Ocular Fluids
Is water nonpolar or polar
polar
What does the polar property of water allow it to do?
solubilize simple and complex molecules (proteins)
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Is water nonpolar or polar
polar
What does the polar property of water allow it to do?
solubilize simple and complex molecules (proteins)
Solubilization in water
weak interactions between the water and solute molecules
What are the weak interactions that are observed in water?
- hydrogen bonds
- ionic bonds
- van deer waals forces
How does oxygen affect electrons
it pulls oxygen towards it, very electronegative
ionic bonds
involves electrostatic attraction between 2 ionic species that are oppositely charged
Van Der Waals forces
attraction involving neutral molecules in gases, liquids and solids
Hydrogen bonds
a IMF that is present between hydrogen and a second EN molecule
Water has the ability to __ with __ atoms
- associate
- charged
In solvation, what element of water would surround Na+?
Oxygen
In solvation, what element of water would surround Cl-?
Hydrogen
When water associated with other polar molecules, what can be observed?
hydrogen bonding
When water is fluid, are hydrogen bonds permanent?
No, constantly made and broken
When water is frozen, are hydrogen bonds permanent?
Yes, this gives ice its ordered structure as it expands
Are hydrogen bonds between water and protein permanent?
No, they are weak and often break
Number of hydrogen bones formed between a protein and water is…?
High
What is the equation of pH
pH = -log [H+]
([H+] = hydrogen concentration)
Why must pH be tightly controlled?
preserving tissue structure and cell viability
What happens to a cell if pH is too high or too low?
Apoptosis - programmed cell death
What is a buffer system?
reaction system that maintains pH in a certain range
What is hydrogen ion concentration (pH) controlled by?
partial ionization of weak electrolytes
What are the 3 types of buffer systems?
- phosphate
- bicarbonate
- protein
How is pH measured in fluids?
pH meter
How is pH measured mathematically?
Henderson-Hasselbach equation
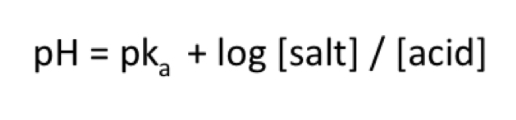
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation?
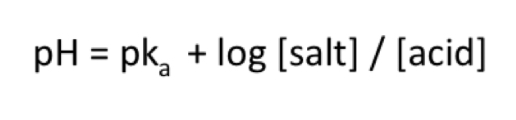
What is a weak electrolyte?
A weak acid that does not fully dissociate in water
What is a dissociation constant?
How much a weak electrolyte ionizes
What is the equation for calculation a weak electrolyte’s dissociation constant?
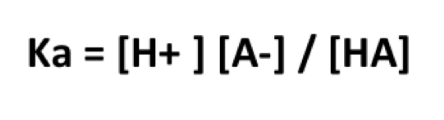
How do you solve for pKa?
pKa = -log [Ka]
What does a pKa value represent?
It is equivalent to the pH value of a solution when it is 50% ionized
Buffer capacity
how much acid or base can be added to the buffer for it to still maintain its intended pH
Range of buffer
the range of which the buffer can neutralize an added acid or base
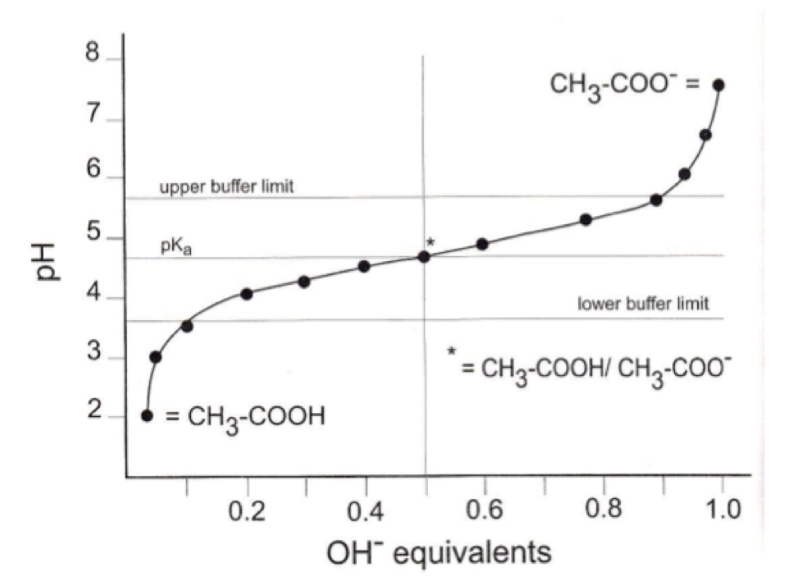
What is the range of a buffer system dependent on?
