Microbiology Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
What is the reagent in the optochin test?
Ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride
2
New cards
What is the optochin test?
* Differentiates between streptococcus veridans and streptococcus pneumonia
* Uses an optochin disc
* Uses an optochin disc
3
New cards
What is the quelling test?
* It can demonstrate capsules in an organism
4
New cards
Which tests are used to identify Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Quelling test, optochin test, bile solubility, latex agglutination/counterimmunoelectrophoresis
5
New cards
What species can sometimes give a false positive for coagulase?
Enterococcus
6
New cards
What is the most common cause of SBE?
Streptococcus viridans
7
New cards
Quantitative vs qualitative
* Quantitative: Numerical measurement
* Qualitative: Quality, not numerical value
* Qualitative: Quality, not numerical value
8
New cards
Is Kirby-Bauer qualitative or quantitative?
Qualitative
9
New cards
What is the kirby-bauer test?
* Qualitative test
* Agar disc diffusion
* Uses mueller hinton agar with a 3-5 mm depth in 100 or 150 mm plates
* Stored at 4 C, pH 7.2-7.4
* Divalent Ca2+ and cationic Mg2+ present affect the results of aminoglycosides, polymixinns, tetracyclines against Pseudomonas
* 4% NaCl enhances the ability to detect MRSA
\
* Agar disc diffusion
* Uses mueller hinton agar with a 3-5 mm depth in 100 or 150 mm plates
* Stored at 4 C, pH 7.2-7.4
* Divalent Ca2+ and cationic Mg2+ present affect the results of aminoglycosides, polymixinns, tetracyclines against Pseudomonas
* 4% NaCl enhances the ability to detect MRSA
\
10
New cards
Is MIC quantitative or qualitative?
Quantitative
\
\
11
New cards
What are dilution tests?
* Quantitative
* Give a more accurate measure of the probable in vivo effect of a drug
* Results are expressed as the minimal concentration to inhibit (MIC) or to kill (MBC) the test strain
\
* Give a more accurate measure of the probable in vivo effect of a drug
* Results are expressed as the minimal concentration to inhibit (MIC) or to kill (MBC) the test strain
\
12
New cards
Why would a dilution test be done?
* Blood cultures: Endocarditis and septicemia
* Patients who fail to respond to adequate therapy
* Patients who relapse while undergoing therapy
* Pediatric cases of meningitis and septicemia
\
* Patients who fail to respond to adequate therapy
* Patients who relapse while undergoing therapy
* Pediatric cases of meningitis and septicemia
\
13
New cards
What is the antimicrobial gradient strip method, E-Test (Epsilometer)?
* Quantitative MIC on agar containing a gradient of antimicrobial agent applied
* 0.5 McFarland and streak to agar twice within 15 minutes of adjusting turbidity
* Do NOT incubate with CO2
\
* 0.5 McFarland and streak to agar twice within 15 minutes of adjusting turbidity
* Do NOT incubate with CO2
\
14
New cards
What is the main test for beta-lactamase?
Chromogenic cephalosporin
15
New cards
What is the D-Test?
* Inducible clindamycin resistance
* Macrolide resistance in Staph and Strep are conferred by the erm gene which results in resistance to erythromycin and either inducible or constitutive resistance to clindamycin
* Macrolide resistance in Staph and Strep are conferred by the erm gene which results in resistance to erythromycin and either inducible or constitutive resistance to clindamycin
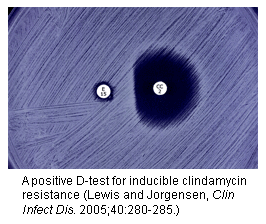
16
New cards
What is the turbidity standard?
0\.5 McFarland
\
\
17
New cards
Extended Specrum B-lactamase (ESBL)
Spontaneous mutations which result in novel B-lactamases can inactivate extended-spectrum cephalosporins, penicillins, and aztreonam
18
New cards
AmpC B-lactamase
Members of Enterobacteriaceae produce plasmid-mediated or chromosomal AmpC B-lactamase which confers resistance to cephamycins
\
\
19
New cards
Carbapenemase B-lactamase (CRE)
* Members of Enterobacteriaceae that produce carbapenemase are often resistant to one or more of the carbapenems
* Acinobacter is a major CRE organism
* Resistance is to carbapenems, penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam
* Acinobacter is a major CRE organism
* Resistance is to carbapenems, penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam
20
New cards
Metallo-B-lactamase
* New Delhi strain
* Pseudamonas was the original organism, but now there are enterobacterialis
* Pseudamonas was the original organism, but now there are enterobacterialis
21
New cards
Bacteriacidal activity of serum
* Testing the antibiotic that’s in the patient’s serum to see if it’s at the level they need to treat that organism
* Known as the Schlichter test
* Do NOT use plasma
* Known as the Schlichter test
* Do NOT use plasma
22
New cards
What is synergism?
Effect of a combination is GREATER than the sum of the effect of each agent tested independently
23
New cards
What is additive or indifferent?
