Hydrocarbon reactions
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Three important reactions of alkanes
combustion, halogenation, dehydrogenation
Combustion of alkane
burn an alkane in oxygen to make carbon dioxide and water
gen eq of combustion of alkane
CnH2n+2 + O2 à nCO2 + (n+1)H2O
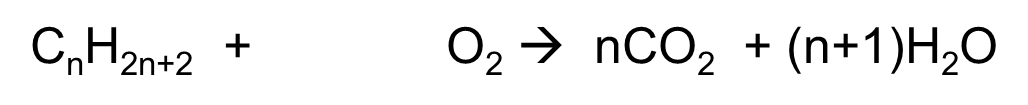
gen eq of alkane combustion example methane
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) à CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
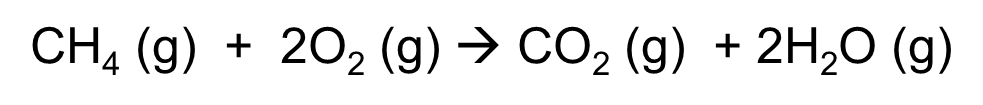
Halogenation alkane
Substituting one hydrogen for one halogen atom (F,Cl,Br,I), needs UV light to catalyse the reaction
Halogenation of alkanes gen eq
CnH2n+2 + X2 à CnH2n+1X + HX
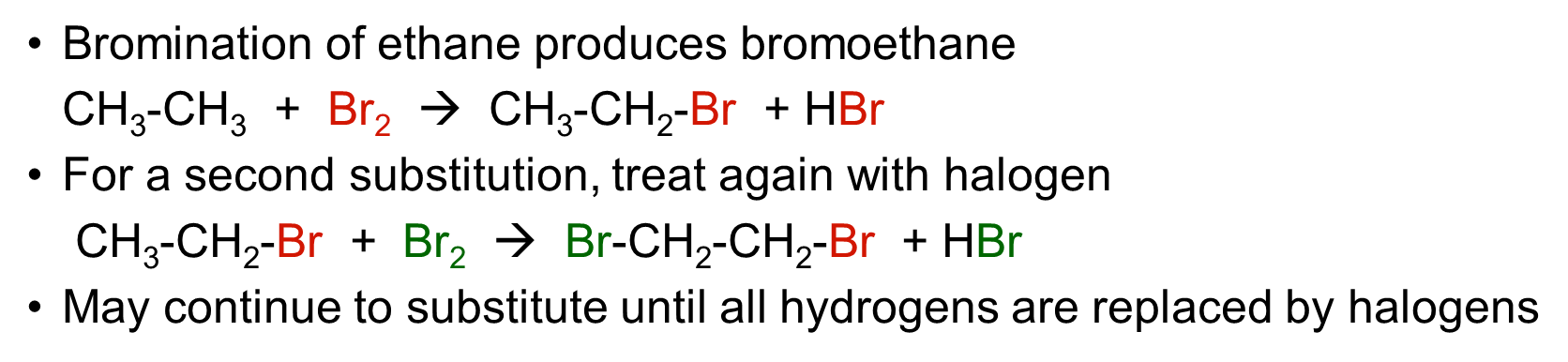
halogenation of alkane: bromination of ethane produces bromoethane
•Bromination of ethane produces bromoethane
CH3-CH3 + Br2 à CH3-CH2-Br + HBr
•For a second substitution, treat again with halogen
CH3-CH2-Br + Br2 à Br-CH2-CH2-Br + HBr
•May continue to substitute until all hydrogens are replaced by halogens
reaction of alkane dehydrogenation
removing heat from hydrogen gas from an alkane, produces alkene, needs heat and catalyst
dehydrogenation fo an alkane usage
oil refining industry to manipulate molecules
dehydrogenation of alkane gen reaction
CnH2n+2 à CnH2n + H2
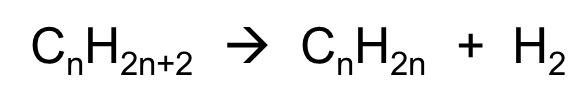
Dehydrogenation of propane produces ___and eq
•Dehydrogenation of propane produces propene
CH3-CH2-CH3 à CH3-CH=CH2 + H2
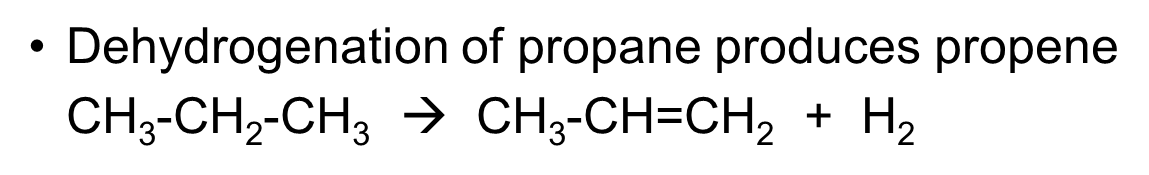
Reaction of alkene
combustion, addition, reduction, oxidation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration, polymerisation
Alkene combustion
burn in oxygen gas and produces carbon dioxide and water
addition alkene-most common nd useful?
