Glucose Non-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli (Exam 2)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What are some general characteristics of glucose non-fermenting GN bacilli?
- Non spore-forming
- Ubiquitous
- Rarely normal flora
- Opportunistic
What are some common conditions that put a patient at risk for colonization by a glucose non-fermenting GN bacillus?
- Immunosuppression
- Foreign body (ex. implants)
- Trauma
What diseases are caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei?
- Melioidosis
- Pneumonia
- Bacteremia
What diseases are caused by Burkholderia cepacia?
- Bacteremia
- Pneumonia
- Septic arthritis
- Peritonitis
What diseases are caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia?
- Skin and skin structure infections
- Bacteremia
- Pneumonia
- UTIs
- CNS infection
- Endocarditis
- Mastoiditis
- Epididymitis
- Cholangitis
- Bursitis
- Peritonitis
What diseases are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
- UTIs
- Bacteremia
- Pneumonia (especially in CF patients)
- CNS infections
- Ocular infections
- Skin infections
Pseudomonas are ______ with one or several polar flagella.
motile
Pseudomonas can be _______ or _______.
fluorescent, non-fluorescent
Pseudomonas aeruginosa gram stain
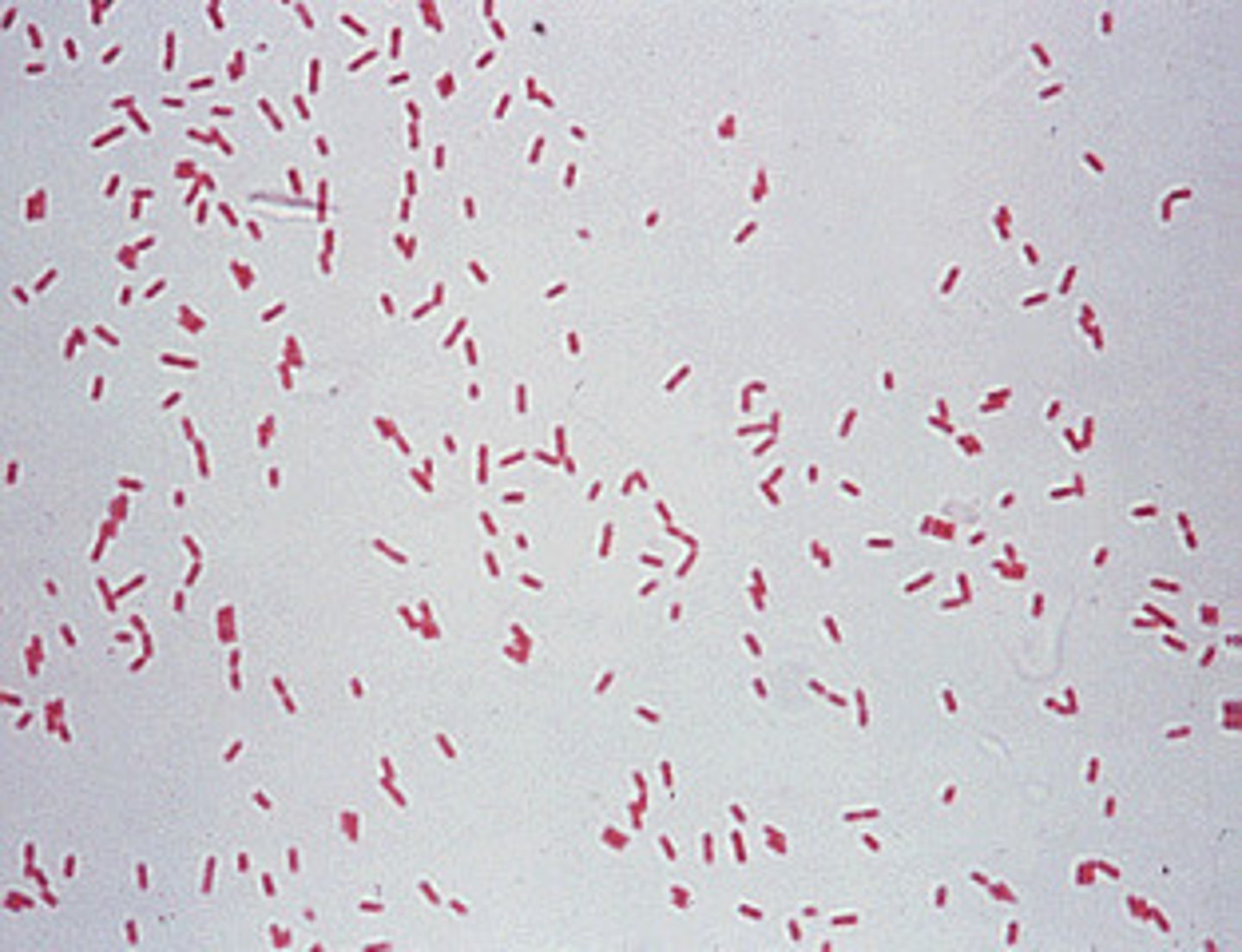
Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonies are ______ in color, large, and most are ______ hemolytic.
