Open Ocean Ecosystems: Plankton, Nekton, and Food Webs
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
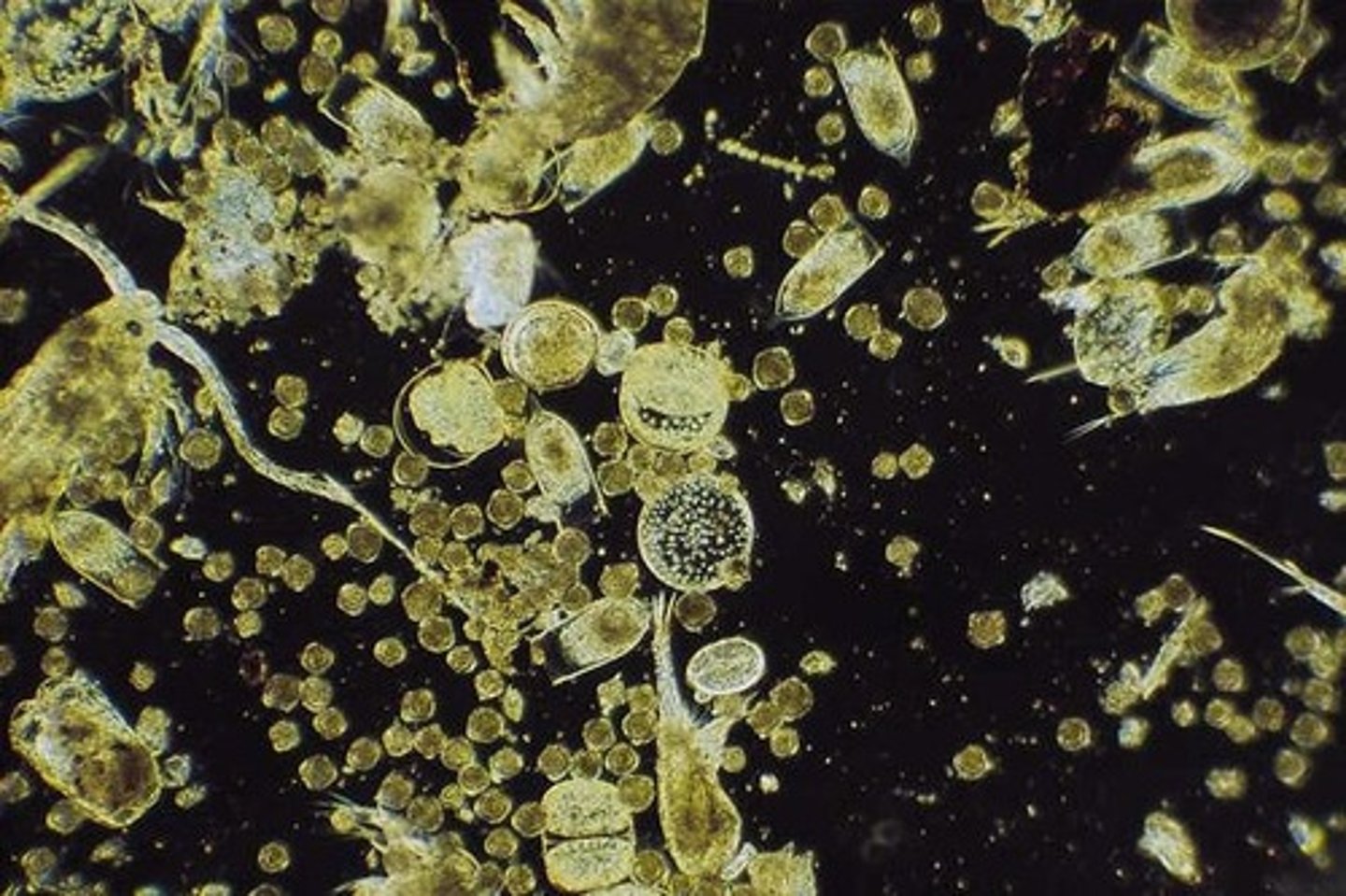
What are plankton?
