Radiologic Evaluation pt 2
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
define fracture
break in structural continuity of bone or cartilage
describe a closed fracture
skin stays intact
describe a open fracture
bone breaks through the skin
What are the different ways to describe a radiologic fx
anatomic site and extent
type
alignment
direction
special features
associated abnormalities
special types
how is anatomic site and extent used to describe radiologic fx
reference points to establish the location of a fx
parts of a long bone shaft that can be used to describe anatomic site and extent of radiologic fxs
proximal, middle, distal thirds
junctions
parts of a long bone ends that can be used to describe anatomic site and extent of radiologic fxs
distal or proximal
intra- or extra-articular
parts of a irregular/flat bones can be used to describe anatomic site and extent of radiologic fxs
intra- or extra-articular
describe this fx using anatomic site and extent
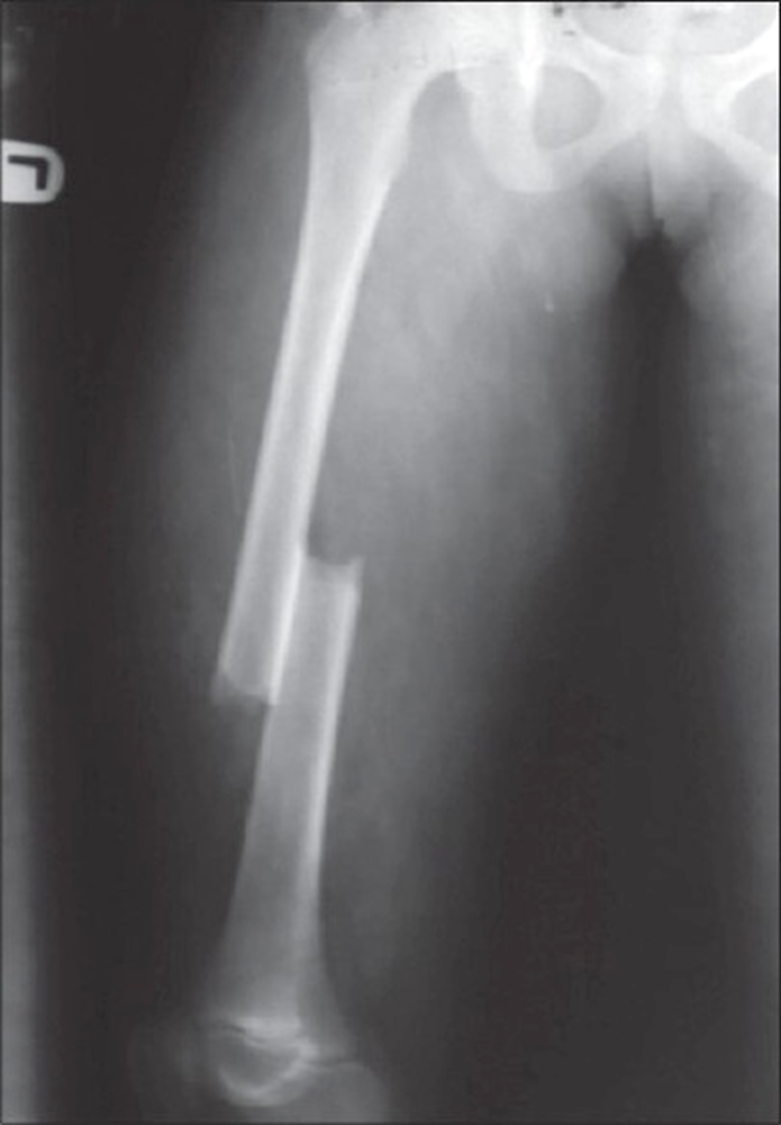
junction of the middle and distal third
describe this fx using anatomic site and extent
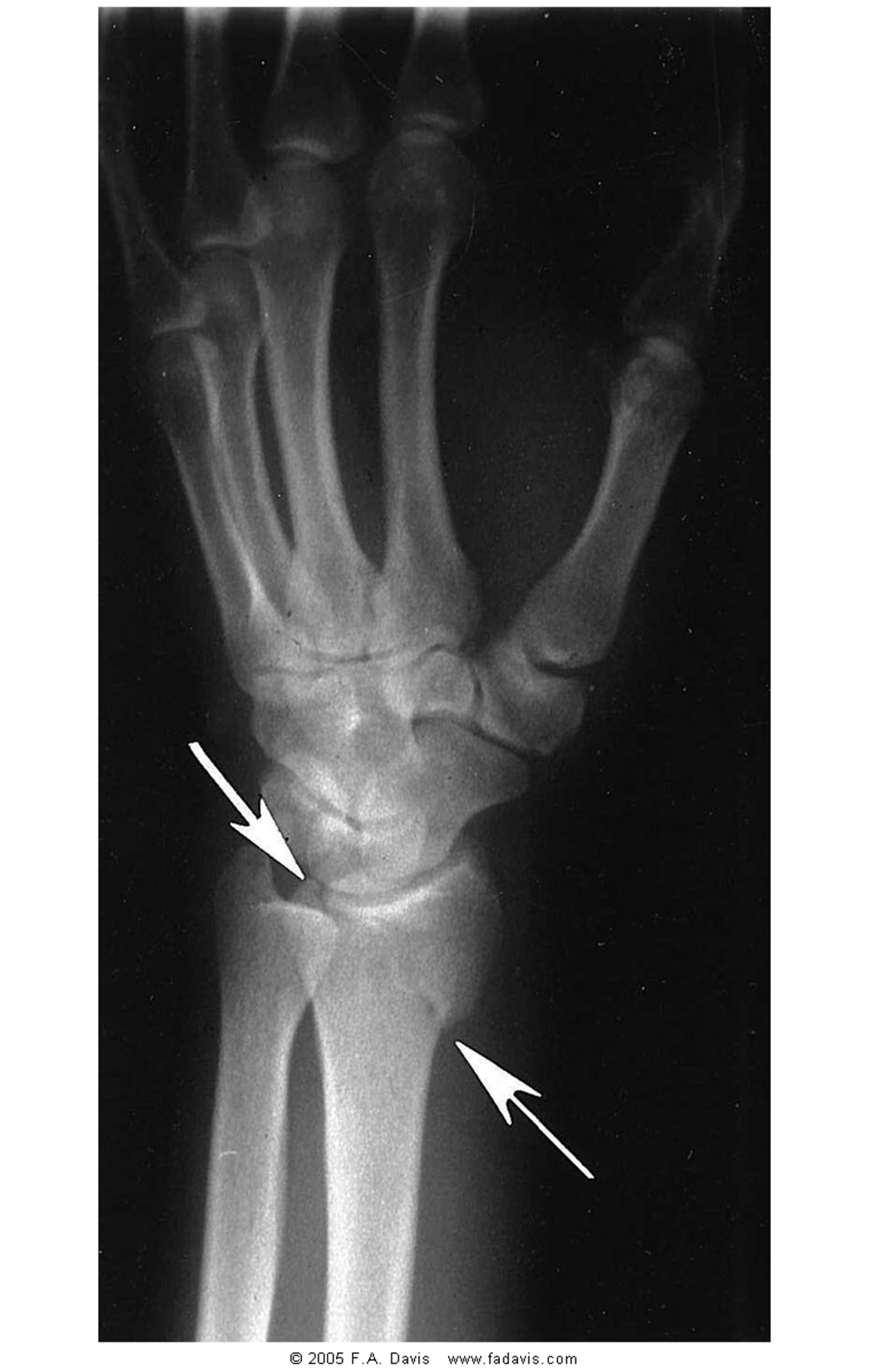
intra-articular
how is type of fx used to describe radiologic fx
complete or incomplete
define complete fx
all cortical margins are broken equaling 2 or more fragments
define incomplete fx
one cortical margin remains intact
What type of fx is more stable, complete or incomplete
incomplete
