6- Kearns - Steroid Hormones
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Some tumors express steroid receptors and depend on _____________ to grow.
hormones
(ex: breast tumors express estrogen and progesterone receptors and depend on estrogen to grow)
An anti-cancer target for hormone dependent tumors is to inhibit ____________.
estrogen
In general, what does a modulator do?
something that drives something else
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) act on what receptor(s)?
act on estrogen receptors (ERa, ERb)
What type of receptor is the estrogen receptor? is it intracellular or extracellular? is it ligand-dependent or ligand-independent? is it cytoplasmic or nuclear?
intracellular, ligand-dependent nuclear receptor
Where is ERa and ERb found in the body?
ERa- female reproductive tract and mammary glands (boobs)
ERb- vascular endothelium, bone, prostate tissue
SERMs are partial ____________. What does that mean?
agonists—- partial agonists mean that depending on the type of tissue, SERMs will either act like an agonist or antagonist
What are the common structural features of SERMs?
core structure is modeled after estradiol
2 aromatic rings (separated by up to 3 spacer atoms)
a 4-substituted phenyl group (between the other aromatics)
size/functionality affects binding affinities for ERa and ERb as well as ability to block the binding of coactivators
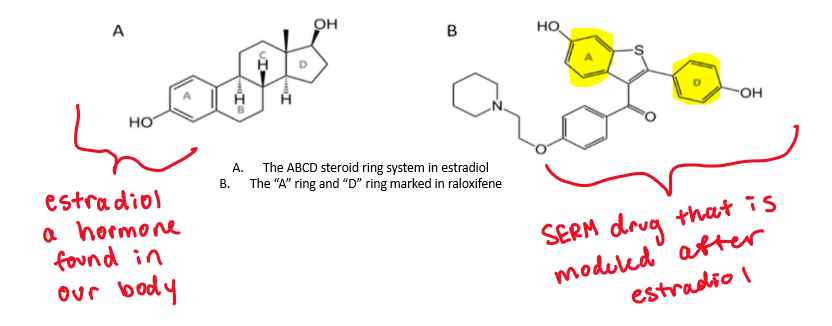
What is the MOA of SERMs?
bind to estrogen receptors (competing with estradiol)
depending on the type of tissue—> SERMs will act as either an agonist or antagonist on estrogen-dependent gene transcription
ex: in breast tissue SERMs will act as an antagonist and without estrogen signaling, estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells are unable to proliferate, leading to the slowing or stopping of tumor growth.
In order to select the right SERM for treatment we must test the cancerous tumor to see what?
if it’s ER+ or ER-
(ER+ means that the tumor is + for expressing estrogen, we wouldn’t want to use a SERM if it’s ER-)
Answer the following about Tamoxifen:
brand name
class
ADMINISTRATION
Uses
MOA
ADRs
Soltamox
SERM
oral admin- PRODRUG
uses: ER+ breast cancer (and prophylaxis), endometrial carcinoma
MOA: estrogen antagonist in ER+ breast tissue
ADRs: think symptoms of menopause— hot flashes, mood swings, CV changes—- ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, THROMBOEMBOLISM
Tamoxifen is a prodrug and requires activation by what enzymes?
kearns said she was going to ask about this
CYP2D6 and CYP3A4
What is administered with Tamoxifen? When? Why?
GnRH analog may be administered with Tamoxifen in PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN. Why? In premenopausal women if you starve the body of estrogen it is bad and may cause osteoporosis
What is the active metabolite of Tamoxifen? When would we give this active metabolite over Tamoxifen?
active metabolite is ENDOXIFEN—> would give over Tamoxifen if liver damage OR taking CYP2D6 and 3A4 inhibitors
What are some common CYP2D6 inhibitors?
bupropion
chloroquine
chlorpromazine
What does SERD stand for? What do they do?
SERD stands for Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulator
they are ER competitive antagonists (pure anti-estrogens)
What drug is a SERD? How is it administered? Uses?
drug: FULVESTRANT (Faslodex)
IM admin
Uses: advanced/metastatic breast cancer
What is aromatase? What does this enzyme do?