Effect of a combination is EQUAL to the sum of the effects of each agent or is no greater than that of the more active drug
24
New cards
What is antagonism?
Effect of a combination is less than the effect of the more active agent
25
New cards
What are the clinical uses of combination therapy?
* Endocarditis caused by Enterococcus
* Tuberculosis
* Tuberculosis
26
New cards
Checkerboard/chessboard titration
Two drugs are diluted as for MIC determinations and then combined in sets consisting of each concentration of one drug against serial dilutions of the other
27
New cards
What is therapeutic drug monitoring?
* Serum levels of antimicrobial agents
* Don’t want the antimicrobial levels in the patient to get too high or low
* Serum samples are drawn at certain times to monitor antibiotic levels
* Don’t want the antimicrobial levels in the patient to get too high or low
* Serum samples are drawn at certain times to monitor antibiotic levels
28
New cards
What is pharmacodynamics?
The absorption/presence of antibiotic in different tissues and sites
29
New cards
What is pharmacokinetics?
Concentration of drug in certain areas
30
New cards
What are the inhibitors of cell wall synthesis?
* B-lactams: Penicillin, cephalosporins
* Carbapenems: Imipenem
* Glycopeptides: Vancomycin
* Monobactams: Aztreonam
* Carbapenems: Imipenem
* Glycopeptides: Vancomycin
* Monobactams: Aztreonam
31
New cards
What are the inhibitors of cell membrane functions?
* Most are against gram positive
* Gram positives: Lipopeptides: Daptomycin
* Gram negatives: Polymixins
* Fungi: Amphotericin B
\
* Gram positives: Lipopeptides: Daptomycin
* Gram negatives: Polymixins
* Fungi: Amphotericin B
\
32
New cards
What are the inhibitors of protein synthesis?
* Gram-positive and negative
* Aminoglycosides
* SPS counteracts aminoglycosides in some blood cultures
* Tetracycline
* Macrolides
* Aminoglycosides
* SPS counteracts aminoglycosides in some blood cultures
* Tetracycline
* Macrolides
33
New cards
What are the inhibitors of nucleic acid? (DNA and RNA)
* Gram positive and negative
* Quinolones
* Fluoroquinolones
* Most inhibit DNA
* Rifampin: RNA
* Nitrofurantoin: Urinary tract only
* Nitromidazoles
* Quinolones
* Fluoroquinolones
* Most inhibit DNA
* Rifampin: RNA
* Nitrofurantoin: Urinary tract only
* Nitromidazoles
34
New cards
What are the inhibitors of folic acid synthesis?
* Sulfa drugs
* Gram positive and many gram negative
* Sulfonamides
* Gram positive and many gram negative
* Sulfonamides
35
New cards
What are the non-genetic causes of antibiotic resistance?
1) Enzymatic destruction
2) Enzymatic modification
3) Altered target (receptors)
4) Decreased uptake
5) Target overproduction
6) Efflux
7) Loss of target structure
2) Enzymatic modification
3) Altered target (receptors)
4) Decreased uptake
5) Target overproduction
6) Efflux
7) Loss of target structure
36
New cards
What are the genetic causes of antibiotic resistance?
1) Intrinsic
2) Acquired resistance (Transfer)
2) Acquired resistance (Transfer)
37
New cards
What are beta-lactams?
Beta lactamase is produced by the organism. It hydrolyzes the beta lactam ring
\
\
38
New cards
What is penicillin?
* Beta lactam
* Not effective against gram negative rods
* Soft tissue and body fluid have the highest concentrations
\
\
* Not effective against gram negative rods
* Soft tissue and body fluid have the highest concentrations
\
\
39
New cards
What is cephalosporin?
* Beta lactam
* Similar tro penicillin, better withstands the action of B-lactamase
* Concentrated in soft tissue, poor concentration of CNS
* Not absorbed well from GI tract
* Treatment for urinary and respiratory infection, but not major systemic infections
* Some nephrotoxicity
* Similar tro penicillin, better withstands the action of B-lactamase
* Concentrated in soft tissue, poor concentration of CNS
* Not absorbed well from GI tract
* Treatment for urinary and respiratory infection, but not major systemic infections
* Some nephrotoxicity
40
New cards
What are the other beta-lactams?
Carbapens: Broadest spectrum of all antimicrobial agents. Referred to as penems
Monobactams: Aztreonam is the only one. Broad spectrum. For gram negatives
Monobactams: Aztreonam is the only one. Broad spectrum. For gram negatives
41
New cards
What antibiotic cannot be used during pregnancy or used on infants?
Tetracyclines. It destroys the enamel of teeth and causes bone damage. Can cause green teeth
42
New cards
What are the urinary tract drugs?
* Nitrofurantoin, nalidixic acid, phosphomycin is urinary tract ONLY
* Fosfomycin is for E. coli and enterococcus
* Fosfomycin is for E. coli and enterococcus
43
New cards
What antibiotic causes ota and renal toxicity?
