ACIDS, BASES, pH, BUFFERS
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
pH
A measure of acidity or alkalinity of water soluble substances (pH stands for 'potential of Hydrogen').
pH (concentration)
A change of one pH unit changes the hydrogen ion concentration by a factor of ten. For example, a solution with a pH of 1 has 10 times more hydrogen ion concentration than a pH of 2; One hundred times more hydrogen ion concentration than a pH of 3 and so forth.
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14.
(O is most acidic + and 14 is most basic + or akaline.)
acidic
Is the point 0 on pH scale an acidic, basic, or neutral solution?
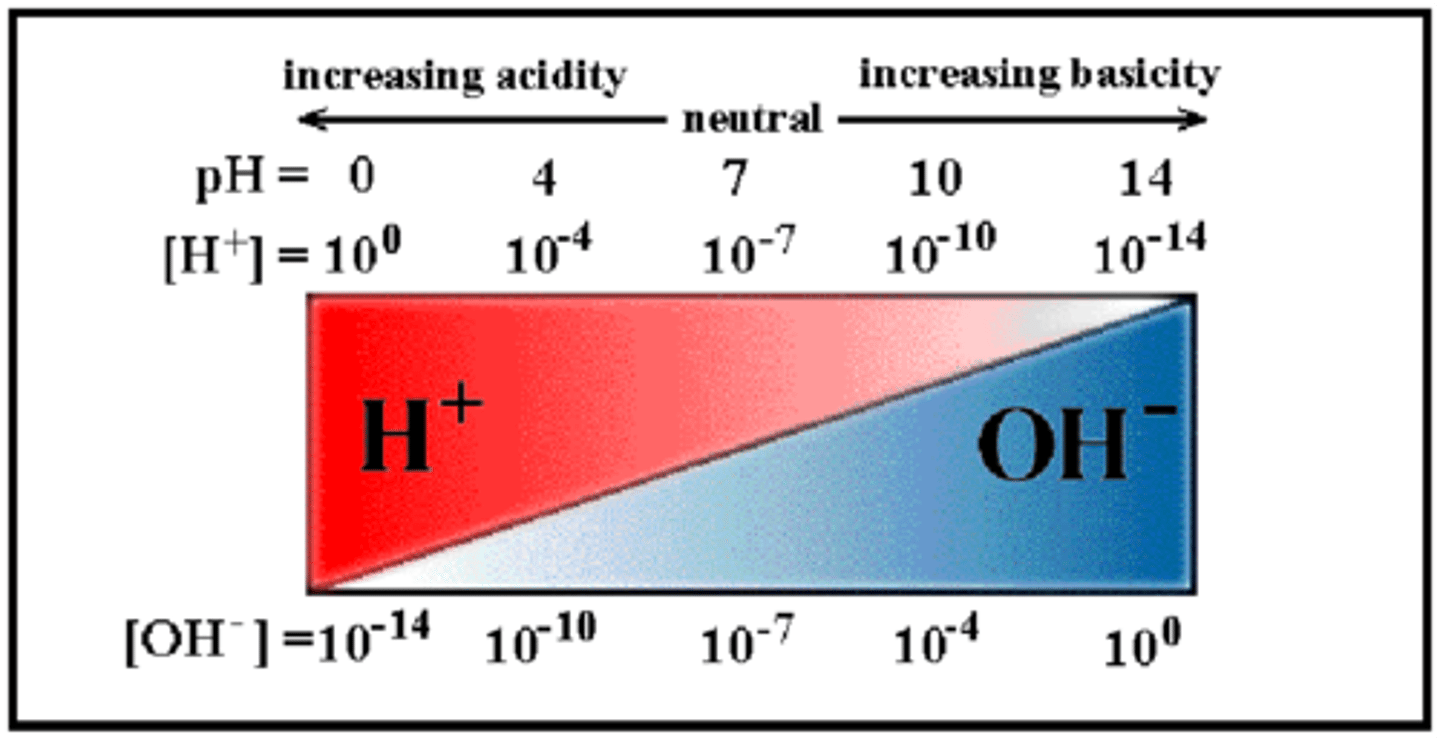
neutral
Is the point 7 on pH scale an acidic, basic, or neutral solution?