aromatase is a CYP19A1 enzyme that converts androgens into estrogens
converts:
androstenedione to estrone
testosterone to estradiol
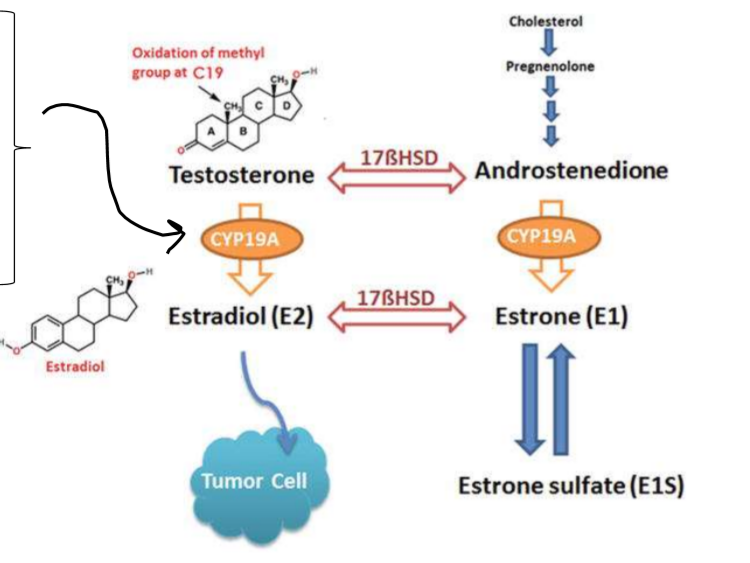
Aromatase inhibitors are typically used to treat breast cancer in _____menopausal women.
a. pre
b. post
b
note: kearns said THERE WILL BE a pre vs. postmenopausal question on the test
—
What is the name of the drug that is an aromatase inhibitor commonly used for breast cancer?
Anastrozole (arimidex)
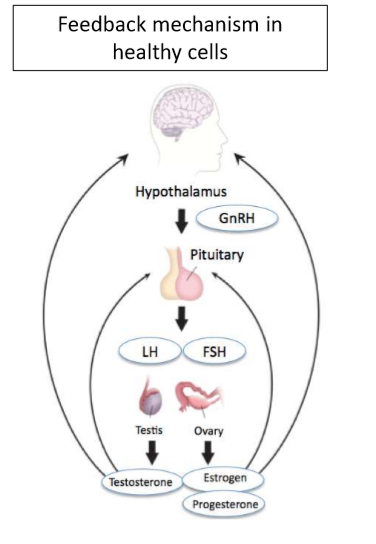
How do GnRH agonists lead to decreased production of sex hormones?
flare- increase release of FSH and LH
desensitization- downregulation of pituitary GnRH receptors
decreased activity of FSH and LH
decreased androgens and estrogens
Continuous use of GnRH agonists treat prostate and breast cancer by…
promoting apoptosis
What drugs are Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone agonists?
Goserelin (Zoladex)
Leuprolide (Eligard, Lupron)
Answer the following about GnRH agonists (Leuprolide and Goserelin):
admin
ADRs
SQ
ADRs: TUMOR FLARE, libido changes
others: edema, HA, hot flashes, mood swings
What can leuprolide be administered with to reduce bone mineral density loss?
norethindrone
What functional group does Leuprolide have?
cholesterol functional group
What is the MOA of antiandrogens?
inhibits synthesis of or antagonize effects of androgens (androgens are hormones like testosterone and DHT)
(competitive antagonists or partial agonists)
block the inhibitory effects of testosterone on gonadotropin secretion
(basically: these cancers depend on testosterone to grow and we inhibit testosterone= cancer dies)
Because antiandrogens also block the inhibitory effects of testosterone on gonadotropin secretion… what does that lead to an increase of? What must it be co-administered with then?
leads to increase in FSH and LH—> co-administered with GnRH agonist like Leuprolide
What drugs (brand/generic) are antiandrogens?
Abiraterone Acetate (Zytiga)
Bicalutamide (Casodex)
Enzalutamide
(mneumonic: think “ABC” or Abiraterone, Bicalutamide, Casodex)
What are the uses of each antiandrogen drug?
Abiraterone Acetate (Zytiga)- CASTRATION RESISTANT PROSTATE CANCER
Bicalutamide (Casodex)- PROSTATE CANCER
Answer the following about abiraterone acetate:
inhibitor of
result of inhibition
administration
inhibitor of CYP17A1
inhibits androgen synthesis aka the precursors of testosterone
oral prodrug
What is the MOA and ADRs of Bicalutamide?
MOA- selective competitive antagonist of the androgen receptor
ADRs: hot flashes, GYNECOMASTIA (bc of indirect increase in estrogen)
Why are steroids given concurrently with anti-cancer medications?
goal is to reduce the action of the immune system—- body sees cancer as an infection and starts having an immune response
uses: lymphomas, N/V, supportive care
What cancer is the ABVD regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
doxorubicin (Adriamycin), bleomycin, vincristine, dacarbazine
What cancer is the CHOP regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine (Oncovin), prednisone
What cancer is the FOLFOX regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
colorectal cancer
leucovorin (folinic acid), fluorouracil, oxaliplatin
What cancer is the FOLFIRI regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
colorectal cancer
leucovorin (folinic acid), fluorouracil, irinotecan
What cancer is the MVAC regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
advanced bladder cancer
methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin (Adriamycin), cisplatin
What cancer is the PCV regimen for? What are the drugs involved?
brain tumors
procarbazine, CCNU (lomustine), vincristine