Organisms that float suspended in the water column and have insufficient swimming apparatus to avoid transport by ocean currents.
What are nekton?
Strongly swimming organisms such as fish, mammals, or squid.
What are benthos?
Organisms that live in intimate association with the ocean bottom.
In which zone do plankton primarily live?
The photic zone.
What type of nekton primarily lives in the photic zone?
Herbivorous nekton.
Where do carnivorous nekton typically reside?
Mostly below the photic zone.
What are the primary types of phytoplankton?
Cyanobacteria, diatoms, silicoflagellates, and coccolithophores.
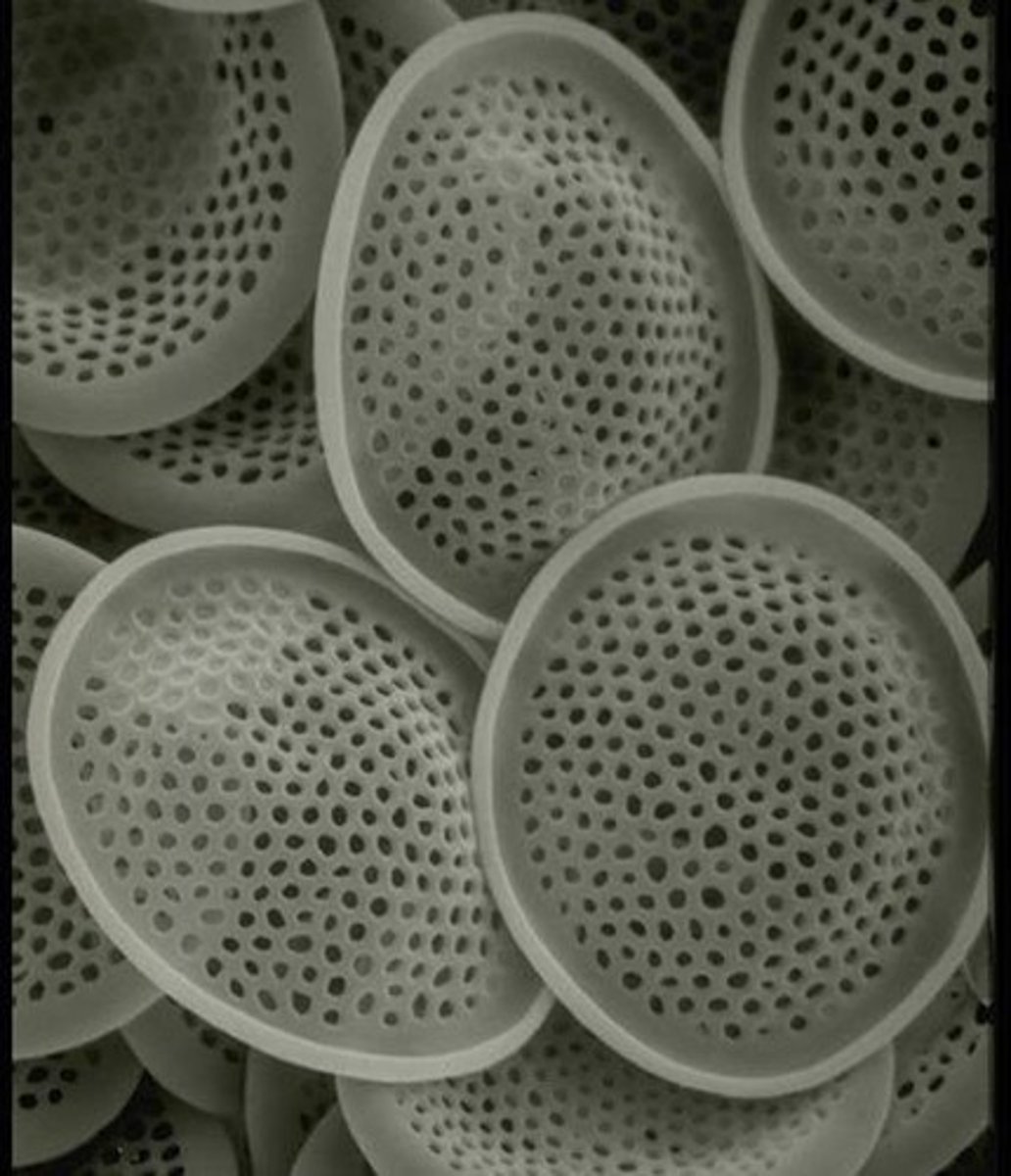

What factors are key to phytoplankton growth?