green, beta
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is acetamide, oxidase, and arginine ______.
positive
Pseudomonas aeruginosa has a ______-like odor.
grape
Pseudomonas aeruginosa grows at ______C.
42C
Pseudomonas aeruginosa has ______, which is unique and gives a blue color.
pyocyanin
Pseudomonas aeruginosa have what other pigments?
- Pyoverdine (green)
- Pyorubin/pyorubrin (red)
- Fluorescein (yello/green)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause ______ or ______ infections.
endogenous, exogenous
What are the intrinsic methods of resistance possessed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
- Inducible AmpC beta-lactamase
- Multi Drug Resistant efflux pumps
What are some acquired methods of resistance that Pseudomonas aeruginosa can develop?
- MDR efflux pumps
- Impermeability mutations (OprD)
- Beta-lactamases
- Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes (rmtA)
- Transmissible quinolone resistance (qnr)
Acinetobacter baumannii gram stain
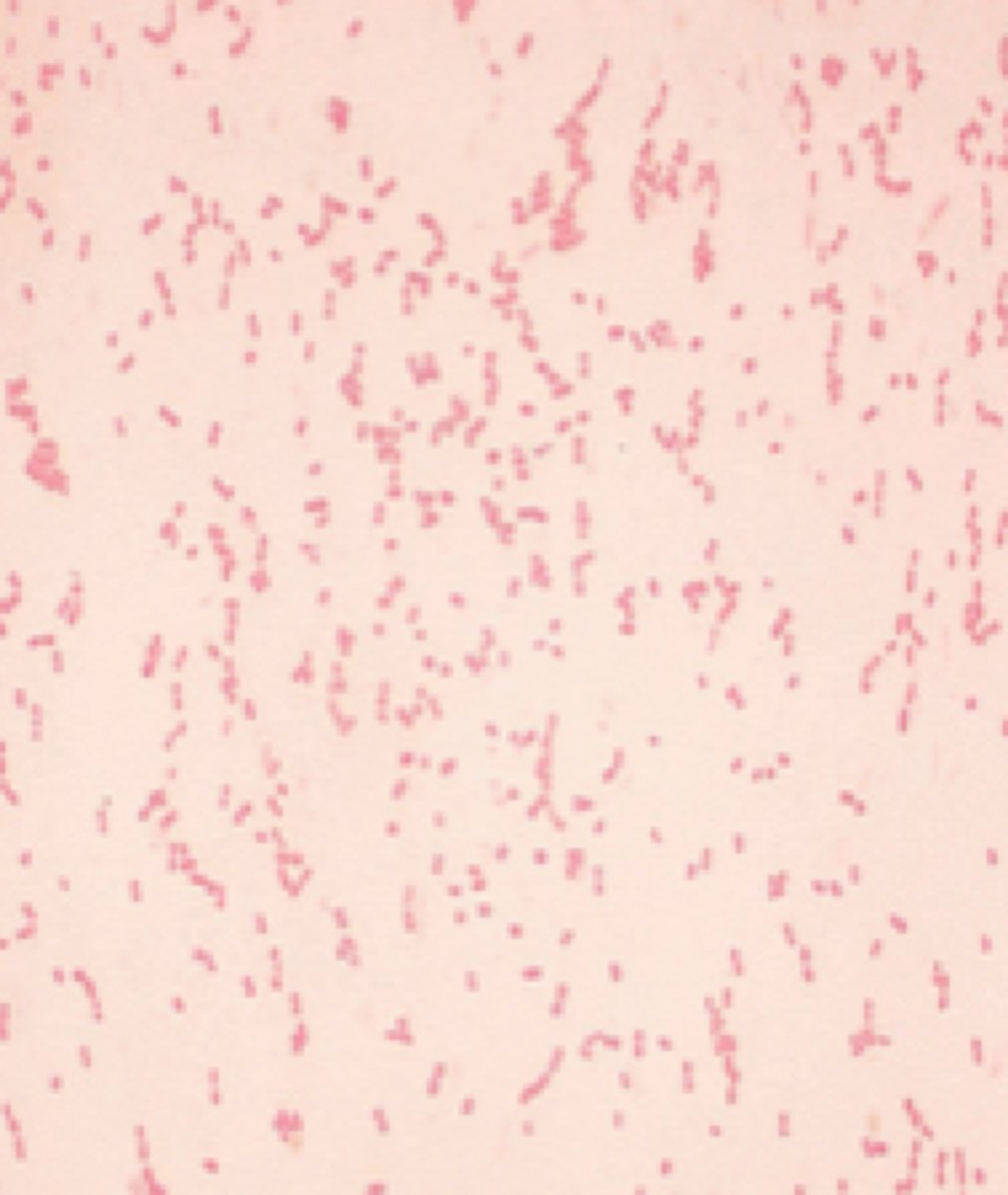
Acinetobacter baumannii gives ______ hemolytic colonies.
