stereoselective synthesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is stereospecificity
only a certain stereoisomer can be produced due to how the reaction proceeds
stereoselectivity
the reaction can produce either stereoisomer but one is preferred
diastereocontrol
controlling which diastereomer is produced
enantiocontrol
controlling which enantiomer is produced
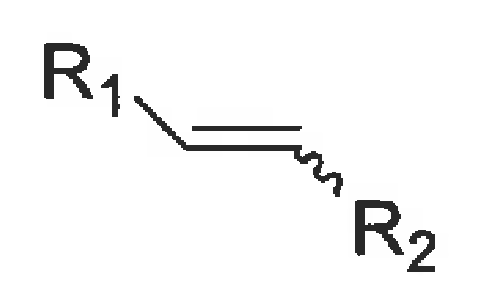
major way of producing alkenes
the Wittig reaction
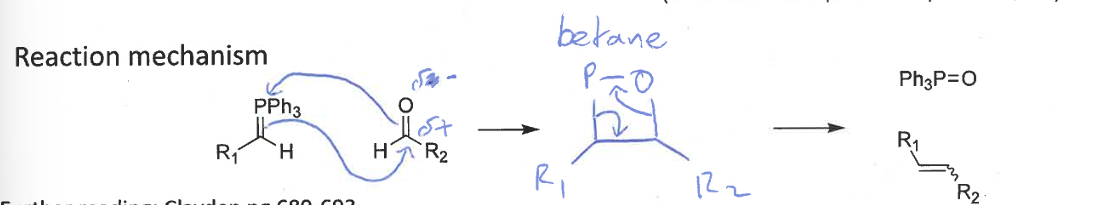
ylid + aldehyde → alkene + Ph3P=O
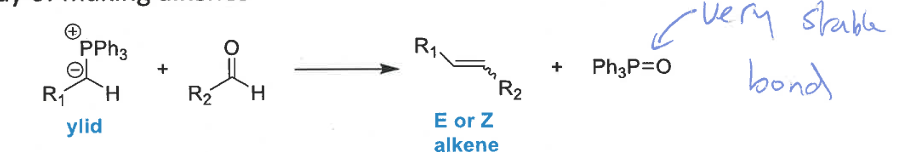
what drives the wittig reaction
the carbonyl is more stable than the alkene but the P=O bond is very strong/stable, driving the reaction
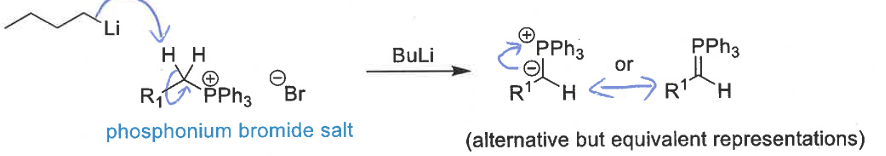
how are ylids formed for the wittig reaction
phosphonium bromide salt + BuLi
wittig reaction mechanism including intermediate
intermediate = betane
collapses into products due to ring strain
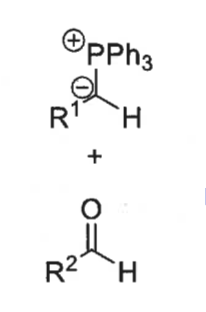
possible intermediates of the wittig reaction
how does this first step happen
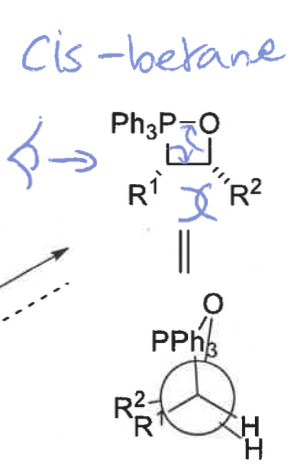
cis and trans betane
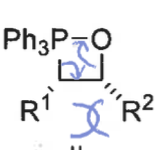
O and P come together at right angles then turn to be parallel in order to form a bond
cis betane structure + newman projection
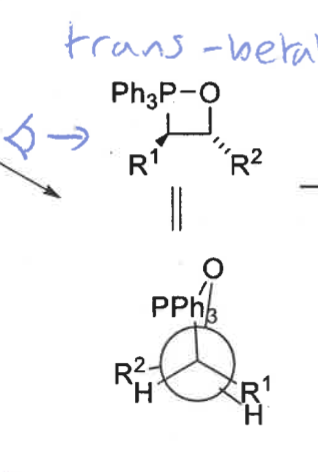
trans betane structure + newman projection
which betane forms fast/slow and which is reversible (+ when?)