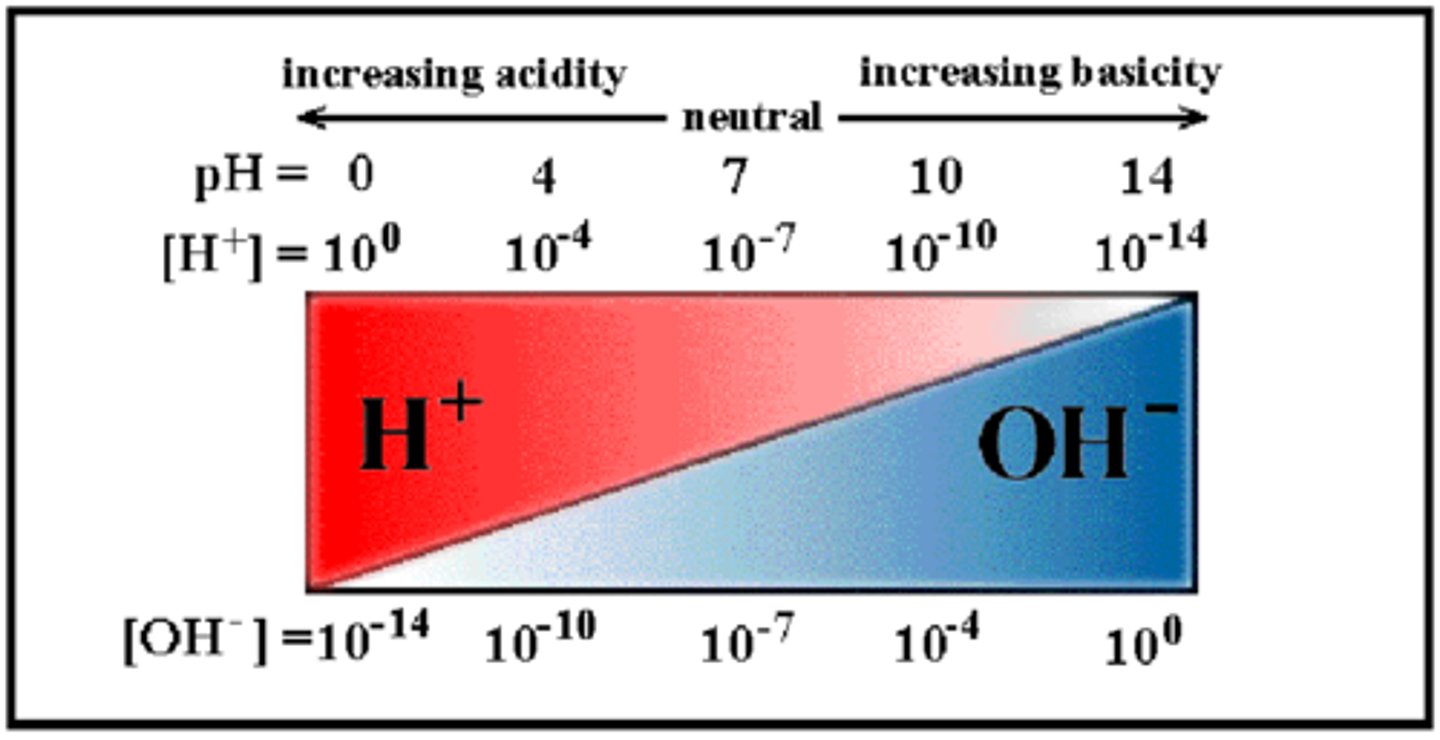
basic (alkaline)
Is the point 14 on pH scale an acidic, basic, or neutral solution?