non
Acinetobacter baumannii colonies will have a ______ hue on MacConkey agar.
purple
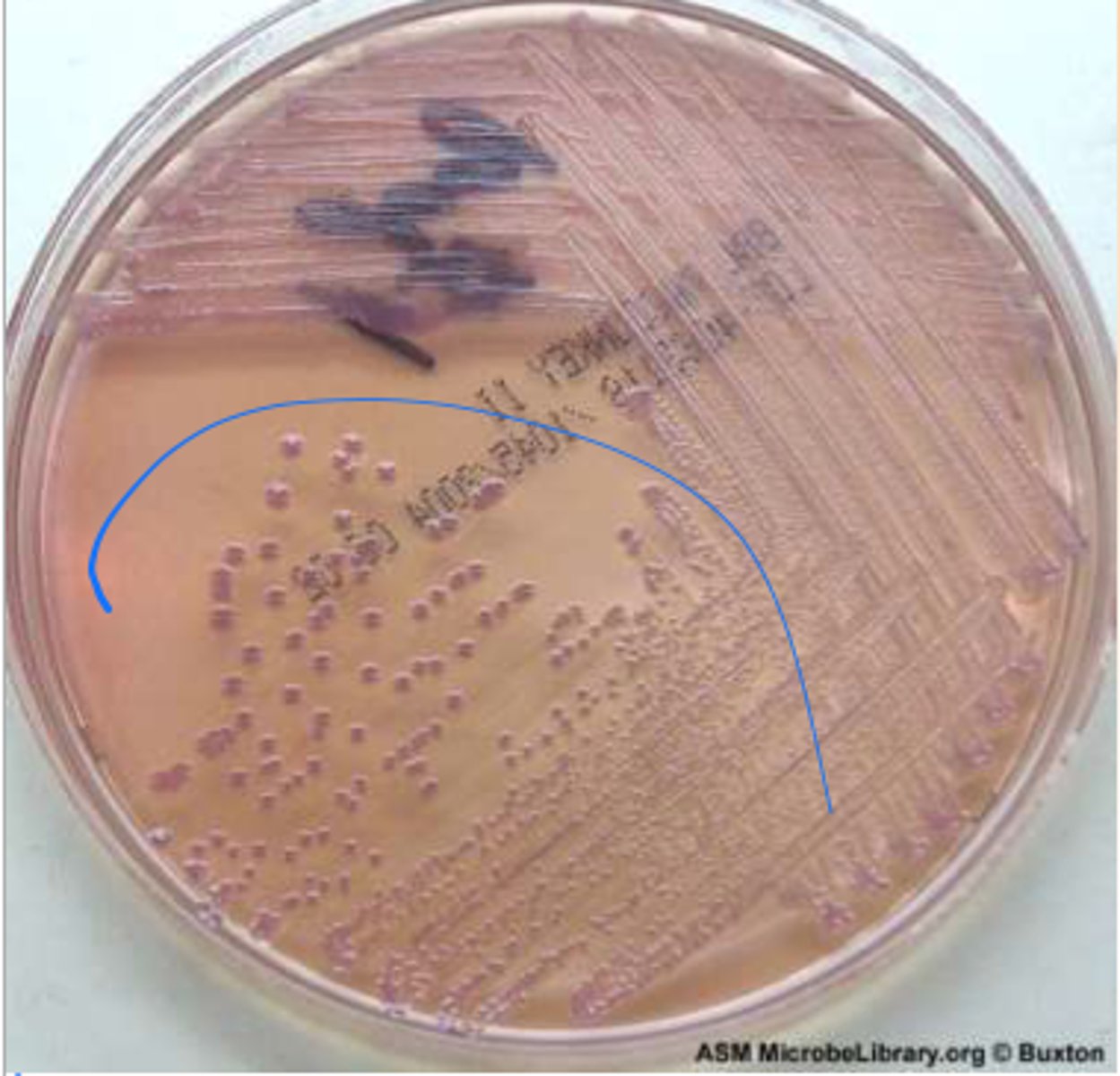
______ resistant Acinetobacter baumannii is becoming a real problem.
Carbapenem (CRAb)
CRAb possesses resistance to ______ major classes of antibiotics.