cis = fast + reversible (when R1 is electron withdrawing group so stabilises ylid)
trans = slow
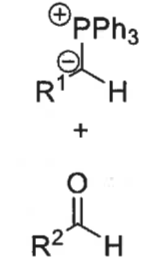
show route to betane transition states and give relative stabilities
cis’s transition state more stable as R groups are on opposite sides
trans’s TS has steric clash from overlapping R groups
wittig product formed from cis betane + speed of formation
Z isomer only - no bond rotation
slow formation
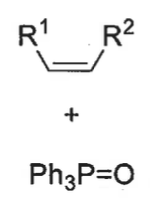
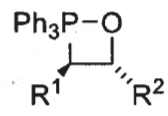
wittig product formed from trans betane + speed of formation
E isomer
fast formation
which of E and Z isomers from wittig is kinetic or thermodynamic product and why
Z isomer (from cis betane) is kinetic product as initial step quicker
E isomer (from trans betane) is thermodynamic product as betane is much more stable

overall wittig reaction to form E and Z isomers with transition states
R groups end up with opposite stereochemistry to what they have in the transition state
the reaction is controlled by the energies of the betane
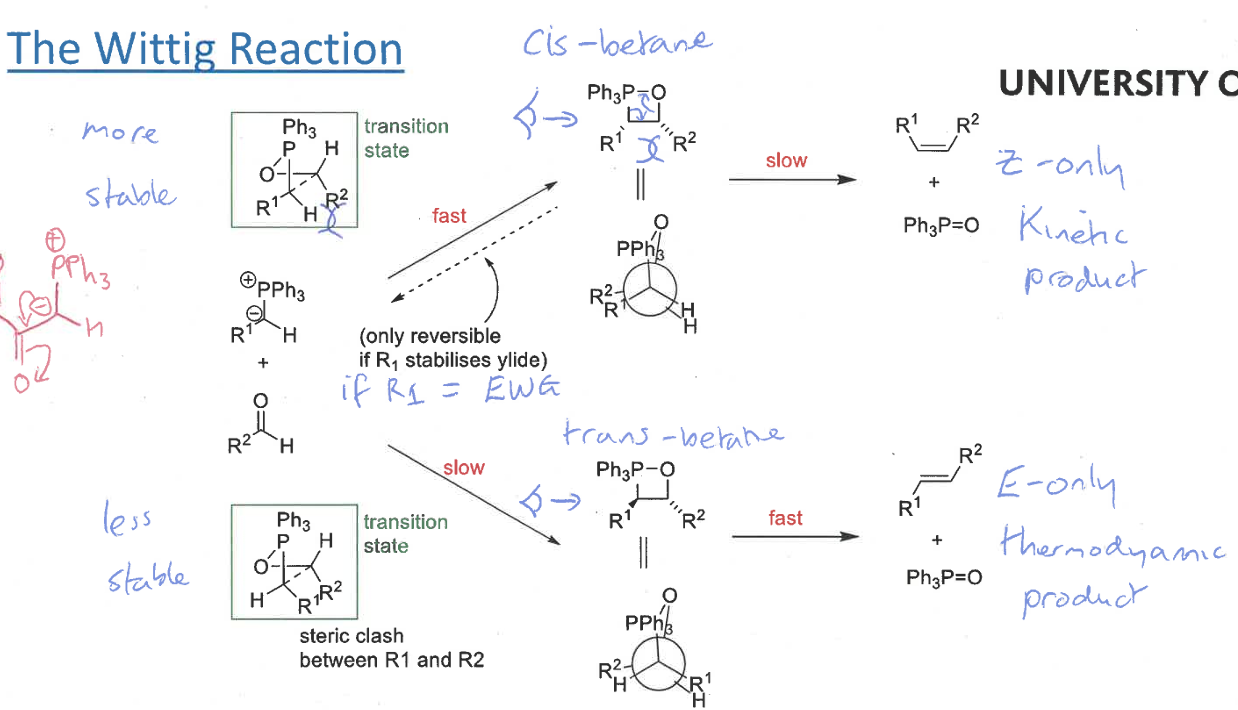
what does the pathway followed depend on
if R1 is EWG, the reaction initially forms the cis-betane but then goes back to the reactants and eventually follows the trans-betane pathway to form the E isomer
if R1 is not EWG, the reaction simply proceeds to form the Z isomer
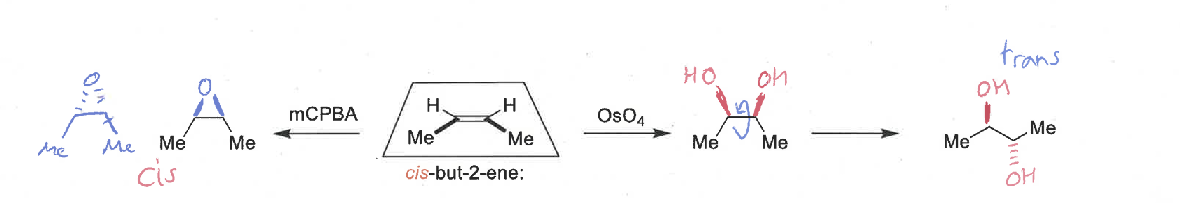
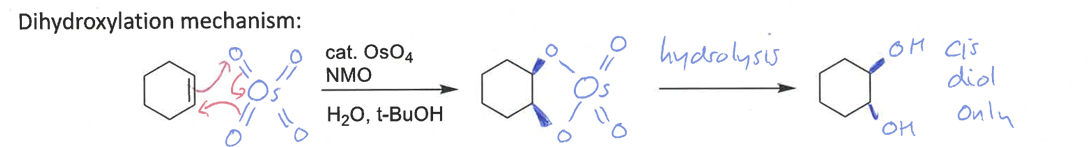
dihydroxylation mechanism and stereospecificity
diastereospecific - forms cis diol only
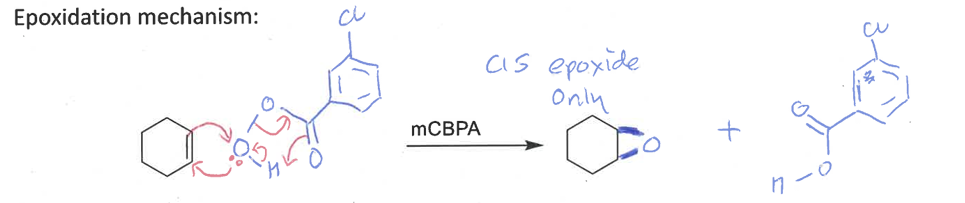
epoxidation mechanism and stereospecificity
diastereospecific - forms cis epoxide only
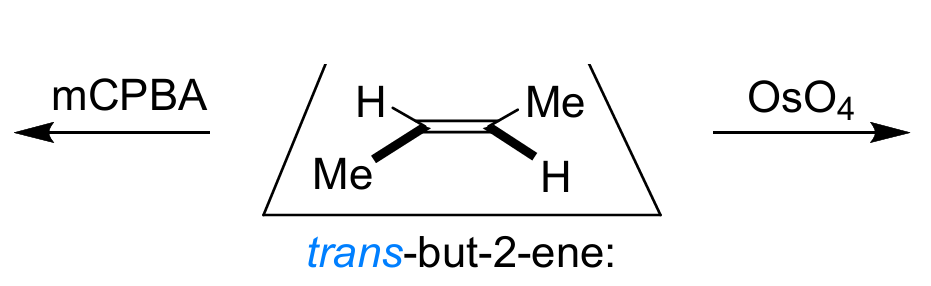
explain the stereospecificty of the alkene dihydroxylation and epoxidation mechanisms
both diastereospecific - the alkene reacts at both ends at the same time in a concerted mechanism so the stereochemistry of the alkene is preserved
show mechanisms
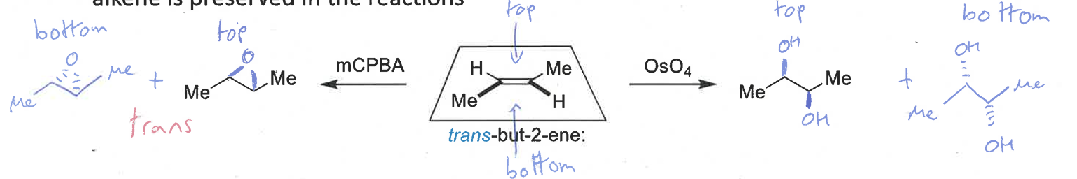
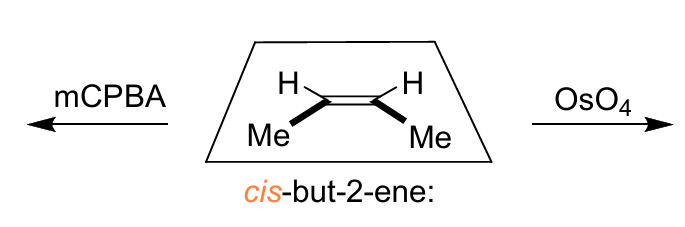
show mechanisms