Aminoglycosides
44
New cards
What is Kawasaki disease?
* Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome
* Toxin is from Staph aureus
* Found in children 5 and under
* Toxin is from Staph aureus
* Found in children 5 and under
45
New cards
What is toxic shock syndrom?
* Patient is acutely ill, febrile, toxemia
* Hypotension, DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)
* Toxin causes the infection
\
* Hypotension, DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)
* Toxin causes the infection
\
46
New cards
Morphology of micrococcaceae
* Spherical, gram positive cocci arranged singly, in pairs, clusters of 4 or 8 organisms
* Catalase positive
* Possess cytochrome enzymes which give a positive catalase
* Non-motile, some pigmented
* Catalase positive
* Possess cytochrome enzymes which give a positive catalase
* Non-motile, some pigmented
47
New cards
At what temperature is motility and pigment produced best at?
25 C
48
New cards
Staphylococcus aureus
* Most important organism in this group
* Can be found in any specimen
* Responsible for a lot of skin infecetions and abscesses
* Furuncles produce sinus tractsm colony grows to other sites and are harder to treat
* Antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus are responsible for hospital acquired infection
* Staph toxin can cause food poisoning
* Metastatic lesions in lung, bone, kidney of 2/3 patients with bacteremia may develop endocarditis
* Can be found in any specimen
* Responsible for a lot of skin infecetions and abscesses
* Furuncles produce sinus tractsm colony grows to other sites and are harder to treat
* Antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus are responsible for hospital acquired infection
* Staph toxin can cause food poisoning
* Metastatic lesions in lung, bone, kidney of 2/3 patients with bacteremia may develop endocarditis
49
New cards
How can an infection caused by Staph aureus be differentiated from Clostridium perfringes and salmonella?
Lack of fever and short duration
50
New cards
Scalded skin syndrome
* Also known as Ritter’s disease
* Generally in newborns, picked up from mom
* Toxin causes skin to be very red
* Generally in newborns, picked up from mom
* Toxin causes skin to be very red
51
New cards
Staphylococcus lugdunensis
* Can cause similar clinical issues as Staph aureus
* Can be typical flora, but also can be a pathogen
* Always significant in endocarditis following cardiac or open chest surgery
* Significant with stitch abscesses
* Colonies exhibit a white pigment
\
* Can be typical flora, but also can be a pathogen
* Always significant in endocarditis following cardiac or open chest surgery
* Significant with stitch abscesses
* Colonies exhibit a white pigment
\
52
New cards
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
* Opportunistic. Second most common cause of UTI
* 10^4 is the significant colony count
* Seen sometimes in innear ear infections
* 10^4 is the significant colony count
* Seen sometimes in innear ear infections
53
New cards
What is the significant colony count of a UTI caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus?
10^4
54
New cards
T/F: All Staphylococcus are salt tolerant
True
55
New cards
Staphylococcus hemolyticus
* Causes hemolysis on blood
* Very resistant to antibiotics
* Very resistant to antibiotics
56
New cards
Primary culture of staphylococcus
* Blood agar and thioglycollate are intially inoculated
* Inoculate at 35 C
* White, golden, yellow or cream colored colonies
* Colonies appear after 24 hours on blood agar
* Inoculate at 35 C
* White, golden, yellow or cream colored colonies
* Colonies appear after 24 hours on blood agar
57
New cards
What gene dermines if Staph aureus is going to me MRSA or not?
Mech A gene
58
New cards
What test separates Staphylococcus and Streptococcus?
Catalase test
59
New cards
Non-hemolytic (Gamma)
* Applies to enterococcus more than anything else
* No lysis of red blood cells around the colony
* No lysis of red blood cells around the colony
60
New cards
Alpha hemolysis
* Green color surrounding the organism due to biliverdin (methemoglobin) released as RBC hemolysis is accomplished
* Most grow better under CO2
* Most grow better under CO2
61
New cards
Alpha prime hemolysis
* Colonnies producing a zone of alpha hemolysis
* Narrow zone encircles the colony with a zone of complete or beta hemolysis
* Narrow zone encircles the colony with a zone of complete or beta hemolysis
62
New cards
Beta hemolysis
* Total lysis of RBC’s around colony
* Clear zone surrounnds the colony
* Clear zone surrounnds the colony
63
New cards
Streptolysin O (SLO) is oxygen ____
labile
64
New cards
Streptolysin S (SLS) is oxygen ____
stable
65
New cards
Group A post-streptococcal diseases
* Acute glomerulonephritis
* Rheumatic fever
* Scarlet fever
* Impetigo
* Toxic shock syndrome
* Necrotizing fascitis
* Rheumatic fever
* Scarlet fever
* Impetigo
* Toxic shock syndrome
* Necrotizing fascitis
66
New cards
What antibiotic is highly concentrated in the biliary tree (liver)?
Penicillin
67
New cards
What antibiotic can cause aplastic anemia?
Chloramphenicol