all (beta-lactams, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides)
What methods of resistance do CRAb have?
- AmpC cephalosporinases
- Acquired ESBL
- Porin mutations
- Efflux pump overexpression
______ enzymes are commonly reported in CRAb.
Oxacillinase (OXA-like)
Acinetobacter are ______ (motile/non-motile), gram negative coccobacilli.
non-motile
Acinetobacter are catalase ______ and oxidase ______.
positive, negative
Acinetobacter are found in ______ and _____.
soil, water
Acinetobacter grows well on ______ agar.
MacConkey
On MAC, Acinetobacter may look pink/purple but do not ferment ______.
lactose
Burkholderia are ______ (aerobic/anaerobic).
aerobic
Burkholderia are ______ forming (spore/non-spore) GN bacilli.
non-spore
Burkholderia are resistant to ______ and ______.
polymyxin B, colistin
Burkholderia cepacia gram stain
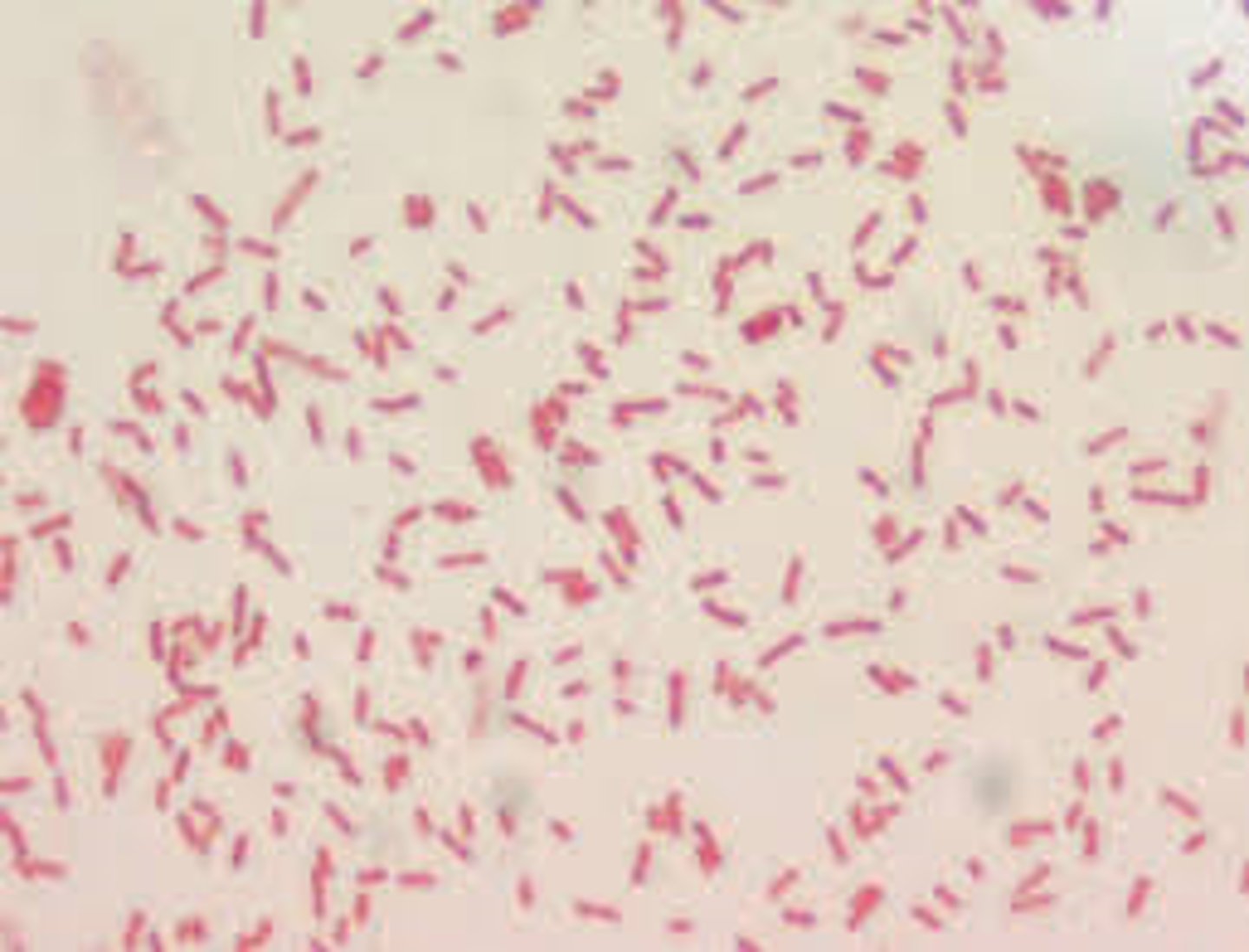
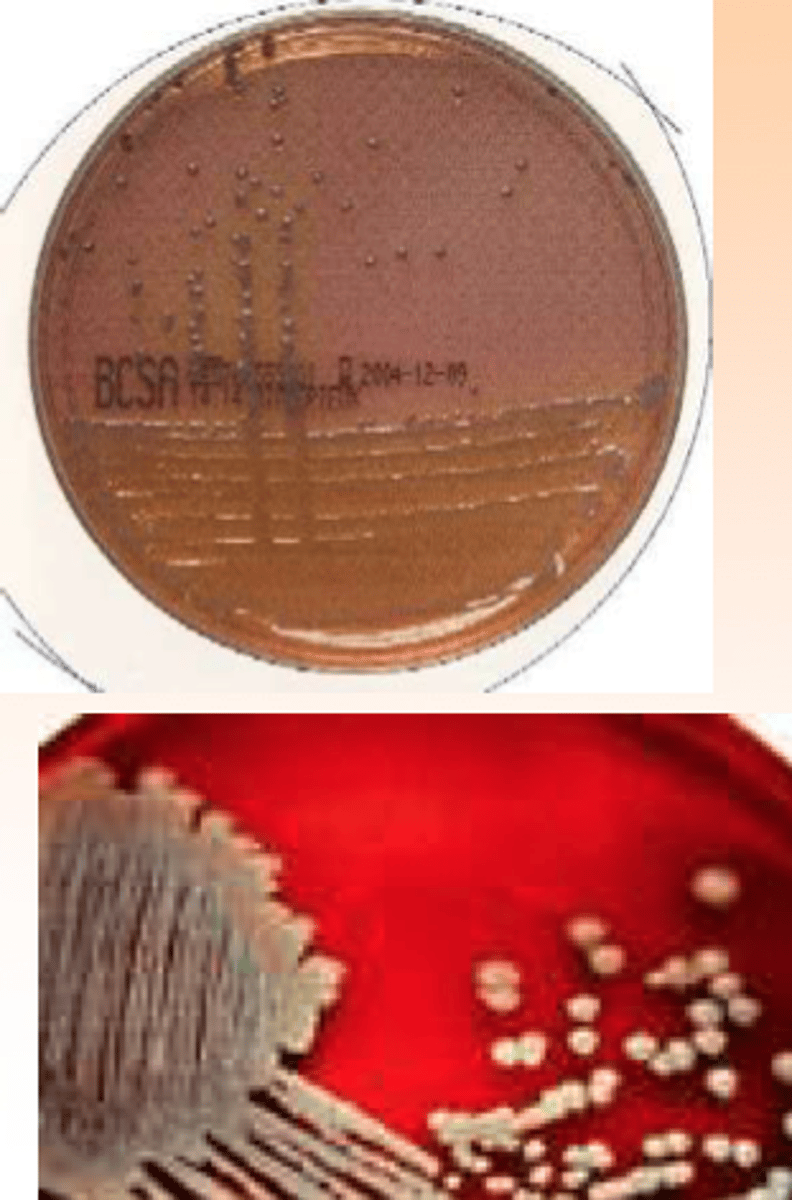
Burkholderia cepacia colonies

Patients with ______ or ______ are at increased risk for infection with Burkholderia cepacia
CGD, CF
Burkholderia cepacia can be a ______ pathogen.
nosocomial
______ antimicrobial resistance is common with Burkholderia cepacia.
Broad-spectrum
80% of Burkholderia infections in the U.S. are caused by what strains?
B. multivorans and B. cenocepacia
15% of Burkholderia infections in the U.S. are caused by what strains?
