Binomial Theorem
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
binomial coefficient
→ derived from r-combination
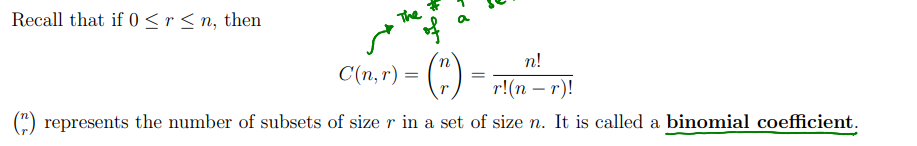
combinatorial proof + the two techniques
proof of the equality of two expressions
a combinatorial proof uses one of the two techniques:
proof by double counting → counting the elements of a set in two diff ways
proof by bijection → find a bijective function b/w two sets, thus showing the sets have the same CARDINALITY (same num of distinct elements)
pascal’s identity
used to help build pascal’s triangle
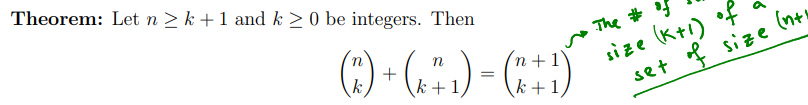
pascal’s triangle
perfectly symmetrical
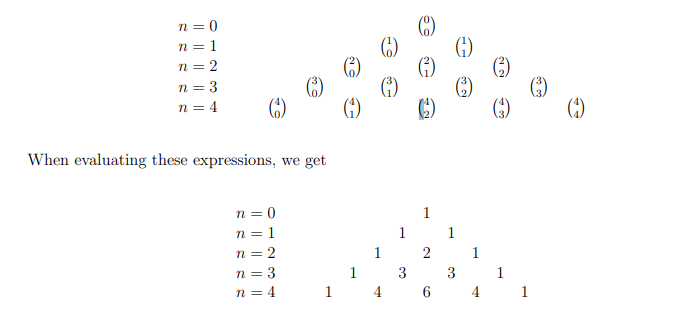
sum of the n’th row of the pascal’s triangle =
2^n
which is the same as the cardinality of the power set P(A) of a set A that contains n elements
binomial theorem formula
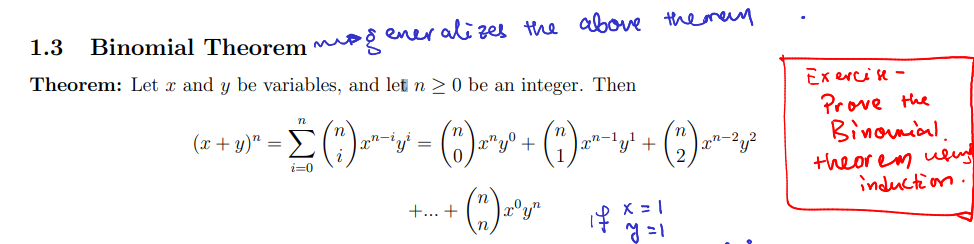
pigeonhole principle
if k + 1 objs or more are stored into k boxes, then at least ONE box contains two or more objs
generalized pigeonhole principle
if N objs are stored into k boxes, then at least one box contains at least N/k objs (bc N objs are unevenly or evenly divided into k groups)