M2: Philosophies of Science
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
science and technology
pervasive in society and thus are usually taken
for granted
plays a crucial role in
Social processes
societal histories
Current and future societal undertakings
science
organized body of knowledge concerning the physical world, both animate and inanimate
science
attitudes and methods through which this body of knowledge is formed
science
method of investigating nature — a way of knowing about nature that discovers reliable knowledge* about it
technology
practical application of science
technology
control or manipulate nature for the benefit of humankind
carl sagan
for him, science is a way of thinking much more than it is a body of knowledge
carl sagan
for him, science is Based on experiment, on a willingness to challenge old dogma, on an openness to see the universe as it really is
carl sagan
for him, science requires courage to question the conventional wisdom
carl sagan
for him, goal for science is to find out how the world works, to seek what
regularities there may be, to penetrate the connections
of things
carl sagan
knowing the universe
robert pirsig
for him, scientific method is to make sure nature hasn’t misled you into thinking you know something you don’t actually know
robert pirsig
for him, scientific method is a careful approach to the beginning of scientific questions
robert pirsig
for him, experimentation is thought of as all of science itself because that is the only part with much visual surface
robert pirsig
on scientific method
true
[true or false]
An experiment is never a failure solely because it fails to achieve predicted results
scientific method
[robert pirsig] Asking the right questions and choosing the right tests and drawing the right conclusions
ludwig fleck
to look, to see, to know
ways of knowing (and doing)
ludwig fleck
- what you think is evidence of what you know
positivist and constructionist approach
[ludwig fleck] 2 ways of knowing what a fact is
positivist approach
[ludwig fleck]
facts are self-evident, that they are simply there
physical phenomena that manifest themselves visibly are held to be factual
constructionist approach
[ludwig fleck]
facts are socially created
facts are facts once people agree that these things constitute a fact
consensus on what was important to understand
accumulation of knowledge
use of experimentation and observation
ludwig fleck
for him, in order to see, one has to know what is essential and what is inessential
ludwig fleck
for him, Facts are created not in and of themselves but because of the cognition of their existence
thought collective
[ludwig fleck] creates a collective mood, and because both understanding and misunderstandings, creates its own peculiar thought style.
professionals and exoterics
[ludwig fleck] As the thought collective becomes more and more complex and sophisticated, it divides itself into the esoteric, the [blank] and [blank]
exoteric individuals
echo the pronouncement professionals gain more authority
thought style
has both the active and passive elements
active elements
[thought style] shape the way people think about the world
passive elements
[thought style] which the members of the thought collective hold to be objective reality
social constructs
the reality of which are likely to change over time as more and more work is put into the ideas shared by the collective
social constructs
nature of the uniqueness of the thought collectives that they are incommensurable
false (may not be; false)
[true or false] what is a fact to one collective may be meaningful or even true to another thought collective
true
[true or false] What is a fact to one collective may not be meaningful or even false to another thought collective
thought styles
not immutable or immune to change
may change once the realization sets in that there are several phenomena that are not accounted for in the standard way of thinking
david moshman
epistemic development and the perils of pluto
epistemic cognition
[david moshman] knowledge about knowledge
epistemic cognition
[david moshman] the process of thinking about one’s forms of knowledge and ways of knowing
epistemic development
[david moshman] Progress in knowledge about knowledge
epistemic development
[david moshman] TWO LEVELS: associated with childhood and with adolescence and adulthood
childhood and adolescence and adulthood
what two levels are associated with epistemic development?
objectivist, subjectivist, rationalist epistemologies
what are the epistemic domains?
objectivist epistemologies
an objective domain of truth
Take facts and logical proofs as paradigm case of knowledge
subjectivist epistemologies
a subjective domain of truth
View knowledge as opinion, and opinion as a matter of taste
rationalist epistemologies
A rational domain of reasonable interpretation
Construe knowledge, in a world of interpretation and inference, as justified belief
objectivist epistemology
matters of truth
objectivist epistemology
WHICH EPISTEMIC DOMAIN CORRESPONDS TO THIS QUESTION?