Where are incomplete fxs most commonly seen
short, flat, or irregularly shaped bones
Who is most likely to have an incomplete fx
children or older adults with metabolic issues
What type of fx is this
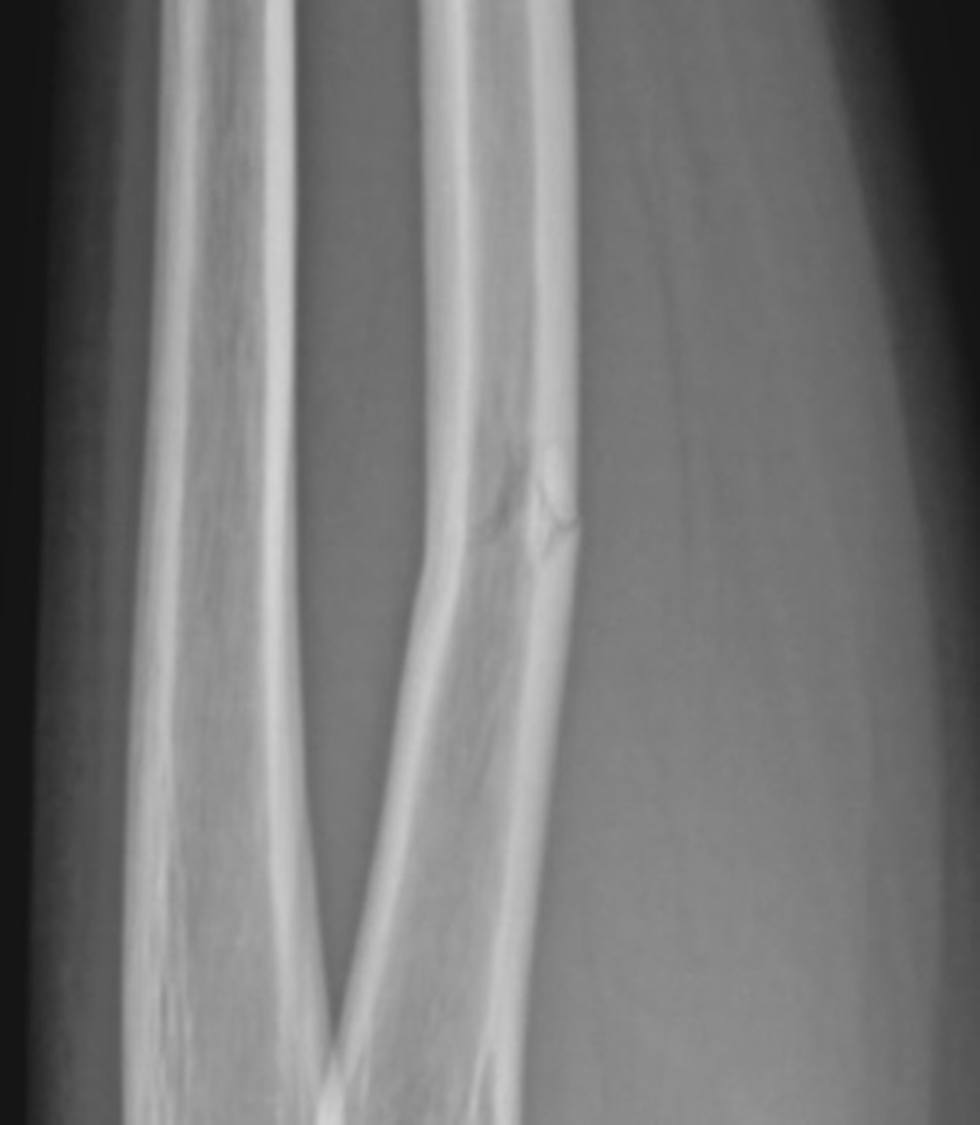
incomplete
how is alignment of fx fragments used to describe radiologic fx
position
displacement
alignment
angulation
define position in terms of fx alignment
the relationship of fragment to normal structure
How is position named
position of distal fragment in relation to proximal
define displacement in terms of fxs
some loss of contact between broken surfaces of the fragments
how is displacement described in terms of fx fragments
degree of displacement (cortical or shaft widths)
what may cause displacement
distraction
overriding
rotation
define nondisplaced fxs
have some degree of contact remaining between the fx and fragments
describe the displacement of this fx
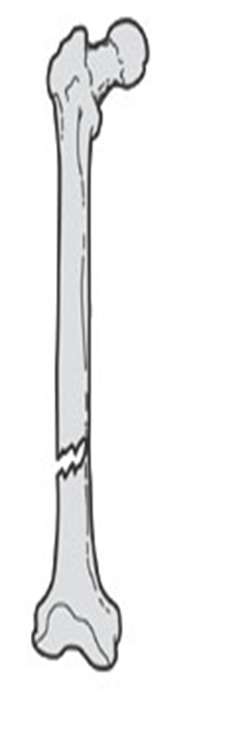
nondisplaced
describe the displacement of this fx
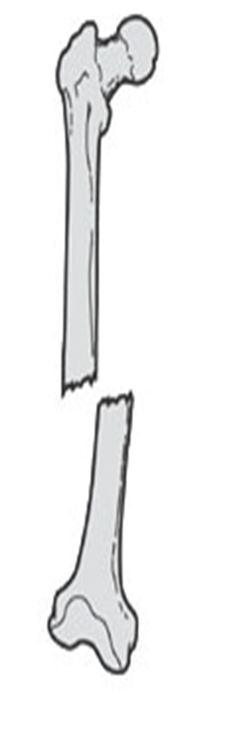
medial
describe the displacement of this fx
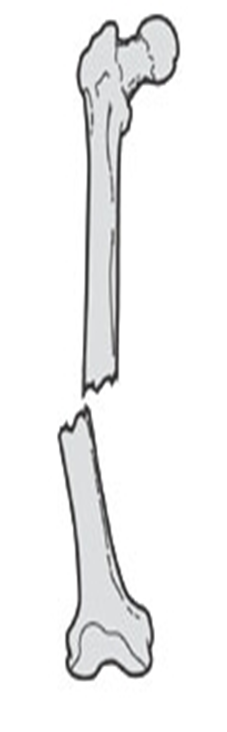
lateral
describe the displacement of this fx
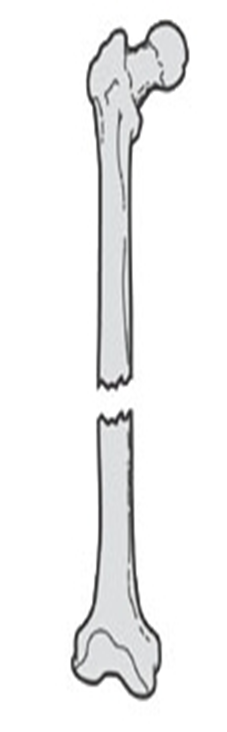
distracted
describe the displacement of this fx
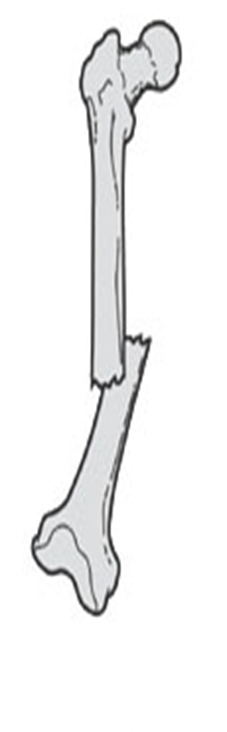
overriding with posterior and superior displacement
describe the displacement of this fx
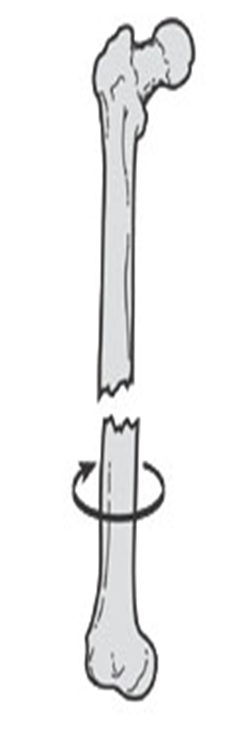
