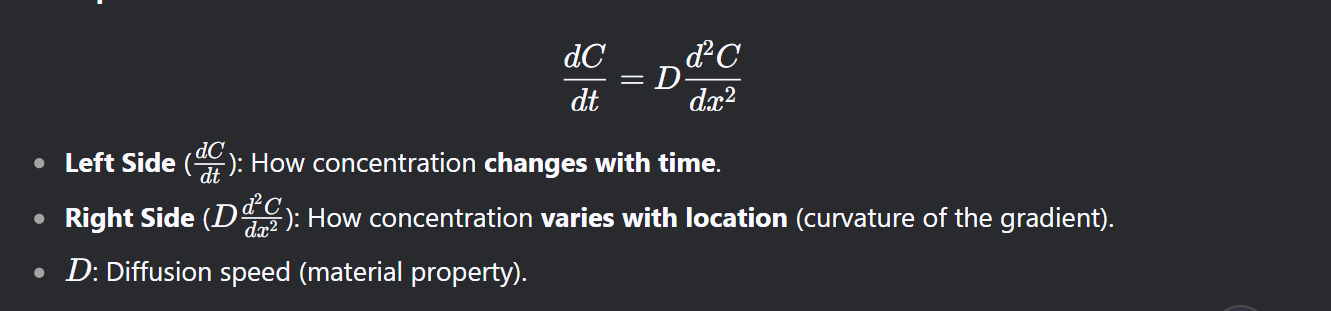Diffusion Quiz Questions for Final
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is diffusion in materials?
Mass transport by atomic motion (atoms "hopping" between lattice sites in solids).
In what states of matter does diffusion occur?
Liquids, gases, and solids.
How does temperature affect diffusion?
Higher temperature increases diffusion rate
What is Brownian motion in diffusion? What states do they apply in?
Random movement of molecules in liquids/gases (e.g., dye spreading in water).
Name the two main diffusion mechanisms in solids.
vacancy diffusion (atoms fill empty sites) and interstitial diffusion (small atoms hop between gaps)
What enables vacancy diffusion in solids?
Presence of empty lattice sites (vacancies) for atoms to hop into.
What is self-diffusion?
Atoms of the same type move around inside a pure elemental solid without any outside atoms being added.
What is interdiffusion in alloys?
Atoms moving from high-concentration to low-concentration regions until uniform (e.g., Cu-Ni mixing).
What is vacancy diffusion?
Atomic movement where atoms exchange positions with vacancies in the lattice.
What two factors determine the rate of vacancy diffusion?
(1) Number of vacancies, (2) Activation energy for atom-vacancy exchange.
What is interstitial diffusion?
Small atoms (like C or H) moving between gaps in a crystal lattice.
Why is interstitial diffusion faster than vacancy diffusion?
No vacancies needed; small atoms move directly through interstitial spaces.
What is flux? Its “formula”?
See figure
The amount of mass/number of atoms diffusing through a unit area per unit time.
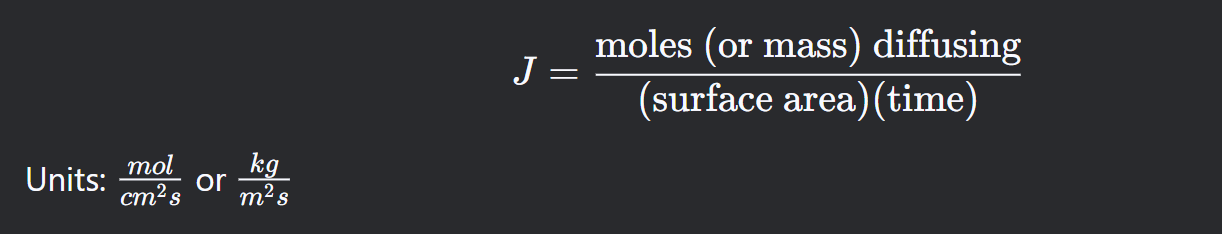
How can diffusion flux be measured experimentally?
By using a thin membrane of known area, applying a concentration gradient, and measuring the diffusion rate.
T/F
Diffusion cant be used to alter or improve the properties of materials during processing, for example, interstitial diffusion
F
It can
What is one application of diffusion in materials processing? Why is it useful?
Case hardening (e.g., carburizing steel by diffusing carbon into the surface).
Creates a hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a tough, softer core.
What is doping?
Adding impurity atoms (e.g., phosphorus) to a material
How is diffusion used in semiconductor manufacturing?
To dope silicon (e.g., with phosphorus) by diffusing dopant atoms into the lattice, creating n-type regions.
What is steady-state diffusion?
Diffusion where the rate (flux) is constant over time, with no net accumulation of atoms.
How is flux related to concentration gradient in steady-state diffusion?
Flux (J) is directly proportional to concentration gradient [dC/dx]
Example: Gas diffusion across a membrane
What is the mathematical expression of Fick's First Law?
J=−D [dx / dC] , where
J is flux [mol/cm²s] or [kg/m²/s]
D is diffusion coefficient [m²/s]
dC/dx is concentration gradient
The negative sign means that diffusion occurs from regions of high concentration to low concentration.
When is steady-state diffusion a valid approximation?
With constant dopant supply (fixed concentration gradient) over short timescales or idealized infinite systems.
Why is steady-state diffusion rarely applicable in real experiments?
Most systems have changing concentrations over time (non-steady-state).
Give one example where steady-state diffusion might apply.
A thin membrane separating two infinite gas reservoirs at constant pressures.
Why does diffusion accelerate at high temperatures?
(1) More vacancies form, (2) Atoms gain thermal energy to overcome Qd
Arrhenius equation?
See figure

Why is interstitial diffusion (e.g., carbon in iron) faster than self-diffusion (e.g., iron in iron)?
Carbon diffuses faster than iron in steel because its small size lets it slip between iron atoms easily, while iron atoms need to wait for empty spaces (vacancies) to move.
How does crystal structure (BCC vs. FCC) affect diffusion rates?
BCC (α-Fe) has more open space → faster diffusion than FCC (γ-Fe).
Why does non-steady-state diffusion slow down over time?
The "full" and "empty" sides become more equal, so atoms move slower.
T/F
Non-steady state takes place in most cases
T
As the concentration increases, the rate of diffusion _____. Concentration is a function of _____ and ____.
decreases
time, position
What does Fick’s Second Law predict?
In non steady state cases, How concentrations change over time and position in real-world diffusion (e.g., carbon spreading in steel).
What is the equation for Ficks 2nd Law
See figure