The Respiratory System (Bio 2201)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Respiratory system
System responsible for gas exchange (bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide from the body.)
Breathing
Involves two basic processes; inspiration and expiration. Inspiration moves air from the lungs back to the external environment to the lungs inside the body. Expiration moves air from the lungs back to the external environment.
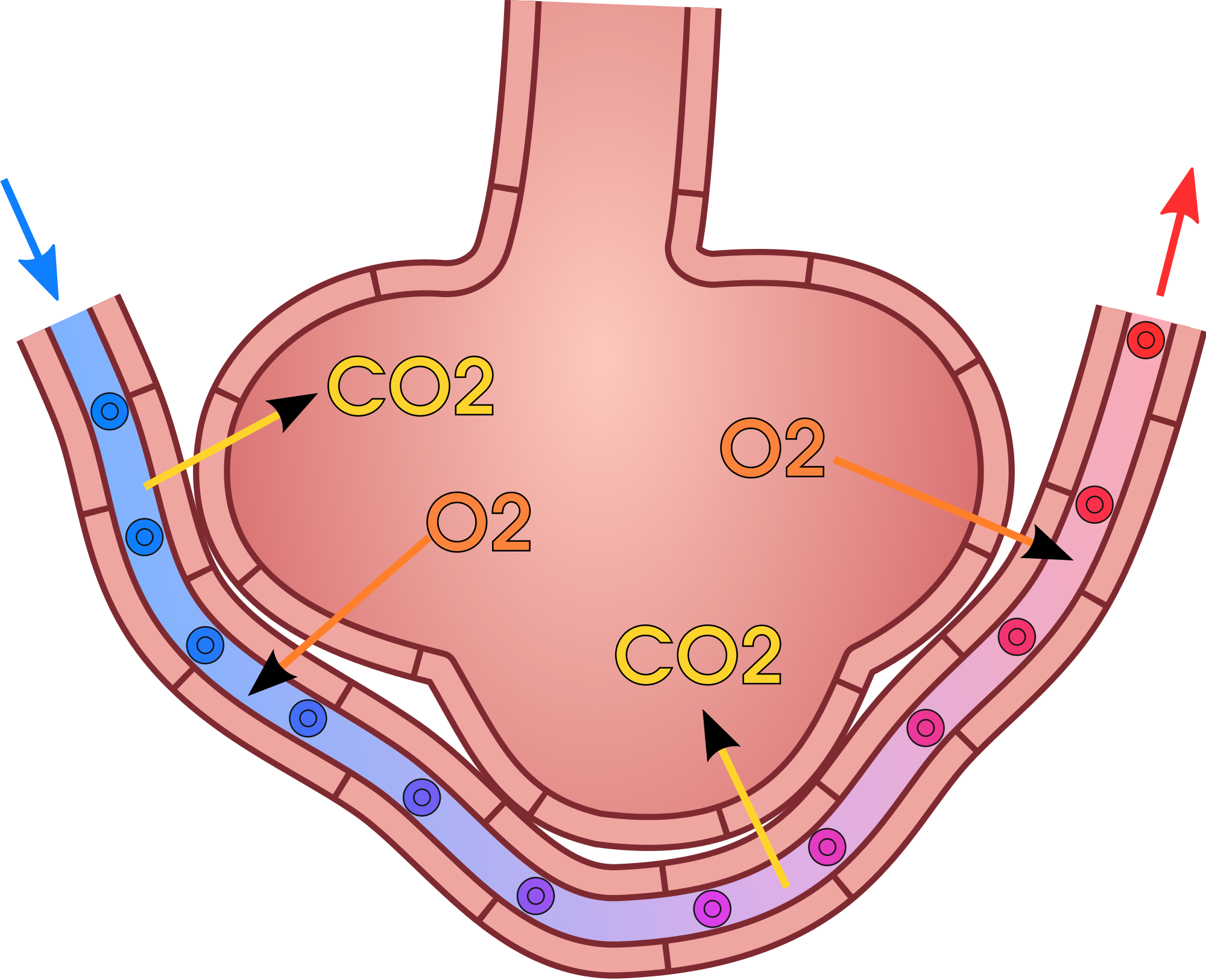
Gas Exchange
the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the blood
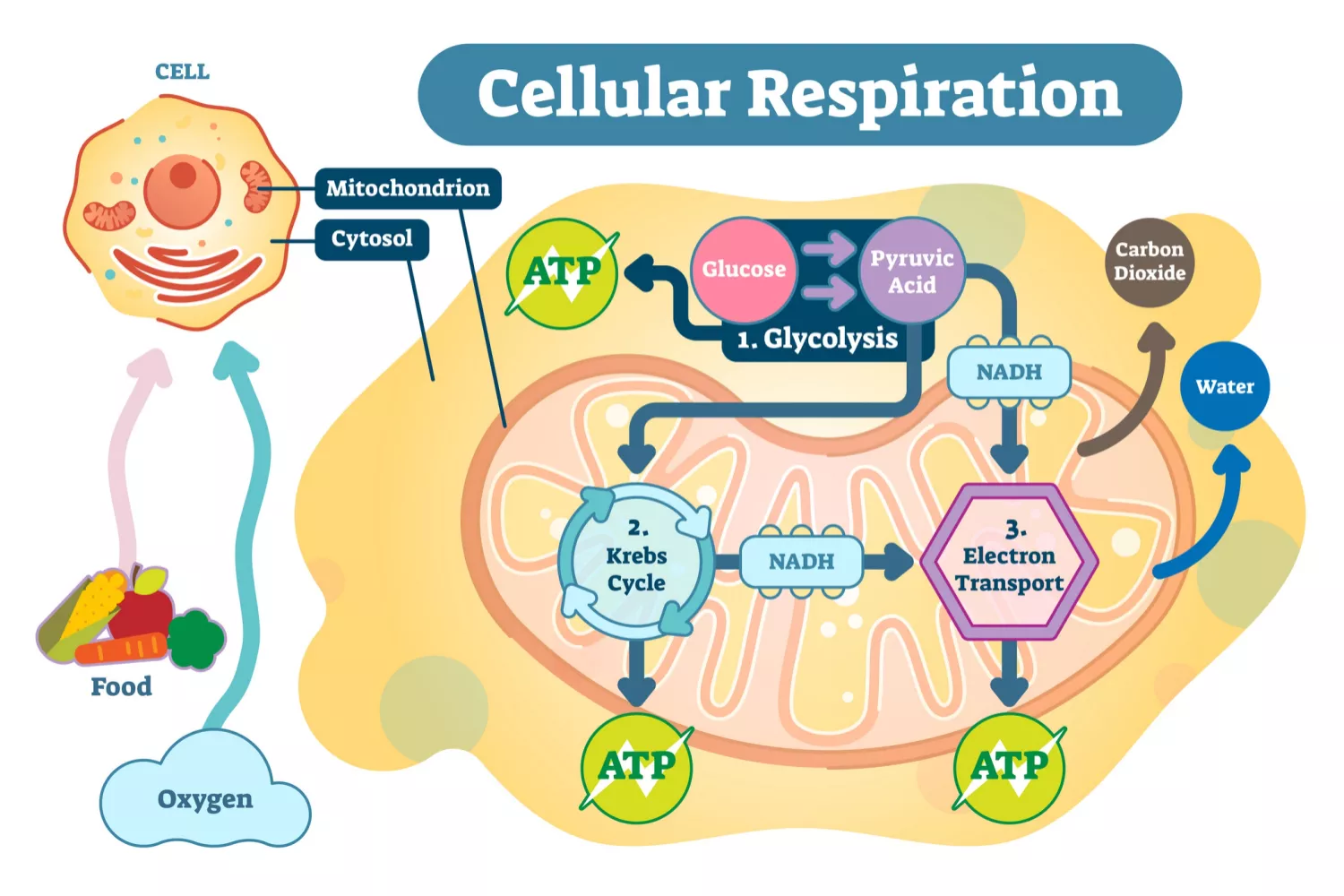
Cellular Respiration
The series of energy-releasing chemical reactions that take place inside cells. it is the final stage in respiration; it is the only means of providing energy for all cellular activities, and it helps the body maintain homeostasis.
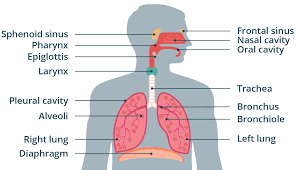
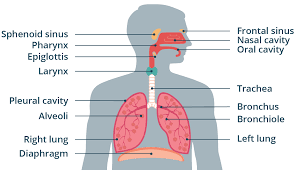
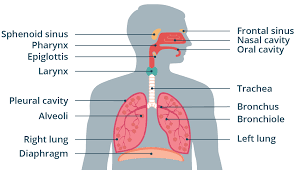
Nasal Cavity
Passage from the nostrils to the back of the throat through which air enters the body. It is lined with ciliated cells. Other cells secrete mucus, which cleans the air by trapping foreign particles.