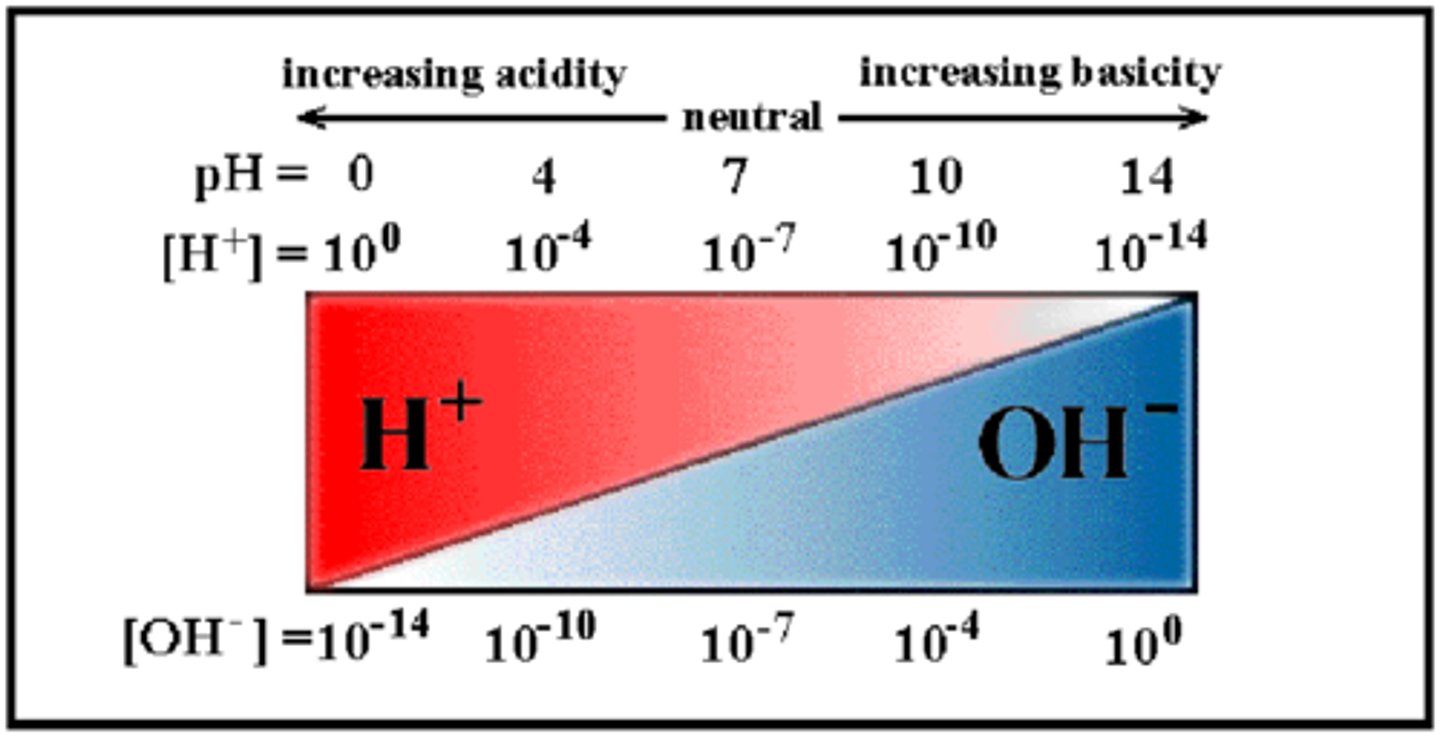
salt
An ionic compound made from the neutralization of an acid with a base.
acid
Any compound that increases the number of hydronium ions when dissolved in water. A substance that tastes sour, reacts with metals and carbonates, and turns blue litmus red.
base
Any compound that increases the number of hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. A substance that tastes bitter, feels slippery, and turns red litmus paper blue.
buffer
A solution that minimizes changes in pH when extraneous acids or bases are added to the solution.
disassociation
the process in which an ionic compound separates into its positive and negative ions in a solution.
neutralization reaction
a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react in aqueous solution to produce a salt and water