Nutrients, light, temperature, and means of staying afloat.
What are the two basic ways for phytoplankton to avoid predation?
By their small size (hard to see) and translucent color (hard to see).
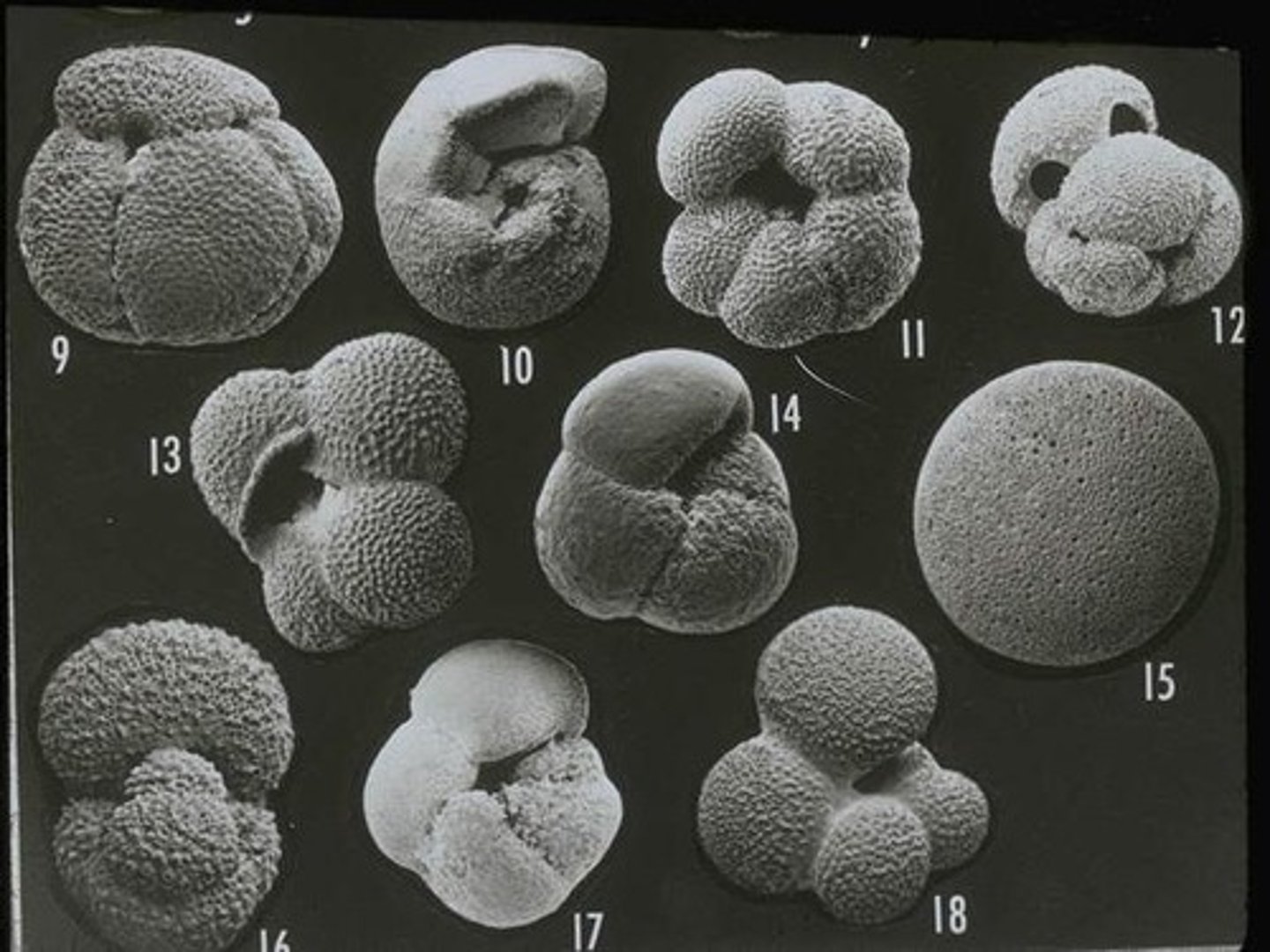
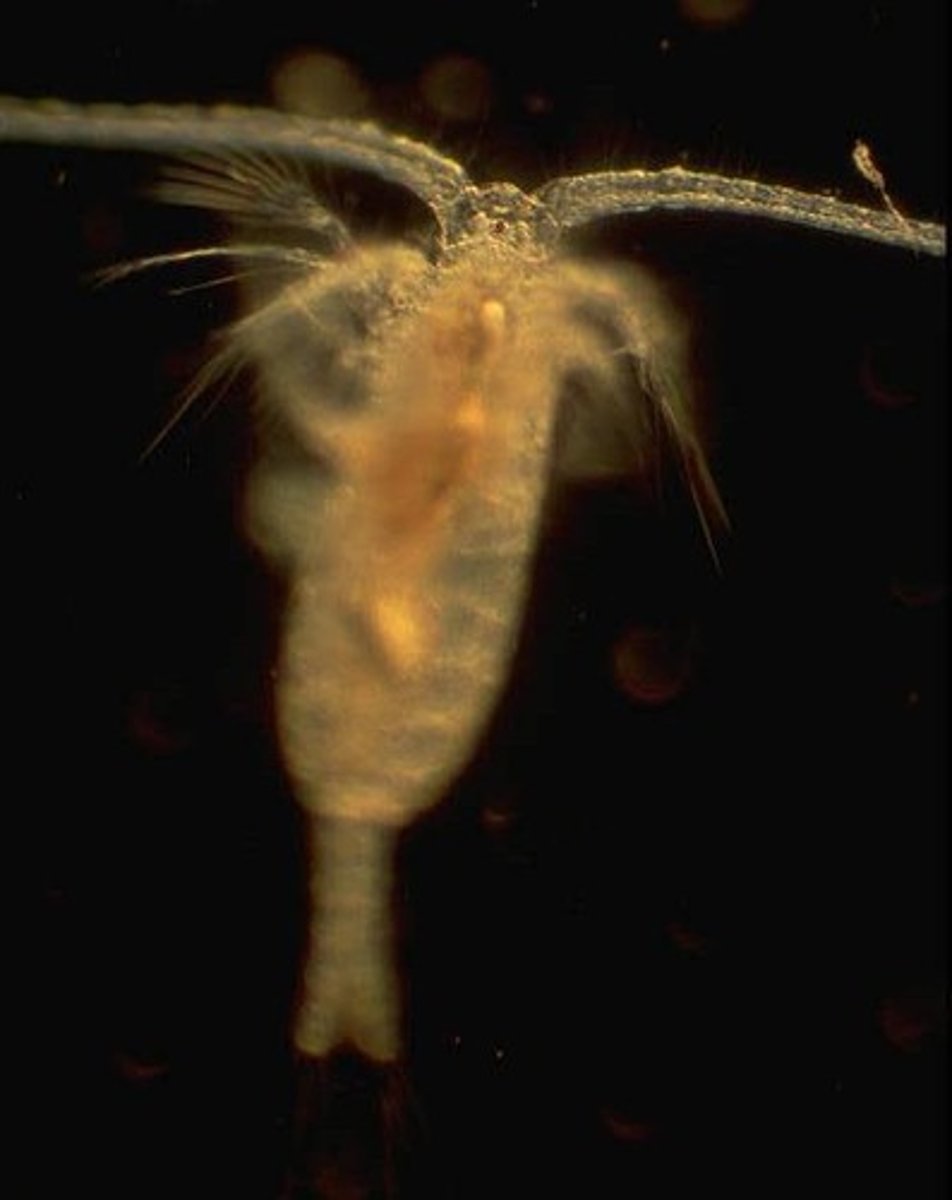
What are the types of zooplankton?