yes common and usefulm break the double bond and use thos electrons to bond with other atoms
examples of addition of alkene: reduction, halogenation
reduction-add hydrogen/oxidation where add oxygen halogenation add CL2 or B2
examples of addition of alkene: hydrohalogenation, hydration, polymerisation
hydrohalogenation-add HCL, HBR, hydration add water, polymerisation, add monomer
reduction of alkene
loss of gain of hydrogen atoms, catalytic reduction of alkenes, is also called hydrogenation, needs mateal catalyst like Pd, Al, Pt, Ni
gen eq of reduction of alkene
•alkene + H2 (g) à alkane
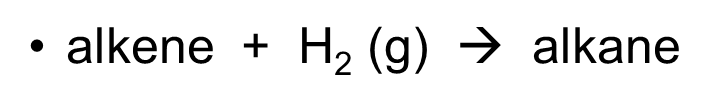
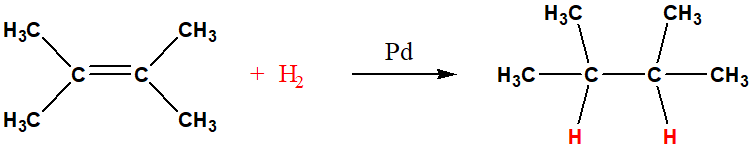
alkene reduction metal catalyst and example
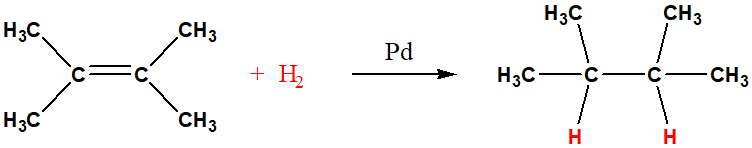
oxidation of alkene
to increase the oxygen content of a molecule
Transiton metal oxides are good oxidising agents for Alkenes?