Is pluto a planet?
objectivist epistemology
WHICH EPISTEMIC DOMAIN CORRESPONDS TO THIS QUESTION?
how many planets are there in our solar system?
subjectivist epistemology
matters of taste
subjective epistemology
WHICH EPISTEMIC DOMAIN CORRESPONDS TO THIS QUESTION?
which planet is the best
rationalist epistemology
matters of interpretation
rationalist epistemology
WHICH EPISTEMIC DOMAIN CORRESPONDS TO THIS QUESTION?
which planet (s) can support life
scientist
[in relation with society] Detached, impersonal and objective person wearing glasses and socially awkward most of the time
scientist
[in relation with society] gatekeeper of often mysterious and arcane knowledge, knowledge that could be either helpful or harmful
priest or priestess
with whom are scientists often equated with?
the holder of seemingly supernatural wisdom
scientist in the normal view
about the pure seeking of knowledge for its own sake, in the hope that one day it would be used
scientists in a post-normal view
providing immediate solutions to problems faced by society
sagan, pirsig, fleck, moshman
philosophers of science
sagan’s philosophy of science
Understanding is a form of ecstasy and illumination
Limitations on the universe allow us for some predictability
pirsig’s philosophy of science
Two types of reasoning inductive and deductive
Discussion on the different hierarchies of methods to be tested in the maintenance of the motorcycle
fleck’s philosophy of science
In order to see, one has to know what is essential and inessential
Thought styles are derived from the collective body
Thought styles isolated from each other will clash
moshman’s philosophy of science
Epistemic cognition (knowledge about knowledge)
3 domains: truth, taste, and interpretation
Discussion on how definitions can impact culture (i.e., genocide, Pluto)
karl popper
for him, for knowledge to be scientific it should be falsifiable and testable.
true
[true or false] Statements derived from dogma though difficult to falsify may not be considered scientific since the mechanism with which to falsify is not readily seen
falsification theory
Subscribes to a certain ideology and dogma that may not necessarily be readily falsifiable and may be considered unscientific
falsification theory
Example of a dogmatic statement: Humans are created equal and are created in the image, and likeness of God
karl popper
who thought of evolutionary diagram of knowledge?
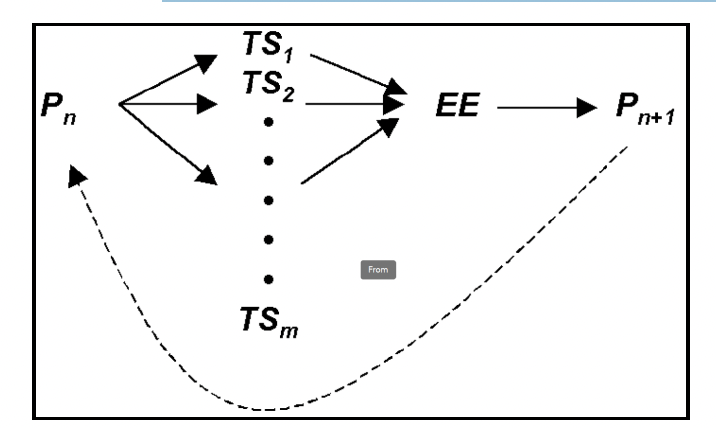
evolutionary diagram of knowledge
“The way of science is paved with discarded theories which were once declared self-evident”
darwin’s principle of natural selection
what principle does the evolutionary epistemology apply to scientific theories and to other forms of knowledge?
evolutionary diagram of knowledge
It is involved with problem-solving and error elimination under different forms of selective pressure.
evolutionary diagram of knowledge
It was the view of Popper that every organism, from the amoeba to Einstein, is constantly engaged in problem-solving.
evolutionary diagram of knowledge
what philosophy is this?
P1: Which model would serve best in sellling a stamp pad?
Temporary Solutions (TS)
TS1: a fashion magazine type of female model.
TS2: an athletic male model
TS3: a young child in pre-school
TS4: a librarian
TS5: a cat.
Error Elimination (EE): a small market test with the various advertisements.
Say the Surviving Solution (SS) is a cat. The Pn+1 would be “which cat is a suitable model for a stamp pad?”
thomas kuhn
created the paradigm shift theory
paradigm shift theory
thomas kuhn
Structure of the scientific revolution
Science does not evolve gradually toward truth.
paradigm shift model
[thomas kuhn] highlights an initial normal science or a thinking with which data are to be associated with
model drift, crisis, and revolution
[paradigm shift theory] stages in the process wherein evidence does not match and support the existing normal science
paradigm shift
what philosophy is this?