distracted and rotated laterally
define “in alignment”
when longitudinal axes of both fragments line up in tandem or parallel
How can angualtion be named by
direction of angular displacement of the distal frag in relation to the proximal
direction of the apex of the angle
describe the angulation of this fx
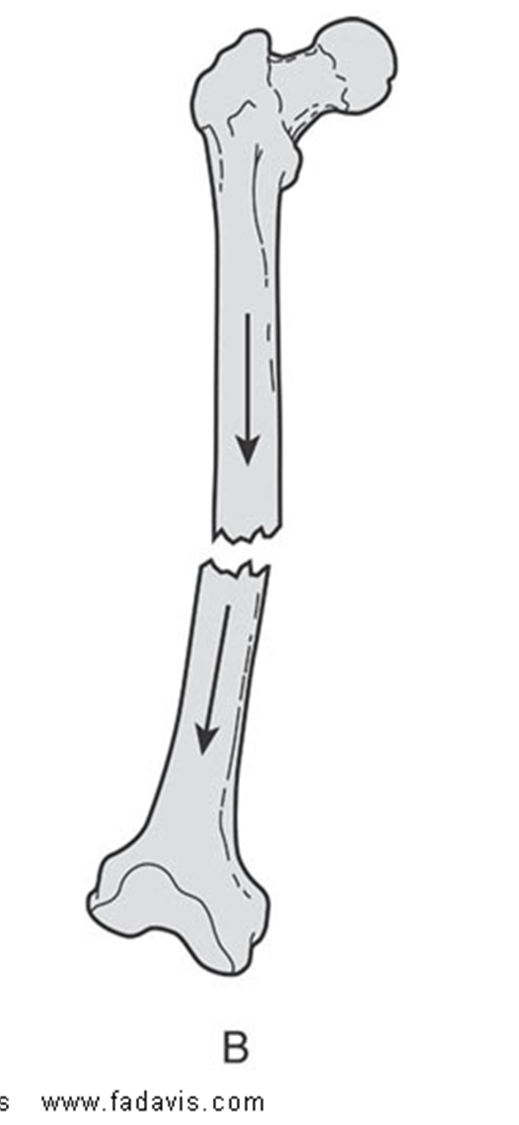
distal fragment is angulated (medial angulation (medial apex) of the fracture site with lateral angular displacement of the distal fragment)
how is direction of fracture lines used to describe radiologic fx
describe in reference to longitudinal bone (transverse, longitudinal, oblique, spiral)
define transverse fx
result of bending force; occurs at R angles to the longitudinal axis
define longitudinal fx
approx. parallel to the shaft
define oblique fx
results of combined forces of compression, bending, and torsion to create a diagonal
define spiral fx
twists along long axis of bone due to torsion
define communicated fx
a break or splinter of the bone into >2 fragments
What typically will cause a communicated fx
crushing force or event
how is special features used to describe radiologic fx
impaction
avulsion
stress fxs
What causes an impaction
compression forces related to axial loading
define impaction
bone is driven into itself
Where does impaction typically occur
in areas of cancellous bone (due to porous nature)
describe the stability of impaction
naturally more stable and close contact