Foraminifera, radiolarians, copepods, and krill.
What is a survival strategy for zooplankton?
Schooling and vertical migration.
What types of nekton are found in open ocean ecosystems?
Fish, sea mammals, birds, reptiles, and squid.
What adaptations do nekton have for buoyancy?
Specialized adaptations like air sacs and liquid fats.
What role do bacteria play in open ocean ecosystems?
They decompose organic matter and recycle nutrients, especially below the photic zone.
What is the oxygen minimum zone?
A region in the ocean where oxygen levels are very low, created by bacteria decomposing organic matter.
What is the difference between phytoplankton and zooplankton?
Phytoplankton are autotrophs, while zooplankton are heterotrophs.
What is bioturbation?
The disturbance of sedimentary deposits by living organisms.
What are cold seeps?
Areas of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide and methane seep out.
What are hydrothermal vents?
Openings in the sea floor that emit hot, mineral-rich water.
What is the primary consumer in the open ocean?
Copepods.
What are the two main types of fish found in open ocean ecosystems?
Bony fish and cartilaginous fish (sharks and rays).
What is schooling in the context of zooplankton?
A survival strategy where zooplankton group together to avoid predators.
What is vertical migration in zooplankton?
The behavior of zooplankton moving to the ocean surface at night to feed and returning to deeper waters during the day.
What is a food chain?
A sequence of animals and plants that feed on each other in a specific order.
What is a trophic level?
Each level in the feeding sequence of a food chain.
What type of organisms always originate a food chain?
Plants, which are the producers.
What is the lowest trophic level in a food chain?
The producer level, represented by plants.
Name the primary consumer in the example food chain provided.
Copepod, which feeds on diatoms.
What is the highest trophic level in the example food chain?
Tertiary Carnivore - Human.
How does energy flow in biological systems?
Energy flows in one direction, while nutrients may recycle.
What does biomass measure in an ecosystem?
The amount of matter per unit volume, which indicates stored energy.
What does a food biomass pyramid illustrate?
The transfer of energy and mass through a food chain.
What is a food web?
A more realistic representation of interconnected food chains in a community.
How do trace elements affect food webs?
They can accumulate in organisms and become hazardous to health as they move through the food chain.
What is ecosystem stability?
The balance between species populations that allows communities to survive.
What factors define environmental resistance?
The combination of biotic and abiotic factors that limit a species' population.
What is ecological succession?
The natural or unnatural evolution of ecosystems over time.
What are pioneer communities?
The first organisms to colonize or recolonize an area.
What are climax communities?
The final stable communities that prevail until external changes occur.
What is the impact of El Niño on fish catches?
El Niño can significantly affect the populations of fish such as anchovies and sardines.
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Autotrophs produce their own food, while heterotrophs consume other organisms.
Define chemosynthesis.
The process by which some organisms produce energy from inorganic compounds.
What is a herbivore?
An animal that primarily feeds on plants.
What is a carnivore?
An animal that primarily feeds on other animals.
What role do scavengers play in an ecosystem?
They consume dead organisms, helping to recycle nutrients.
What is a food pyramid?
A graphical representation showing the energy or biomass at each trophic level.
What is a habitat?
The natural environment in which an organism lives.
What organism is at the lowest level of a food chain?
Autotrophs.
In a simple food chain--diatoms, copepods, fish--which has the highest biomass?
Diatoms.
Each level of a food chain is called a?
Trophic level.
What is the term for an ecosystem changing to something else?
Succession.
Organisms that float in the ocean and follow the moving ocean currents are called?
Plankton.
What nektonic organisms are dominant in the surface ocean?
Herbivores.