B. vietnamiensis, B. cepacia, B. dolosa
What selective medias can be used to enhance the recovery of Burkholderia cepacia complex?
- Psuedomonas cepacia selective agar (PCSA; hot pink)
- Burkholderia cepacia selective agar (BCSA; purple with yellow or pink zone)
- Oxidative-fermentative polymyxin bacitracin lysine (uncommon; yellow)
Burkholderia pseudomallei is acquired through environmental exposure to ______ and ______.
soil, water
Most people who contract Burkholderia pseudomallei don't develop ______.
clinical infection
50% of Burkholderia pseudomallei cases cause ______, 50% cause ______.
pneumonia, bacteremia
Positive Burkholderia pseudomallei blood culture within 24 hours indicates an increased risk of ______.
mortality
Burkholderia pseudomallei can become a ______ infection.
latent (can reactivate)
Burkholderia pseudomallei and mallei are category ______ select agents for HHS and USDA.
A (etiologic agents - dangerous)
Stenotrophomonas are ______ due to polar flagella.
motile
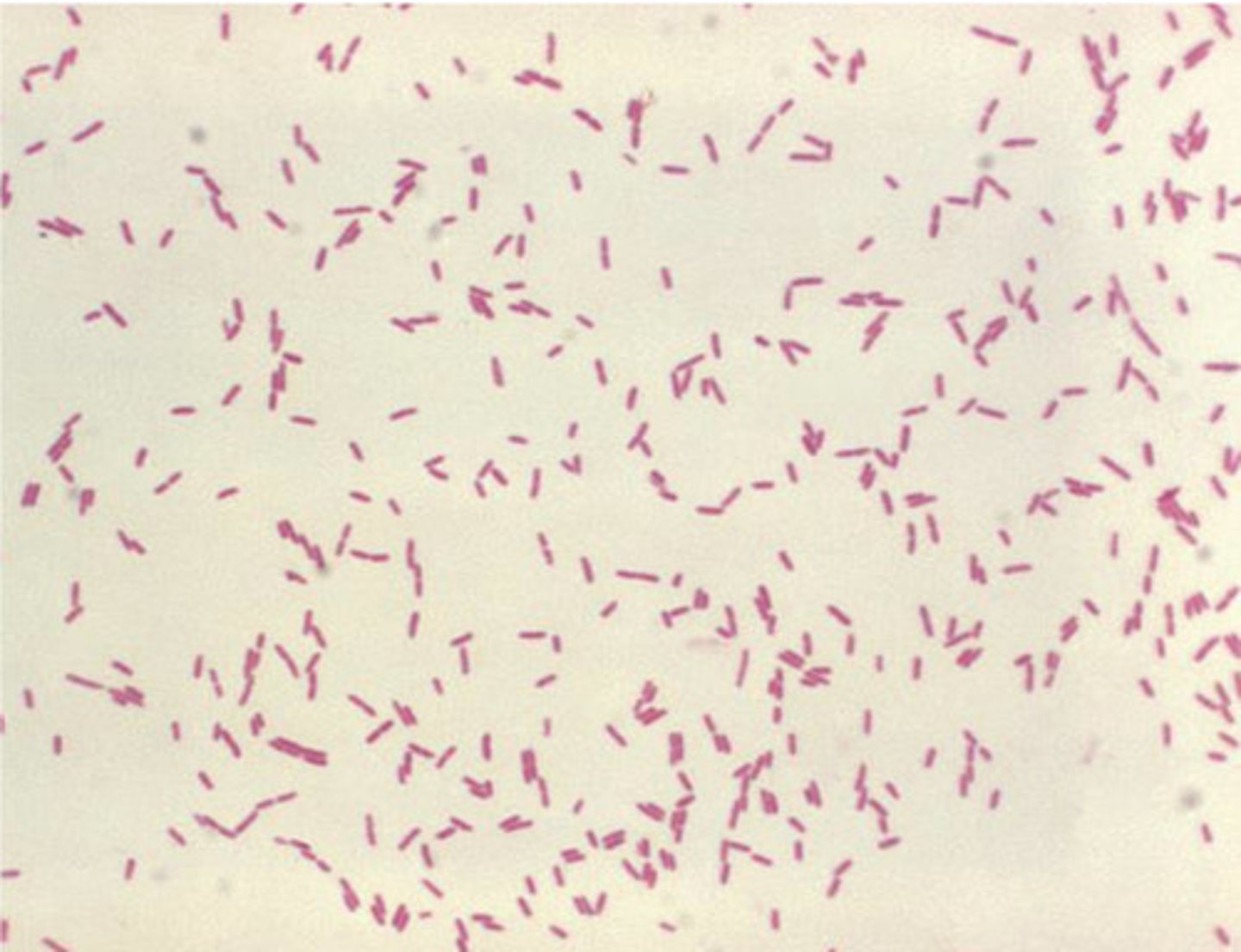
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia gram stain
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia colonies
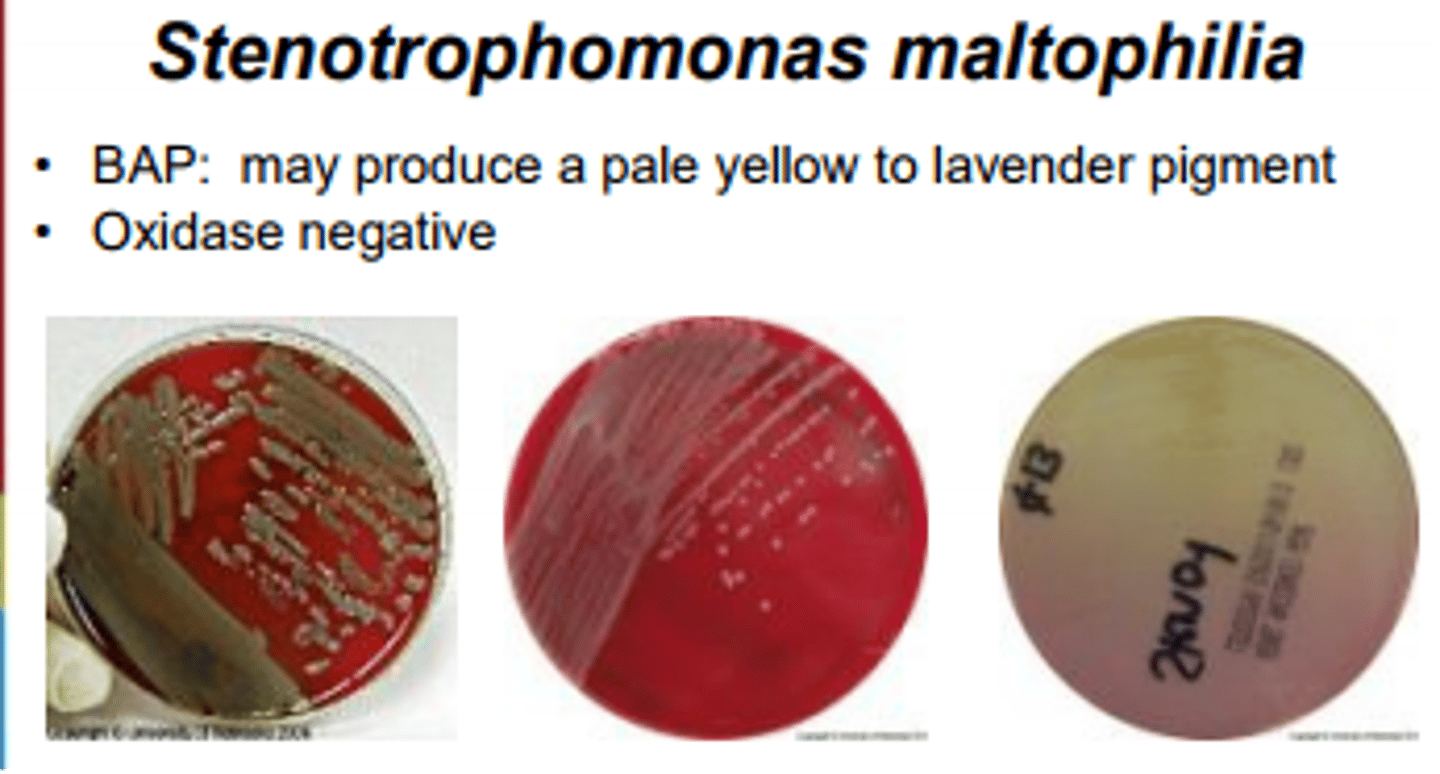
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia has substantial ______ rates.
morbidity/mortality
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is multidrug ______.
resistant
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is oxidase ______.
negative (20% of strains are positive)
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia can grow on MacConkey agar but is ______ fermenting.
non-lactose
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia can oxidize ______ and ______.
glucose, maltose
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is DNase and lysine decarboxylase ______.
positive
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia possesses ______ hydrolysis.
gelatin
What intrinsic methods of antimicrobial resistance does Stenotrophomonas maltophilia possess?