Theory: Exposure to violent/improper themes (images, literature, etc.) promotes violent action/improper (murder, robbery, rape, disrespect to women).
Extension of theory: Videogames filled with violent themes promote crimes.
Normal Science: Test the hypothesis for men who play violent video games. Design a study as to whether the increase in the amount of violent video games resulted in higher crime rates.
Model Drift then Model Crisis: No evidence showed that more violent video games increased crime rates.
rational construction theory
involves the idea of a core theory surrounded by a protective belt of auxiliary hypothesis which interacts with outside data and evidence
imre lakatos
invented the rational construction theory
auxiliary hypotheses
[rational construction theory] ideas derivable form a certain core theory which in turn may or may not be supported by data and evidence
core theory
[rational construction theory] can be strengthened or weakened depending on the evidence and its alignments with the auxiliary theory
rational construction model
what philosophy is this?
Core Theory: Increasing price of goods decreases its demand.
Auxiliary Hypothesis: Adding sugar tax to the prices of beverage would decrease the consumption of sugary drinks.
Data/Evidence: There was decrease in sales of softdrinks in the Philippines after the implementation of TRAIN Law on sugar.
carl hempel
created the paradox of confirmation
paradox of confirmation
[carl hempel] a warning to scientists that instances that confirms a theory do not imply that the theory is correct.
paradox of confirmation
[carl hempel] Group of generalizable examples that challenge the adequacy of specific formal accounts of when evidence confirms a theory
paradox of confirmation
what philosophy is this?
For the idea that the maximum speed of light is 300,000,000 m/s. It does not mean that since every measured speed of light of various light sources were observed to be less than 300,000,000 m/s that the maximum speed of light is less than or equal to 300,000,000 m/s. A single measurement of a light source with speed greater than 300,000,000 m/s would render the theory false.
paradox of confirmation
what philosophy is this?
1. The statements “ (1) all ravens are black” and “ (2) something that is not black is not a raven” are logically equivalent. They are contrapositives of each other.
2. If an instance of a raven being black proves statement (1), then an instance of statement (2) being logically equivalent to (1) also proves statement (1).
3. The existence of a green shirt (a non-black non-raven) would also confirm statement (1).
john dewey
created the instrumentalism philosophy
instrumentalism
[john dewey] explains that the purpose of science is in predicting useful phenomena
instrumentalism
[john dewey] a way of thinking in that the ideas of science do not have attachment to absolute truths. Maintains that thought, theories, and concepts are instruments for solving practical problems
instrumentalism
what philosophy is this?
Geocentric Model of the Earth and Farming Practices.
The geocentric model of the earth in its previous state and various forms was able to predict seasons. This is enough knowledge for farmers to use its (geocentric model) prediction for their agricultural needs. The truth of whether the earth is the center, or the sun is the center of our planetary system is irrelevant to the farmer.
instrumentalism
what philosophy is this?
Grades and the Current Educational System.
The truth on whether grades measures skills and proficiency are irrelevant. What is important is that the system of grading allows teachers and the educational system to control of behavior of the student population
paul feyerabend
created the epistemological anarchism
paul feyerabend
[epistemological anarchism] critiqued the idea that there is method to doing science. The growth of knowledge may not be necessarily be rooted in the scientific enterprise.
paul feyerabend
[epistemological anarchism] Argued that there are no universally valid methodological rules for scientific inquiry
epistemological anarchism
[paul feyerabend]
holds that there are no useful and exception-free methodological rules governing the progress of science or the growth of knowledge.
holds that the idea of the operation of science by fixed, universal rules is unrealistic, pernicious, and detrimental to science itself.
epistemological anarchism
what philosophy is this?
Ideas that surprisingly came out of nowhere. (i.e., not from scientific method, etc.)
epistemological anarchism
what philosophy is this?
The best way to create an encyclopedia is not by hiring the best staff for the right amount of money, but by letting random people write articles for free.
epistemological anarchism
what philosophy is this?
The behavior of particles at very small distances is probabilistic.