pKa
what does log [salt]/[acid] represent?
log of the ration of the ionized anion to the non ionized acid of the weak electrolyte
What is the equation for a phosphate buffer?
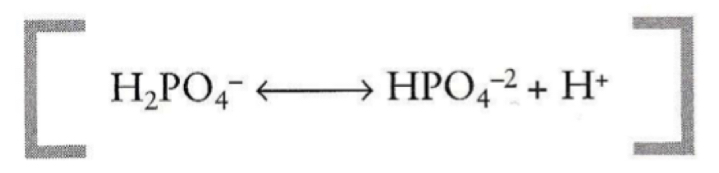
What is the most common buffer present within cells?
phosphate buffer
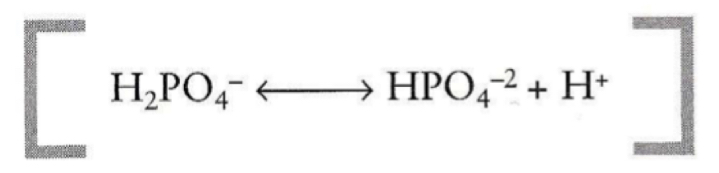
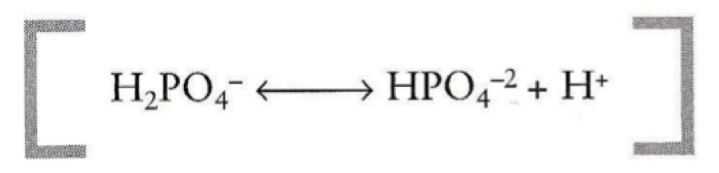
What is the pKa and buffer range of a phosphate buffer?
- pKa = 6.86
- range of: 5.86-7.86
What is the equation for a bicarbonate buffer?
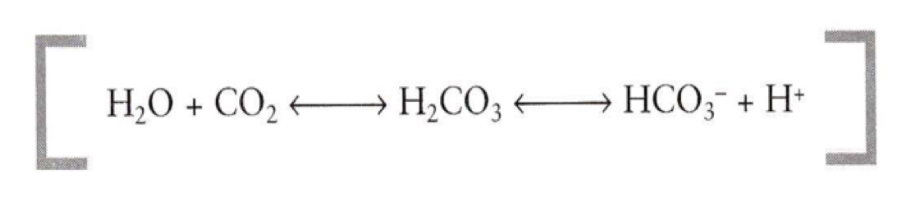
Why is a bicarbonate buffer more complex?
CO2 can be removed with expired air
What can your breathing influence?
- HCO3-/H2CO3 ration
- extracellular pH of blood and ocular fluids
What can happen when you are hyperventilating?
respiratory alkalosis, blood pH can raise to 7.9
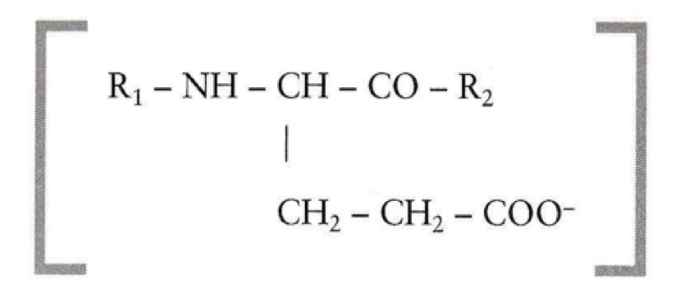
What is the equation of a protein buffer
Why are protein buffers important?