- MDR efflux pumps
- L1 and L2 beta-lactamasese
- Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes
- Qnr gene family
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia has ______ virulence.
low
The first line of treatment against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is ______.
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Second line agents against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia are ...
Fluoroquinolones, minocycline, cefiderocol
Shewanella putrefaciens
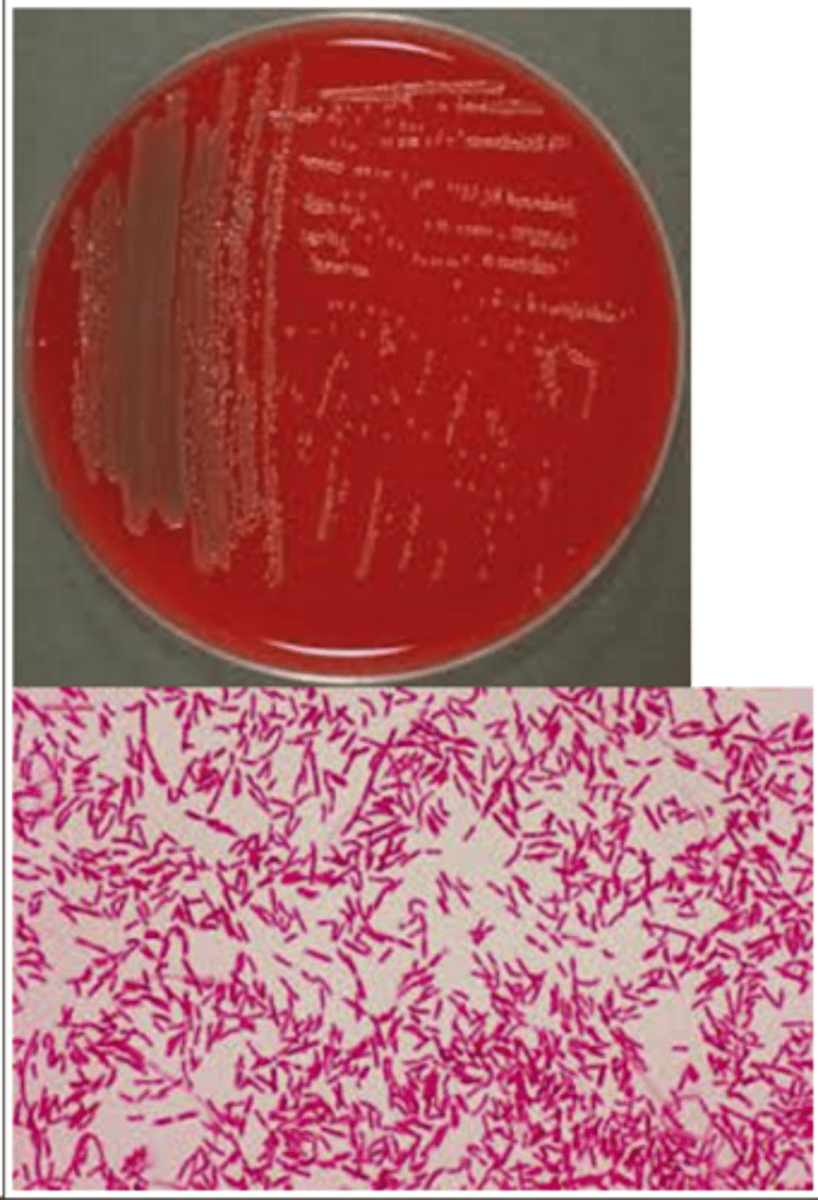
Shewanella putrefaciens is oxidase and H2S _______.
positive
Shewanella putrefaciens is indole ______ and ______ (motile/non-motile).
negative, motile
50% of Shewanella putrefaciens strains produce acids from ______.
glucose
Shewanella putrefaciens is ______ resistant.
colistin
OF test - fermentation result
Yellow for both aerobic and anaerobic tubes
OF test - oxidation result
Yellow at the top of the aerobic tube, green in the anaerobic tube
______ is overlayed at the top of one of the OF tubes to create an anerobic environment.
Mineral oil
What are the fluorescent Pseudomonas species?
- P. aeruginosa
- P. fluorescens
- P. stutzeri
What are the nonfluorescent Pseudomonas species?
- P. pseudoalcaligenes
- P. alcaligenes
- P. luteola
- P. oryzihabitans
Patients with CF have abnormal transport of ______ and ______ across respiratory epithelium.
sodium, chloride