Turbinate Bones
Very thin bones that project into the nasal cavity. Serve an important function by increasing the surface area of the nasal cavity. They are covered in cilia and mucus-secreting membrane.
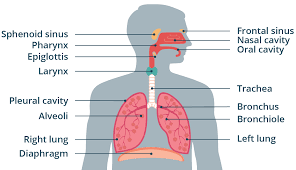
Pharynx
Passageway that that connects back of the mouth and nasal cavity to larynx and esophagus.
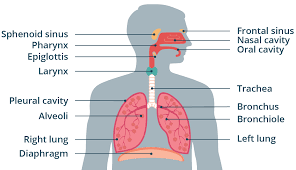
Epiglottis
Flap of cartilage over entrance of trachea.
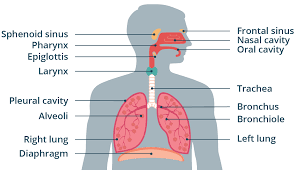
Trachea
flexible tube through which air moves from the mouth to the bronchi. Also known as the windpipe.
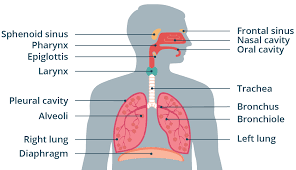
Bronchi
Passageways that branch from trachea into lungs. Contains C-shaped cartilaginous rings that surround and are part of the bronchus wall.
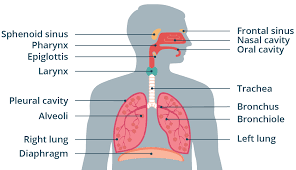
Bronchioles
Passageways that branch from bronchi into lobes of lungs. Do not have C-rings.
Mucus
Captures foreign particles, such as microscopic pollutants and pathogens.
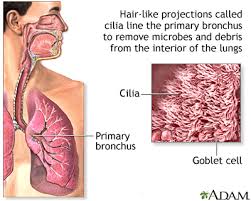
Cilia
Moves the foreign particles up into the upper respiratory tract.
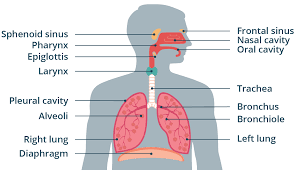
Lungs
Principle organs of respiration. Site of gas exchange in the human body.
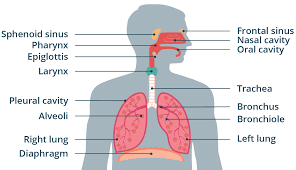
Alveoli
Gas exchange structures within the lungs. The wall is one cell thick and is surrounded by a network of tiny capillaries. Lined with a fluid that permits the diffusion of gases and that helps to keep them from collapsing and prevents their sides from sticking together and closing.
Capillaries
Tiny blood vessels. Walls are one cell thick.
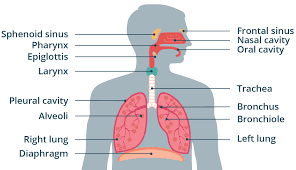
Diaphragm
Sheet of muscle separating thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Inspiration
Movement of air into lungs, the external rib muscles and diaphragm contract.
Expiration
Movement of air out of lungs. The diaphragm and the rib muscles relax reducing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
Tidal Volume
Volume of air inspired and expired in normal breathing at rest.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
The additional volume of air that can be taken into the lungs, beyond a regular inspiration.
Expiratory Reserve Volume
Additional volume of air that can be forced out of the lungs, beyond a regular expiration.
Vital Capacity
Total volume of gas that can be moved in or out of lungs.
Residual Volume
Amount of gas left in lungs after a full expiration.
Tar
The word for the solid particles suspended in tobacco smoke.
Carbon Monoxide
A poisonous gas. It is odorless and colourless. In large doses it quickly causes death because it takes the place f oxygen in the blood.
Oxidizing Chemicals
Highly reactive chemicals that can damage the heart muscles and blood vessels of people who smoke. They react with cholesterol, leading to the build-up of fatty material on artery walls. Their actions lead to heart disease, stroke and blood vessel disease.
Metals
Tobacco smoke contains several that cause cancer, including arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, lead and nickel.
Radioactive Compounds
Tobacco Smoke contains —- —- that are known to be carcinogenic.