodine solution are we putting on the onion peel?
one drop (or the lab will 💥)
what are we using to GENTLY scrape the inside lining of our cheeks?
toothpick
what is mr borg's biggest rule in the lab?
common sense :)
what drop of liquid are we putting on our slide along with our cheek cells?
methylene blue
what is the wet-mount technique
placing a fluid solution on a slide, keeping the onion cell in a solution, and then covering the onion cell and the solution with a cover slide. (makes it so that the cells are easier to stain and you can see it more visibly)
what do the focusing knobs on a microscope do?
move the stage up and down until the image is clear
how do you calculate total magnification?
ocular lens x objective lens= total magnification

how do you carry a microscope?
one hand on the arm and one hand under the base