They are present both inside and outside of cells
Ionizable groups n proteins have __ pKa values
altered
prediction of exact buffering tendencies and capacities of proteins are __
difficult
Ocular fluids include:
- aqueous fluids
- vitreous
- precorneal tears
What two blood vessels make the major circle of iris?
- anterior ciliary artery
- branch of LPCA
What vein is draining the blood from the eye?
vortex veins
What are the ocular physiological functions of blood
- nourishment and removal of waste components of ocular cells
- a source of generation for IOP
- a source of information of aqueous and vitreous fluid
- homeostasis of retinal functions
What is the pH of blood?
7.4, (can vary from 7.33-7.45)
Gases carried in the blood
- oxygen
- nitrogen
- CO2
Partial pressure of O2 in Ocular capillary bed
only 50mmHg
Partial pressure of O2 in Arterial blood
83-108mmHg
Partial pressure of CO2 in venous blood
38-50mmHg
Albumin
Protein that carries water-insoluble components
Calcium
Soluble ion that is responsible for: blood clotting, enzyme activation, hormone activity and muscle contraction
Cholesterol
Lipid that is not soluble in blood
Globulin
Water-soluble protein involved in immunological functions
Glucose
Water-soluble sugar that has great importance as a nutrient
Hemoglobin
Protein that carries O2 to cells
Phosphate
Water-soluble, important for phosphate buffer, protein function and cellular energy
Potassium
Principal cation of intracellular fluid, important for enzyme function
Triglycerides
lipid class, not soluble in blood
Aqueous humor
a controlled filtrate of blood produced by ciliary body (non-pigmented ciliary epithelium)
What drains aqueous humor from the AC?
episcleral veins
What is the importance of aqueous humor?
- only source of nourishment for cells of corneal endothelium and epithelium
- stroma keratocytes
- lens
- source of antioxidants
Processes involved in aqueous humor production
- diffusion
- ultrafiltration
- active secretion
Does aqueous humor have RBCs?
NO, it is a filtrate of blood
What does aqueous humor give rise to in the eye?
IOP, which maintains the shape of the eye
- it also protects to some extent from the physical shock
How is aqueous humor different from blood?
decreased protein component, no cellular components
- reduced buffering capacity due to this
ascorbic acid concentration is higher
Why is aqueous humor still able to maintain pH even though it has a decreased buffering capacity?
due to comparable amounts of phosphate and bicarbonate
Vitreous humor
a mixture of fluid and gel
How much of vitreous is water?
98%
What are the ratios of gel/fluid initially, and with age?
- Initially: 80%gel/20%fluid
- With age: 40%gel/60%fluid
Describe the gel portion of vitreous humor
a stiff, semi-rigid precipitate having collagens and proteoglycans
What causes a retinal detachment to occur?
- increase in proportion of fluid with age
- breakdown of type 2 collagen
- destabilization of retinal surface
- retinal detachment
What causes thee viscoelasticity of the vitreous?
due to proteoglycans (hyaluronic acid) and collagens
What are special properties of the vitreous gel?
capability to reform its original shape, and has some flow property
Comparisons of vitreous to blood
- ascorbate levels are high
- protein and hyaluronic acid is high
- sodium and glucose content is lower
- potassium level is low
- vitreous is clear
Precorneal tears
a film between the inside of lids and the cornea
Role for tears
- lubricating fluid
- protects the eyes from microorganisms
- temporary disposition for topical drugs
- comprised of 3 layers
What are the 3 layers of tear film?
- lipid
- aqueous
- mucin
How can tears protect from Gram+ bacteria?
tears have enzyme called lysozyme
Comparison of tears to blood
tears are more dilute
potassium concentration is 7x higher than blood
ascrobate and glucose levels are lower
- not a source of nourishment for corneal and conjunctival cells
Where does the cornea get its nutrients from?
aq. humor
Where do conjunctival cells receive nourishment from?
interstitial fluid and local blood supply
Globulin range
2.3-3.5 gm/mL
Cholesterol range
140-250 mg/100mL
Glucose range
70-105 mg/100mL
13-16 g/100mL
3-4.5 mg/100mL
Potassium range
~ 105mmol/liter in red blood cells
Triglycerides range
35-140 mg/100mL