types od imaction fxs
depression and compression
define depression fx
one bone is driven into another
define compression fx
both surfaces of a bone are forced together
define avulsion fx
fragments of bone are pulled away from the main body of bone OR passive resistance of a ligs against a tensile force
Where does avulsion typically occur
bony prominences
how is associated abnormalities used to describe radiologic fx
dislocations
subluxations
soft tissue damage
additional names for stress fx
microfx
fatigue fx
insufficency fxs
what causes stress fxs
repetitive minor trauma on normal bone
What is the difference between fatigue and insufficiency fxs
fatigue: excessive stress on healthy bone; normally in young/active
insufficiency: normal stress on pathologic bone; normally old/inactive
locations for fxs in children
diaphyseal
metaphyseal
physeal
epiphyseal
What are the difficulties with fx assessment in children
epiphyseal growth plates
dense growth lines
secondary centers of ossification
large nutrient foramina
define greenstick fxs
shaft is fractures on the tension side while the cortex and periosteum remains intact on the compression side
describe a torus
impaction fx that results in buckling of the cortex
Where are torus typically seen
at the metaphyseal region due to amount of cancellous bone and newly remodeled trabecular bone
define plastic bowing fxs
compression forces exceed the point in which elastic recoil returns causing a microfx
types of incomplete fxs in children
greenstick
torus
plastic bowing
Type 1 epiphyseal fx on the Salter-Harris classification
fx line extends through the physis, separating and displacing the epiphysis from normal position
prognosis for type 1 epiphyseal fx
good for normal growth
Type 2 epiphyseal fx on the Salter-Harris classification
fx line extends through the physis and exits through the metaphysis creating a triangular wedge that displaces with epiphysis
prognosis for type 2 epiphyseal fx
good for normal growth
Type 3 epiphyseal fx on the Salter-Harris classification
fracture line extends from the joint surface through the epiphysis across the physis
Type 4 epiphyseal fx on the Salter-Harris classification
fracture line extends from the joint surface through the epiphysis, physis, and metaphysis
Type 5 epiphyseal fx on the Salter-Harris classification
fracture is a crush type injury that damages the physis by compression
prognosis for type 3 epiphyseal fx
partial growth arrest is a possibility and surgical fixation may be warranted
prognosis for type 4 epiphyseal fx
partial growth arrest is possible and surgical fixation may be necessary
prognosis for type 5 epiphyseal fx
eventual growth arrest
Phases of Fx healing
GFs involved
how fixation impacts healing
callus formation process
hematoma forms
metabolic reaction occurs
organization/ossification
new bone proceeds toward and bridges the gap
callus is formed