yes transition metal oxides are good oxidising agents
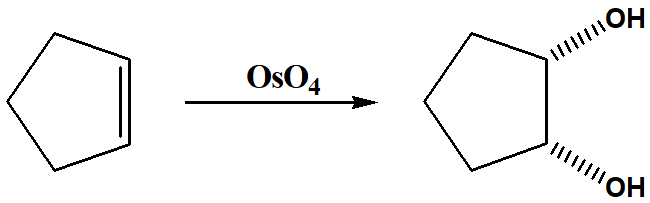
oxidising agents for alkene in lab
•permanganate (MnO4-) goes from purple to brown (MnO2)
•dichromate (Cr2O72-) goes from orange to green (Cr3+)

halogenation alkene
chlorine and bromine gas only because fluorine is too violent and iodine wont react
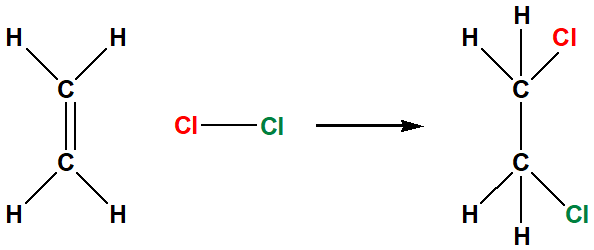
result of halogenation of alkene
break the alkene’s double bond and break the halogen-to-halogen bond, results in haloalkane (alkyl halide)
alkene hydrohalogenation
HX adds to symmetric alkene or HX add to an assymetric alkene
Hydration alkene
use Markovnikov’s rule to predict produce, us acid catalyst to star (HCL, H2SO4)
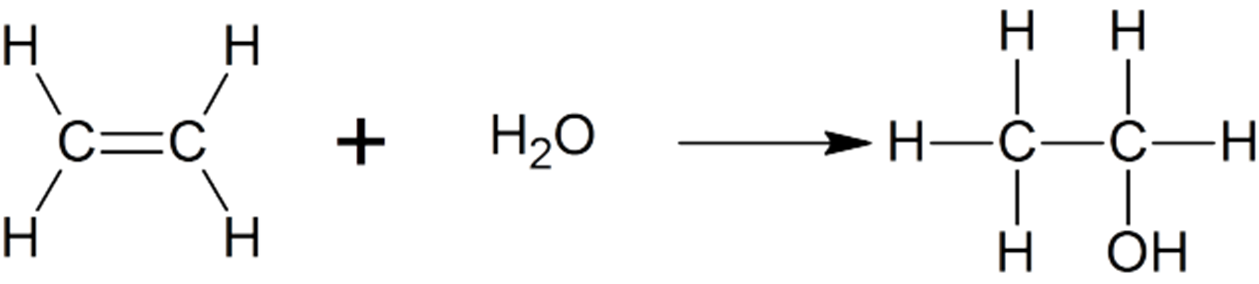
polymerisation of alkene
chan-growth, joining monomer units without loss of atoms
example of polymerisation of an alkene

polyethylene formation
monomer is an alkene, polymer is an alkane
requires catalyst
ethene (ethylene) polyethylene
Reaction of aromatic hydrocarbonds
combustion, substitution
substitution of aromatic hydrocarbon
1 or more of hydrogens around benzene ring can be replaced by another atom or group, will not do additon and break aromatic ring
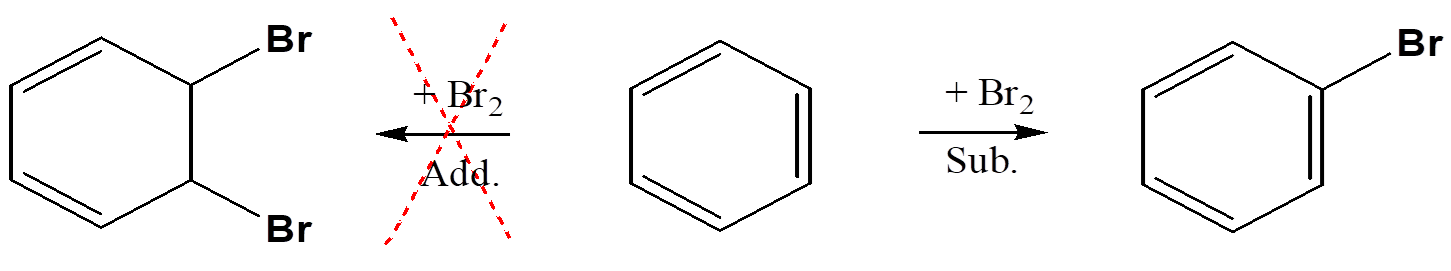
substitution reactions-replacing a hydrogen atom of aromatic hydrocarbon:halogenation, nitration, sulfonation
halogenation-add Cl, Br, I to aromatic ring, nitration-add NO2 group, sulfonation-add SO3H group
substituion reactions replacing a hydrogen atom aromatic hydrocarbon: alkylation, acylation
alkylation-add R group where R=CH3, CH2Ch3, acylation-add COR group where C is double bonded to O